- What is quantitative marketing?
- Characteristics of quantitative marketing research
- Pros and cons of quantitative marketing
- Quantitative marketing research process roadmap
- Quantitative marketing data collection techniques
- Types of quantitative research questions
- Statistical analysis techniques used in quantitative research
- Errors in quantitative marketing research
- Market research in the app industry
- Summing up
- Frequently asked questions

Have you heard of the term ‘Quantitative Marketing’?
Yes? No? Maybe?
Whether you’re someone who has never heard of quantitative marketing or someone who has little knowledge about the same, this article will be beneficial for you.
When discussing marketing research, we usually have two options, or rather two types of research: Qualitative and Quantitative. Qualitative research relies on descriptive and holistic responses and analysis, whereas quantitative research focuses on numbers, statistics, and specific data.
Let’s begin the article by discussing quantitative marketing in detail.
- What is quantitative marketing?
- Characteristics of quantitative marketing research
- Pros and cons of quantitative marketing
- Quantitative marketing research process roadmap
- Quantitative marketing data collection techniques
- Types of quantitative research questions
- Statistical analysis techniques used in quantitative research
- Errors in quantitative marketing research
- Market research in the app industry
- Summing up
- Frequently asked questions
What is quantitative marketing?
Quantitative marketing is the science of understanding markets and making better decisions using empirical facts collected via research. It is a complicated but necessary component of any marketing activity and requires the application of quantitative research methods to the field of marketing research.
This method involves asking questions to a target group through surveys, polls, and questionnaires. Marketers use this information to gather and comprehend the demands of consumers in the marketplace and develop strategies and marketing plans.
Marketing is an interactive process in which both buyers and sellers should agree on the four Ps of marketing: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. Market research helps to achieve this agreement.
We live in a digital era where data is the new fuel. Companies’ fate depends on how well they can collect and analyze data to draw meaningful conclusions. Firms rely on quantitative methods to draw these conclusions because these methods provide systematic, detailed information about the problem or the target group.
Characteristics of quantitative marketing research
The following are the key characteristics of quantitative marketing research:
- Large sample size: Quantitative research uses a large sample size to gather the data. This sample size is representative of the entire target population.
- Hypothesis: Quantitative research depends upon a hypothesis, and the goal is to prove or disprove the same.
- Dependent on quantitative data: As the name suggests, this research methodology relies on numbers, statistics, or other quantifiable data to draw conclusions.
- Structured: This method follows a structured approach to data collection and analysis.
- Close-ended: The questions are close-ended to facilitate better data analysis and avoid ambiguity.
- Reusable outcome: Researchers can use the results obtained for the prior study of the subsequent research problem.
- Generalization: The outcome can be generalized to the whole population because of the large sample size.
Pros and cons of quantitative marketing
The below tables summarize the key advantages and disadvantages of quantitative research.
| Advantages | |
| Produces quantitatively rational theories | The outcomes of quantitative marketing are numerical, which enables organizations to make well-thought decisions. |
| Easily analyzable data | Researchers receive exact responses in quantitative research, making evaluating the data more accessible. |
| Respondents participation | The questions in this type of research are close-ended and specific, and quick to answer. Thus, there are high chances of respondents’ participation. |
| Cheaper brand awareness | Quantitative market research is also a way to create brand awareness through online mediums. This method is way cheaper than other modes of promotion. |
| Disadvantages | |
| Limited | Although quantitative research gathers data from a large group, it doesn’t provide the reasoning behind that data. Thus, the interpretation is limited. |
| Structured | The limited opportunity to deviate from a structured answer is both a strength and a weakness of quantitative market research questions. While this provides valuable data, the questions do not allow for validation because of how the survey is designed. |
| Sampling error | There is a chance that the respondents who participate in the survey may not be representative of the entire population. Thus, there is a sampling error risk. |
| It might not be trustworthy. | Sometimes, the respondents are not willing to give out too much information. They might also provide incorrect data leading to false outcomes in the research. |
Quantitative marketing research process roadmap

The quantitative research process follows a five-step process, which is as follows:
1. Problem definition
The first stage is defining the problem statement. It requires answering a few questions like:
- What is the point of conflict?
- What do we aim to find a solution to?
- Which information is needed?
Here, you must also create a hypothesis based on which you will assess your final result.
For example, suppose the problem statement is ‘Consumer perception of travel apps among teenagers in the USA.’ The hypothesis can be ‘Teenagers in the USA do not prefer using travel apps.’ The final result of the research will either prove or disprove the hypothesis.
You need to note that both the problem statement and the hypothesis must be specific regarding the idea, the target population, age group, the region, etc.
2. Research design
The next stage requires you to create the research design. Here, you need to specify what methodologies you will use to conduct the research. Research design establishes an outline for the study and guides how the research will be conducted.
The critical elements of research design are:
- Specific purpose statement
- Research techniques and methods
- Type of Research
- Possible objections to the research
- Settings for the study
- Timeline of the research
- Assumptions and limitations of the study
3. Data collection
Once you define the problem statement and the research design, you must begin with the actual research by collecting relevant data from various sources. The data collection technique will differ based on the type of research: primary or secondary. Ideal research involves elements of both primary and secondary research.
| Primary research | It is a type of research in which the researcher gathers first-hand information from the target population by conducting surveys, experiments, interviews, etc. |
| Secondary research | It is a type of research in which the researcher relies on already published information and the research already conducted to draw conclusions for the current study. |
4. Data analysis and interpretation
Collected data is of no use by itself, and you need to analyze and interpret the data to generate meaningful conclusions. You can create charts, tables, graphs, and other diagrams to quickly present and analyze the information.
However, you must note that data analysis and interpretation are two different processes. Data analysis is the process of structuring, organizing, transforming, and modeling the data to observe trends and patterns. On the other hand, data interpretation assigns meaning to the analyzed data. It involves determining the relationship between different variables, how the information is significant to us, and so on.
5. Report writing
The final stage in the research process is writing a report. A report is usually very detailed and contains all the findings and conclusions of the research.
It includes headings such as:
- Executive summary
- Introduction
- Research objective
- Research Methodology
- Primary and secondary research findings
- Charts and diagrams for data analysis
- Data interpretation
- Conclusion
- Annexure
Marketers can use this report to understand the market trends, draft marketing strategies, present the findings to the clients, and for future marketing purposes.
Quantitative marketing data collection techniques
As discussed earlier, data collection is of two types: primary and secondary data collection. The techniques for both these methods are as follows:
Primary data collection techniques

1. Surveys
This technique typically requires the respondents to answer a list of questions related to the research problem. Quantitative research surveys have close-ended questions easing the respondent’s work and making the results specific and accurate. Traditionally, researchers relied on pen and paper to conduct surveys by individually contacting the sample. But now, we have tools like Google Forms and Microsoft Forms, making reaching a wider group of people easier.
2. Interviews
Interviews involve a detailed interaction between the researcher and the interviewee. Quantitative interview questions are structured to gather extensive information from the participants. The researcher can conduct the interview face-to-face, over the telephone, or via video conference.
3. Observations
This technique does not require asking any questions to people. It involves the recording of factual information through observation. The researcher observes instances and notes down the key highlights. This type of data collection is objective as it does not depend on a person’s memory or personal bias.
Secondary data collection techniques
The secondary research does not require the researcher to personally collect the data by contacting a group of people. It depends on the data already available or what someone else has recorded. Based on this information, the researcher draws insights and inferences. Secondary data sources can include research papers, blogs, books, videos, etc.
Types of quantitative research questions
The questions that researchers ask while conducting quantitative research are specific compared to open-ended qualitative questions, which are harder to analyze.
The major types of quantitative market research questions are:
1. Net promoter score
You can ask this question to determine customer satisfaction and brand shareability. Based on the responses, you can divide the respondents into three categories: promoters, passives, and detractors. This question usually has a 0-10 scale providing an efficient perspective about brand recommendation.
For example,
Considering your experience with us, how likely would you recommend our services to a friend?
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
10- Very likely
2. Likert scale
This question evaluates a respondent’s opinion toward a particular situation. It has two extreme opinions at each end of the scale. This type of question is usually asked to know the agreement level of the respondent to a particular statement or situation. It typically has 5, 7, or 9 options to choose from.
For example,
Do you agree with the statement, “App marketing is as crucial as the other app development stages”?
| Strongly disagree | Disagree | Neutral | Agree | Strongly agree |
3. Semantic scale
A semantic differential rating scale is used to generate quantitative data about ideologies, products, or events with drastically opposing answers at the polar points of the scale to quantify their implicative meaning.
For example,
How satisfied are you with our customer service?
| Extremely dissatisfied | Dissatisfied | Neutral | Satisfied | Extremely satisfied |
4. Multiple-choice
These questions are crucial as they help in getting the best responses. The reason is that the marketer gives the respondent the exact options to choose from, and the analysis thus becomes more straightforward and quantifiable. The question can be designed in a way that the respondent can choose either only one option or multiple options.
For example,
Which video streaming platform do you prefer using?
- YouTube
- TikTok
- Netflix
- Amazon Prime Video
- Hulu
- Disney+
Statistical analysis techniques used in quantitative research
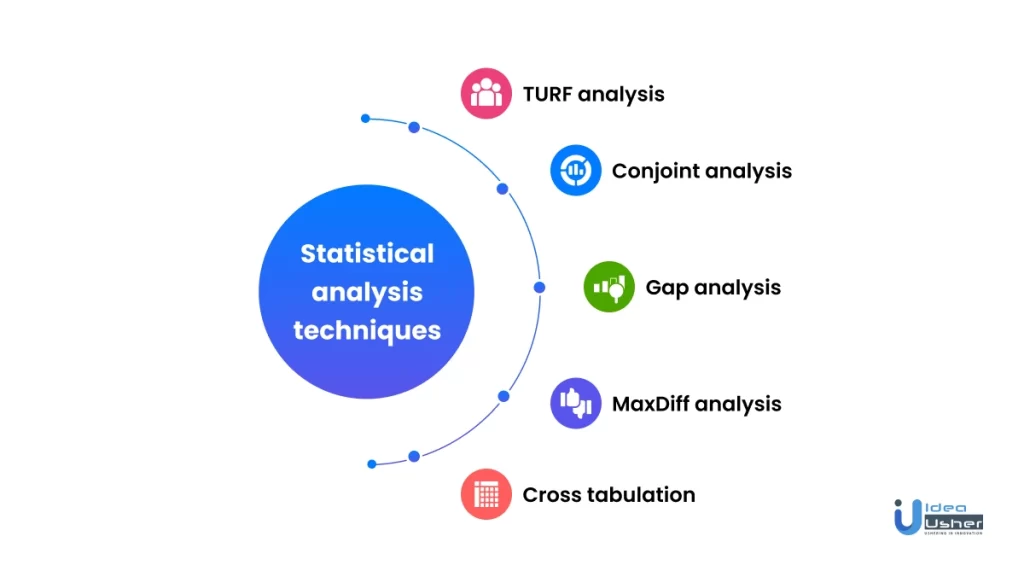
Various statistical analysis techniques can be used to analyze quantitative research data. Some of them are listed below:
1. TURF analysis
Total Unduplicated Reach and Frequency (TURF) analysis is a statistical approach to assess the potential of market research for a combination of products and services. With firms launching products and services regularly and new markets being explored daily, it becomes inevitable to leave no stone unturned in ensuring the products are well-received in new areas.
For example, if an app company wishes to launch a new feature, TURF analysis can help answer the following questions:
- What market share will we receive if we introduce Feature X in our app?
- Where should we promote this feature to get maximum reach in the app industry?
2. Conjoint analysis
Conjoint analysis is a way of determining the worth of numerous aspects for customers, such as pricing, features, and benefits that lead to purchasing a specific product or service. With the increasing technology integration in devices and gadgets, this analysis method has become common for product pricing, market positioning, and product introduction.
3. Gap analysis
Gap analysis is a technique for assessing the difference between the desired and the actual performance of a product or service. By measuring this, a firm can make efforts to close the gap and make its features more enticing.
Businesses use gap analysis to answer the following questions:
- What is the current position of the company?
- Where do we wish to reach?
- What can we do to close the gap?
4. MaxDiff analysis
MaxDiff analysis, also known as best-worst scaling, is used to gauge survey respondents’ preference scores for multiple attributes such as product features, brand image, activities around branding, etc. This technique is similar to conjoint analysis; however, MaxDiff analysis is easier and more comprehensive in analyzing critical situations.
5. Cross tabulation
As the name suggests, cross-tabulation allows you to compare two or more categories in a tabular format for quicker analysis. Researchers utilize cross-tabulation to look for hidden relationships in data. It’s great for market research and surveys as a cross-tab report depicts the relationship between two or more study questions.
Errors in quantitative marketing research
The following table summarizes the different types of errors that might arise while conducting quantitative marketing research:
| Random sampling errors: 1. Sample too small 2. Non-representative sample 3. Incorrect sampling method selection | Research design errors: 1. Bias introduced 2. Measurement error 3. Data analysis error 4. Scaling error 5. Population definition error 6. Question formation error 7. Sampling frame error |
| Interviewer errors: 1. Questioning errors 2. Cheating errors 3. Recording errors 4. Respondent selection error | Respondent errors: 1. Non-response error 2. Inability error 3. Falsification error |
Apart from the above errors, the study can also have hypothesis errors, which are of two types:
- Alpha error, in which the study outcomes lead to the rejection of the hypothesis even though it is true.
- Beta error, in which the study outcomes lead to the acceptance of the hypothesis even though it is false.
Market research in the app industry
App development is a sector that requires intensive research about the market. It includes the analysis of the target audience, the competitors, and the various other associated factors. A business starting in this sector might find it overwhelming to conduct thorough market research without proper guidance. As a result, it is better to consult app development experts for this task.
Idea Usher is a technology company providing various digital services like app development, blockchain development, AI and IoT-related services, etc. In addition to qualified app developers, we also have experts who assist clients in understanding the feasibility of their app idea by conducting a thorough analysis of the target market. Once the feasibility is confirmed, we help turn the app idea into reality through our development services.
Contact us to get a clear vision of your app idea and take off your app business.
E-mail: [email protected]
Phone Numbers : (+91) 946 340 7140, (+91) 859 140 7140, and (+1) 732 962 4560
Summing up
Quantitative marketing research is an excellent way for marketers to understand the market situation and plan their marketing strategies accordingly. The results obtained through the research can be used to derive insightful conclusions because of their precise nature.
Expert tip: Always aim to keep your research objective, specific, and bias-free to ensure better outcomes and marketing decisions.
Frequently asked questions
Here are a few exciting FAQs about quantitative marketing.
Q1. What is an example of quantitative research in marketing?
A great example of quantitative research in marketing is conducting surveys to determine the potential demand for a particular product, service, or feature.
Q2. Why is quantitative research important in marketing?
Quantitative research is necessary because it provides marketers with objective, reliable data to identify trends and patterns for better marketing decisions.
Q3. Which is better: quantitative or qualitative marketing research?
Both these methods of market research have their pros and cons. You should do quantitative analysis if you need quick, specific, and quantifiable data. However, you should consider qualitative research if you need descriptive, theoretical information.







Mayank Sharma