Fintech software represents a convergence of cutting-edge technologies enabling financial institutions to deliver their services swiftly and efficiently in an ever-connected world driven by mobile and web platforms. The architecture of FinTech incorporates components strategically crafted to address existing challenges within the sector, providing a digital-first solution.
The sector’s promises and widespread adoption have led to a notable surge in new businesses entering this dynamic space. As the fintech industry gains traction and companies increasingly leverage sophisticated technologies and algorithms to drive their offerings, securing the right talent for fintech projects emerges as a paramount challenge for enterprises seeking to enhance their software development capabilities or modernize existing systems.
With this blog, we aim to provide you with a comprehensive guide on how you can develop financial software for your FinTech business.
What Is Financial Software Development?
Financial software development involves creating a diverse range of solutions catering to banking, stock trading, daily financial operations, and more. This intricate process encompasses various aspects, including adherence to regulatory compliance, seamless integration with legacy systems, scalability considerations, and a focus on user experience. The primary goal of financial software developers is to optimize the operations of financial institutions and businesses, increasing efficiency, supporting informed decision-making, and ultimately driving higher profitability.
Here are the several key components that are crucial in financial software development:
1. Customization
Developing tailored solutions for specific industries like banking, financial services, and insurance is crucial, ensuring alignment with their unique requirements.
2. Technologies & Tools
Developers leverage various technologies and tools, including cloud computing, artificial intelligence, machine learning, and blockchain, to build robust and reliable financial software.
3. User Experience
An important aspect of financial software development is ensuring a user-centric design, making the software not only easy to use but also visually appealing for enhanced user engagement.
4. Regulatory Compliance
Adhering to strict regulations and guidelines is paramount to ensure the security and reliability of financial software products.
5. Integration
Seamless integration with existing systems and platforms is a common requirement in financial software development, enhancing the overall user experience by connecting disparate elements.
6. Maintenance And Support
Ongoing responsibilities, including rigorous testing, maintenance, and updates, are critical in financial software development. Addressing end-user concerns and issues forms an integral part of this continuous support.
The financial software development process typically unfolds through various stages, commencing with defining the FinTech model, selecting appropriate software solutions, rigorous testing and maintenance, and finally, evaluating user feedback to implement continuous improvements. The development lifecycle duration varies, ranging from 4-5 months to a year or more, contingent on the project’s scope and the level of customization required.
While all financial software can be considered a part of FinTech, not all FinTech is financial software.
Key Stats Of The Fintech Market
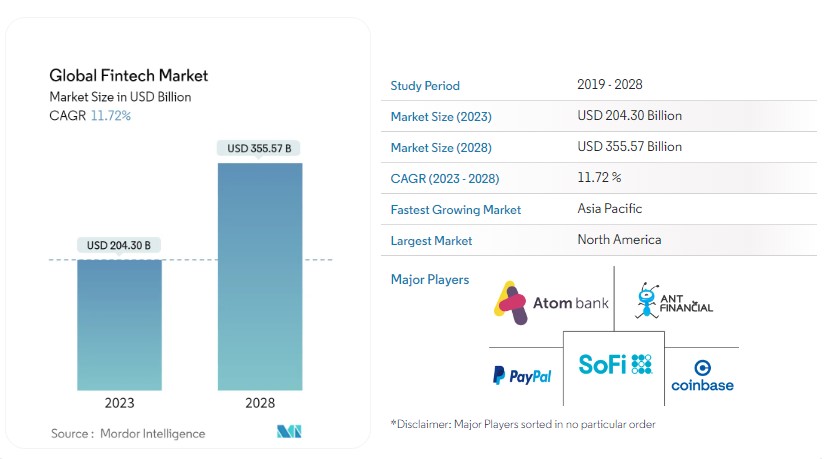
The estimated size of the Global Fintech Market is USD 204.30 billion in 2023, with expectations of reaching USD 355.57 billion by 2028. This growth is projected at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 11.72% during the forecast period from 2023 to 2028.
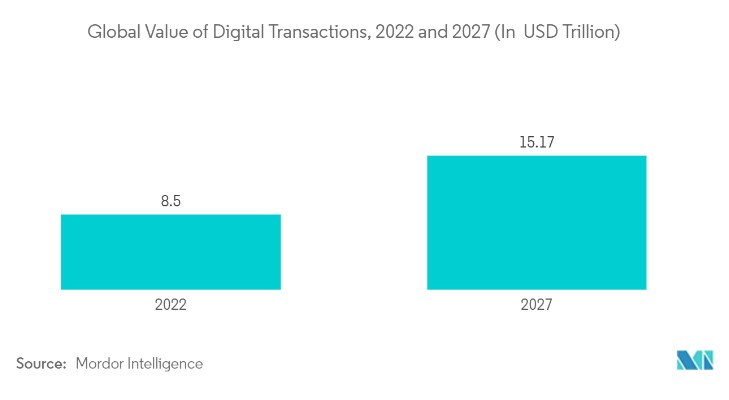
Moreover, as per another report, digital investment takes the lead with a projected AUM of US$116.20 billion in 2023. Looking at individual users, the average AUM is expected to be around US$215.60 within the Digital Investment market during the same period. Notably, the Digital Assets market is on track for a substantial revenue surge, showing an impressive growth of 33.1% in 2024. As we shift focus to Digital Payments, the user base is set to soar, reaching a staggering 5,480 million users by 2027. In terms of total AUM, the Digital Investment market is anticipated to hit US$116.20 billion in 2023. It’s crucial to understand that the distinctive nature of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) in the FinTech sector prevents their combination into a single, overarching number representing the entire industry.
According to a report by Allied Market Research, the market size of global fintech technologies reached $110.57 billion in 2020 and is anticipated to achieve $698.48 billion by 2030, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 20.3% from 2021 to 2030. Key drivers for this growth include increasing consumer demand for online financing, a rise in the integration of advanced technologies into the operational frameworks of banks and financial institutions, and a rapid expansion of innovative technologies, such as artificial intelligence, enhancing decision-making capabilities in business operations. Notably, these factors have contributed to the accelerated adoption of fintech technologies, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic.
How Big Is The Finance Software Market?
The 2021 valuation of the global financial services software market stood at $118.65 billion, with a projected increase to $282.71 billion by 2031, manifesting a 9.2% Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) from 2022 to 2031.
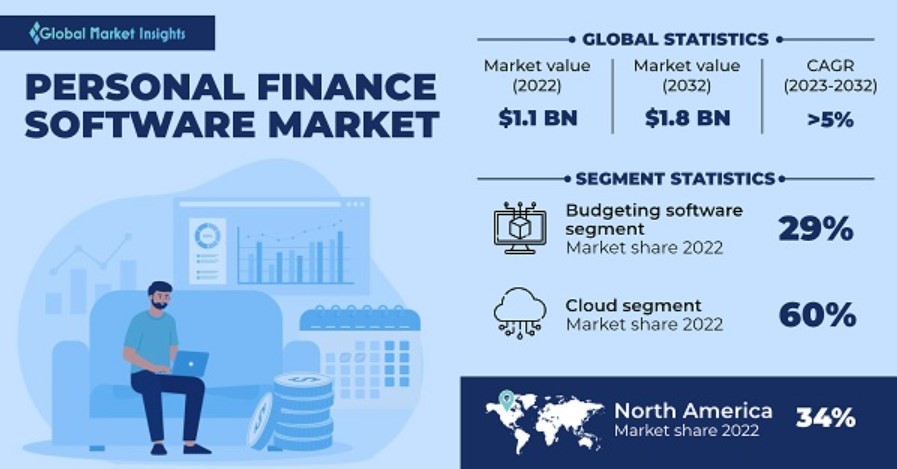
Additionally, in another study, the Personal Finance Software Market recorded a value of USD 1.1 billion in 2022 and anticipates a CAGR surpassing 5% between 2023 and 2032. This growth is attributed to the ongoing digital transformation in the financial sector, where consumers increasingly opt for digital solutions over traditional methods, such as pen-and-paper or spreadsheets. The shift is fueled by the convenience, accessibility, and automation inherent in digital tools, facilitating easier financial management, expense tracking, and planning via digital devices.
Why Must Businesses Invest In The Development Of Financial Software?
The strategic choice to invest in financial software development is no longer an option; it’s a foundational necessity. This imperative extends far beyond mere operational enhancements. It encompasses a transformative journey, redefining business success.
1. Operational Excellence Through Streamlined Processes
Financial software is crucial for operational efficiency, automating and simplifying intricate financial processes. This goes beyond routine tasks, reducing manual efforts and optimizing resources for enhanced efficiency.
2. Data Precision Illuminates Informed Decision-Making
The essence of financial software lies in its capacity to provide precise financial data. This precision serves as a guiding light, directing businesses towards sharp and well-informed decision-making, navigating them away from uncertainties.
3. Dynamic Scalability For Business Growth
As businesses embark on the journey of expansion, financial software stands as a flexible ally. Its innate scalability seamlessly adapts to escalating data volumes and intricacies, ensuring uninterrupted growth without the shackles of technological constraints.
4. Cost-Efficiency Through Task Automation
The automation capabilities of financial software extend beyond merely improving efficiency; they translate into substantial cost savings over time. As manual tasks are replaced with automated precision, this shift enhances overall budgetary management in a manner consistent with fiscal prudence.
5. Fortified Security Shielding Financial Fortunes
In an era dominated by digitization, the security of financial software has become paramount. Robust security features shield sensitive financial data, erecting an impregnable defense against potential threats and fortifying the financial backbone of businesses.
6. Revolutionizing Customer Experience
Going beyond its function as a backend powerhouse, financial software plays a pivotal role in transforming the customer experience. User-friendly interfaces and features redefine how customers interact, nurturing satisfaction and loyalty that exceeds conventional expectations.
7. Investor Allure With Predictable Revenue And Capital Efficiency
Financial software isn’t just a tool for operational prowess; it’s a beacon for potential investors seeking stable and lucrative opportunities. Its track record of delivering predictable revenue and capital efficiency becomes a magnet for those discerning investors navigating the financial possibilities.
In the bigger picture, the forecasted surge of the global financial software market surpassing $2.38 billion by 2027 signifies more than just an investment; it’s a strategic move. Choosing to adopt the future of financial software isn’t a causal decision; it’s a dedication to technology and a keen awareness of market trends. This dedication propels businesses to the forefront, setting the path for long-term success in the ever-changing dynamics of business.
10 Innovative Fintech Business Ideas To Start With
Dive into the innovation with these compelling FinTech business ideas, each designed to meet evolving market needs and redefine financial experiences:
1. Digital Banking App
Craft a digital banking app that redefines traditional financial services, automating transactions and elevating user experiences. This sector is often hailed as a prime opportunity for FinTech startups, offering the potential for significant growth and user engagement.
2. Peer-to-Peer Payment Solutions
Develop peer-to-peer payment solutions that empower users to effortlessly send and receive money without the constraints of traditional banking systems. This approach taps into the growing demand for efficient, decentralized financial transactions.
3. Personal Finance Management App
Introduce a personal finance management app dedicated to helping users navigate their financial journeys. From expense tracking to future financial planning, this app has become a trusted ally in users’ efforts toward financial well-being.
4. Robo Advising Software
Unleash the power of algorithms with robo-advising software. These automated advisors provide financial guidance and investment management with minimal human intervention, catering to an audience seeking smart, technology-driven investment solutions.
5. Loan Lending App
Streamline the loan application and approval process with a user-friendly loan lending app. Simplify the traditionally complex world of loans, making financial assistance more accessible to a broad user base.
6. RegTech App
Address the growing need for regulatory compliance with RegTech apps. These solutions efficiently guide businesses through compliance processes, minimizing costs and ensuring adherence to evolving regulations.
7. Stock Trading App
Bring stock trading to users’ fingertips with an intuitive stock trading app. Enable seamless buying and selling of stocks directly from mobile devices, catering to the rising interest in individual stock investments.
8. Digital Wallets
Innovate digital wallets to facilitate electronic transactions, online purchases, and contactless payments. Enhance security and user convenience, making your digital wallet a go-to choice for modern, tech-savvy consumers.
9. Blockchain Applications
Harness the potential of blockchain technology to create secure and transparent financial systems. Explore applications that redefine how transactions are conducted, emphasizing security and trust.
10. Crowdfunding Solutions
Pioneer new dimensions of crowdfunding platforms, enabling individuals and businesses to access funding from a diverse and extensive network. Revolutionize fundraising by offering innovative approaches and engaging community-building features.
Must-Have Features For Financial Software Systems
Financial software systems aim to offer users a suite of robust tools for efficient financial management. While the features of a FinTech app vary based on its model, certain indispensable functionalities are commonly shared across most financial software systems. Here are key features that typically find a place in every FinTech app:
1. Top 15 Features For User Panel
1.1. Account Management
Users should have the ability to easily register, create profiles, and manage their accounts. A centralized account dashboard is crucial, offering a comprehensive summary of balances, transactions, and other relevant information.
1.2. Transaction History
A detailed transaction history feature with robust search and filter options ensures users can track their financial activities effectively. Real-time updates on transactions contribute to a transparent and up-to-date overview.
1.3. Fund Transfer
Seamless and secure fund transfer capabilities, including interbank transfers, should be a priority. Additional functionalities such as scheduled and recurring transfers enhance user convenience.
1.4. Bill Payment
Integration with bill payment services streamlines the process of settling utility bills. Users should be able to schedule payments and receive timely reminders to avoid missed deadlines.
1.5. Budgeting and Financial Planning
Empower users with tools for budget creation, tracking, and financial goal setting. The platform should offer insights to help users make informed decisions about their finances.
1.6. Alerts and Notifications
Customizable alerts for various account activities, low balances, and important updates provide users with proactive insights. Notifications for upcoming bills and scheduled transactions enhance financial management.
1.7. Mobile Accessibility
A user-friendly mobile app is essential for on-the-go access. Mobile features such as check deposit and intuitive navigation contribute to a positive user experience.
1.8. Security Features
Implement robust security measures, including two-factor authentication, to safeguard user accounts. Regular security updates and compliance with industry standards are critical for maintaining trust.
1.9. Customer Support
Accessible customer support through live chat, FAQs, and a support ticket system ensures users can easily get assistance. In-app support features contribute to a seamless user experience.
1.10. Secure Authentication
User authentication is a top priority for the financial software system, incorporating robust security measures such as two-factor authentication and biometric login options. These features enhance the protection of user accounts and sensitive financial information, ensuring a secure and trustworthy user experience.
1.11. Model-Specific Functions
Tailoring the user experience, the system offers model-specific functions that align with individual financial goals and preferences. Users benefit from personalized financial advice, recommendations, and features that cater to their unique needs, contributing to a more engaging and relevant financial management experience.
1.12. Payments
Facilitating seamless financial transactions, the software provides a variety of payment options, including peer-to-peer transfers and digital wallets. Users can easily manage payments, supporting multiple methods and currencies for enhanced flexibility and convenience.
1.13. Dashboard
A user-friendly dashboard serves as the central hub for financial activities, offering intuitive visualizations of account summaries and trends. Customizable widgets empower users to tailor their dashboard, providing quick access to crucial financial information and enhancing overall usability.
1.14. Reports and Analysis
The financial software delivers quick overviews of account balances, expenses, and income directly on the dashboard. For in-depth analysis, users can generate detailed financial reports featuring interactive graphs and charts, empowering them with valuable insights for informed decision-making.
1.15. Mobile Accessibility
With secure authentication options, the mobile app provides users on-the-go access to their financial information. The mobile dashboard offers a condensed yet comprehensive view, allowing users to manage their finances conveniently from their mobile devices.
2. Top 18 Features For Admin Panel
2.1. User Management
Admin tools for monitoring user registration and managing user accounts are essential. Implement robust authentication and authorization controls to ensure secure access.
2.2. Transaction Monitoring
Real-time monitoring of transactions aids in fraud detection. Admins should have the capability to approve or reject transactions, adding an extra layer of security.
2.3. Account Management
Admins should be equipped with tools to manage user accounts and profiles efficiently. Access to account activity logs and audit trails is crucial for transparency and compliance.
2.4. Reporting and Analytics
Comprehensive reporting tools provide admins with insights for financial analysis. Customizable dashboards displaying key performance indicators aid in decision-making.
2.5. Compliance and Security
Admin tools for monitoring compliance and ensuring security standards are met are paramount. Regular security audits and updates should be implemented to address vulnerabilities.
2.6. System Configuration
Configurable settings for interest rates, fees, and other financial parameters allow admins to adapt the system to changing requirements. Integration with external financial systems and APIs enhances functionality.
2.7. Customer Support Tools
Admin tools for efficiently handling user support tickets contribute to a responsive support system. System alerts for potential issues help admins address concerns promptly.
2.8. Backup and Recovery
Regular data backups and a robust disaster recovery plan are critical for data integrity. Admins should have tools for restoring data in case of system failures.
2.9. Scalability
A scalable architecture is essential to accommodate a growing user base and increasing transaction volumes. Features like load balancing and performance optimization contribute to a scalable system.
2.10. Secure Authentication
The admin panel prioritizes secure authentication with role-based access controls. Admins have the tools to monitor and manage user authentication settings, ensuring the overall security and integrity of the financial software system.
2.11. Model-Specific Functions
Configuration tools empower administrators to customize model-specific functions, adapting the system to evolving user needs and market trends. Regular updates and improvements based on user feedback contribute to the continuous enhancement of the software’s offerings.
2.12. Payments
Admins are equipped with monitoring and approval tools for overseeing large or suspicious transactions, enhancing the security of financial transactions. Integration testing features ensure the seamless adoption of new payment methods and features.
2.13. Dashboard
The admin dashboard provides key metrics on user activity and system performance, enabling administrators to monitor the health of the financial software system. Admin tools for addressing any issues with the user dashboard contribute to a smooth and efficient user experience.
2.14. Notification
Admins receive real-time alerts for potential security threats or system vulnerabilities, allowing for swift response and resolution. Communication tools within the admin panel facilitate the dissemination of important updates to users, ensuring transparent and effective communication.
2.15. Integrations
Admin tools for managing third-party integrations and APIs are integral to the system’s functionality. Compatibility testing is conducted to guarantee seamless integration with external systems, enhancing the overall capabilities of the financial software.
2.16. Reports and Analysis
Advanced reporting tools empower administrators to analyze user behavior and system usage comprehensively. Data export features facilitate the generation of detailed financial reports, supporting strategic decision-making and system optimization.
2.17. Backup and Recovery
Admins have access to tools for managing data backup schedules and recovery procedures, ensuring the integrity of financial data. Regular testing of backup and recovery processes contributes to the system’s resilience in the face of potential disruptions.
2.18. Scalability
Admin tools for monitoring system performance and scalability are crucial for accommodating a growing user base. Planning and implementation of scalability measures based on user growth trends ensure the continued efficiency and responsiveness of the financial software system.
How To Develop Financial Software For Fintech Businesses?
While each fintech software project possesses its unique characteristics, the general process for creating customized financial software typically adheres to a consistent set of stages, as outlined below:
1. Define The Financial Software Concept And Identify Its Niche
Clearly define the purpose, target audience, and unique value proposition of the financial software. Conduct market research specific to financial services, define user personas in the context of financial goals, and incorporate compliance considerations for financial regulations.
Expert Advice:
- Engage with potential users and stakeholders early in the process to gather valuable insights.
- Understand the pain points in existing financial solutions to tailor your software accordingly.
- Leverage focus groups, surveys, and interviews to gain a deep understanding of user needs.
- Analyze competitor offerings to identify gaps in the market.
2. Address Regulatory Compliance
Understand and address the legal and regulatory requirements specific to financial software in target markets. Incorporate compliance considerations into the planning and architecture stages. Ensure adherence to financial regulations, data privacy laws, and industry-specific security standards.
Expert Advice:
- Collaborate with legal experts and regulatory consultants to navigate complex financial regulations.
- Stay updated on changes in financial laws to ensure ongoing compliance.
- Establish a dedicated compliance team or hire consultants with expertise in financial regulations.
- Build flexibility into the software to adapt to evolving compliance requirements.
3. Define Financial Features And Functionalities
Determine the key financial features and functionalities critical for the success of the software. Create a detailed project plan with a focus on financial data security, integration with financial APIs, and functionalities relevant to financial transactions and analytics.
Expert Advice:
- Prioritize features that add significant value to users and align with industry trends.
- Consider scalability and flexibility to accommodate future feature enhancements.
- Involve financial experts in feature planning. Create a roadmap for feature releases, starting with core functionalities and gradually introducing advanced features.
4. Discovery And Planning For Financial Software
Plan the development process, considering the unique requirements of financial software users and industry standards. Conduct market research specific to financial technology, define user personas with a focus on financial needs, and create a project plan with technologies tailored to financial data processing.
Expert Advice:
- Conduct a thorough market analysis to identify emerging trends and potential disruptions.
- Align development timelines with market demand to gain a competitive edge.
- Incorporate feedback loops to adapt to market changes during development.
5. Assemble A Skilled Financial Software Development Team
Assemble a team with expertise in financial technology and software development. Consider the expertise needed for financial data security, compliance with financial regulations, and integration with banking and financial systems.
Expert Advice:
- Seek individuals with experience in both finance and technology.
- Establish a collaborative environment where developers understand the financial implications of their work.
- Invest in continuous training to keep the team updated on financial technology trends.
- Consider partnerships with fintech experts for specialized insights.
6. Create A Secure And User-Friendly Financial Ux/Ui Design
Design a secure, intuitive, and user-friendly interface tailored to financial software requirements. Use design tools suitable for financial applications. Collaborate with UX/UI designers to create wireframes and prototypes, ensuring the responsiveness of financial dashboards and analytics.
Expert Advice:
- Prioritize security without compromising user experience. Iterate design prototypes based on user feedback to achieve optimal usability.
- Conduct usability testing with actual users to identify pain points.
- Implement design patterns common in the financial industry for familiarity.
7. Develop A Minimum Viable Product (Mvp) For Financial Software
Develop an MVP to validate financial concepts and gather user feedback. Implement financial data security measures, plan for integration with financial APIs, and utilize automated testing for continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD).
Expert Advice:
- Focus on core functionalities that showcase the unique value proposition.
- Use the MVP phase to validate assumptions and gather user feedback for future enhancements.
- Implement analytics to track user interactions with the MVP. Be agile and ready to pivot based on user feedback.
8. Conduct Rigorous Testing For Financial Software
Conduct thorough testing specific to financial transactions, data accuracy, and security. Conduct unit testing for financial algorithms, integration testing with financial APIs, and security testing to ensure compliance with financial data protection standards.
Expert Advice:
- Engage external security auditors to identify potential vulnerabilities.
- Simulate real-world financial scenarios in testing. Leverage automated testing tools for efficiency and consistency.
9. Deploy Financial Software
Make the financial software available to users in a secure and compliant manner. Choose a hosting solution suitable for financial data, set up continuous deployment pipelines with an emphasis on security, and deploy the software in a staging environment for final financial data integrity testing.
Expert Advice:
- Implement continuous deployment to streamline updates and ensure minimal downtime.
- Prioritize data migration planning during deployment.
- Monitor system performance closely during the initial rollout.
10. Regularly Update And Maintain Financial Software
Regularly update the financial software to add new financial features, enhance existing functionalities, and address any financial data security concerns. Plan regular maintenance tasks specific to financial data, updates based on industry changes, and improvements informed by user feedback. Utilize monitoring tools tailored to financial performance metrics.
Expert Advice:
- Communicate updates transparently to users.
- Implement automated update notifications.
- Leverage user feedback channels for continuous improvement.
11. Monitor And Maintain Financial Software Performance
Ensure the ongoing performance of the financial software, addressing any financial data concerns promptly. Implement monitoring tools specific to financial data integrity and performance. Set up error tracking and logging focused on financial transactions. Plan regular maintenance tasks and updates based on financial industry changes.
Expert Advice:
- Implement proactive monitoring to identify performance issues before they impact users.
- Regularly conduct system audits to ensure ongoing compliance.
- Establish a dedicated support team for rapid issue resolution.
- Use performance data to inform future scalability planning.
Technology Stack Used In A Fintech Application
To develop a robust and reliable app, it’s crucial to carefully select the appropriate technologies. The choice of the technology stack should align with factors such as the target audience, app goals, industry-specific requirements, and the integration of third-party interfaces.
In creating your custom fintech app, consider exploring these technologies. This thoughtful approach ensures a seamless and efficient development process that caters to the specific needs of your intended users and aligns with the goals of your application.
| Programming languages | Java or Kotlin for Android, Swift or Objective-C for iOS |
| Frontend | HTML, CSS, JavaScript |
| Backend | Python, C++, Ruby |
| Frameworks | Ruby on Rails, Django, Spring |
| Database | PostgreSQL, MySQL, MongoDB |
| Cloud environment | AWS, Google, Azure |
| Payment Gateway | Braintree, Stripe, Paypal |
8 Essential Regulations For Developing FinTech Software
Regardless of the scope or cost of FinTech regulations, their importance to the success of a FinTech application cannot be overstated. Compliance not only helps businesses steer clear of substantial fines but also fosters trust with users engaging with the software. Let’s delve into the essential regulatory compliances that businesses in the FinTech sector must address:
1. Data Privacy
Safeguarding data remains a pivotal legal concern within the fintech sector. Fintech enterprises amass and utilize substantial volumes of client data, eliciting concerns regarding the ethical use and protection of this information. Failure to adhere to anti-data-leak regulations in financial technology may lead to substantial penalties.
2. Money Laundering
Fintech establishments are obligated to conform to anti-money laundering (AML) directives. These directives necessitate financial entities to enact measures preventing and detecting money laundering, encompassing customer identification, screening, transaction monitoring, and reporting of suspicious activities.
3. GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
GDPR stands out as one of the most widely observed data protection regulations in the EU. It outlines the procedures for businesses in gathering, processing, and storing EU users’ data. Non-compliance with GDPR can result in fines reaching up to €20 million. Similar regulations, such as Consumer Data Rights (CDR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), align with GDPR principles and are crucial for every FinTech brand to follow.
4. KYC (Know Your Customer)
The Know Your Customer process is a regulatory requirement that every financial firm must adhere to. This fundamental process aims to verify a user’s identity and risk profile, contributing to the reduction of instances related to money laundering and fraud. Compliance with KYC is standard practice for financial service providers and banks.
5. FTC (Federal Trade Commission)
In the United States, FinTech businesses encounter multiple regulatory frameworks, with the Federal Trade Commission being a prominent one. Relevant regulations for the FinTech domain include the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) and the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA). The GLBA mandates financial software development services institutions to protect customer data and maintain transparency in its processing. Simultaneously, the FCRA covers consumer credit information, which is particularly relevant for FinTech apps dealing with lending or processing user credit scores.
6. PCI DSS Compliance (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard)
PCI DSS is a regulation governing credit card payments, ensuring secure transaction processing. Businesses preparing for PCI DSS compliance need to address six key areas to secure their app transactions. Non-compliance may result in fees ranging from $5,000 to $100,000 payable monthly.
7. EFTA (Electronic Fund Transfer Act)
Regulated by the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau, the Electronic Fund Transfer Act oversees electronic money transfers via ATMs, POS terminals, and debit cards. This compliance is designed to protect users in the event of transaction errors, such as funds being transferred to the wrong account.
8. PSD2 (Payment Services Directive)
The Payment Services Directive (PSD2), operating within the European Union, meticulously oversees payment services and providers across the expansive territories of the EU and the European Economic Area (EEA). Introduced to enhance competition and security, PSD2 mandates financial institutions to provide open banking APIs, fostering innovation and empowering consumers with greater control over their financial data. By regulating payment services, PSD2 not only ensures standardized practices but also propels the financial industry toward a more interconnected, secure, and consumer-centric future in the dynamic realm of European financial services.
Top 7 Innovative Technologies To Optimize Financial Software
Here is a list of the top technologies that can help to make your fintech software successful:
1. Artificial Intelligence
The successful implementation of artificial intelligence (AI) hinges on the availability of extensive data, making finance an ideal candidate for this technology. In financial software development, AI facilitates fraud detection, advanced analytics, and predictive modeling, empowering businesses to navigate the financial dynamics with data-driven decisions. AI’s impact spans from the front office to the back office, streamlining processes, enhancing accuracy, and boosting efficiency.
For customers, AI technology can be leveraged to create personalized products, automate transactions, implement robo-advisors, conduct KYC processes, offer chat interfaces, and more. In back-office operations, AI contributes to creating intelligent processes such as faster claim processing, fraud detection, and assessing customers’ lending capabilities.
2. Blockchain
Blockchain technology is pushing FinTech into a transformative era, introducing applications like Distributed Ledger Technology, Crypto Exchange, NFTs, Decentralized Finance, and KYC. This technology enhances the financial sector’s immutability and speed, offering solutions to persistent issues such as reliance on centralized systems, lack of trust, high operational costs, and slow processes.
Blockchain addresses these challenges by enabling faster transactions through consensus algorithms, supporting crypto lending, ensuring regulatory compliance through immutability, establishing digital identities, and creating innovative funding models. As demonstrated in a core banking solution project, blockchain integration extends functionalities like wire transactions with crypto, cryptocurrency trading, wallet recharge, and payments using Bitcoin and Ethereum. This project underscores that the full potential of blockchain integration in software is yet to be explored.
3. Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has been a significant topic in banking and FinTech, liberating companies from non-core activities like managing data centers and IT infrastructure while fostering new business models such as banking-as-a-service and open banking. Through diverse operative and business use cases, the cloud delivers various benefits to the sector, including improved security, lower infrastructure costs, real-time access to software, and enabling usage-based payment models.
The advantages offered by cloud computing, both on operational and business fronts, suggest that financial institutions will continue to prioritize cloud-powered financial services software development. This strategic approach not only facilitates the launch of new businesses but also enhances market responsiveness and scalability for improved customer experiences.
4. Open Banking
The advent of open banking has become a pivotal force in reshaping the financial landscape. Open banking initiatives allow for the secure sharing of financial data between different financial institutions through Application Programming Interfaces (APIs). This transformative approach fosters innovation by enabling third-party developers to create new financial products and services.
For financial software development, embracing open banking means creating interoperable systems that can seamlessly connect with external platforms and services. It opens avenues for personalized financial solutions, improved customer experiences, and enhanced competition within the industry. As financial institutions increasingly adopt open banking practices, collaboration and integration become key strategies to stay ahead in the evolving FinTech ecosystem.
5. Open Source, SaaS, And Serverless
Breaking down conventional barriers, open source, Software as a Service (SaaS), and serverless technologies empower financial institutions. They liberate these organizations from the constraints of developing every software component in-house. With the adoption of serverless architecture, the focus shifts from the mere execution of code to the strategic creation of it, thereby fostering innovation and operational efficiency within the financial domain.
6. No-Code And Low-Code
In software development, no-code and low-code platforms emerge as democratizing agents. They redefine the conventional approach to crafting financial software by facilitating rapid development, seamless customization, and a notable reduction in errors. As a result, legacy systems fade into obsolescence, making way for innovative solutions to take the forefront in the financial sector.
7. Regulation And Compliance Technology (RegTech)
Navigating the complexity of regulations, Regulation and Compliance Technology (RegTech) serves as a dependable compass for financial entities. Its proficiency lies in the efficient management of regulatory processes, covering aspects such as monitoring, reporting, and compliance. A cohort of companies specializing in RegTech ensures a judicious and cost-effective approach to adhering to regulatory requirements, thereby guaranteeing compliance within the dynamic landscape of financial regulations.
Alongside these technological advancements, it is advisable to explore leading personal finance software options in 2024. These include prominent choices like Simplifi, Quicken Deluxe, Greenlight, NerdWallet, Rocket Money, Credit Karma, Credit Sesame, and WalletHub. Delving into these platforms can significantly enhance your financial management capabilities, offering a diverse range of tools and features to cater to various financial needs. Consider these software solutions as valuable assets in navigating and optimizing your personal finances in the year ahead.
Challenges With Financial Software Development
Financial software development can be a challenging process for entrepreneurs due to the complex nature of the financial industry. Here are some of the major challenges that businesses may face when developing financial software
1. Security And Privacy
Ensuring the security and privacy of sensitive data is crucial in financial systems. Developing software that can prevent data breaches, cyberattacks, and unauthorized access is a significant challenge for almost any system.
2. Legacy Systems
Many financial institutions still rely on legacy systems that are outdated and difficult to integrate with modern software. This can make it challenging to develop new financial software that can work seamlessly with existing systems.
3. Regulatory Compliance
The financial industry is heavily regulated, and financial software developers must adhere to strict regulations and guidelines to ensure the security and reliability of their products.
4. Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity threats are a constant concern for financial software developers. They must develop software that can protect against cyberattacks and data breaches, which can be costly and damaging to both the business and its customers.
5. Changing Customer Expectations
Customers’ expectations are constantly evolving, and financial software developers must keep up with these changes to remain competitive. This can include developing new features and functionality that meet the needs of customers.
6. Rapid Changes
The financial industry is characterized by both stability and reluctance for quick changes, but regulatory compliance and new technologies require rapid adaptation.
7. Integrations
Financial software development often involves integrating with existing systems and platforms to seamlessly connect and enhance the user experience. This can be challenging due to the complexity of these systems and the need to ensure compatibility and security.
10 Best Financial Software Solutions
1. Simplifi by Quicken
Simplifi is a robust and user-friendly financial tool that assists in tracking spending, categorizing expenses, and creating customizable spending plans. It facilitates automatic spending plans, helps achieve savings goals, and offers insights into future cash flows, making it a powerful and user-centric choice for financial management.
2. Quicken Deluxe
Tailored for power users, Quicken Deluxe stands out with an extensive set of personal finance tools. It surpasses competitors with flexible transaction tracking, customizable reports, and advanced features for investment tracking. It’s the top choice for those seeking feature-rich financial software.
3. Greenlight
Greenlight is a smart debit card designed to aid parents in monitoring their child’s spending habits. It enables parents to pay allowances, manage chores, and set spending controls. The app incorporates lessons on earning, saving, spending, and giving, providing a comprehensive financial education platform for kids.
4. NerdWallet
NerdWallet is a free tool for credit monitoring and financial management. It offers insights into credit and spending habits, providing a holistic view of credit finances. Users can make informed decisions to achieve financial progress with the help of this comprehensive financial management tool.
5. Rocket Money
Rocket Money is a budgeting and bill management app that ensures users stay on top of monthly spending. Operating on a freemium model, it provides basic budgeting and subscription management for free, with additional features like bill negotiation and enhanced customization available through paid options.
6. Credit Karma
Credit Karma is a free app focused on credit score management. It simplifies access to credit scores, aids in understanding credit profiles, and offers tools for credit protection. All credit-related information is consolidated in one place for user convenience.
7. Credit Sesame
Credit Sesame offers free credit score monitoring, credit reports, and identity protection tools. It goes beyond monitoring by providing personalized recommendations for various financial products, including loans and credit options. This enhances members’ credit and spending power.
8. WalletHub
WalletHub is a free app facilitating easy credit score checking and improvement insights. Users can access their credit reports seamlessly through this platform. It simplifies credit management and aids users in maintaining financial health.
9. FreshBooks
FreshBooks, a cloud-based accounting software, streamlines client invoicing, expense tracking, and payment acceptance via credit card and bank transfer. It includes features for time tracking, project management, and handling accounts payable and receivable.
10. MoneyGuidePro
MoneyGuidePro offers sophisticated financial solutions featuring custom report templates, estate planning tools, net worth statements, and risk management features. It provides comprehensive guidance for financial planning, making it an advanced choice in the financial software landscape.
Top 10 Fintech Trends In The Industry
The FinTech industry is witnessing several emerging trends that are reshaping the sector and making financial services more accessible and convenient. Here are some of the latest FinTech trends:
1. Embedded Finance
Financial institutions increasingly offer embedded solutions, integrating financial services into non-banking platforms. This trend is set to expand further, transforming how consumers access and use financial products.
2. Regulatory Scrutiny Of Embedded Finance Offerings
The surge in financial services embedded in non-traditional platforms raises regulatory scrutiny. Expect increased awareness and interventions to ensure compliance and consumer protection.
3. Fintechs As Data Organizations
Fintech firms are transitioning into data-centric organizations. Beyond financial services, they are becoming key data providers, leveraging insights to enhance offerings and user experiences.
4. ESG-focused Fintechs
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) considerations are gaining prominence. Fintech companies with ESG capabilities are poised to attract growing interest as ethical investing becomes a priority.
5. Dealmaking In Underdeveloped Regions
Investors are strategically targeting underdeveloped regions for fintech investments. This trend aims to address financial service gaps and promote inclusivity in underserved jurisdictions.
6. Unicorn Status
The proliferation of unicorn companies, particularly in the US, is reshaping perceptions of unicorn status. In developed markets, achieving unicorn status may become less exclusive and impactful.
7. Data Integration And Analytics
Managing the burgeoning volume of data is crucial. Fintechs are focusing on seamless data integration and advanced analytics to derive meaningful insights for informed decision-making.
8. AI And Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) continue to be integral in FinTech. These technologies enhance customer service, streamline operations, and fortify security measures against fraudulent activities.
9. Cryptocurrency Tokenization
With cryptocurrencies gaining mainstream acceptance, the trend of tokenization is becoming more prevalent. Fintech platforms are exploring innovative ways to tokenize assets and transactions.
10. Mobile And Electronic Payments
Mobile and electronic payment methods are gaining traction due to their convenience and speed. The widespread adoption of these payment modes is reshaping traditional transactional landscapes.
Things To Consider Before Outsourcing Financial Software Development Team
When outsourcing a FinTech software development team, consider the following aspects:
1. Expertise
When engaging a financial software development agency, prioritize assessing their expertise in the specific model you aim to pursue. The closer their alignment with your business model, the better they can navigate the digital landscape’s nuances. Validate their expertise through reviews, case studies, and testimonials from their previous works.
2. Understanding Of Compliances
In the data-intensive FinTech sector, a crucial factor is the consultants’ profound knowledge of compliances. The chosen financial software development team must comprehend compliance intricacies, demonstrating the ability to build features, execute integrations, and design solutions that align seamlessly with regulatory requirements.
3. Price Quote And Delivery Timeline
As you explore options, the selection process may eventually come down to evaluating price quotes and delivery timelines. While opting for the agency with the lowest price and quickest delivery may seem appealing, exercise caution. Prioritize a firm that not only offers competitive pricing and a reasonable timeline but also emphasizes the assurance of delivering quality solutions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, developing financial software for fintech businesses is a critical aspect of their success in today’s digital economy. By leveraging technologies such as blockchain, artificial intelligence, and machine learning, fintech companies can create innovative solutions that streamline operations, enhance security, and improve the overall customer experience. However, it is essential to prioritize regulatory compliance, data security, and scalability throughout the software development process. Embracing a customer-centric approach and staying abreast of the latest industry trends is a key to sustaining success in the ever-evolving financial software development for FinTech businesses.
How Can Idea Usher Help You?
At Idea Usher, we specialize in innovative technology solutions and advanced Financial Software Development. Our commitment extends beyond technology; we are dedicated to crafting solutions that navigate the complexities of building a robust platform for financial services. Our proficient team endeavors to design intelligent, user-centric platforms, ensuring your business takes the lead in the dynamic landscape of Financial Software Development.
Excited to dive into the realm of building a Financial Software Solution for your Fintech Business? Click here to schedule a complimentary consultation and initiate your journey toward advanced financial services today.
Work with Ex-MAANG developers to build next-gen apps schedule your consultation now
FAQs
Q: What are the key stages of fintech application development?
A: Fintech application development typically involves several key stages, including requirement gathering, UI/UX design, MVP (Minimum Viable Product) development, testing, deployment, and ongoing maintenance.
Q: What are the must-have features for financial software systems?
A: Must-have features for financial software systems often include robust security measures, seamless integration with banking systems, real-time data analytics, scalability, and compliance with financial regulations.
Q: How much does it cost to build financial software?
A: The cost of building financial software can vary significantly based on factors such as the scope of the project, desired features, development time, and the rates of the software development team. It is recommended to consult with a financial software development company to get a tailored cost estimate.
Q: What are the top groundbreaking FinTech trends that will revolutionize the industry?
A: The FinTech industry is experiencing several groundbreaking trends, including the widespread adoption of blockchain technology, the rise of decentralized finance (DeFi), the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning, and the expansion of digital payment solutions.
Q: How can a financial software development company help with my FinTech project?
A: A reputable financial software development company can assist with various aspects of your FinTech project, including requirement analysis, custom software development, security implementation, regulatory compliance, quality assurance, and ongoing support and maintenance.