- What Is RPA?
- How RPA Works?
- The Reasons Behind the Growth of RPA
- Factors Driving The Cost Of Robotic Process Automation
- Examples Of Organizations And Their Cost of RPA Implementation
- Challenges In Finding The Cost of RPA Implementation
- How To Determine The Cost Of RPA Implementation?
- How Businesses Can Cut Down on RPA Implementation Expenses and Accelerate ROI?
- Conclusion
- How Idea Usher Can Help?
- FAQ

Digital transformation is a strategic need for modern businesses seeking to remain competitive and grow in a quickly changing business environment. This need is highlighted by the fact that 56% of CEOs experienced increased revenue from digital innovations, demonstrating the substantial influence that adopting digital technology may have on a company’s bottom line.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) stands out as a critical enabler among the many technologies fueling this digital transformation. RPA refers to employing software robots or “bots” to automate repetitive and rule-based operations that humans previously handled.
This technology enables businesses to simplify processes, increase productivity, and reallocate human resources to more valuable tasks.
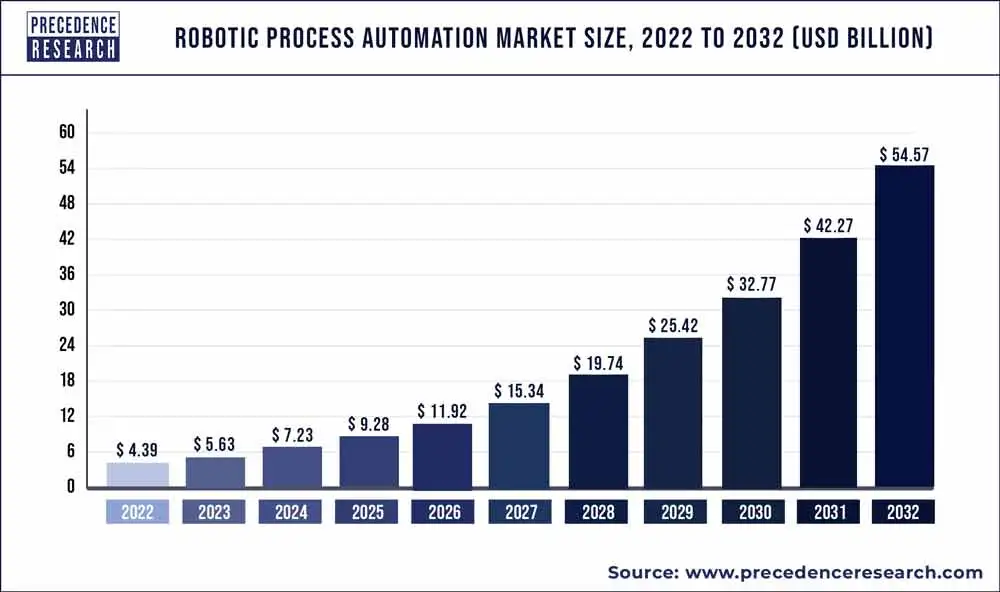
Source: PrecedenceResearch
However, since numerous factors affect price, figuring out the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) for RPA software is challenging. The number and kind of bots, the number of users, the frequency of usage, and the deployment environment (cloud or on-premise) are some variables that add to the complexity of RPA cost estimates.
Even while proper cost assessment is important, many RPA providers, similar to their IT competitors, prefer greater pricing transparency, causing the need for careful investigation.
This blog aims to provides various crucial aspects, offering estimates to help you set expectations and avoid mistakes that might affect the expected return on investment of your RPA deployment.
- What Is RPA?
- How RPA Works?
- The Reasons Behind the Growth of RPA
- Factors Driving The Cost Of Robotic Process Automation
- Examples Of Organizations And Their Cost of RPA Implementation
- Challenges In Finding The Cost of RPA Implementation
- How To Determine The Cost Of RPA Implementation?
- How Businesses Can Cut Down on RPA Implementation Expenses and Accelerate ROI?
- Conclusion
- How Idea Usher Can Help?
- FAQ
What Is RPA?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a technology that uses software robots or “bots” to automate repetitive and rule-based tasks within business processes. These tasks typically involve data entry, data extraction, and other routine activities that are time-consuming for humans. RPA enables organizations to streamline their operations, improve efficiency, and reduce the likelihood of errors by allowing bots to perform these tasks with speed and accuracy.
RPA bots mimic human interactions with digital systems by interacting with user interfaces, such as entering data into forms, clicking buttons, and navigating between applications. Unlike traditional automation solutions, RPA does not require extensive coding or integration efforts. Instead, it works at the user interface level, making it accessible to non-technical users and allowing for quick implementation and deployment.
One of the key advantages of RPA is its ability to work across various applications and systems without significant changes to existing infrastructure. This makes it a versatile tool for organizations with diverse software environments. RPA can be applied in various industries, including finance, healthcare, customer service, and manufacturing, providing benefits such as increased productivity, cost savings, and improved compliance with regulations.
As organizations continue to embrace digital transformation, RPA plays a crucial role in augmenting human capabilities and enabling businesses to adapt to rapidly changing market conditions. By automating mundane and repetitive tasks, RPA allows employees to focus on more strategic and value-added activities, ultimately contributing to overall business success. However, it’s important to note that while RPA offers numerous benefits, careful planning and governance are essential to ensure successful implementation and optimal results.
How RPA Works?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) works by employing software robots or bots to automate repetitive and rule-based tasks that are traditionally performed by humans. The process involves the following key steps:
1. Process Understanding and Design
Before implementing Robotic Process Automation (RPA), a comprehensive understanding of the targeted business process is crucial. This involves identifying and documenting repetitive tasks, rules, and decision points within the process. Following this, RPA developers design a workflow or script that instructs the bot on how to navigate through the process, interact with various applications, and handle exceptions that may arise during automation.
2. Bot Deployment
Once the RPA script is developed, the software bot is deployed to the environment where it will perform the designated tasks. This deployment can occur on a server, virtual machine, or a cloud-based platform. Importantly, RPA bots operate at the user interface level, interacting with applications and systems like human users.
3. User Interface Interaction
RPA bots interact with the user interface of applications, performing tasks such as reading and inputting data into forms, clicking buttons, copying and pasting information, and navigating through screens. Their versatility extends to handling web-based interfaces and desktop applications, making them adaptable to various IT environments.
4. Data Processing and Integration
RPA bots can extract data from different sources and perform basic data processing tasks. This includes validating data, conducting calculations, and making decisions based on predefined rules. Integration with existing systems is achieved through the bot’s ability to interact with APIs, databases, and other technologies.
5. Exception Handling and Reporting
RPA bots are programmed to handle exceptions and errors that may occur during the automation process. This includes addressing scenarios where the application interface undergoes changes, or unexpected issues arise. Detailed logging and reporting mechanisms are typically implemented to track the bot’s activities, providing insights into process performance and facilitating continuous improvement.
6. Scalability and Monitoring
RPA solutions are designed to be scalable, allowing organizations to simultaneously deploy multiple bots to handle a large volume of tasks. Continuous monitoring is essential to ensure the bots are running efficiently and any issues or changes in the business process can be promptly addressed. This scalability and adaptability make RPA a valuable tool across various industries and business functions.
The Reasons Behind the Growth of RPA
The expansion of RPA is influenced by a confluence of factors, including the rising licensing costs imposed by legacy RPA platforms, the size of RPA teams within organizations, and the increasing complexity of RPA toolchains.
1. Rising Licensing Costs
One of the primary contributors to the growing total cost of ownership (TCO) for Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is the upward trend in licensing costs imposed by legacy RPA platforms and vendors. As the demand for RPA solutions continues to rise, providers are capitalizing on their market share by incrementally increasing licensing fees. Organizations heavily invested in these platforms may burden themselves with escalating costs, impacting their overall budget allocation for automation initiatives. Understanding why RPA vendors raise their prices involves enhanced features, improved security measures, and ongoing support services, all contributing to the rising financial commitment required to sustain RPA implementations.
2. Growing RPA Teams
Organizations are witnessing a substantial expansion in the size of their automation teams, according to research conducted by Blueprint. Establishing RPA Centers of Excellence (CoE) is becoming increasingly prevalent, with 50% of organizations already setting up such centers. For those without a CoE, 40% have imminent plans to establish one. The growth in headcount dedicated to managing and scaling RPA initiatives is a significant factor contributing to the increase in operational expenses and the overall TCO. Larger teams are essential for the effective deployment, maintenance, and continuous improvement of RPA processes, yet they inevitably come with associated costs, including salaries, training, and infrastructure.
3. Growing RPA Toolchains
Organizations are increasingly reporting the utilization of multiple tools within their automation toolchains. Beyond the core RPA platform used for automation development, delivery, orchestration, and monitoring, companies are incorporating an average of 5 tools into their RPA toolchains. These supplementary tools often include work management solutions such as Jira, testing suites, and process discovery tools. While this diverse toolchain enhances the capabilities of RPA implementations, it also contributes to the expansion of the TCO. The integration and maintenance of multiple tools demand additional resources, both in terms of finances and skilled personnel.
Factors Driving The Cost Of Robotic Process Automation
The cost of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is influenced by many factors, reflecting the complex nature of implementing automation solutions. Here are factors to consider.
1. Dynamics of RPA Vendor Pricing
The cost of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is significantly influenced by the pricing models adopted by RPA vendors. Major players like UiPath, Automation Anywhere, and Microsoft Power Automate dominate the market. The subscription-based nature of these tools often includes licensing fees, and the choice between cloud-based or on-premises deployment affects overall costs. Cloud-based options might offer cost advantages when bundled, while on-premises solutions could be more economical with long-term commitments. Typically, vendor licensing fees make up around 30% of total RPA costs, which is comparable to the expense of a full-time employee performing manual tasks.
| Vendor | Automation Anywhere | IBM RPA | UiPath RPA | Microsoft Power Automation |
| Trial period | 30-day | 30-day | 60-day | 30-day |
| Monthly price for (1 developer & 30 users) | $875 | $981 | $420 | $615*** |
| Monthly price for ( 1 developer & 30 users) | $6,500** | $5,665 | $4,200 | $1,965*** |
| Monthly price for (10 developers & 1,000 users) | $8,750* | $8,359 | $42,000* | $16,650*** |
| Monthly price for (10 developers & 1,000 users) | $87,500* | $48,000 | $42,000* | $30,150*** |
Note: We’ve established the following assumptions for each vendor:
Purchasing 10 times the starter package results in acquiring 10 times the number of developer seats.
For calculation purposes, this entails:
** $250 per developer seat, in addition to 10 attended bots priced at $500 each and 10 unattended bots priced at $125 each.
Also, We’ve operated under the assumption that every employee within the organization, whether they are developers or end users, requires a license. Hence, volume is determined by the total number of employees who fall into these categories.
The cost of the attended RPA package is $15 per month per user, while the unattended automation package, Power Automate Process, is $150 per month. This results in two different situations:
- Scenario 1: Attended RPA is only used by end users.
- Scenario 2: All end users must either utilize unattended RPA directly or have unattended RPA bots handle their data.
2. Sustaining, Supporting, and Expanding RPA Costs
Ongoing maintenance, support, and the potential scaling of RPA efforts add to the overall cost. As RPA bots interact with existing software applications, changes to these systems may necessitate reconfigurations and updates to the RPA setup. Companies often underestimate the importance of planning for scalability, leading to unforeseen costs. Developing a comprehensive RPA implementation strategy from the outset can help manage software dependencies, implement proactive change management, and align stakeholders. Proactive planning is crucial to avoiding disruptions and additional costs associated with RPA scaling and maintenance.
3. Diverse Characteristics of RPA Bots
The diversity in RPA tools and their capabilities contributes significantly to the cost variations. Factors such as the number of bots, their cognitive abilities, and the complexity of tasks they handle are crucial cost drivers. Simple bots with limited functions, like converting PDFs to CSV files, may incur lower costs, while more sophisticated bots operating across multiple applications and conditions require intricate configurations and longer implementation times. Careful consideration of processes for automation is vital, with operations taking less than 30 minutes and performed frequently being ideal candidates for cost-effective bot-driven automation.
4. Inceptive Analysis, RPA Consulting, and Engineering Costs:
Before implementing RPA, thorough process analysis, consulting, and engineering are essential. While RPA tools don’t demand new platforms or major infrastructure upgrades, they require meticulous upfront design and understanding of the processes to be automated. Companies often seek the expertise of RPA development firms, which conduct process reviews, identify automation candidates, and provide technology stack advice. The consulting phase involves creating a high-level RPA architecture and implementation roadmap. Hourly rates for RPA consultants and engineers vary, ranging from $15 to $60 depending on the vendor and country.
5. Expenses Associated with Third-Party RPA Integrations
RPA tools rely on connections to IT systems through APIs, and the cost of these integrations contributes to the overall RPA expenses. Not all necessary APIs are provided or supported by the RPA vendor by default. If integrations with services like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud are required, additional costs arise. The expense increases with the volume of data and server calls handled by the bots. Approximately 5% of the total RPA costs can be attributed to add-on tools necessary for effective integration.
Examples Of Organizations And Their Cost of RPA Implementation
Dzmitry Kliuchnik, Python Team Lead at ITRex Group, shared cost estimates for various RPA projects in the insurance sector. These estimates serve as examples to help understand potential costs based on industry, project requirements, and automation needs.
1. Insurance Claims Processing through RPA Automation
ITRex Group collaborated with an insurance company to implement an RPA solution for claims processing in the insurance sector. The project involved automating and extracting relevant information from various documents, validating the data, and updating the claims management system. The team comprised two RPA developers, one business analyst, and one project manager.
Over the course of 10 weeks, the RPA tool was developed, tested, and deployed. The estimated cost for this insurance-focused RPA implementation was between $20,000 and $40,000. This budget covered development efforts, necessary support, and potential customization to integrate the RPA tool seamlessly with the existing claims processing infrastructure.
2. HR Onboarding Processes in Banking through RPA
A leading bank collaborated with ITRex Group to streamline their HR onboarding processes using RPA. The project involved automating the collection and validation of employee data, document verification, and updating HR systems. The RPA solution is integrated with the bank’s HR software.
The project team, consisting of one project manager, two RPA developers, and one HR process expert, completed the implementation in nine weeks. The estimated cost for this RPA solution in the banking sector, ranged from $30,000 to $60,000. This budget covered development, testing, deployment, and any necessary adjustments to ensure seamless integration with the existing HR infrastructure.
3. Manufacturing Inventory Management
A manufacturing company sought ITRex Group’s expertise to implement an RPA solution for optimizing inventory management. The goal was to automate inventory tracking, order processing, and stock level monitoring. The RPA tool integrated with the company’s ERP system.
The project team, consisting of three RPA developers, one project manager, and one logistics expert, completed the implementation in four months. The estimated cost for this manufacturing-focused RPA system was between $80,000 and $120,000. This budget covered development efforts, infrastructure configuration, and training for employees involved in the inventory management process.
These examples highlight the variability in RPA costs based on industry, project complexity, and specific automation needs. It’s essential for organizations to carefully assess their requirements and engage with RPA experts to determine a tailored solution that aligns with their business objectives.
Challenges In Finding The Cost of RPA Implementation
Businesses must be aware of the following challenges surrounding the estimation of RPA implementation costs before entering into the realm of automation.
1. Lack of Standardized Measurement in RPA
The absence of a standardized unit of measure in the realm of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) presents a significant challenge for businesses. Bots, being the fundamental units of RPA, lack a consistent metric for comparison. Unlike traditional units like lines of code or Full-Time-Equivalents (FETs), bots from different vendors are not interchangeable, making it challenging for organizations to accurately gauge their automation needs. This lack of standardization hampers the ability to assess the true value and efficiency of RPA solutions, leading to ambiguity in pricing structures.
2. Challenges in Comparing RPA Products
Comparing RPA products across different companies proves to be a daunting task due to the absence of a standardized pricing model. The prevalent use of various pricing configurations, often centered around the “number of bots” or output-pricing models, makes it nearly impossible to conduct an apples-to-apples comparison. This lack of uniformity hinders informed decision-making for businesses seeking the most cost-effective and efficient RPA solution, as each vendor’s pricing structure adds a layer of complexity to the evaluation process.
3. Rigidity in RPA Pricing Models
The inflexibility of pricing models in the RPA market poses a challenge for both buyers and vendors. Without a universally accepted valuation of automation, vendors have the liberty to determine the perceived value of their RPA products. This creates a disconnect between what businesses prioritize, such as cost savings from human labor replacement, and what vendors account for in their pricing structures. The rigid pricing models limit the negotiation space for organizations and may result in suboptimal financial arrangements that do not align with the actual benefits derived from RPA implementation.
4. Comprehensive Consideration of Software Costs
While RPA licensing costs are a critical aspect, viewing them in isolation can be misleading. The true cost of business automation extends beyond licensing fees and includes implementation, training, and administration costs. Failure to account for these additional expenses can lead to inaccurate ROI calculations. It is essential for organizations to recognize that licensing costs typically constitute around 30% of the overall expenses throughout the RPA solution’s lifespan. Properly factoring in all associated costs ensures a comprehensive understanding of the investment required and enables businesses to make more informed decisions regarding the adoption of RPA technology.
How To Determine The Cost Of RPA Implementation?
Determining the cost of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) implementation involves various factors specific to each organization and its processes. Here are some steps to help you estimate the cost:
1. Process Assessment and Complexity Analysis
Organizations should start by thoroughly documenting the processes earmarked for automation. Understanding the intricacies of each process is crucial. Assess the complexity level as it directly impacts the type of RPA solutions required. More intricate processes may necessitate advanced RPA tools, potentially affecting overall implementation costs.
2. Infrastructure Requirements
A careful evaluation of the existing IT infrastructure is vital. Determine whether upgrades or additional resources are needed to support RPA implementation. Scalability is a key consideration to ensure that the infrastructure can accommodate future expansions in RPA usage without compromising performance.
3. Software Licensing and Tools
Selecting the appropriate RPA software is a critical decision. Consideration should be given to licensing fees, subscription costs, and any additional charges for support or updates. It’s essential to choose a solution that aligns with the organization’s specific requirements and budget constraints.
4. Customization and Integration
Assess the need for customization in the chosen RPA software to align it with specific organizational processes. Additionally, evaluate the level of integration required with existing systems and applications. Understanding these aspects is crucial for estimating the development effort and associated costs accurately.
5. Training and Change Management
Implementing RPA necessitates training employees on the new tools and methodologies. Budget for training costs and also consider expenses associated with change management to facilitate a seamless transition to automated processes. Employee readiness is a key factor in the success of RPA implementation.
6. Development and Deployment
Break down the development process into phases, estimating the time and resources required for each. Include costs for coding, thorough testing, and successful deployment of RPA bots. A well-structured development plan ensures a systematic and efficient implementation process.
7. Maintenance and Support
Account for ongoing maintenance costs, including regular updates, bug fixes, and system monitoring. Allocate budget for technical support services to address any issues that may arise during the operation of RPA bots. Proactive maintenance is essential to ensure the longevity and effectiveness of the automated processes.
8. Compliance and Security
Examine the compliance requirements for RPA implementation, such as data protection regulations. Allocate funds for security measures to safeguard sensitive information processed by RPA bots. Ensuring compliance and security is not only a legal requirement but also essential for maintaining the trust of stakeholders.
9. ROI Analysis
Conduct a detailed Return on Investment (ROI) analysis to assess the financial viability of RPA implementation. Evaluate both tangible and intangible benefits, including increased efficiency, error reduction, and improved employee satisfaction. A comprehensive ROI analysis provides a clear understanding of the long-term value of RPA.
10. Pilot Project Costs
Consider initiating a pilot project to test the feasibility and benefits of RPA on a smaller scale. Use the costs associated with the pilot project as a basis for estimating expenses for full-scale implementation. Pilots provide valuable insights and help refine the implementation strategy.
11. Contingency Budget
Allocate a contingency budget to account for unforeseen challenges or changes in requirements during the RPA implementation process. Flexibility is crucial as it allows organizations to adapt to unexpected circumstances without jeopardizing the overall success of the automation initiative.
12. Vendor Selection
If outsourcing aspects of the implementation, carefully evaluate potential vendors and obtain detailed quotes. Consider the reputation, experience, and reliability of chosen vendors. A well-informed vendor selection process contributes significantly to the overall success of the RPA implementation.
How Businesses Can Cut Down on RPA Implementation Expenses and Accelerate ROI?
Each RPA implementation carries a unique budget and cost-saving potential based on organizational nuances. However, specific considerations can be instrumental in optimizing costs and accelerating the return on investment (ROI). Here are key strategies to keep in mind when embarking on RPA implementation:
1. Treating RPA as a Business Engine
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) should not be viewed as a standalone solution but as a vital engine that enhances and streamlines existing business processes. To maximize its potential, businesses should align RPA with their strategic goals. By understanding RPA as an enabler rather than a panacea, organizations can set realistic expectations and focus on specific areas where automation can bring the most value. This approach ensures a more measured and effective implementation, contributing to faster return on investment (ROI).
2. Seamless Integration with Existing Systems
RPA implementation should not disrupt existing IT ecosystems; instead, it should seamlessly integrate with diverse software applications. This integration allows RPA tools to source data across the organization’s infrastructure and interact with target applications in a manner consistent with human employees. This approach not only facilitates a smooth transition but also capitalizes on the strengths of both RPA and existing systems, enhancing overall efficiency.
3. Audits and Scalability Planning
Before diving into RPA development, conducting thorough audits and devising a high-level implementation plan with scalability in mind is crucial. This strategic foresight ensures that RPA deployment aligns with the organization’s long-term objectives. Scalability considerations help in accommodating future growth and evolving business needs, making the RPA system a sustainable and adaptable solution over time.
4. Cross-Functional Teamwork and Stakeholder Engagement
Successful RPA implementation relies heavily on cross-functional teamwork and active engagement with stakeholders. Involving representatives from various departments ensures a comprehensive understanding of business processes and their automation requirements. Stakeholder input is invaluable for identifying pain points, prioritizing processes for automation, and garnering support throughout the implementation journey.
5. Process Optimization before Automation
Optimizing business processes before automating them is a fundamental step toward a fault-free RPA rollout. This involves identifying bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement. Streamlining processes first ensures that automation is applied to the most efficient workflows, maximizing the benefits derived from RPA. This methodical approach contributes to a smoother transition and minimizes disruptions during implementation.
6. Addressing Education and Resistance Challenges
A significant hurdle in RPA implementation often stems from a lack of education and awareness about the technology. Overcoming this challenge requires comprehensive training programs for employees, ensuring they understand the benefits and nuances of RPA. Additionally, addressing any resistance from IT departments is essential. Emphasizing the collaborative nature of RPA, where it complements human tasks rather than replacing jobs, can help overcome resistance and foster a culture of innovation.
7. Data Formatting and AI-Based Automation
Data quality is pivotal for the success of RPA initiatives. Ensuring that data is appropriately formatted and optimized for bot-driven manipulation is essential. Implementing AI-based automation tools can partially address challenges related to data manipulation. These tools can enhance the ability of RPA bots to interpret and process unstructured data, leading to more accurate and reliable automation outcomes.
Conclusion
The steady growth of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is undeniably tangible, marked by subtle yet substantial advancements. This surge in adoption is propelled by several factors, with the escalating costs from vendors being a notable driver.
As the demand for RPA solutions rises, vendors are adapting their pricing models, potentially influencing the overall total cost of ownership (TCO) for organizations implementing these automation tools.
There is a growing need for skilled professionals to manage and oversee the deployment of RPA solutions, as organizations embrace automation to streamline and optimize their operations. The recruitment and retention of qualified personnel contribute to the overall costs associated with RPA implementation, impacting the TCO.
In navigating the evolving landscape of RPA, organizations must remain cognizant of these factors to make informed decisions about their automation strategies. While RPA undoubtedly offers significant benefits in terms of process efficiency and productivity, a nuanced understanding of the growing costs associated with its implementation is crucial for maximizing returns and ensuring a sustainable digital transformation journey.
By addressing these considerations, businesses can better position themselves to harness the full potential of RPA while managing the associated costs effectively.
How Idea Usher Can Help?
Idea Usher emerges as an essential ally in the successful implementation of Robotic Process Automation (RPA), providing a comprehensive package of services to simplify and improve business operations.
The company plays a critical role in leading enterprises through the complexity of automation adoption by combining an expert understand of RPA technology with industry-specific details.
Organization’s entire approach to RPA adoption, which includes personalized solutions, extensive training, and continuing support, distinguishes it as a useful partner for enterprises looking to realize the benefits of automation in their operations.
Our RPA Implementation Process
Our RPA implementation strategy are as follows:
1. Infrastructure Analysis
During the first phase of our RPA deployment, we concentrated on thoroughly studying the environment of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and its connection with Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN).
2. Tailoring the RPA Solution
Leveraging the flexibility offered by UI Path, we customized workflows to seamlessly integrate with existing business processes. This step ensured that the RPA solution was not just a standalone entity but an integral part of the overall operational framework.
3. Testing and Quality Assurance
Real-world scenarios, encompassing variations in company profiles and data structures were simulated to validate the adaptability of the bot. Continuous feedback loops were established, allowing for fine-tuning and optimization of the solution.
4. Facilitating Training and Onboarding
To facilitate a smooth transition to the automated solution, comprehensive training sessions were conducted. These sessions highlighted the functionalities, benefits, and best practices for leveraging the RPA bot.
5. Proactive Monitoring and Support
Post-deployment, our commitment to excellence extended to the implementation of a proactive monitoring system. This system was designed to track the performance of the RPA bot in real time, allowing us to identify and address potential issues promptly.
Here is a case study about how we successfully implemented RPA solutions for our client’s business.
Contact us today to know more about how we can help you with our RPA implementation services.
FAQ
Q. How much does it cost to use RPA?
A. The cost of implementing Robotic Process Automation (RPA) can vary widely depending on several factors, including the complexity of the processes to be automated, the scale of implementation, licensing fees for RPA software, training costs, and ongoing maintenance expenses. Generally, organizations should budget for software licenses, infrastructure costs, consulting and implementation services, and employee training. Getting a detailed quote from RPA vendors based on specific organizational needs is advisable.
Q. How do you calculate the cost of an RPA project?
A. Calculating the cost of an RPA project involves considering various components. This includes the licensing fees for the RPA software, infrastructure costs for hosting and running the bots, implementation and consulting services, employee training, and ongoing maintenance expenses. Organizations should thoroughly analyze the processes to be automated, assess the required software and hardware, and factor in the time and effort needed for implementation. It is crucial to work closely with RPA vendors and consider initial and ongoing costs to get an accurate estimate.
Q. How does RPA save cost?
A. RPA can save costs in several ways. Firstly, by automating repetitive and rule-based tasks, RPA reduces the need for human intervention, leading to increased operational efficiency and productivity. It minimizes errors, thereby decreasing the costs associated with manual errors. Additionally, RPA allows organizations to operate 24/7 without incurring additional labor costs. By streamlining processes and improving accuracy, RPA contributes to cost savings in the long run, making it a valuable investment for many businesses.
Q. Which RPA tool is best?
A. The choice of the best RPA tool depends on specific organizational needs, requirements, and preferences. Several reputable RPA tools, including UiPath, Automation Anywhere, Blue Prism, and others, are available. Each tool has its strengths and weaknesses, and the decision should be based on factors such as ease of use, scalability, integration capabilities, community support, and cost. It’s advisable to conduct a thorough evaluation, possibly through a proof of concept, and consider factors like user-friendliness, vendor support, and the tool’s alignment with the organization’s automation goals before making a decision.











Gaurav Patil