Entrepreneurs and businesses looking forward to venturing into the video conferencing industry have only one question – How Does Zoom Make Money?
During this COVID-19 pandemic, start-ups, MNCs, educational institutions, healthcare providers, and anyone who wanted to communicate by video conferencing opted for Zoom Meetings predominantly. For such reasons, the company has reached new heights with social distancing and remote work being implemented worldwide.
As per the reports by SensorTower of the Top Apps Worldwide for 2020 by Downloads, Zoom made it to the top list in all three categories: App Store Downloads, Google Play Downloads, and Overall Downloads.
If you’re an entrepreneur or a business that wishes to replicate an application like Zoom, then you’re at the right place.
This blog post will give you insights into the business and revenue models of Zoom and ultimately give you the answers to your question, “How Does Zoom Make Money?“
Let’s get started.
Zoom Facts and Stats
| Founded | April 21, 2019 |
| Headquarters | San Jose, California, United States |
| Founder | Eric Yuan |
| Services | Videotelephony, Business Telephone Systems, Online Chat |
| Business Model | Freemium Model |
| Number of Investors | 18 |
| Total Funding Amount | $148M |
| Employees | 2.532 (2020) |
| Website | https://zoom.us/ |
Success Timeline – Early History and Growth

Before we understand how Zoom makes money, let’s have a quick look at Zoom’s success timeline – its early history, growth, and success.
2011
Eric Yuan (founder of Zoom) left Cisco Webex in April, where he worked as a corporate vice president, to start a new company with 40 engineers. Zoom was initially named Saasbee, Inc.
In June, the company raised $3M in seed money from Subrah Iyer (founder of WebEx), Dan Scheinman (former Cisco SVP and General Counsel), Matt Ocko, TSVC, and Bill Tai (Venture Capitalists).
2012
After changing its name from Saasbee, Inc. to Zoom in May, the company decided to launch a beta version of its program in September, which could host conferences with up to 15 participants.
Stanford University became Zoom’s first customer in November.
2013
Zoom finally set up its services and raised $6M in a Series A round of funding in January. It launched version 1.0 of the program, which increased the total number of conference participants to 25. By the end of the first month, Zoom had 400,000 users.
Over the months, Zoom established partnerships with various service providers. In September, it raised $6.5M in a Series B round of funding, bringing its user base to 3 million.
2015
Zoom raised $30M in a Series C round of funding in February. By this time, the total number of active users reached 40 million, and over 65,000 organizations subscribed to its services.
In October, the company launched version 2.5, which enabled users to host conferences with a maximum of 50 participants for standard plans and up to 1,000 participants for business plan subscribers.
2017
Zoom raised $100M in a Series D round of funding in January, achieving a $1B valuation.
Throughout the year, Zoom introduced several new products, such as telehealth services, and added features like multiple screens and device meetings, calendar integration, and initial AI Speech Recognition capabilities.
2019
Zoom became a public company via an IPO. At the end of its first trading day, the company’s valuation reached $16B.
As the COVID-19 pandemic began spreading in some countries, many companies, universities, and institutions switched to remote working, distance learning, and online social interaction. This led to a surge in the number of Zoom users.
2020
Zoom gained 2.22 million users by February, surpassing the number of users acquired during the entire year of 2019.
In March, the number of daily meeting participants reached 300 million. By June, the company’s valuation had soared to $67B.
By September, Zoom’s stock prices surged by 569%, and its market capitalization reached $129B. By the end of October, the market capitalization rose to $140B, making Zoom’s value higher than ExxonMobil, a 130-year-old company. However, in November, the company experienced a 15% drop in stock prices.
In December, Zoom focused on enhancing its security features, responding to criticisms over data privacy and security concerns earlier in the year. The company launched end-to-end encryption for all users and introduced several updates to improve platform stability and usability. Additionally, Zoom continued expanding its enterprise services, targeting industries such as education, healthcare, and government. Despite stock fluctuations, Zoom maintained its position as a dominant player in the video conferencing market, ending the year with strong financial performance and continued user growth.
2021
Zoom continued to grow, with a strong emphasis on hybrid work solutions. The company launched “Zoom Events,” a platform to host virtual and hybrid events. Zoom also expanded its integrations with third-party platforms, enhancing user flexibility.
The company reported a 50% increase in revenue compared to 2020, as businesses and educational institutions maintained their reliance on remote communication tools. Zoom further invested in its AI capabilities, rolling out advanced features like real-time transcription and improved background noise cancellation.
2022
In 2022, Zoom introduced features focused on enhancing user engagement, such as immersive view and gesture recognition. It also launched its “Zoom Contact Center,” aimed at providing business customer service solutions.
Zoom’s market presence grew in emerging markets as the demand for flexible communication tools persisted. The company also partnered with several major corporations to provide tailored solutions for their communication needs. By the end of the year, Zoom’s revenue growth slowed slightly as global demand normalized.
2023
Zoom pivoted towards enterprise solutions, focusing heavily on its “Zoom IQ” suite for advanced AI-driven analytics and insights. The company also expanded its telehealth offerings, integrating with major healthcare providers to streamline virtual consultations.
In addition, Zoom acquired a smaller AI startup to enhance further its AI capabilities, including sentiment analysis and meeting summaries. By mid-2023, Zoom had over 500,000 enterprise customers, reflecting its shift towards B2B solutions.
2024
Zoom introduced its “Zoomverse” platform, combining virtual reality with video conferencing to offer immersive meeting experiences. This marked the company’s entry into the metaverse, targeting industries such as education, gaming, and corporate training.
The company also announced plans to develop blockchain-based authentication features to address growing security demands. By the end of 2024, Zoom maintained a leading position in the video conferencing industry, adapting to evolving market trends and user needs.
Now that we’ve seen how Zoom has grown and achieved success over the past few years, let’s move on to knowing.
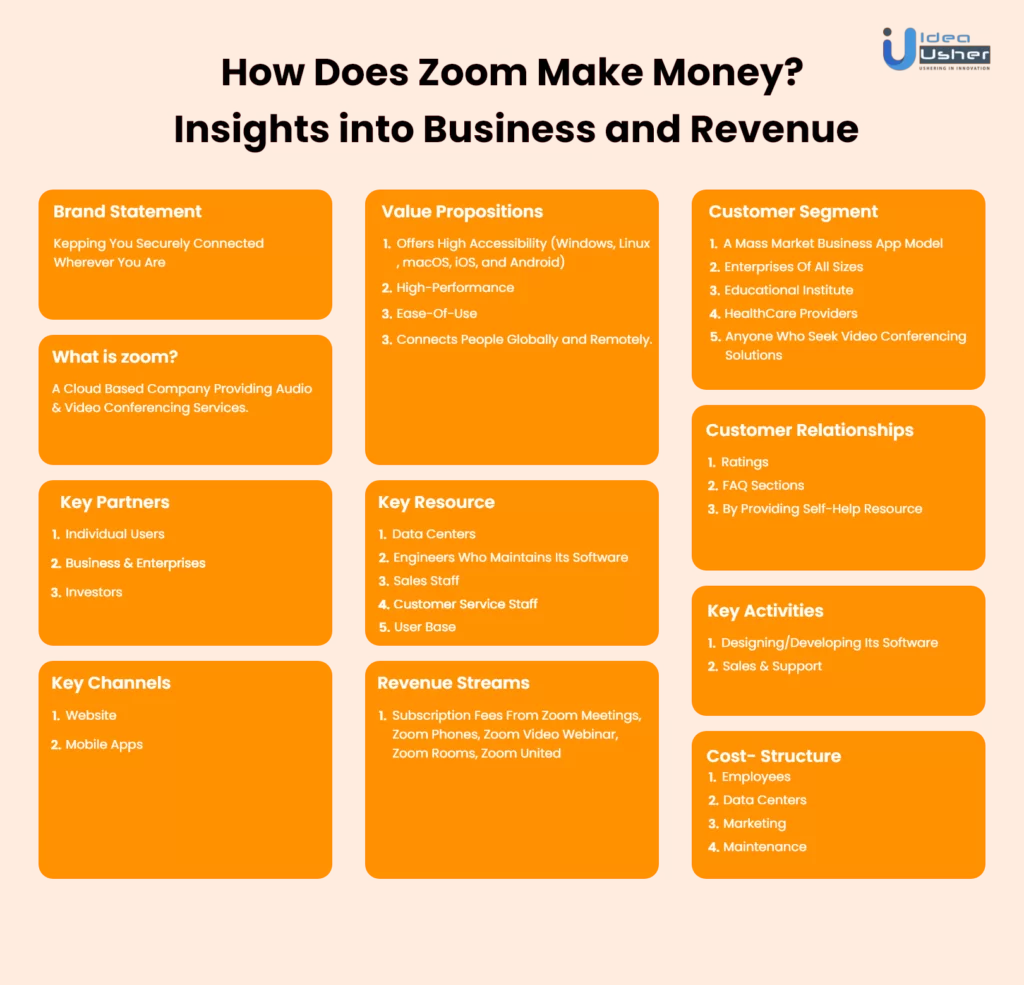
Business Model Explained

Zoom provides video telephony services, which means that it offers a platform to communicate with people via both audio and video in real time. To understand how Zoom makes money, we need to understand its business model.
It mainly targets businesses and enterprises of all sizes, healthcare providers, educational institutions, and anyone seeking video conferencing solutions. Therefore, these constitute the customer segments of Zoom.
Coming onto its value proposition, it offers high accessibility as it is available across all platforms (Windows, Linux, macOS, iOS, and Android), high performance, ease-of-use, and, most importantly, it connects people globally and remotely.
To sum it up, one can use Zoom for business meetings, training programs, online conferences, job interviews, webinars, etc., on any platform without any hassle.
Here’s the Zoom Business Model Canvas that gives you a brief overview of and how it works.
Get in touch with us today, and our experts will help you develop an application just like Zoom.
Additionally, Zoom operates on a freemium business model. Now, you may ask – “What is freemium?”
Freemium is a business model where the company provides limited services to its users without charging any fee. The intention behind providing these is to hook the customers and make them subscribe to the upgraded services.
Most of us think that Zoom is a basic video conferencing service. However, it is much more than that.
Let’s discuss each service separately so that we can understand Zoom generates revenue.
Zoom Meetings
Zoom Meetings is the company’s core offering, and it is also the most used service. It allows its users to communicate via video conferencing and offers a feature called Zoom Chat where users can drop text messages, URLs, and other content.
Subscription Models:
1. Basic (Free)
- Best for personal meetings.
- Host meetings with up to 100 participants for free.
- Time limit: 40 minutes for group meetings; unlimited for 1:1 meetings.
2. Pro
- Designed for small teams.
- Host unlimited group meetings with up to 100 participants.
- Includes features such as social media streaming and 1 GB of cloud recording.
- Price: $149.90/year/license.
3. Business
- Ideal for small and medium businesses.
- Host meetings with up to 300 participants.
- Additional features: single sign-on, cloud recording transcripts, company branding, and managed domains.
- Price: $199.90/year/license.
4. Enterprise
- Suited for large businesses.
- Host meetings with up to 500 participants.
- Additional features: unlimited cloud storage, dedicated customer success manager, and transcription.
- Price: $300.00/year/license.
Prices may vary depending on location and currency.
Zoom Phone
Zoom Phone makes the application a complete collaboration product for businesses and companies. It offers traditional phone capabilities within the application, making Zoom a one-stop solution for calling, messaging, and video conferencing.
Subscription Models:
1. US & Canada Metered
- Includes a US and Canada number.
- Metered calls from multiple devices.
- Price: $120.00/year/license.
2. US and Canada Unlimited
- Unlimited calling within the US and Canada.
- Includes advanced phone features.
- Price: $180.00/year/license.
3. Pro Global Select
- Unlimited domestic calling in over 40 countries and territories.
- Includes all features from the previous models.
- Price: $240.00/year/license.
Prices may vary depending on location and currency.
Zoom Video Webinar
Zoom Video Webinar allows users to host webinars with anywhere between 100 to 10,000 participants, depending on the pricing plan. It includes interactive features like polling, Q&A sessions, likes, and upvotes, as well as a variety of business-friendly features.
- Pricing: Starts at $400.00/year/license and goes up to $64,900.00/year/license.
- For webinars with 10,000+ participants, users need to contact Zoom’s sales team.
Zoom Rooms
Zoom Rooms is designed to make video conferencing seamless and efficient. It offers features like:
- One-click joining.
- 1080p HD video and audio.
- Support for 1,000 video participants or 10,000 webinar viewers.
- Calendar integrations.
- Offers a 30-day free trial (credit card required).
- Pricing starts at $499.00/year/license.
3 Things to Learn From Zoom
1. Address the Target Market’s Problems
- While Skype was a great communication tool, its UX was complicated, and users needed accounts to join meetings. Zoom addressed these gaps with one-click joining and an excellent UX.
2. Build a Product That Sells Itself
- Eric Yuan focused on creating a robust application with standout features. By targeting early adopters who loved the product, word-of-mouth marketing naturally followed.
3. Leverage Free Services
- The free version of Zoom Meetings helped the platform gain traction. Once users saw the value, many upgraded to paid models for advanced features.
Conclusion
Zoom’s journey from a startup to a market leader demonstrates the importance of understanding customer needs, focusing on product development, and leveraging strategic pricing. If you’re inspired to turn your ideas into a world-class project, get in touch with us today, and our experts will help you develop an application just like Zoom..
Work with Ex-MAANG developers to build next-gen apps schedule your consultation now
Faq
Q2. How much does it cost to develop an app similar to Zoom?
- The cost can range from $50,000 to $500,000 depending on features, platform compatibility, and development complexity.
Q3. How long does it take to build a video conferencing app?
- Development can take 6 to 12 months, depending on the app’s complexity and the size of the development team.
Q4. What tech stack is recommended for a Zoom-like app?
- Frontend: ReactJS, AngularJS.
- Backend: Node.js, Python, or Java.
- Database: MySQL, PostgreSQL, or MongoDB.
- Real-time communication: WebRTC, Twilio, or Agora.
- Cloud services: AWS, Google Cloud, or Azure.