Enterprise teams increasingly look to blockchain for auditability, automation, and shared state, but public on-chain deployments are not always a direct fit for internal or regulated use cases. Data sensitivity, access control, and governance requirements often demand a more controlled environment. These needs are shaping how enterprises approach blockchain adoption through enterprise blockchain apps on Base, where on-chain logic can be deployed privately without exposing workflows or data to open networks.
Private on-chain applications shift the focus from open participation to permissioned access and system governance. Smart contracts still enforce rules and automation, but identity management, role-based permissions, and integration with existing enterprise systems become central. Enterprises can leverage Ethereum compatibility and lower transaction costs while maintaining tighter control over how applications are accessed and operated using Base.
In this blog, we explain how enterprises can build private on-chain apps using Base by covering deployment models, architectural considerations, and the design choices involved in balancing blockchain transparency with enterprise-grade control and security.

What Are Private On-Chain Applications?
Private on-chain applications are blockchain-based systems where business logic and verification run on-chain, while sensitive data, workflows, and access remain controlled. Unlike fully public dApps, these applications are designed for enterprises that need auditability and trust guarantees without exposing proprietary information.
Built on Base, private on-chain apps use Ethereum-compatible smart contracts for enforcement and finality, paired with off-chain systems for confidentiality and scale.
How Private On-Chain Apps Differ from Public dApps?
Private on-chain apps differ from public dApps by offering controlled access, data privacy, and governance. They support enterprise use cases requiring compliance, confidentiality, and operational control.
| Aspect | Public dApps | Private On-Chain Applications |
| Access Model | Permissionless, open to anyone | Restricted to approved users or roles |
| Data Visibility | All transactions and data are public | Only proofs or state changes are on-chain |
| Primary Use Case | Consumer-facing and open ecosystems | Enterprise workflows and internal systems |
| Privacy Control | Minimal or none | Granular, role-based visibility |
| Compliance Readiness | Limited | Designed for audits and regulations |
| Integration | Web3-native tooling | Enterprise systems and workflows |
Why Businesses Are Building Private On-Chain Apps on Base?
Base gives enterprises a practical way to build private or permissioned on-chain applications without sacrificing Ethereum security, performance, or developer flexibility. Its architecture supports controlled access, predictable costs, and scalable execution for internal and partner-facing use cases.
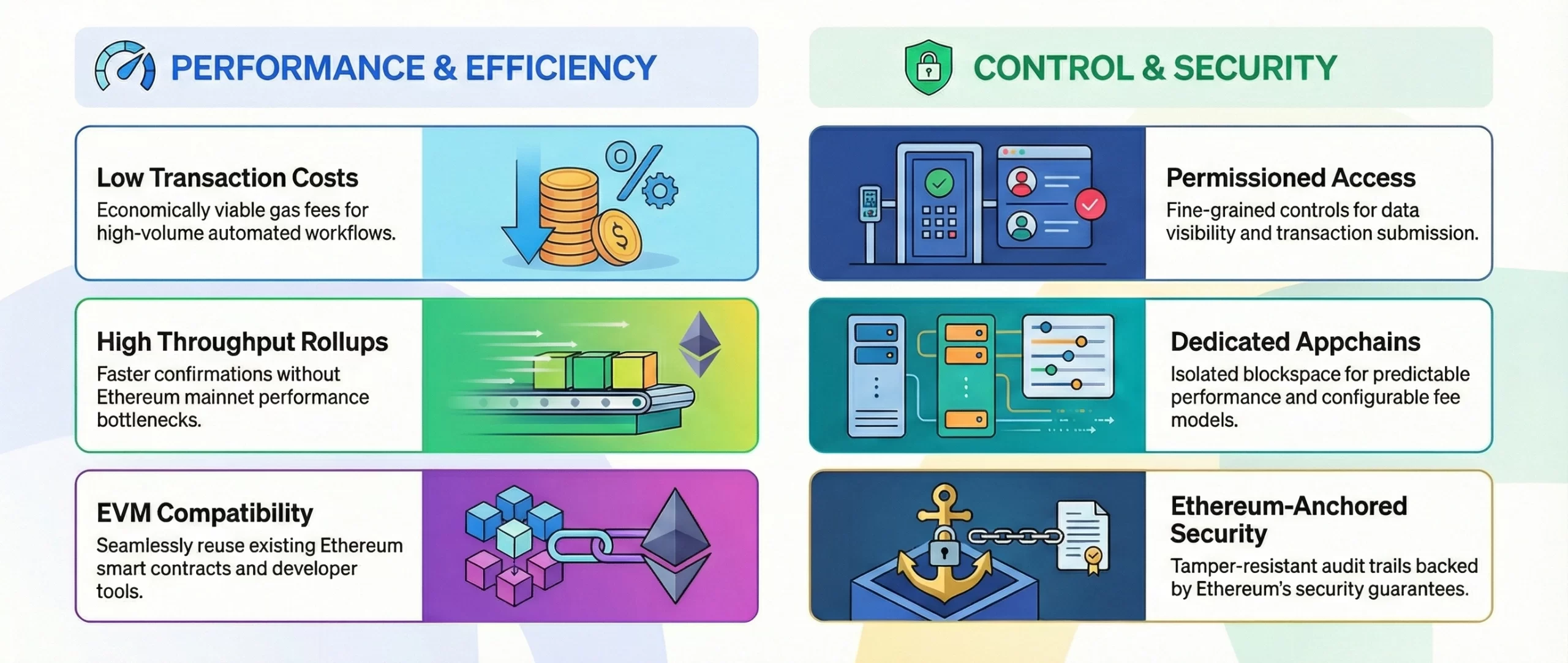
1. EVM compatibility
Base is fully EVM-compatible, allowing businesses to reuse Ethereum smart contracts, wallets, SDKs, and development workflows. This significantly reduces development time and risk when building private on-chain systems using familiar tooling.
2. Low transaction costs
By operating as an Ethereum Layer-2, Base enables consistently low gas fees. This makes frequent internal transactions, automated workflows, and on-chain state updates economically viable for enterprise-scale private applications.
3. High throughput
Base processes transactions off the Ethereum mainnet using rollup technology, delivering higher throughput and faster confirmations. Enterprises can support real-time or high-volume operations without performance bottlenecks.
4. Appchains and dedicated blockspace
Base Appchains allow businesses to deploy dedicated environments with isolated blockspace. This ensures predictable performance, configurable fee models, and operational separation for private enterprise workloads.
5. Permissioned access
Enterprise blockchain apps on Base can implement fine-grained permissioning layers. Businesses can control who can read data, submit transactions, or interact with smart contracts, ensuring confidentiality for sensitive workflows.
6. Ethereum-anchored security
Even private applications benefit from Ethereum’s security guarantees. Transaction data is periodically anchored to Ethereum, providing tamper resistance, verifiability, and strong audit trails for compliance use cases.
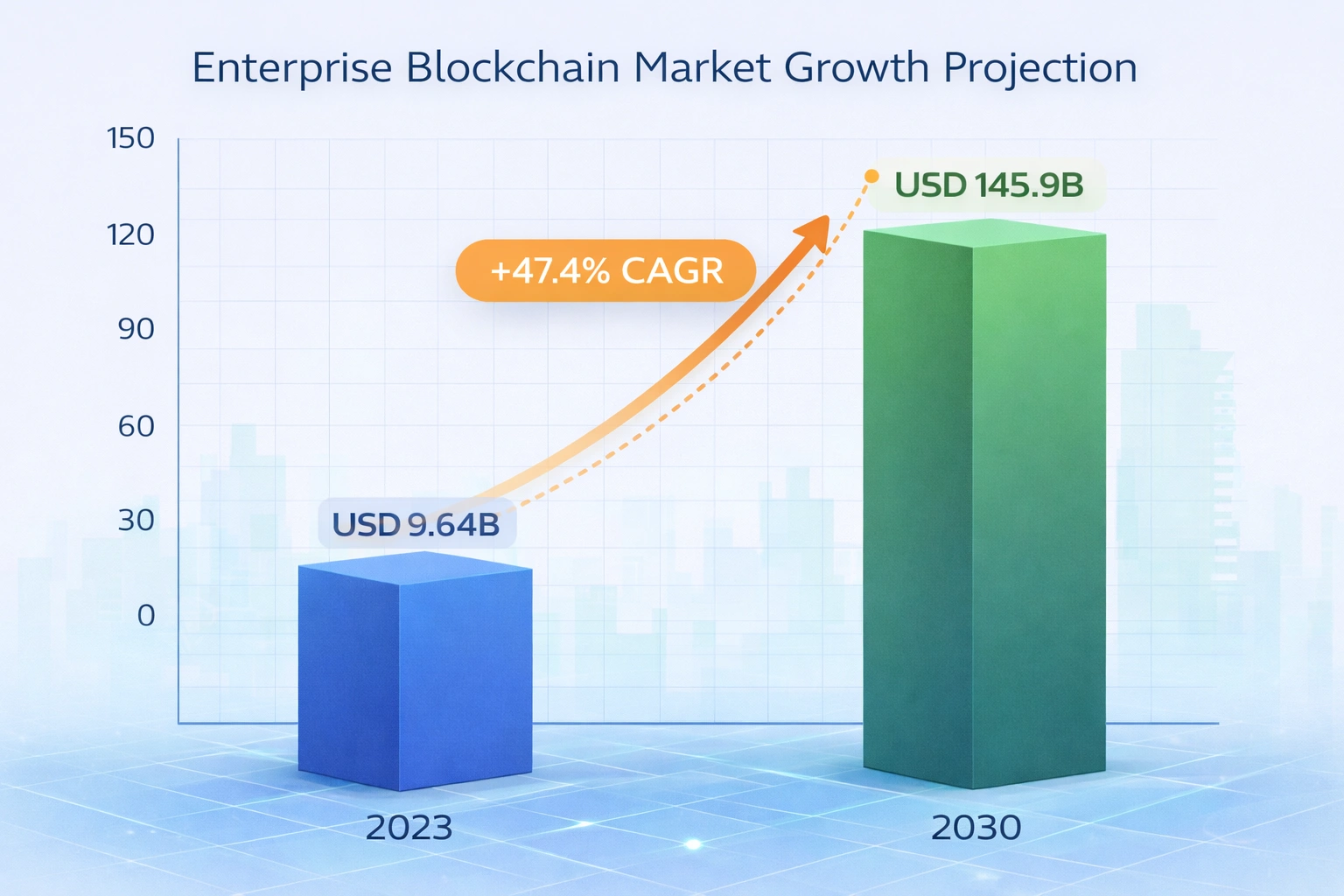
Key Market Takeaways of Private On-Chain Apps
The global enterprise blockchain market is projected to grow from about USD 9.6 billion in 2023 to approximately USD 145.9 billion by 2030, driven by rising adoption of decentralized solutions for transparency, security, and efficiency in business processes.
Base generating $75.4 million in 2025 and capturing 62% of Layer 2 revenue signals strong developer adoption and sustained on-chain activity. This reflects an active ecosystem where builders benefit from scalable infrastructure, predictable costs, and growing network usage with effective execution.
Base’s Revenue Growth Signals Demand for On-Chain Apps
Base’s revenue performance reflects more than financial metrics. It highlights real usage and ecosystem maturity that builders consider before launching on-chain applications.
- Consistent developer activity: High revenue share points to frequent deployments and transactions
- Production-ready infrastructure: Indicates the network can support live, scalable applications
- Lower execution risk: Established usage reduces uncertainty for new app launches
- Ecosystem confidence: Signals trust from developers, users, and enterprises
How Network Adoption Supports App Scalability
Strong adoption on Base creates conditions that help applications scale sustainably over time rather than relying on short-term traction.
- Growing user demand: Active networks attract users already interacting on-chain
- Predictable operating costs: Helps teams plan growth and maintenance effectively
- Improved performance reliability: Higher throughput supports expanding workloads
- Alignment with enterprise needs: Supports private, compliant, and scalable app models
Types of Private On-Chain Apps Businesses Can Build on Base
Businesses use private on-chain apps on Base to gain auditability, automation, and programmable trust while keeping sensitive logic and data permissioned. Below are the main types of enterprise blockchain apps on Base to build as private on-chain apps.
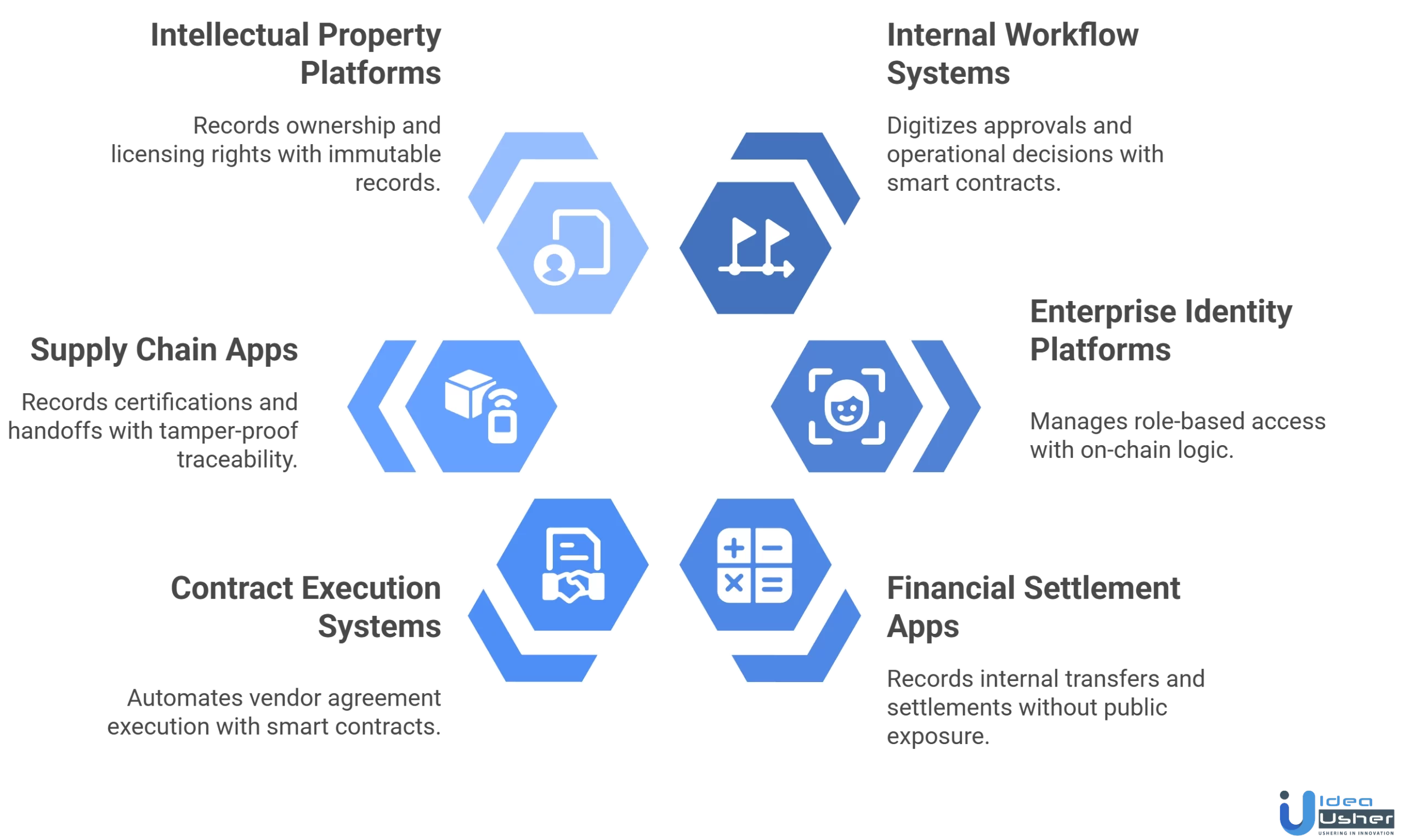
1. Internal Workflow and Approval Systems
Private on-chain workflow apps digitize approvals, policy sign-offs, and operational decisions. Smart contracts enforce rules, record timestamps, and create audit trails. This reduces manual coordination, improves accountability, and ensures verifiable execution without exposing internal data.
Example: Enterprises use Safe on Base to enforce multi-signature approvals and record internal authorization workflows without exposing data publicly.
2. Enterprise Identity and Access Control Platforms
These platforms handle role-based access with on-chain logic, keeping identity data off-chain. Permission changes are verifiable, consistent, and auditable, reducing security risks, unauthorized access, and simplifying management across departments and partners.
Example: Role-based access systems built with Lit Protocol on Base allow enterprises to gate applications and data using programmable conditions.
3. Financial and Internal Settlement Apps
Private on-chain finance apps record internal transfers, cost allocations, and settlements without exposing balances publicly. On-chain verification offers a single source of truth, reduces disputes, and enhances transparency, while keeping sensitive data confidential.
Example: Enterprises leverage Circle infrastructure on Base to record internal settlements using USDC while keeping reconciliation logic permissioned.
4. Contract Execution and Coordination Systems
These systems automate vendor or partner agreement execution using smart contracts, enforcing milestones, approvals, and conditions programmatically, while keeping commercial terms off-chain. This lowers disputes, manual oversight, delays, and enhances coordination and reliability.
Example: Contract workflows integrated with Chainlink on Base verify real-world events before triggering on-chain contract execution.
5. Supply Chain and Operation Apps
Private on-chain supply chain apps record certifications, inspections, and handoffs. Only validated state changes are stored on-chain, ensuring tamper-proof traceability. This aids audits and compliance while keeping contracts, pricing, and proprietary info private.
Example: Supply-chain verification systems built using Gelato on Base automate event recording while keeping operational data private.
6. Intellectual Property and Licensing Platform
Private on-chain IP platforms record ownership, licensing rights, and usage with immutable records. On-chain proof enforces compliance, maintains confidentiality, and reduces disputes, improving transparency in IP management.
Example: IP and licensing tools built on Zora allow enterprises to verify ownership and licensing actions while keeping underlying agreements private.

Core Features of Private On-Chain Apps on Base
Private on-chain apps built on Base are designed to deliver verifiable execution, controlled access, and enterprise-grade reliability without exposing sensitive data publicly. Below are the core features that define such applications and make them viable for real-world business use.

1. Permissioned Access and Participation
Private on-chain apps restrict who can read, write, or execute on-chain actions. Access is enforced through smart contracts and off-chain authorization layers, ensuring only approved users, teams, or partners can interact with sensitive workflows.
2. On-Chain Execution with Off-Chain Privacy
Critical actions such as approvals, settlements, or state changes are executed on-chain for immutability, while sensitive data, documents, and business logic remain off-chain. This balances transparency with confidentiality.
3. Smart Contract–Based Rule Enforcement
Business rules, workflows, and permissions are encoded into smart contracts. Once deployed, these rules execute consistently without manual intervention, reducing errors, disputes, and reliance on centralized control systems.
4. Verifiable Audit Trails and Traceability
Every approved on-chain action is timestamped and tamper-resistant. Enterprises gain cryptographic audit trails that simplify compliance, internal audits, and dispute resolution without exposing operational details.
5. Scalable and Cost-Efficient Transactions
Base’s low and predictable transaction fees make it feasible to record frequent internal actions on-chain. This is critical for enterprise workflows that require high-volume execution without escalating operational costs.
6. Flexible Identity and Role Management
Private on-chain apps support role-based access control, multi-signature approvals, and permission hierarchies. Identity data can remain private while access decisions are verifiable through on-chain state.
7. Automated Settlements and Payout Logic
Financial actions such as internal transfers, settlements, or revenue distribution can be automated using smart contracts. This ensures accuracy, transparency, and faster execution without manual reconciliation.
8. Enterprise-Ready Governance Controls
Platform administrators can manage onboarding, permissions, upgrades, and policies through defined governance mechanisms. Base provides a neutral enforcement layer that prevents unauthorized rule changes.
Development Process for Enterprise On-Chain Apps on Base
The development process for enterprise blockchain apps on Base involves secure architecture, integration planning, and compliance-focused design. Our developers follow proven blockchain frameworks to deliver reliable, scalable enterprise applications.
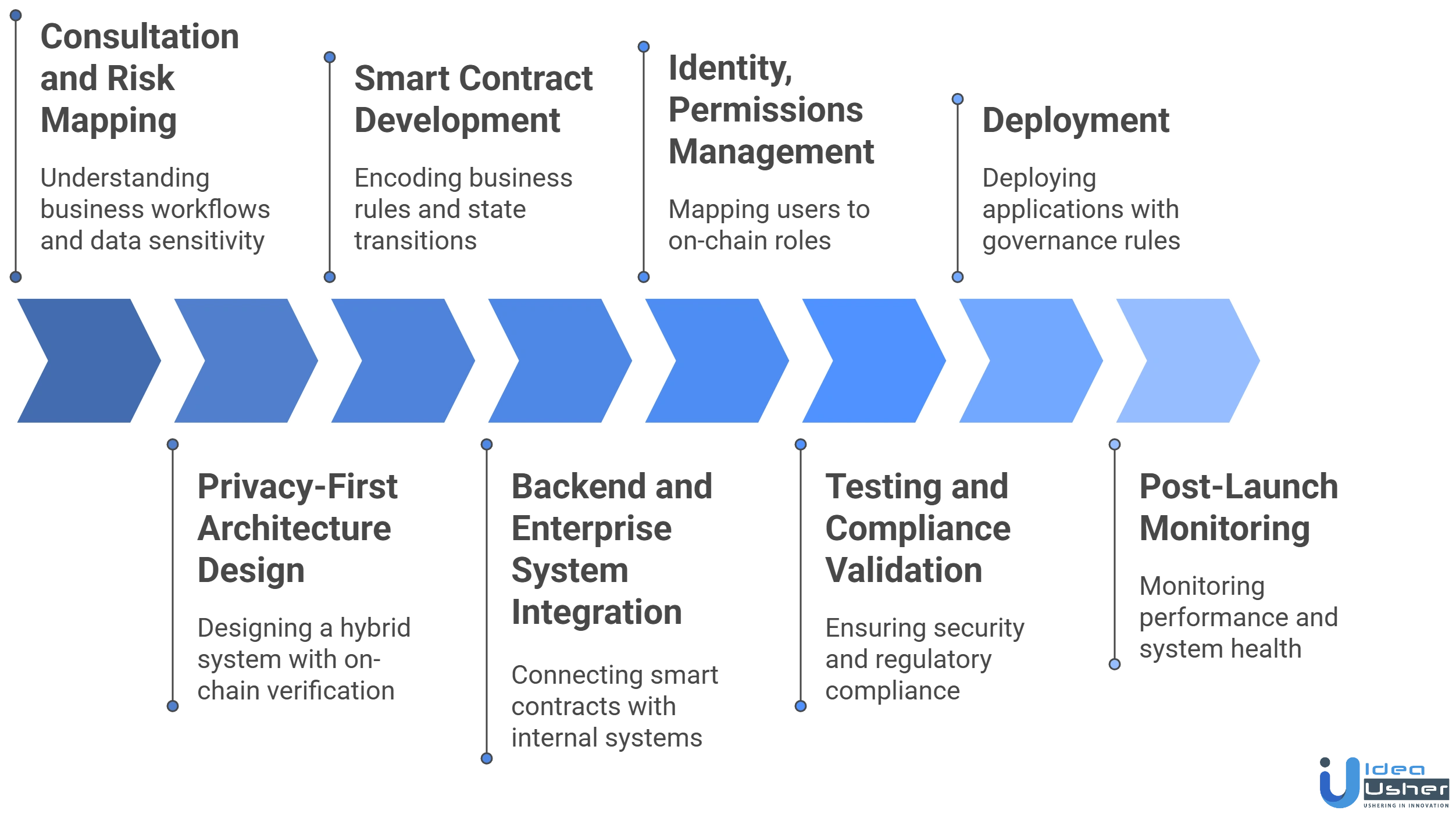
1. Consultation and Risk Mapping
We begin by working with you to understand business workflows, data sensitivity, compliance constraints, and integration points. This phase identifies what must be on-chain, what must remain off-chain, and where privacy boundaries are required.
2. Privacy-First Architecture Design
Our architects design a hybrid system where smart contracts handle verification and enforcement, while sensitive data stays within enterprise-controlled systems. Role definitions, permission models, and audit requirements are finalized before development begins.
3. Smart Contract Development
We develop smart contracts on Base to encode business rules, approvals, and state transitions. Contracts are designed with strict role-based access, predictable execution paths, and clear auditability to support enterprise governance.
4. Backend and Enterprise System Integration
Our developers build backend services that connect smart contracts with internal systems such as ERPs, CRMs, identity providers, and data stores. This ensures on-chain execution fits naturally into existing enterprise workflows.
5. Identity, Permissions, and User Management
We integrate enterprise identity systems to map users and services to on-chain roles. This allows enterprises to manage access using familiar IAM tools while maintaining verifiable execution on-chain.
6. Testing and Compliance Validation
Before deployment, we conduct extensive testing across smart contracts, integrations, and workflows. Security reviews validate permission boundaries, failure handling, and data integrity to meet enterprise and regulatory expectations.
7. Deployment and Governance Setup
We deploy applications to Base with defined governance rules, upgrade paths, and monitoring. Enterprises retain operational control while relying on Base for decentralized execution and finality.
8. Post-Launch Monitoring
After launch, we monitor performance, execution accuracy, and system health. Feedback from real usage informs controlled enhancements without disrupting business-critical workflows.
Architecture of a Private On-Chain App Built on Base
An enterprise blockchain apps on Base follows a hybrid architecture. Core verification and rule enforcement run on-chain, while sensitive data and enterprise workflows remain off-chain. The table below breaks down the architecture into clear, enterprise-relevant components.
| Architecture Layer | Purpose | How It Works on Base |
| Smart Contract Layer | Rule enforcement and verification | Smart contracts on Base handle permissions, state changes, approvals, and execution logic with Ethereum-grade security. |
| Access Control & Roles | Restrict who can perform actions | Role-based permissions are enforced at the contract level, ensuring only authorized users or systems can trigger specific operations. |
| On-Chain State & Proofs | Verifiable system state | Only essential state transitions, hashes, or proofs are written on-chain, avoiding exposure of sensitive enterprise data. |
| Off-Chain Data Layer | Store confidential information | Business data, documents, and operational details remain in enterprise databases or secure storage systems. |
| Backend Services | Orchestration and integration | Backend services coordinate user actions, validate permissions, and sync enterprise systems with on-chain events. |
| Enterprise Identity Systems | User and role management | Existing IAM, SSO, or directory systems integrate with the app to map enterprise identities to on-chain roles. |
| Transaction Management | Reliable execution handling | Systems manage transaction submission, confirmation, retries, and failure handling for enterprise-grade reliability. |
| Monitoring & Audit Tools | Visibility and compliance | Logs, dashboards, and alerts track on-chain activity, contract execution, and system health for audits and reporting. |
| Integration Layer | Connect internal and external systems | APIs connect ERPs, CRMs, compliance tools, and partner systems to the on-chain application workflow. |

Cost Considerations for Building Private On-Chain Apps on Base
Cost considerations for building enterprise blockchain apps on Base depend on architecture, security, and integration needs. They outline key factors influencing development budgets and long-term operational planning.
| Project Stage | Scope Focus | Typical Investment Range |
| Discovery & Architecture | Requirements mapping, privacy design, integration planning | $15,000 – $30,000 |
| Enterprise MVP | Core workflows, role-based access, Base deployment | $60,000 – $110,000 |
| Production-Ready System | Full integrations, security reviews, monitoring | $120,000 – $180,000 |
| Large-Scale Deployment | Multi-team, partner access, governance layers | $180,000+ |
These ranges reflect real enterprise delivery, not proof-of-concept builds.
A. What Actually Drives Cost
Private on-chain apps are not priced like public dApps or prototypes. Costs increase based on how tightly the system must integrate with enterprise operations. Key cost drivers include:
- Depth of privacy and permission controls
- Number of internal and external integrations
- Security and audit requirements
- Transaction volume and reliability expectations
- Governance and upgrade planning
These factors matter more than raw feature count.
B. Privacy and Compliance Add Cost
Private on-chain apps require more than basic smart contracts. Designing systems that isolate sensitive data, enforce permissions, and remain audit-ready increases engineering effort and testing scope.
Enterprises should expect higher upfront costs in exchange for:
- Reduced compliance risk
- Faster audits
- Lower operational friction over time
C. Integration with Existing Enterprise Systems
Connecting on-chain logic to ERPs, CRMs, IAM systems, and internal databases often accounts for a significant portion of development cost. These integrations:
- Require custom middleware
- Must handle failures gracefully
- Need long-term maintenance
D. Ongoing Operational and Maintenance Costs
Ongoing operational and maintenance costs are essential for sustaining private on-chain applications. Enterprises must plan for:
- Contract monitoring and transaction management
- Infrastructure and backend maintenance
- Controlled upgrades and change management
- Security reviews for new workflows
How Privacy Works on Base Without Breaking Decentralization?
Enterprises often assume privacy and decentralization are trade-offs. In practice, enterprise blockchain apps on Base achieve privacy through architectural separation, not by weakening decentralization. The key is understanding what belongs on-chain and what must remain off-chain.
1. Separating Verification from Data Storage
On Base, decentralization is preserved by keeping verification and enforcement on-chain, while sensitive business data remains off-chain. Enterprises typically:
- Execute rules and state changes through smart contracts
- Store confidential data in internal systems or secure databases
- Anchor proofs, hashes, or state references on-chain
This ensures actions are verifiable without exposing proprietary information.
2. Permissioned Access on a Public Network
Privacy does not require a private blockchain. Instead, enterprises use permissioned interaction models on a public execution layer. Smart contracts on Base can:
- Restrict who can call specific functions
- Enforce role-based permissions
- Validate identities before execution
The network remains decentralized, even though application access is controlled.
3. Role-Based Smart Contract Design
Enterprise smart contracts are designed with explicit roles such as administrators, operators, auditors, or partners. Each role:
- Has limited, predefined capabilities
- Cannot override contract rules
- Is recorded on-chain for accountability
This preserves decentralization at the protocol level while enabling enterprise governance at the application level.
4. Off-Chain Data with On-Chain Proofs
Rather than publishing data, enterprises publish cryptographic guarantees. Common patterns include:
- Hashing documents or records and storing hashes on-chain
- Writing state transitions without raw data
- Verifying conditions without revealing inputs
This allows external validation without data disclosure.
5. Decentralized Validators, Not Private Control
Unlike private blockchains, Base does not rely on enterprise-controlled validators. Transaction ordering, settlement, and finality remain decentralized and independent of the enterprise. This avoids:
- Vendor lock-in
- Single points of failure
- Trust concentration
Enterprises gain privacy without owning or controlling the network.

Key Challenges Enterprises Face and How Our Developers Solve Them
Building enterprise blockchain apps on Base face challenges beyond technology, including compliance, operations, and internal alignment. Below are key issues and how our developers solve them in real-world implementations.
1. Privacy Expectations vs Blockchain Reality
Challenge: Enterprises often assume privacy requires private blockchains or hidden execution, leading to architectural missteps and delayed implementation.
Solution: We design hybrid architectures where verification and enforcement run on-chain, while sensitive data is kept off-chain, ensuring privacy requirements are met without compromising decentralized execution.
2. Compliance and Legal Pushback
Challenge: Compliance teams may hesitate due to concerns around auditability, data exposure, and regulatory interpretation of on-chain systems.
Solution: Our developers work closely with compliance stakeholders to map workflows, define on-chain boundaries, and produce clear audit trails that satisfy regulatory and internal governance requirements.
3. Integrating with Enterprise Systems
Challenge: Most enterprises rely on ERPs, CRMs, identity providers, and internal tools that were never designed for blockchain integration.
Solution: We build middleware and integration layers that allow smart contracts to interact with existing systems without disrupting current operations or forcing full-stack replacements.
4. Managing Multi-Team Permissions
Challenge: As applications scale, managing roles, approvals, and permissions across departments or external partners becomes complex and error-prone.
Solution: Our developers implement strict role-based access controls at the smart contract level, ensuring every action is authorized, traceable, and enforced consistently.
5. Fear of Losing Operational Control
Challenge: Enterprise leaders often worry that decentralization means losing control over critical systems or workflows.
Solution: We design governance and control mechanisms into the application layer, allowing enterprises to retain operational oversight while relying on Base for neutral execution and finality.
Top Private On-Chain App Built on Base
Private on-chain applications on Base enable enterprises to execute secure, permissioned workflows with blockchain-level transparency. These platforms demonstrate how Base supports compliant, scalable, and production-ready private systems across industries.
1. Safe
Safe is widely used on Base to build private approval workflows, treasury controls, and multi-signature authorization systems. Enterprises use it to enforce internal permissions, role-based execution, and audit-ready transaction trails without exposing operational data publicly.
2. Coinbase Onchain Tools
Coinbase’s onchain tooling on Base enables enterprises to build permissioned blockchain applications for compliance, reporting, and internal financial operations. These tools support private execution while retaining verifiable on-chain records suitable for regulated environments.
3. Circle USDC
Circle’s programmable wallet infrastructure on Base allows businesses to build private payment flows, internal settlements, and controlled treasury systems using USDC. Execution is verifiable on-chain while access and logic remain fully permissioned.
4. Lit Protocol
Lit Protocol enables enterprises on Base to build private access-controlled applications, where data, content, or actions are gated by programmable conditions. Identity data stays off-chain, while access decisions are cryptographically verifiable.
5. Chainlink
Chainlink-powered apps on Base are used to build private contract execution systems that depend on real-world data. Enterprises keep sensitive business logic off-chain while using on-chain verification to enforce execution rules securely.
Conclusion
Building private on chain applications using Base gives enterprises a practical path to combine blockchain transparency with controlled access. This discussion covered architectural choices, security considerations, and deployment strategies that support enterprise requirements. Base enables scalability, predictable costs, and compatibility with existing systems, making adoption more approachable. When designed with clear governance and compliance in mind, enterprise blockchain apps on Base can streamline operations, improve data integrity, and support long-term innovation. A structured approach helps organizations move forward with confidence while aligning blockchain capabilities with real business objectives.
Partner with IdeaUsher to Launch Private On-Chain App on Base!
IdeaUsher works with enterprises to build private, secure, and compliant on-chain applications using Base. We focus on delivering blockchain solutions that integrate seamlessly with existing business systems while maintaining control and governance.
Why Work with IdeaUsher?
- Enterprise-Grade Blockchain Expertise: We design private on-chain architectures aligned with compliance and operational needs
- Base-Compatible Solutions: Our team builds scalable applications optimized for Base’s performance and cost efficiency.
- Custom Business Workflows: We tailor smart contracts and access controls to match enterprise processes.
- Security-First Development: Regular audits, controlled upgrades, and long-term maintenance planning are built in.
Review our case studies to understand how we help enterprises launch their blockchain solutions in the market.
Work with Ex-MAANG developers to build next-gen apps schedule your consultation now
FAQs
A.1. Enterprises choose Base for its scalability, lower transaction costs, and compatibility with Ethereum tooling. It allows private on chain apps to benefit from blockchain transparency while maintaining control over access, data, and operational governance.
A.2. Data privacy can be ensured through permissioned access, off chain data storage, encrypted transactions, and controlled smart contract logic. Proper architecture design helps enterprises balance transparency with confidentiality and regulatory requirements.
A.3. Yes, private on chain apps can integrate with ERP systems, databases, and internal tools through APIs and middleware. This allows enterprises to extend blockchain functionality without disrupting existing operational workflows.
A.4. Governance is managed through role based access, approval workflows, and smart contract controlled permissions. Enterprises can define clear decision making structures to manage upgrades, access rights, and operational changes securely.

























