- Types Of Apps In The Healthcare Industry
- Benefits Of Healthcare Apps
- Advanced Development Trends In Healthcare Applications
- Must Have Features In Healthcare Apps
- Cost Affecting Factors To Consider To Develop a Healthcare Application
- Monetization Models Of A Healthcare Application
- How To Develop A Healthcare App?
- Top 5 Successful Healthcare Apps In The Market Right Now
- Tech Stack To Consider To Develop a Healthcare Application
- Conclusion
- How Idea Usher Can Help?
- FAQ

Digitalization has had a far-reaching impact on many aspects of our lives, including healthcare.
Nowadays, individuals can conveniently book appointments with their physicians, access blood test results, and even engage in mental health therapy sessions, all through the convenience of a mobile application.
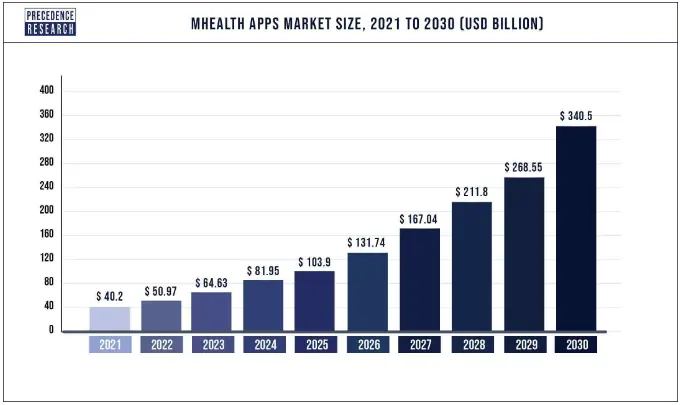
Source: PrecedenceResearch
A rapidly expanding market signifies substantial demand and lucrative prospects for entrepreneurs. This growth trend indicates a great landscape for innovative healthcare startups to thrive and capture market share, offering valuable solutions in an increasingly digitized healthcare ecosystem.
However, launching a medical startup necessitates a thorough analysis of ideas, trends, and developmental procedures.
Whether it involves developing an app for telemedicine, electronic health records, or patient health management tools, this guide offers comprehensive insights into the essential factors to consider throughout the development of a healthcare application.
- Types Of Apps In The Healthcare Industry
- Benefits Of Healthcare Apps
- Advanced Development Trends In Healthcare Applications
- Must Have Features In Healthcare Apps
- Cost Affecting Factors To Consider To Develop a Healthcare Application
- Monetization Models Of A Healthcare Application
- How To Develop A Healthcare App?
- Top 5 Successful Healthcare Apps In The Market Right Now
- Tech Stack To Consider To Develop a Healthcare Application
- Conclusion
- How Idea Usher Can Help?
- FAQ
Types Of Apps In The Healthcare Industry
Understanding the distinct audiences of mobile medical solutions is essential for developing effective health apps. These solutions typically cater to three primary groups: patients, healthcare professionals, and administrative staff. Identifying these target audiences beforehand can significantly inform the development process of a health app.
I. Health Apps for Patients:
Health apps designed for patients aim to empower individuals to take control of their own health and wellness. These applications provide tools and resources to help users monitor their health conditions, track their fitness goals, access medical information, and manage their medications.
- Appointment scheduling and reminders: These apps help patients schedule appointments with healthcare providers conveniently and send them reminders to ensure they don’t miss their appointments.
- Self-diagnosing: These apps provide information and tools for users to perform self-assessment of their symptoms and potential conditions, though they often come with disclaimers and recommendations to consult a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis.
- Habit tracking: These apps assist users in tracking and managing their health-related habits, such as medication adherence, diet, exercise, and sleep patterns, to promote overall wellness.
- Fitness and wellness: These apps offer features like workout routines, calorie tracking, step counting, and meditation guides to help users maintain a healthy lifestyle.
- Social networking: These platforms connect patients with similar health concerns, allowing them to share experiences, advice, and support with each other.
- Telehealth: These apps enable patients to consult with healthcare providers remotely via video calls, chats, or phone calls, making healthcare more accessible and convenient.
- Mental health: These apps provide resources, tools, and support for managing mental health conditions such as anxiety, depression, stress, and PTSD through activities like mindfulness exercises and mood tracking.
- IoT medical products: These apps are designed to work with Internet of Things (IoT) devices such as wearable sensors and smart home health monitors to track and manage health data.
- Women’s health: These apps focus on women’s specific health needs, including menstrual cycle tracking, fertility tracking, pregnancy monitoring, breastfeeding support, and menopause management.
II. Health Apps for Providers
Health apps for medical personnel are designed to streamline workflows, enhance communication, and improve patient care within clinical settings. These applications offer functionalities tailored to the needs of healthcare professionals, including electronic health record (EHR) access, medical reference tools, clinical decision support systems, telemedicine capabilities, and secure messaging platforms.
- Remote patient monitoring: These apps allow healthcare providers to remotely monitor patients’ health data, such as vital signs, medication adherence, and symptoms, often using wearable sensors or home monitoring devices.
- Telemedicine: These apps enable healthcare providers to conduct virtual consultations with patients, offering diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up care without the need for in-person visits.
- Diagnosis: These apps assist healthcare providers in diagnosing medical conditions by providing access to medical databases, symptom checkers, and decision support tools.
- EHR: Electronic Health Record (EHR) apps allow healthcare providers to access and update patients’ medical records electronically, facilitating efficient documentation, communication, and coordination of care.
- Medicine reference: These apps provide healthcare professionals with access to comprehensive databases of drug information, including dosages, interactions, side effects, and prescribing guidelines.
- Hospital mobile app ERPs: Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) apps tailored for hospitals enable efficient management of resources, such as personnel, inventory, and finances, to optimize operations and improve patient care.
- Clinical communication: These apps facilitate secure communication and collaboration among healthcare team members, allowing for quick exchange of patient information, consultation, and coordination of care.
- Appointments management: These apps help healthcare providers manage their schedules, appointments, and patient bookings efficiently, reducing wait times and optimizing clinic workflow.
III. Health Apps for Medical Administration Staff
Health apps for medical administration staff cater to the administrative needs of healthcare organizations, such as hospitals, clinics, and healthcare networks. These applications focus on optimizing operational processes, managing resources, and ensuring regulatory compliance.
- Doctor/nurse marketplace: These platforms connect healthcare facilities with available doctors, nurses, and other medical professionals for temporary or permanent staffing needs.
- EMR/EHR: Electronic Medical Record (EMR) or Electronic Health Record (EHR) apps designed for medical administration staff facilitate the management and maintenance of patients’ medical records, including data entry, storage, retrieval, and analysis.
- Inventory management: These apps assist medical facilities in managing their inventory of medical supplies, equipment, and pharmaceuticals, optimizing procurement, usage, and replenishment to ensure adequate supply levels and minimize waste.
- Billing: Billing apps streamline the process of generating and managing medical bills, claims, and invoices, including patient billing, insurance claims processing, and revenue cycle management.
- Practice management applications: These comprehensive applications offer features for managing various aspects of medical practices, including scheduling, billing, electronic medical records, inventory, and reporting, to enhance efficiency and productivity.
Benefits Of Healthcare Apps
Healthcare applications have revolutionized the way healthcare is delivered, providing numerous benefits for both doctors and patients alike. These innovative tools leverage technology to enhance efficiency, accessibility, and quality of care in the healthcare industry.
I. Benefits For Doctors
Healthcare apps offer doctors streamlined workflows, access to comprehensive patient data, and efficient communication channels, empowering them to deliver higher quality care with greater ease and effectiveness.
1. Enhanced Efficiency
Health apps are designed to streamline various administrative tasks, such as appointment scheduling, prescription refills, and record-keeping, which allows doctors to dedicate more time to direct patient care. By automating routine processes and providing tools for task management, these apps help doctors prioritize their workload efficiently. Integration with electronic health record systems eliminates the need for manual data entry during patient consultations, enabling quick access to comprehensive patient information.
2. Precision in Diagnosis
Healthcare apps leverage AI-powered diagnostic algorithms to analyze patient symptoms and medical data, aiding doctors in making accurate diagnoses. These apps provide decision support systems that offer evidence-based recommendations for treatment options, reducing diagnostic errors and improving patient outcomes. Remote monitoring tools track patient vital signs and symptoms, allowing for early detection of health issues and proactive intervention.
3. Preventing Stress and Burnout
Healthcare apps play a crucial role in alleviating stress and preventing burnout among doctors by automating administrative tasks and providing resources for self-care and wellness. Task automation reduces the administrative burden on doctors, allowing them to focus more on patient care. These apps also include workload management features to help doctors balance their caseloads and prioritize urgent cases effectively. Additionally, wellness resources within the app promote healthy lifestyle habits and coping strategies for managing stress.
4. Enhanced Communication
Healthcare apps facilitate seamless communication and collaboration among healthcare professionals, regardless of geographical barriers. Secure messaging features enable real-time communication between doctors, nurses, pharmacists, and other members of the healthcare team, improving care coordination and patient outcomes. Care coordination tools allow multidisciplinary teams to collaborate on patient care plans and track progress efficiently. Video conferencing capabilities support remote consultations and telemedicine visits, enhancing access to specialty care for patients in underserved areas.
5. Efficient Hospital and Equipment Management
Healthcare apps leverage IoT sensors and predictive analytics to optimize hospital operations and equipment management. IoT sensors monitor equipment usage, performance, and maintenance needs in real-time, minimizing downtime and maximizing efficiency. Predictive analytics algorithms forecast equipment failures and maintenance requirements, enabling proactive interventions to prevent disruptions in patient care.
6. Cost Reduction in Healthcare Provision
Healthcare apps offer numerous opportunities for cost reduction in healthcare provision through process optimization, preventive care initiatives, and value-based care models. Process optimization and automation reduce overhead costs associated with manual administrative tasks and paperwork, improving operational efficiency and resource utilization. Preventive care initiatives supported by health apps help reduce the incidence of costly complications and hospital readmissions, leading to significant cost savings over time.
II. Benefits For Patients
Patients benefit from healthcare apps through increased convenience, personalized treatment plans, and better access to medical services, empowering them to take control of their health and well-being like never before.
1. Higher Quality Care
Healthcare mobile applications revolutionize the delivery of healthcare by providing patients with personalized treatment plans tailored to their unique conditions and needs. Through automation, these applications enable healthcare providers to offer comprehensive monitoring and follow-up, ensuring that patients receive the highest quality of care. Patients benefit from prompt alerts regarding medication schedules, appointments, and important health milestones, helping them stay on track with their treatment plans. Additionally, the accessibility of specialist expertise through telemedicine features ensures that patients can easily connect with doctors regardless of geographical barriers.
2. On-Demand Accessible Care
Healthcare mobile applications provide patients with the convenience of immediate medical assistance anytime, anywhere, reducing the need for unnecessary emergency room visits. Through virtual consultations, patients can efficiently receive medical advice without the constraints of in-person appointments, saving both time and resources. Furthermore, these applications facilitate the delivery of medications directly to patients’ doorsteps, ensuring timely access to essential treatments. Integration with wearable devices allows for remote monitoring of vital signs and health parameters, providing real-time data to healthcare providers for better decision-making.
3. Better Control Over Health Data
Patients gain better control over their health data through healthcare mobile applications, which enable easy export of medical records for sharing with other healthcare providers. Robust privacy controls ensure that patients can manage access to their health information, maintaining confidentiality and compliance with data protection regulations. Additionally, interoperability with electronic health record systems enables seamless exchange of information between different healthcare providers, preventing duplication of tests and procedures.
4. Secure Payments
In-app payment functionality in healthcare mobile applications offers patients convenient and secure transactions for settling medical bills, ordering prescriptions, and paying for healthcare services. Patients receive detailed invoices and receipts for all transactions, promoting transparency and accountability in healthcare finances. With robust encryption and security protocols, these applications safeguard patients’ financial information, minimizing the risk of data breaches and fraud.
5. Engagement
Healthcare mobile applications foster patient engagement through educational resources, interactive tools, and health-tracking features. Patients are empowered with knowledge about their conditions and treatment options, enabling them to actively participate in their healthcare journey. The ability to track progress, set goals, and monitor health metrics promotes accountability and motivation. Additionally, integration with online forums and support groups creates a sense of community and peer support among patients facing similar health challenges.
Advanced Development Trends In Healthcare Applications
Innovations in healthcare are rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence, blockchain, IoT, big data analytics, and AR/VR technologies. From intelligent chatbots to blockchain-enabled data sharing and immersive AR/VR experiences, these cutting-edge solutions are reshaping the future of healthcare.
1. AI and ML Applications in Healthcare
Artificial intelligence (AI) paired with machine learning (ML) algorithms is revolutionizing various aspects of healthcare. One significant application lies in intelligent chatbots embedded in healthcare apps, capable of learning about patients’ conditions during conversations. These chatbots facilitate early diagnosis and personalized treatment by analyzing patient data efficiently. Additionally, AI plays a crucial role in medical imagery analysis, identifying patterns in images such as X-rays and MRIs. This enables faster and more accurate diagnoses, ultimately improving patient outcomes. Symptom tracking and analysis apps powered by ML algorithms further contribute to proactive healthcare management by detecting trends and predicting potential health issues.
2. Blockchain
Blockchain technology offers transformative solutions to various challenges in the medical field, particularly addressing the interoperability issue. Integration with multiple electronic health record (EHR) systems enables secure and seamless sharing of patient data among healthcare organizations. Moreover, blockchain facilitates transparent and traceable medicine tracking within supply chains, ensuring the authenticity and integrity of pharmaceutical products. Decentralized patient portals empower individuals to control access to their health data, enhancing privacy and security.
3. IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) continues to reshape healthcare with its expanding range of applications beyond remote patient monitoring. Smart medical appliances equipped with IoT capabilities enable real-time data collection and analysis, enhancing healthcare delivery and patient outcomes. Wearable devices featuring advanced sensors, such as electrocardiogram (ECG) and electrodermal activity (EDA) sensors, provide valuable insights into patients’ health status, facilitating early intervention and personalized care. Additionally, IoT solutions support medical inventory management, optimizing supply chain processes and ensuring timely availability of essential resources.
4. Big Data
Addressing the challenge of big data is essential for developing scalable healthcare applications that leverage AI, ML, and IoT functionalities. Architecting datasets capable of handling massive volumes of data and performing millions of calculations in real-time is crucial for powering intelligent healthcare solutions. By effectively managing big data, healthcare systems can unlock valuable insights, improve decision-making processes, and optimize patient care delivery.
5. AR and VR Applications
Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies offer promising applications in various medical contexts, beyond their conventional use in gaming. AR-based therapy sessions provide patients with immersive experiences, facilitating remote rehabilitation and mental health treatments. Surgeons benefit from AR simulations for training purposes, enabling them to practice complex procedures in a safe and controlled environment. Moreover, AR technology supports medical education by enhancing learning experiences and providing interactive training modules for students.
Must Have Features In Healthcare Apps
Healthcare apps have revolutionized the way individuals access medical information and manage their well-being. Explore must have features empowering apps to streamline the process.
1. Integrations With Health Tracking Platforms
To ensure the effectiveness of a healthcare application, seamless integration with popular health tracking platforms like Google Fit, HealthKit, and Samsung Health is paramount. This integration facilitates the synchronization of vital health data, exercise routines, and other metrics across multiple devices. Users benefit from a holistic view of their health, as the application consolidates data from various sources into one cohesive platform. Moreover, customizable data insights derived from this integrated data offer users personalized analytics and recommendations for improving their health outcomes.
2. Patient And Doctor Profiles
Patient and doctor profiles serve as the cornerstone of a healthcare application, facilitating efficient communication and comprehensive care management. Patients can maintain detailed medical histories within their profiles, including past diagnoses, medications, allergies, surgeries, and family medical history. This comprehensive overview enables healthcare providers to make informed decisions and tailor treatment plans to individual patient needs.
3. Telemedicine Options
Telemedicine options are increasingly essential in modern healthcare applications, providing remote access to medical services and improving patient outcomes. Real-time video consultations enable patients to connect with healthcare providers from the comfort of their homes, facilitating visual assessments, remote examinations, and virtual care delivery.
Secure file-sharing features allow patients to upload medical documents, images, and test results for review by healthcare providers during telemedicine appointments. This ensures comprehensive assessment and diagnosis, even in remote settings. Integration with remote monitoring devices and wearables enables continuous monitoring of vital signs, health metrics, and medication adherence outside traditional healthcare settings.
4. Reminders And Notifications
Effective reminders and notifications are integral components of healthcare applications, helping users stay on track with their medication schedules and health goals. These features leverage the mobile platform’s capabilities to provide timely and relevant notifications tailored to individual user needs. Time-based reminders ensure users never miss a dose of their medication or forget important health-related tasks. Users can set up personalized reminders for medication intake, appointments, exercise routines, and other health-related activities.
5. Personalized Health Tracking
Personalized health tracking is a cornerstone feature of modern healthcare applications, empowering users to take a proactive approach to their well-being. Through comprehensive tracking of various health metrics and activities, users gain valuable insights into their health status and progress towards their wellness goals. The application collects and analyzes data on parameters such as physical activity, sleep patterns, nutrition, and vital signs, offering users personalized recommendations and actionable insights for optimizing their health.
6. Nutrition And Dietary Planning
Nutrition and dietary planning features are essential components of comprehensive healthcare applications, enabling users to make informed decisions about their dietary habits and nutrition intake. These features offer users tools and resources for tracking food consumption, monitoring nutritional content, and planning balanced meals that align with their health goals and preferences.
7. Community Support And Engagement
Community support and engagement features play a vital role in fostering a sense of belonging, accountability, and motivation among users of healthcare applications. By connecting users with peers, support groups, and health communities, these features create a supportive environment where users can share their experiences, seek advice, and provide mutual encouragement on their wellness journey.
8. Emergency Medical Assistance
Emergency medical assistance features provide users with essential tools and resources for accessing timely and appropriate medical care in emergency situations. Whether facing a medical crisis, injury, or sudden illness, users can rely on these features to quickly connect with emergency services, communicate critical information, and receive prompt assistance when needed most. One of the primary functionalities of emergency medical assistance features is the provision of emergency contact information and medical identification.
9. Health Education And Resource Library
Health education and resource libraries serve as valuable repositories of information, tools, and resources to empower users with knowledge and support their health and wellness journey. These features provide users with access to a wide range of educational content, articles, videos, infographics, podcasts, and interactive tools on various health topics, ranging from preventive care and disease management to lifestyle modifications and wellness strategies.
Cost Affecting Factors To Consider To Develop a Healthcare Application
Developing a healthcare application involves a myriad of factors that can significantly impact costs. From the complexity of the app’s features to compliance requirements and integration with existing systems, numerous elements must be considered to ensure a successful and cost-effective development process. Here are six key cost-affecting factors to consider:
1. Feature Complexity and Scope
The complexity and scope of features within a healthcare application are among the primary determinants of development costs. Healthcare apps can range from simple appointment scheduling tools to comprehensive telemedicine platforms with advanced diagnostic features. Each additional feature adds complexity to the development process, requiring more time and resources to implement. For example, integrating real-time video conferencing for telemedicine consultations involves building robust communication infrastructure, ensuring HIPAA compliance for patient data security, and implementing user-friendly interfaces.
2. Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Compliance with healthcare regulations such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), and FDA guidelines is non-negotiable for healthcare applications. Ensuring compliance adds an extra layer of complexity to development and ongoing maintenance, impacting costs significantly. Developing a HIPAA-compliant healthcare application requires implementing robust security measures to protect sensitive patient data, conducting regular security audits, and maintaining strict access controls.
3. Integration with Existing Systems
Healthcare applications often need to integrate with existing electronic health record (EHR) systems, laboratory information management systems (LIMS), billing software, and other healthcare IT infrastructure. Seamless integration is critical for ensuring interoperability and providing users with a cohesive experience across multiple platforms. However, integrating with legacy systems can be challenging and time-consuming, especially if they use outdated technologies or lack standardized interfaces.
4. Scalability and Performance Requirements
Healthcare applications must be designed to accommodate varying levels of usage and scale to support growing user bases and evolving business needs. Scalability and performance considerations significantly influence development costs, as building a scalable architecture requires robust infrastructure, efficient database management, and optimized code. Investing in cloud-based infrastructure and microservices architecture can enhance scalability by enabling on-demand resource allocation and horizontal scaling.
5. User Experience (UX) Design and Usability
A seamless and intuitive user experience is paramount in healthcare applications, as it directly impacts user engagement, satisfaction, and ultimately, the success of the product. Investing in UX design and usability testing is crucial for creating an application that is easy to navigate, aesthetically pleasing, and accessible to users of all abilities. However, designing and refining the user experience involves iterative processes such as wireframing, prototyping, and user testing, which require dedicated time and resources.
6. Data Security and Privacy Measures
Healthcare applications handle sensitive patient information, making data security and privacy paramount concerns. Implementing robust security measures to protect patient data from unauthorized access, breaches, and cyber threats is essential but can significantly impact development costs. Encryption, authentication mechanisms, access controls, and regular security audits are among the measures necessary to safeguard patient data and maintain compliance with regulatory requirements.
Monetization Models Of A Healthcare Application
Monetization strategies for a healthcare application vary depending on its target audience and functionality. Whether it’s designed for patients, healthcare providers, or integrated with IoT devices, there are several avenues to generate revenue:
1. Subscription Model
A subscription model offers a structured revenue stream for healthcare applications, ensuring regular payments from users in exchange for access to the app’s features or services. This approach works well for both mobile and web-based healthcare solutions, providing developers with predictable income and users with ongoing access to updated features. To implement a subscription model effectively, developers may offer various subscription tiers or plans with different levels of access or features, catering to the diverse needs of users.
2. Service Sales
In the healthcare industry, service sales entail offering one-time purchases for specific services within the application, such as virtual consultations, personalized health coaching, or premium content. Unlike subscription models, service sales provide users with flexibility, allowing them to pay only for the services they need without committing to ongoing subscriptions. Developers can optimize service sales by identifying high-demand services and pricing them competitively. By delivering high-quality services and ensuring a seamless user experience, developers can encourage repeat purchases and build customer loyalty.
3. Sponsorship
Sponsorship agreements in healthcare apps involve partnering with medical equipment brands or healthcare product manufacturers to promote their products or services within the application. This can include featuring sponsored content, recommending specific brands, or integrating sponsored functionalities. By collaborating with relevant sponsors, developers can enhance the user experience and generate additional revenue streams. However, it is crucial to maintain transparency and integrity when integrating sponsored content to preserve user trust and credibility.
4. Licensing
Licensing involves selling usage rights to healthcare organizations or businesses for the use of the application’s software. This model provides developers with recurring revenue streams while granting licensees access to specialized software solutions and support services. Developers can optimize licensing models by offering flexible licensing options, such as per-user licenses or enterprise agreements, to accommodate varying organizational needs. Clear licensing agreements and terms are essential to avoid misunderstandings and ensure compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
5. Pay Per Download
Pay-per-download models involve charging users a fee to download the healthcare application from app stores. While this model was more prevalent in the past, it has become less popular due to the rise of free alternatives and the challenge of convincing users to pay upfront without trying the app first.
Developers can still succeed with pay-per-download models by offering compelling value propositions and effective marketing strategies. This may include providing trial versions, offering discounts or promotions, and highlighting unique features or benefits. By understanding user preferences and market dynamics, developers can effectively leverage pay-per-download models to generate revenue and expand their user base.
6. Device Sales
Integrating hardware and software packages can provide value to users and generate revenue for developers through device sales. This approach involves bundling the healthcare application with IoT devices or medical sensors, offering users a comprehensive solution for their healthcare needs.
Developers can optimize device sales by ensuring compatibility, usability, and customer support to deliver a seamless user experience. By offering bundled packages at competitive prices, developers can attract customers and differentiate their offerings from standalone software solutions.
7. Patient Data Monetization
Patient data monetization involves collecting anonymized patient data and medical information within the application and selling it to pharmaceutical companies or medical research institutions. This can be a lucrative revenue stream, but it requires strict adherence to privacy regulations and ethical considerations. Developers must prioritize data security and privacy to protect user confidentiality and maintain trust. By implementing robust data encryption, anonymization techniques, and consent management processes, developers can ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and mitigate privacy risks.
How To Develop A Healthcare App?
From addressing regulatory compliance to designing user-friendly interfaces, each step in the development process plays a crucial role in delivering a successful app. In this section, we’ll explore key steps and considerations to help you navigate the complexities of healthcare app development effectively.
1. Market Analysis
Conducting a comprehensive market analysis is the foundation of a successful healthcare app. By delving into your target market’s dynamics, trends, and opportunities, you can gain valuable insights to inform your app development strategy. Identifying your audience and analyzing competitors’ strengths and weaknesses allows you to differentiate your app effectively. Through surveys, interviews, and focus groups, you can gauge the demand for your app and align it with users’ evolving needs, ensuring its relevance and competitiveness in the market.
2. Understand Your Audience
In healthcare app development, understanding your audience is paramount. Creating detailed user personas and conducting thorough interviews and surveys helps you gain profound insights into users’ preferences, pain points, and expectations. By empathizing with your audience and considering cultural sensitivities and accessibility requirements, you can design a healthcare app that resonates with users and drives meaningful engagement and outcomes.
3. Choose App Type
Selecting the right type of healthcare app is crucial for meeting users’ needs effectively. Health and wellness apps focus on promoting overall well-being, while telemedicine apps facilitate remote consultations and medical reference apps provide comprehensive medical information. Understanding the unique features and functionalities of each app type allows you to tailor your app to address specific healthcare challenges and deliver value to users.
4. Design the User Interface
The user interface (UI) design significantly impacts the overall user experience (UX) of your healthcare app. By designing intuitive navigation, maintaining consistent branding, and ensuring accessibility, you can enhance usability and create a seamless experience for users. Prioritizing user-centered design principles and incorporating feedback from usability testing helps refine the UI to meet users’ needs and preferences effectively.
5. Ensure HIPAA Compliance
Compliance with regulations such as HIPAA is essential to safeguarding patients’ protected health information (PHI). Implementing access controls, data encryption, and HIPAA-compliant services ensures the privacy and security of sensitive healthcare data. By adhering to HIPAA requirements and partnering with compliant vendors, you can mitigate legal and security risks and build trust with users and healthcare providers.
6. Develop The Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
Developing a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) allows you to validate your app idea and gather feedback from users early in the development process. By identifying core features, adopting an iterative development approach, and establishing a feedback loop, you can refine your app based on real-world usage and user input. Building an MVP enables you to minimize development risks, test market viability, and iterate on your app’s features and functionality to deliver a compelling healthcare solution.
Top 5 Successful Healthcare Apps In The Market Right Now
In today’s digital age, healthcare apps have revolutionized the way people access medical services and manage their well-being. Among the multitude of options available, certain apps stand out for their innovation, user experience, and effectiveness. Here, we’ll delve into the top five successful healthcare apps currently making waves in the market.
1. Kry
Kry offers video appointments with physicians and psychologists, providing convenient access to healthcare services. With over 800,000 patients treated and a 5-star rating from 97% of its patients, it has established itself as a trusted platform. One notable feature is its multilingual support, with doctors and psychologists fluent in 25 different languages. Operating 24/7, prioritizes accessibility and convenience, allowing users to book appointments at their preferred time and location.
2. CareZone
CareZone simplifies medication management and adherence to doctor’s instructions. Users can maintain an up-to-date medication list, aided by reminders to stay on schedule. The app organizes crucial information in one easily accessible place, making it ideal for individuals managing their health or caring for others. By allowing users to capture medication details through photos, CareZone streamlines the process of tracking dosages and schedules, demonstrating scalability in medical app development.
3. Headspace
Headspace promotes mental well-being through guided meditations, workouts, and mindfulness exercises. Offering hundreds of guided sessions, including SOS meditations for stress relief, it caters to various wellness needs. With its emphasis on everyday mindfulness, Headspace aims to help users reduce stress, improve sleep quality, and enhance overall happiness. Its short, accessible sessions make mindfulness practices achievable even in busy schedules. By incorporating workouts and mindful cardio exercises, Headspace promotes holistic well-being, addressing both physical and mental health concerns. With its user-friendly interface and diverse content library, Headspace continues to empower users on their journey to emotional resilience and inner peace.
4. PatientsLikeMe
PatientsLikeMe serves as a social network and research platform for individuals with similar health conditions. By connecting users with supportive communities and facilitating one-on-one interactions, it fosters a sense of belonging and empowerment. The app features smart tracking tools to monitor health changes over time, providing valuable insights into symptom management and treatment effectiveness. With its DailyMe feature for logging daily experiences, PatientsLikeMe encourages ongoing support and engagement among its users.
5. Hinge Health
Hinge Health specializes in managing chronic musculoskeletal conditions, such as back or joint pain, through personalized exercise therapy. Utilizing IoT technology, the app integrates a tablet and wearable sensors to deliver real-time feedback during stretches and exercises. Users progress through personalized therapy sessions at their own pace, guided by the app’s adaptive difficulty levels. By leveraging wearable technology, Hinge Health optimizes the effectiveness of pain management strategies, highlighting advancements in digital healthcare solutions.
Tech Stack To Consider To Develop a Healthcare Application
Developing a healthcare application requires careful consideration of various factors, including security, scalability, regulatory compliance, and user experience. Here’s a list of tech stack commonly used in building healthcare applications:
1. Programming Languages
- Java/Kotlin, Swift/Objective-C: For native mobile app development (Android and iOS respectively).
- JavaScript/TypeScript: For web-based applications or hybrid mobile apps using frameworks like React Native or Ionic.
2. Frameworks and Libraries
- React.js, Angular, Vue.js: For building web-based frontend applications.
- Express.js, Django, Flask: For backend development.
- Spring Boot: For Java-based backend development.
- Flutter: For cross-platform mobile app development.
3. Database
- MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB: Common choices for healthcare applications due to their robustness, scalability, and ability to handle sensitive data.
- Ensure compliance with regulations like HIPAA by implementing proper encryption and
- access controls.
4. Cloud Services
- Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), Microsoft Azure: For hosting the application, storage, database, and other services.
- Firebase: For real-time database, authentication, and hosting for smaller-scale applications or rapid prototyping.
5. Security
- SSL/TLS: For encrypting data transmitted over networks.
- OAuth/OpenID Connect: For secure authentication and authorization.
- JWT (JSON Web Tokens): For stateless authentication.
- HIPAA/HITECH compliance: Ensure compliance with healthcare regulations.
6. APIs and Interoperability
- HL7, FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources): Standards for healthcare data exchange.
- RESTful APIs: For communication between frontend and backend systems.
- SOAP APIs: For legacy systems integration.
7. Data Analytics and Machine Learning
- Python (with libraries like TensorFlow, PyTorch, scikit-learn): For implementing machine learning algorithms for tasks like predictive analytics, disease diagnosis, or image analysis.
- Big Data Technologies (Hadoop, Spark): For handling and processing large volumes of healthcare data.
8. Monitoring and Logging
- ELK Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana): For logging, monitoring, and visualization of application logs and metrics.
- Prometheus, Grafana: For monitoring system and application metrics.
9. Testing
- Unit testing frameworks for backend and frontend.
- Integration testing frameworks.
- End-to-end testing frameworks like Selenium for web applications or Detox for mobile apps.
10. DevOps Tools
- CI/CD pipelines: Jenkins, GitLab CI, Travis CI, etc., for automated build, test, and deployment.
- Configuration Management: Ansible, Chef, Puppet, etc., for managing infrastructure as code.
Conclusion
The integration of digital technology into the healthcare sector is proving to be a transformative force, benefiting both patients and medical professionals alike. With each passing day, there is a growing demand for innovative tools and platforms that facilitate seamless connectivity between patients and healthcare providers.
Moreover, developing healthcare applications presents a unique opportunity to prioritize and strengthen preventive care initiatives. These applications have the potential to revolutionize the way healthcare is approached.
However, there are many challenges when developing a healthcare app, which require technical expertise from app developers. Businesses should collaborate with app development companies to leverage their expertise in creating innovative healthcare applications that enhance patient engagement, streamline processes, and improve healthcare outcomes.
With specialized knowledge and experience, app development firms can translate healthcare needs into user-friendly digital solutions, driving transformative change in the industry and fostering a competitive edge.
How Idea Usher Can Help?
Idea Usher is proud to have extensive experience in crafting a diverse range of web and mobile healthcare applications. Our foundation lies in the commitment to assist providers and medical organizations in creating exceptional apps that resonate with customers.
With a track record of serving over 500 clients, including Fortune 500 giants like Gold’s Gym and Honda, as well as emerging indie brands, Idea Usher specializes in hybrid apps, mobile apps, and tailored websites, all geared towards driving business growth for our clients.
Our portfolio showcases a wide array of healthcare specialties, including remote patient monitoring, telehealth, mental health, lightweight EHRs for clinics, lab testing solutions akin to Uber, fitness and wellbeing apps, IoT integration, and enterprise-grade healthcare applications, all powered by AI technology.
Drawing from our wealth of experience in developing mobile and cloud-based healthcare apps, we understand the critical factors for success: delivering an engaging user experience and maintaining unwavering focus on customer needs. This is why we always start custom developing mobile apps with rapid prototyping.
Here is a case study of the Mediport app, we have developed for our client that you can check to gain an idea of our expertise in the healthcare app development industry.
Contact us today to understand more about how we can help with our healthcare app development services.
FAQ
Q. In what ways can an mHealth application benefit healthcare providers?
A. An mHealth (mobile health) app can greatly benefit healthcare providers by streamlining various aspects of patient care. These apps can facilitate remote patient monitoring, allowing providers to track vital signs, medication adherence, and symptoms in real-time. Additionally, mHealth apps can improve communication between patients and providers through secure messaging systems, enabling quicker responses to patient inquiries and concerns. Furthermore, these apps can assist in accessing electronic health records (EHRs) on-the-go, enhancing the efficiency of clinical decision-making and reducing administrative burdens.
Q. Are there any strategies to reduce the cost of developing healthcare applications?
Lowering healthcare application development costs can be achieved through several strategies. One approach is to leverage open-source software and existing frameworks to reduce development time and expenses. Additionally, utilizing agile development methodologies can help in efficiently managing resources and adapting to changing requirements throughout the development process. Furthermore, collaborating with experienced developers who specialize in healthcare applications can help avoid costly mistakes and ensure a streamlined development process.
Q. What cutting-edge technologies should be considered for integration into a healthcare application?
A. Integrating advanced technologies into a healthcare application can significantly enhance its functionality and usability. Some worthwhile technologies to consider include artificial intelligence (AI) for predictive analytics and personalized patient recommendations, machine learning algorithms for diagnostic assistance and pattern recognition, and blockchain for ensuring the security and integrity of patient data. Furthermore, integrating Internet of Things (IoT) devices for remote monitoring and wearable technology for continuous health tracking can further enrich the app’s capabilities.
Q. How long does it take to create a healthcare application?
A. The time required to develop a healthcare app can vary depending on various factors such as complexity, features, regulatory requirements, and team expertise. Typically, a basic healthcare app with essential features may take several months to develop, while more complex apps with advanced functionalities may require a year or more. It’s crucial to conduct thorough planning and feasibility analysis to establish realistic timelines and milestones for the development process.
Q. How businesses can discover the proper outsourced team to create a healthcare mobile app?
A. Finding the right outsourced team for developing a healthcare mobile app involves thorough research and careful evaluation. Look for teams with extensive experience in healthcare application development, preferably with a portfolio showcasing successful projects in the field. Additionally, consider factors such as the team’s technical expertise, adherence to regulatory standards such as HIPAA compliance, communication skills, and the ability to understand and accommodate your specific requirements and goals. Seeking recommendations, conducting interviews, and requesting proposals can help in selecting a competent and reliable outsourcing partner.










Gaurav Patil