Sometimes, people suffer from limited access to banking services and poor credit histories, which limits their ability to save, invest, or borrow money when needed. This issue leads to low returns on savings, slower loan processing, and other concerns related to their finances. DeFi platforms like MakerDAO are solving these problems by offering more accessible, transparent, and better financial services using the most advanced blockchain technology.
This convenience is pushing the demand for more efficient solutions. Even the market for DeFi suggests that the total value locked in these platforms will exceed $231.19 billion in 2030. Thus, building a better and feature-rich decentralized platform undoubtedly presents a significant opportunity. In this blog, we will explore the cost, features, and process of developing a DeFi lending platform like MakerDAO. We will cover everything you need to know to build an ideal solution that meets the increasing demand for decentralized financial services.
MakerDAO: Overview
MakerDAO was introduced in 2015 by Danish entrepreneur Rune Christensen. It was officially launched on the Ethereum mainnet in December 2017. Its primary function is to create and maintain Dai, which is a stablecoin that is designed to maintain a value close to the US dollar. Users can generate Dai by locking up their cryptocurrency in smart contracts known as Maker Vaults, which act as collateral. This mechanism ensures that Dai remains stable, even when the value of the underlying collateral fluctuates.
The governance of MakerDAO is managed by MKR token holders, who have the authority to vote on important decisions. These decisions include setting interest rates and determining which types of collateral can be used within the system. In addition to its governance structure, MakerDAO is characterized by several key features:
- Decentralization: The system operates without any central authority.
- Transparency: All transactions and operations are accessible to the public on the blockchain.
- Stability: Dai is intended to maintain a steady value in relation to the US dollar.
- Adaptability: The system can adjust to market changes through decisions made by the community.
MakerDAO has shown a strong business model and has proven capable of managing the inherent volatility of the cryptocurrency market. In the past year, this platform has generated approximately 400 million USD in annual revenue. It has played a key role in the growth of decentralized finance and has inspired several similar project developments.
What Makes MakerDAO Unique?
MakerDAO is unique in its approach to maintaining the stability of its stablecoin. Unlike stablecoins like USDT or USDC, which are backed by cash reserves, Dai uses several different methods that keep it stable and adaptable to market fluctuations:
- Stability Fees: These are fees charged when users create Dai from MakerDAO’s Vaults. These fees are adjusted based on Dai’s market value to keep it close to $1. If Dai’s value rises above $1, fees increase to limit CDPs; if it falls below $1, fees decrease to encourage borrowing.
- Overcollateralization: MakerDAO requires users to deposit more collateral than the amount of Dai they generate. The minimum collateralization ratio is set at 150%. This extra margin helps maintain the stability of Dai.
- Automatic Liquidation: If the value of the collateral falls below the required 150% ratio, MakerDAO’s system automatically sells the collateral to cover the debt. This makes sure that users keep enough collateral in their positions.
- MKR Dilution: When large amounts of collateral are liquidated, MakerDAO mints new MKR tokens to cover the losses. This process reduces the overall supply of MKR tokens and affects the holdings of existing token owners.
How Does MakerDAO Work?
MakerDAO is a decentralized platform, and here’s an overview of its functioning:
- Collateral Mechanism: Initially, MakerDAO permitted users to deposit ether to generate Dai. Over time, it expanded to accept various ERC-20 tokens, broadening the types of assets that can be used.
- Collateralized Debt Positions: To acquire Dai, users lock their cryptocurrency in Maker Vaults. These Vaults use CDPs, which are smart contracts that manage the collateral and issue Dai tokens.
- Loan Repayment: Users must repay their loans by returning the Dai they borrowed. The collateral remains in the Vault until the debt is settled. Upon repayment, the Dai is destroyed, and the original collateral is returned to the user.
- Liquidation Process: If the collateral’s value drops below a certain threshold or the loan is not repaid, the CDP undergoes liquidation. The protocol then sells the collateral to recover the outstanding debt, thereby ensuring Dai’s stability.
- User Access: Setting up and managing a CDP is accessible with an Ethereum wallet. Once issued, Dai can be used for various activities, including trading, investing in other cryptocurrencies, or earning returns within the DeFi space.
Key Market Takeaways For DeFi Lending Platform
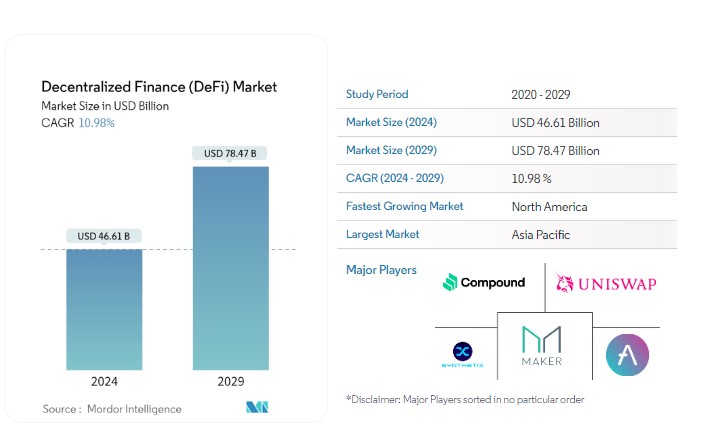
The decentralized finance (DeFi) market is experiencing rapid growth with several important trends:
- Strong Growth: The DeFi sector is expected to grow at a remarkable rate of 46.0% annually from 2023 to 2030, reflecting its significant impact on the financial industry.
- Market Size: In 2024, the DeFi market is projected to be worth USD 46.61 billion. By 2029, this is anticipated to increase to USD 78.47 billion, showing a steady annual growth rate of 10.98% during this period.
- Revenue Forecast: Revenue in the DeFi market is expected to reach USD 26.17 billion in 2024. It is predicted to grow at an annual rate of 9.07%, reaching USD 37.04 billion by 2028.
- Revenue Per User: The average revenue per user in the DeFi lending sector is forecasted to be USD 1,378 in 2024, which indicates the growing value and acceptance of DeFi services.
- Growth Drivers: The rise of DeFi lending platforms is driven by their ability to streamline financial transactions by removing traditional intermediaries, which leads to greater efficiency and accessibility.
Understanding MakerDAO’s Core Components
The Maker Protocol includes several important parts that help keep Dai stable and functional. Here are the components of MakerDao:
1. Maker Vaults
Maker Vaults are smart contracts where users deposit assets to create Dai. The system locks these assets until the Dai is paid back with a fee. If the value of the assets drops too low, the system will sell them to cover the Dai debt and to keep it stable.
2. Dai
It is designed to stay close to $1 USD. Unlike other stablecoins backed by fiat currency, Dai is supported by cryptocurrencies in Maker Vaults. This setup helps maintain Dai’s value without needing a central authority.
3. MKR Tokens
MKR token holders govern the Maker Protocol. They vote on key decisions like which assets can be used as collateral, setting risk levels, and making updates to the system. They can also be sold to cover any shortfalls in collateral if needed.
4. Collateral Assets
The Maker Protocol accepts various Ethereum-based assets as collateral. These assets are chosen for their stability and liquidity, which helps manage risk effectively. Using a range of collateral types ensures that the system remains secure and resilient.
5. Liquidation Mechanisms
The Maker Protocol has processes to handle Vaults with too little collateral. If the value of the collateral falls below a certain level, the system sells the assets to repay the Dai. This prevents bad debt and keeps Dai secure.
6. Oracles And Price Feeds
Oracles provide real-time price data for assets in Maker Vaults. This information is important for determining collateral value and making liquidation decisions. This reliable pricing helps maintain the stability of the entire system.
7. Dai Savings Rate
The DSR provides an opportunity for Dai holders to earn interest by depositing their Dai into a designated account. The interest rate here, which is set by MKR holders, plays an important role in regulating the supply and demand of Dai. This feature adds value to holding Dai and supports its stability.
Business And Revenue Model Of MakerDAO
MakerDAO has a unique model focused on keeping its stablecoin stable at $1 while generating revenue through specific mechanisms:
1. Revenue From Stability Fees
MakerDAO earns revenue primarily through stability fees. Users who borrow Dai pay this fee, which helps manage the risks associated with issuing the stablecoin and supports MakerDAO’s operational costs. This fee is a key part of MakerDAO’s revenue structure.
2. Liquidation Premiums
Another revenue source is liquidation premiums. When collateral is sold during a liquidation process, if it fetches a higher price than its original value, the excess amount can contribute to MakerDAO’s revenue. This adds an additional layer of income beyond stability fees.
3. Real-World Assets
MakerDAO has started using real-world assets, like short-term US Treasuries, as collateral. This move increases revenue from stability fees because these assets provide more value and stability. Adding real-world assets helps diversify and boost the protocol’s income.
4. Dai Savings Rate
The Dai Savings Rate allows Dai holders to earn interest on their holdings. Although this costs the protocol, it makes Dai more appealing and encourages users to hold more Dai. This increased use supports MakerDAO’s revenue indirectly.
5. Governance Fees
Governance in MakerDAO is conducted through MKR tokens, which give holders the power to make key decisions about the protocol. Some of these governance actions may require fees. These fees contribute to MakerDAO’s revenue. This system helps align governance decisions with the financial needs of the protocol and supports its ongoing operation and stability.
Features That Make MakerDAO Popular Among Its Users
MakerDAO has gained significant popularity in the decentralized finance sector due to several important features. These elements effectively meet the needs and preferences of its users:
1. Stable Value Management
MakerDAO focuses on keeping the value of Dai close to $1 USD. This stability is important for users who wish to avoid the price fluctuations seen with other cryptocurrencies. Collateral, here, backs each Dai to ensure its consistent value and provides a reliable option for digital transactions.
2. Decentralized Governance
Governance within MakerDAO is conducted by MKR token holders. This approach prevents any single entity from dominating the protocol, thereby reducing the risk of manipulation. Decisions are made collectively by the community, and all actions are transparently recorded on the Ethereum blockchain, which promotes fairness and accountability.
3. Flexible Collateral Options
Users can use various Ethereum-based assets as collateral within MakerDAO. This flexibility accommodates different risk levels and investment preferences. The protocol adjusts to market conditions through community voting and makes sure that it remains effective and relevant over time.
4. Interest-Earning With The DSR
The Dai Savings Rate feature allows users to earn interest on their Dai holdings. Depositing Dai into the DSR generates additional returns, making it more appealing compared to other digital assets. This feature provides users with a clear incentive to hold and use Dai.
5. Integration With DeFi Protocols
MakerDAO integrates smoothly with other DeFi protocols and gives users access to a broad range of financial services and products. This integration improves the usefulness of Dai and offers more opportunities for financial management within the DeFi ecosystem.
6. Strong Security Measures
MakerDAO ensures strong security. It takes advanced measures and regular reviews to help protect user funds from potential threats. These security protocols ensure that assets remain safe while building trust among users.
Development Steps For DeFi Lending Platform Like MakerDAO
Developing a DeFi lending platform involves several steps, and each stage addresses different aspects:
1. Collateralization And Liquidation Mechanisms
A well-designed collateralization system supports various asset types, such as cryptocurrencies, NFTs, and potentially tokenized real-world assets. Implementing a dynamic collateral ratio system is essential, as it adjusts based on market fluctuations, asset risks, and borrower creditworthiness. This approach ensures that the system remains stable and secure. Additionally, include mechanisms for handling undercollateralized positions, such as automated auctions or decentralized processes, to manage risk and protect assets effectively.
2. Stability Mechanisms
Maintaining the stablecoin’s value close to a target, such as $1 USD, is a fundamental thing to do when building a platform, particularly like MakerDAO. To achieve this, develop a system that monitors and adjusts the stability fee based on changing market conditions. This mechanism helps to keep the stablecoin’s value consistent and provides users with a reliable asset for transactions. These regular adjustments make sure that the stablecoin remains effective despite market volatility.
3. Flash Loans With Collateralization
Flash loans offer the ability to borrow funds without upfront collateral but with the condition that the loan is repaid within the same transaction. To eliminate risks associated with flash loans, you can introduce measures such as requiring collateral to be deposited before the loan is executed. These safeguards help prevent misuse and ensure that transactions are secure and your platform is protected from potential abuse.
4. Governance And Community Involvement
A governance framework allows users to influence protocol decisions through voting. So, establish a governance token to grant voting rights on changes and improvements. In addition to this, engage the community in these decisions to make sure that the platform evolves with user needs and preferences. This involvement can establish transparency and build a sense of ownership.
5. Oracle Integration
Accurate price data is important for effective collateral management. Integrate reliable Oracles to provide real-time information on asset values. It is important to ensure the security and reliability of the Oracle system to prevent manipulation and maintain accurate valuations. This integration supports sound risk management and helps to sustain the platform’s stability.
6. Risk Management And Insurance
A comprehensive risk assessment model is necessary to evaluate collateral assets and borrower risks. Continuously monitor these risks to maintain platform stability. Additionally, offer insurance products to protect users from potential losses caused by market fluctuations or system failures. This added protection improves user confidence and ensures a safer platform environment.
7. Cross-Chain Compatibility And DeFi Integration
Design the platform to easily integrate with other DeFi protocols and enable users to access a variety of financial products. With this, make sure to implement cross-chain compatibility, as it can enable the platform to operate across multiple blockchains. This functionality can broaden the platform’s reach and improve its utility within the broader DeFi ecosystem while making it more accessible and versatile.
Tech Stack For MakerDAO Like DeFi Lending Platform Development
Developing a DeFi lending platform like MakerDAO requires some of the essential components:
| Component | Description | Tech Stack |
| Blockchain Platform | The underlying blockchain network on which the platform operates. | Ethereum, Solana, Avalanche, Polygon |
| Smart Contract Programming Language | The language used to write the platform’s smart contracts. | Solidity, Vyper, Rust |
| Decentralized Oracles | Providers of real-time price feeds and other data to smart contracts. | Chainlink, Band Protocol, UMA |
| Decentralized Storage | A decentralized storage solution for storing large datasets or documents. | IPFS |
| Frontend Development | Tools and frameworks for building the user interface. | React, Angular, Vue.js |
| Backend Development | Tools and frameworks for building the server-side of the platform. | Node.js |
| Security Tools and Libraries | Tools and libraries for ensuring the security of the platform. | Security audits, OpenZeppelin |
| DevOps Tools | Tools for automating development, testing, and deployment. | CI/CD, Terraform, Ansible |
| Monitoring and Analytics Tools | Tools for tracking platform performance and user behavior. | Blockchain explorers, analytics tools |
| NFT Integration | Tools and libraries for handling NFTs as collateral. | NFT-specific libraries or frameworks |
| Risk Assessment Models | Machine learning models for assessing the risk associated with borrowers and collateral. | Machine learning libraries or frameworks |
| Decentralized Insurance Protocols | Protocols for implementing decentralized insurance mechanisms. | Insurance-specific libraries or frameworks |
| Cross-Chain Interoperability Solutions | Tools for interacting with multiple blockchains. | Cross-chain protocols or bridges |
Top Revenue Generating Methods That Are In Trend For DeFi Lending Platform
DeFi lending platforms use several methods to earn revenue. Here are some of the most effective strategies:
1. Yield Farming
Yield farming encourages users to contribute liquidity to lending pools in exchange for high interest rates or rewards in the form of platform tokens. This practice enhances liquidity and attracts a larger user base. The platform generates revenue from the interest earned on these assets and the fees charged for borrowing.
2. Flash Loans
Flash loans enable users to borrow substantial amounts of funds without needing collateral as long as the loan is repaid within the same transaction. This feature supports activities such as arbitrage and adds a layer of flexibility for users. Each flash loan transaction collects a small fee, which provides a steady revenue stream for the platform. Since the loan is secured within the transaction, this method minimizes risk while offering a profitable avenue for income. incur
3. Stablecoin Borrowing And Lending
Stablecoins such as USDC, USDT, and Dai are popular due to their stable value. Platforms offer borrowing and lending services for these coins. They earn revenue from the interest charged on loans and fees from borrowers. This method provides a steady income, as stablecoins are widely used and trusted.
4. Cross-Chain Lending
Cross-chain lending enables users to borrow and lend assets across different blockchains. This broadens the platform’s market and enhances its capabilities. In this case, revenue comes from fees for cross-chain transactions and interest on lent assets. This approach attracts a wider range of users and supports increased liquidity.
5. Interest Rate Spread
DeFi platforms often maintain a difference between the interest rates offered to lenders and those charged to borrowers. This difference is the platform’s profit margin. Proper management of this spread ensures that the platform generates revenue while meeting the needs of both lenders and borrowers.
Cost Of Developing A DeFi Lending Platform Like MakerDAO
Here’s the estimated breakdown of the costs for developing a DeFi lending platform like MakerDAO:
| Component | Description | Min Cost (USD) | Max Cost (USD) |
| Market Research and Feasibility Study | Conducting thorough market research to understand demand, competition, and regulatory landscape. | $200 | $5,000 |
| Design and Prototyping | Creating wireframes, UI designs, and prototypes to visualize the platform. | $1,000 | $10,000 |
| Blockchain Development | Developing smart contracts for collateral management, Dai generation, liquidation mechanisms, and governance. | $2,000 | $20,000 |
| Frontend Development | Building the user interface and experience (UI/UX) for the platform. | $2,000 | $10,000 |
| Backend Development | Developing the backend infrastructure to support the platform. | $1,000 | $15,000 |
| Oracle Integration | Integrating reliable oracles to provide real-time price feeds for collateral assets. | $1,000 | $5,000 |
| Security Audits | Conducting comprehensive security audits of smart contracts and the overall platform. | $1,000 | $10,000 |
| Regulatory Compliance | Ensuring the platform complies with relevant regulations and legal requirements. | $500 | $5,000 |
| Testing and Quality Assurance | Performing rigorous testing, including unit testing, integration testing, and user acceptance testing. | $500 | $10,000 |
| Marketing and Community Building | Promoting the platform, building a community, and encouraging participation in governance. | $500 | $5,000 |
| Maintenance and Updates | Ongoing maintenance, updates, and improvements based on user feedback and market conditions. | $300 | $5,000 |
| Total Cost Range | – | $10,000 | $100,000 |
Cost-Affecting Factors To Consider For DeFi Lending Platform Development
Developing a DeFi lending platform involves several factors that can impact development costs:
- Oracle Integration: Integrating Oracles for accurate price feeds and market data significantly impacts development costs due to the complexity and security requirements of these systems.
- Governance Mechanism: Implementing a decentralized governance system, such as the MKR token model, adds complexity and expense to the development process, requiring careful planning and execution.
- Risk Management And Liquidation: Designing risk management and liquidation mechanisms is important for platform stability, involving intricate programming and rigorous testing, which increases development costs.
- Interoperability: Ensuring that the platform is compatible with other DeFi protocols or blockchains demands additional development efforts and integration work, which can raise costs.
- Scalability: Building a platform capable of handling growing user numbers and transaction volumes requires advanced infrastructure and optimization techniques, impacting both development and long-term operational expenses.
- DeFi Ecosystem Dynamics: The DeFi ecosystem introduces new technologies and standards, necessitating ongoing adaptation and updates that can affect development timelines and costs.
- Smart Contract Complexity: The development of smart contracts for collateral management, stablecoin generation, and governance involves high complexity, requiring extensive development and thorough testing, which drives up costs.
Conclusion
Developing a DeFi lending platform like MakerDAO is a great opportunity in the growing decentralized finance market. MakerDAO has set a strong example with its stable system, transparent governance, and flexible collateral options. So, if you are considering building one, we would advise you to focus on key aspects like solid collateral mechanisms, reliable oracles, and strong security measures that can help your platform meet the increasing demand for decentralized financial services. Or, you can get in touch with blockchain experts with your concept of a DeFi lending platform, and they will lay out the perfect plan of action for you. As DeFi continues to grow, building a platform that is well-designed and full of useful features could offer significant benefits and help you shape the future of DeFi!
Looking To Develop A DeFi Lending Platform?
A DeFi lending platform is a promising venture, and we understand what it takes to build one. Our team, with over 50,000 hours of experience, has successfully developed several blockchain projects, including MOGO, Salvacoin, SteliNovas, EQL, etc., demonstrating our expertise in this area. With our experience in blockchain development, we can be a reliable partner in creating a DeFi lending platform that meets industry standards and user expectations. We aim to deliver a solution that is technically sound, user-friendly, and unique. Let’s work together to create a platform that leads the future of decentralized finance.
Work with Ex-MAANG developers to build next-gen apps schedule your consultation now
FAQ
How does MakerDAO make money?
MakerDAO earns revenue primarily through stability fees and liquidation penalties. When users borrow Dai by locking up collateral, they pay a stability fee, which is essentially interest on the loan. If the collateral value drops too much, it can be liquidated, with a penalty fee charged, both contributing to MakerDAO’s income.
What is the MakerDAO lending Protocol?
The MakerDAO lending protocol allows users to borrow Dai, a stablecoin, by locking up assets like Ethereum as collateral. This decentralized system uses smart contracts to maintain Dai’s value close to $1, ensuring stability while enabling users to access liquidity without selling their underlying assets.
What is the point of MakerDAO?
MakerDAO aims to provide a decentralized, stable currency that is not subject to the volatility of traditional cryptocurrencies. It enables users to borrow Dai against collateral, ensuring financial stability and accessibility while offering a decentralized alternative to traditional financial systems.
How long does it take to build a platform like MakerDAO?
Building a platform like MakerDAO can take anywhere from 6 months to over a year, depending on the complexity, team expertise, and resources available. This timeline includes phases like planning, development, testing, and deployment, as well as implementing security measures and regulatory compliance.
Is MakerDAO a lending platform?
Yes, MakerDAO functions as a lending platform within the decentralized finance ecosystem. It allows users to borrow the stablecoin Dai by locking up collateral, typically Ethereum. This system provides a decentralized way to obtain liquidity without selling assets, operating without traditional financial intermediaries.

























