In recent years, traditional insurance has struggled to adapt to the speed and openness of a digital world. Long wait times and unclear policies have led people to question the fairness of the system. Businesses and investors now expect something more direct and reliable. With decentralized finance growing so quickly, this change can finally happen. On-chain insurance platforms like Nayms offer a way to rebuild trust through smart automation and open data.
They allow insurance to be written on-chain while capital providers and underwriters interact directly. Nayms also lets users tokenize risk and process claims automatically with full transparency. This kind of system could truly redefine how trust and protection operate in the global economy.
We’ve built several blockchain-driven insurance and financial platforms over the years, powered by distributed ledger technology and smart contract automation. So in this blog, we’ll walk you through how you can build an on-chain insurance platform like Nayms. You’ll discover the technology that powers it and learn step by step how such a decentralized insurance model can come to life.
Key Market Takeaways for On-Chain Insurance Platforms
According to AlliedMarketResearch, the digital insurance platform market is growing at a remarkable pace, rising from $96.34 billion in 2020 to an expected $279.51 billion by 2030. This expansion is powered by digital transformation, automation, and the growing use of blockchain to build smarter, more transparent insurance systems. Insurers are using these technologies to create flexible products, simplify claims, and meet the changing expectations of tech-savvy customers.

Source: AlliedMarketResearch
Platforms like Etherisc and Uno Re are leading the evolution of on-chain insurance. Etherisc makes it easy for businesses to design blockchain-based insurance products that handle events such as flight delays, crop losses, or natural disasters with automated claims and transparent processes.
Uno Re focuses on trading and managing risk exposure for DeFi-related threats, offering coverage against smart contract exploits and exchange hacks. Together, they represent a shift toward user-driven, decentralized models that remove traditional middlemen.
Partnerships are also driving innovation in this space. Bright Union, a DeFi insurance marketplace, brings multiple decentralized providers under one roof to make coverage comparison simple and accessible. By collaborating with InsurAce, Neptune Mutual, and OpenCover, Bright Union is helping expand the range of available policies while improving overall user experience and accessibility for on-chain insurance.

What Is Nayms Platform?
Nayms is an on-chain insurance platform that bridges traditional insurance with the digital asset economy. It enables insurers, brokers, and capital providers to build, manage, and trade insurance programs entirely on-chain using cryptocurrencies or tokenized assets.
Operating under a Bermuda-licensed regulatory framework, Nayms combines the transparency of blockchain with the reliability of regulated insurance. The platform empowers participants to capitalize on digital insurance ventures, launch segregated captives, and trade risk efficiently, all within a trusted and compliant ecosystem.
Here are some of its standout features,
On-Chain Balance Sheet
Nayms allows insurance programs to be funded and operated directly using cryptocurrencies or project tokens. This creates a live, on-chain balance sheet that simplifies administration and reduces dependency on complex off-chain legal structures.
Tokenisation and Trading
The platform tokenizes both capital and liabilities, transforming insurance risk into tradable digital assets. Participation tokens represent ownership and exposure within insurance pools, enabling seamless, transparent trading across the ecosystem.
Segregated Accounts and Digital Captives
Users can create regulated, segregated accounts, or digital captives, for self-insurance. These accounts can be funded with native crypto or third-party assets, offering full compliance with Bermuda’s established insurance regulations.
Alternative Capital Sources
Nayms connects traditional insurers and brokers to a global pool of alternative capital providers. By tapping into uncorrelated capital sources, the platform expands access to reinsurance and diversified risk-sharing opportunities beyond conventional markets.
Automated Transaction Rails
Through smart contract automation, Nayms streamlines premium collection, claims payouts, and revenue management. This reduces administrative overhead and increases efficiency for brokers, underwriters, and capital providers alike.
Regulatory Compliance
As a platform licensed by the Bermuda Monetary Authority for both digital asset business and insurance, Nayms ensures every transaction and entity operates under a clear and secure legal structure. This gives participants confidence in the platform’s legitimacy and oversight.
Discretionary Fund
The Nayms Discretionary Fund, backed by the NAYM token, acts as an additional protection layer within the ecosystem. It provides liquidity support and acts as a safety net for users, strengthening trust and resilience across the marketplace.
How Does the Nayms Platform Work?
The Nayms platform works by letting people create insurance programs on the blockchain, where investors can fund these programs and earn from the premiums while policyholders get protected against risks. Everything runs through smart contracts, so payouts and records stay transparent and secure. You could think of it as a digital marketplace where insurance becomes open, tradable, and community-driven.
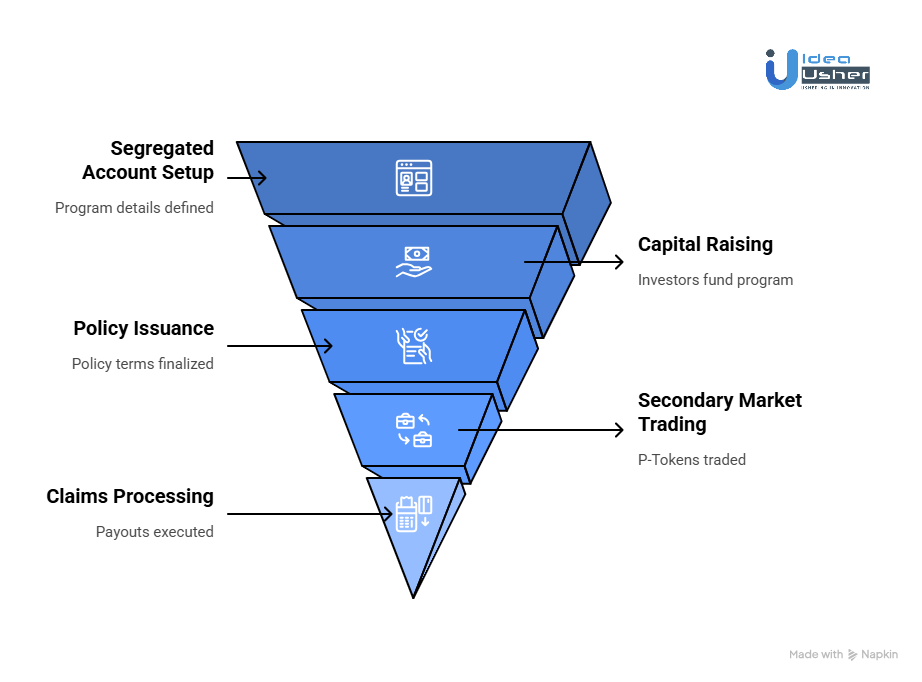
Step 1: Creating the Insurance Program
Every insurance program begins with a broker or corporate entity, such as a DAO, crypto exchange, or traditional business, that needs coverage for a specific risk. This could range from smart contract exploits to natural disasters.
- Through Nayms, they create a Segregated Account, a legally and technically isolated “cell” on-chain that mirrors a captive insurance structure. This ensures that each program’s assets and liabilities remain independent from others.
- Within this SegAcct, they define the program’s details, including the type of risk, policy terms, premium amount, and required capital.
Behind the scenes, the platform deploys a dedicated smart contract that acts as the program’s treasury and policy manager. This contract is fully auditable and compliant, forming the legal and operational backbone of the insurance cell.
Step 2: Raising Capital Through Tokenization
Once the SegAcct is created, it must be funded. Investors who have completed KYC and Anti-Money Laundering verification can explore available insurance programs on the Nayms marketplace.
When an investor chooses to participate, they contribute capital in assets such as USDC, ETH, or BTC. In return, they receive Participation Tokens (P-Tokens), which represent three key rights:
- Ownership: A proportional share of the capital pool.
- Liability: An obligation to cover potential claims.
- Economic Benefit: Entitlement to a share of premiums and investment returns.
This tokenization process transforms traditional, illiquid insurance risk into a tradeable digital asset, allowing investors to enter or exit positions efficiently.
Behind the scenes, the minting of P-Tokens effectively securitizes insurance risk, creating a transparent and liquid market for it.
Step 3: Underwriting and Policy Issuance
Once capital has been raised, the broker finalizes the insurance policy with the policyholder using Nayms’ built-in tools. The legal policy document is drafted off-chain, while a cryptographic hash of the document is recorded on the blockchain and linked to the SegAcct.
This creates an immutable, tamper-proof audit trail that verifies the existence and authenticity of every policy.
The policyholder then pays the premium in cryptocurrency, which is automatically transferred to the SegAcct’s treasury and becomes part of the pool’s earnings available to P-Token holders.
This step ensures alignment between the legal framework and blockchain implementation, maintaining regulatory compliance and technological integrity.
Step 4: The Secondary Market for Risk
One of Nayms’ most innovative features is its secondary market for insurance risk. Investors holding P-Tokens are not required to wait until the policy expires to exit their position.
Instead, they can sell their tokens to another verified investor on Nayms’ built-in matching marketplace. This enables liquidity and price discovery similar to traditional financial markets.
Behind the scenes, Nayms employs a regulated trading engine and compliance layer that ensures only approved wallets can trade these securities, maintaining both market integrity and legal compliance.
Step 5: Claims Processing and Payouts
When a covered event occurs, the claims process activates automatically or through human validation, depending on the type of policy.
Parametric Policies
If the policy is based on measurable data (for example, “payout if wind speeds exceed 100 mph”), decentralized oracle networks such as Chainlink verify the data and trigger an instant payout from the SegAcct’s smart contract.
Adjudicated Policies
For more complex claims, a designated underwriter or claims adjuster validates the event. After verification and a potential review period, the smart contract executes the payout to the policyholder.
Once a payout is made, the SegAcct’s total capital decreases, and the value of each P-Token adjusts to reflect the updated capital position. This creates a transparent feedback loop between claims performance and investor value.
What is the Business Model of the Nayms Platform?
Nayms operates as a digital marketplace for on-chain insurance. Brokers, insurers, investors, and policyholders can create and manage insurance programs entirely on the blockchain. Each policy and capital pool is represented as a smart contract that automates premiums, claims, and settlements.
This model eliminates much of the administrative overhead found in traditional insurance systems, reducing friction and cost while ensuring transparent tracking of funds and risk.
Revenue Generation
A mix of transactional and service-based income drives Nayms’ revenue:
- Transaction Fees: A percentage fee is charged on the creation, placement, and trading of insurance contracts and capital tokens on the platform.
- Platform and Subscription Fees: Insurers and brokers pay for access to Nayms’ tools, regulatory infrastructure, and on-chain transaction rails.
- Service Fees: Additional income comes from custodial and reporting services, as well as structured product facilitation.
By automating much of the back-office work through blockchain logic, Nayms can scale efficiently while opening new revenue opportunities tied to the volume of capital flowing through its ecosystem.
Tokenization and Capital Efficiency
A key innovation in Nayms’ model is tokenized capital pooling. Insurance capital is fractionalized into tokens, allowing investors to gain exposure to specific risk classes or insurance programs. These tokens can be traded in secondary markets, providing liquidity and diversification that traditional insurance vehicles typically lack.
This approach expands the pool of potential capital providers beyond conventional reinsurers, addressing capital shortages in specialized risk areas such as digital assets.
Regulatory Framework
Nayms operates under dual licenses from the Bermuda Monetary Authority as both a Digital Asset Business and an Innovative General Business Insurer.
This regulatory standing ensures full compliance with insurance and digital asset regulations, establishing a foundation of trust for institutional participants. The Bermuda framework also allows Nayms to operate under a recognized and flexible regime for crypto-based insurance programs.
Financial Performance and Funding
To date, Nayms has raised roughly $14 million from investors including UDHC, Keyrock, Coinbase Ventures, New Form Capital, and Tokentus Investment AG.
- A 2023 private round led by UDHC secured about $3.5 million at an $80 million valuation, following earlier seed rounds that funded platform development and regulatory milestones.
- Industry estimates place Nayms’ annual revenue around $2.8 million, with approximately $110,000 in revenue per employee, signaling sustainable early-stage growth and operational focus.
Strategic Position and Partnerships
Nayms positions itself at the intersection of insurance, capital markets, and blockchain infrastructure.
- By partnering with major players such as Aon, it facilitates blockchain-enabled insurance syndicates that function similarly to Lloyd’s of London cells, which are segregated and regulated entities managed via smart contracts.
- This design provides clarity around capital, governance, and regulatory oversight while enabling transparent, automated claims through Oracle verification.
Nayms’ model directly addresses the capacity gap in crypto-related insurance by providing a scalable, compliant platform for insuring and financing digital asset risks with tokenized capital.

Other Business Models for an On-Chain Insurance Platform
While Nayms has pioneered the regulated insurance marketplace model, the broader on-chain insurance sector remains full of untapped opportunities. Entrepreneurs and investors entering this field must carefully choose the right business model to capture value and achieve long-term profitability.
By analyzing existing approaches and emerging players, we can identify several viable models, each with distinct revenue mechanics and growth potential.
1. The DeFi Mutual Model
This model functions as a decentralized mutual owned and governed by its token holders. Members contribute capital to a shared treasury, which is used to cover crypto-native risks such as smart contract bugs, exchange failures, and protocol hacks.
Revenue comes from premiums paid by users who buy coverage, while profits are distributed to capital providers. The platform earns income by taking a small facilitation fee from each premium.
Nexus Mutual exemplifies this model. As of late 2023, its capital pool (Total Value Locked or TVL) fluctuated around $150 million. The platform collects a 2% fee on all premiums, while the remaining funds are distributed to the mutual’s members.
Revenue Potential and Example Calculation
Let’s assume a new platform launching with a TVL of $50 million.
If 10% of that pool ($5 million) is actively used for underwriting and the average policy lasts 90 days, the pool cycles through its capacity four times per year.
- Annual Premium Volume: $5M × 4 = $20M
- Platform Fee (2%): $20M × 2% = $400,000
At larger scales, with $150M in TVL and higher utilization, annual platform fees could exceed $1–2 million. The success of this model depends directly on capital efficiency and utilization rate.
2. The Parametric Specialist Model
This model uses predefined data triggers to automate payouts. Instead of human claims adjusters, oracles verify when an event occurs, such as a hurricane exceeding a certain wind speed or a sharp drop in ETH’s price.
Because payouts are fast and transparent, these products can command higher premiums. The platform earns revenue from both the premiums and a service fee for operating the oracle-based infrastructure.
Neptune Mutual popularized this model for crypto hacks. During the FTX collapse, its dedicated coverage pool for FTX users saw massive demand, proving the need for rapid, event-based payouts in the DeFi space.
Revenue Potential and Example Calculation
Consider a platform, offering parametric coverage for crypto exchange failures.
- Coverage Purchased: $10M over a 3-month period
- Premium Rate: 5%
- Total Premiums: $10M × 5% = $500,000
- Platform Fee (15%): $500,000 × 15% = $75,000
If the platform runs 10 similar events per year, annual revenue would exceed $750,000. This model is highly scalable because it requires minimal claims management once the Oracle infrastructure is in place.
3. The Custom Pool Architect Model
This model focuses on providing infrastructure that allows anyone to create their own insurance pool. The platform itself does not underwrite risk but enables users to design, fund, and manage customized pools for specific assets, protocols, or events.
Revenue comes from pool creation fees, a percentage of premiums distributed, and trading fees from secondary market transactions of pool tokens.
For example, Tidal Finance allows users to build personalized coverage pools that target particular risks. Reserve providers can select which pools to support, creating a flexible marketplace for specialized risk management.
Revenue Potential and Example Calculation
For example, let’s take a platform that facilitates 100 active pools with a combined TVL of $25 million.
- Pool Creation Fee (0.1% of TVL): $25M × 0.1% = $25,000
- Premium Fee (3% of $2.5M in annual premiums): $2.5M × 3% = $75,000
- Trading Fees (0.3% of $25M annual trading volume): $25M × 0.3% = $75,000
Total Annual Revenue: $25,000 + $75,000 + $75,000 = $175,000
As institutional players enter and larger pools are created, this model can scale rapidly. Revenue grows in proportion to both TVL and secondary market activity.
How to Develop an On-Chain Insurance Platform Like Nayms?
We build powerful on-chain insurance platforms that combine blockchain trust with real-world compliance. Over the years, we’ve helped many clients launch platforms like Nayms that actually work in the market. When you work with us, you’ll see how smoothly regulation, technology, and user experience can come together to create something truly valuable.
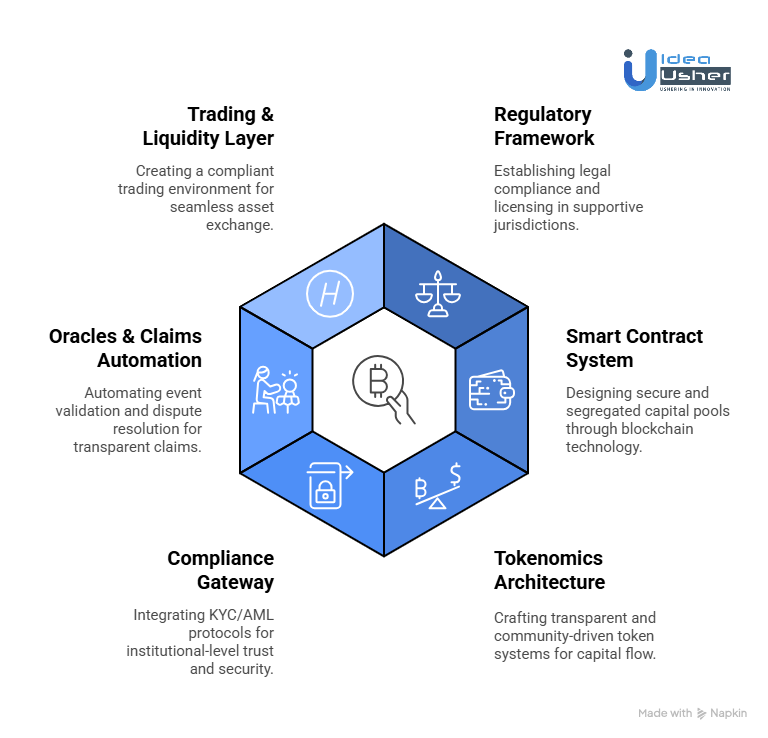
1. Regulatory & Jurisdictional Framework
We begin by identifying suitable jurisdictions such as Bermuda, Gibraltar, or Malta that support digital asset insurance licenses. Our legal and compliance team collaborates with local regulators to define a clear licensing pathway. At the same time, we develop RegTech modules that automate compliance and onboarding, ensuring our clients operate within fully approved legal frameworks from day one.
2. Make Smart Contract System
Our blockchain engineers design a Segregated Account Contract framework that allows independent capital pools for each insurance program. Using formal verification, we ensure that legal segregation aligns perfectly with the on-chain smart contract logic, eliminating fund intermixing risks and ensuring full auditability.
3. Tokenomics for Capital Participation
We craft a tokenomics architecture that features both Participation Tokens (P-Tokens) for investors and governance tokens for ecosystem governance. Each token’s lifecycle, including minting, burning, redemption, and secondary trading, is carefully designed to support transparent capital flow and community-driven governance while maintaining regulatory compliance.
4. Build Compliance & Identity Gateway
To ensure institutional-level trust, we integrate KYC/AML protocols and blockchain-based compliance oracles. This layer enforces wallet whitelisting, transaction monitoring, and real-time compliance reporting, ensuring only verified participants can interact with the platform’s financial instruments.
5. Oracles & Claims Automation
We connect the platform with decentralized oracle networks like Chainlink to automate event validation and trigger claim settlements. Our claims management module also includes dispute resolution and arbitration layers, providing a transparent, tamper-proof claims process for both insurers and participants.
6. Develop Trading & Liquidity Layer
Finally, we build a compliant on-chain trading environment for P-Tokens, integrating AMM or hybrid order book models to provide liquidity and efficient price discovery. This ensures investors can seamlessly trade their positions while maintaining full regulatory transparency and asset security.
Common Challenges an On-Chain Insurance Platform Like Nayms
Building an on-chain insurance platform is more than a technical project; it’s about merging blockchain technology with the strict standards of regulated finance. After guiding several clients through this process, we’ve identified four recurring challenges and proven ways to overcome them.
Challenge 1: Navigating Global Regulations
Creating an on-chain insurance platform means entering the world of regulated finance. Once your platform handles institutional money or real insurance contracts, you face complex, jurisdiction-specific laws.
Choosing the wrong jurisdiction or license can lead to severe fines or even shutdowns. Nayms set a strong example by obtaining dual licenses from the Bermuda Monetary Authority. Similar complexity exists in the EU, UK, and US.
Our Proven Solution
We approach compliance as part of the product design.
- Regulatory Mapping: We identify jurisdictions with frameworks that support digital assets and insurance, such as Bermuda’s IIGB and DABA licenses.
- RegTech Partnership: Our network of RegTech and legal consultants manage the licensing process while we embed compliance requirements into your technology stack.
- Compliance Layer: We integrate tools like Sumsub or Trulioo for KYC/AML and build on-chain permissioning logic to restrict access to verified investors.
This ensures a compliant foundation from day one and turns regulation into a strategic advantage.
Challenge 2: Making Smart Contracts Legally Enforceable
Smart contracts execute code, but insurance policies are legal contracts. When disputes arise, code alone doesn’t hold up in court. Without a clear link between your blockchain code and your legal agreements, institutional players won’t participate. The challenge is aligning your digital logic with real-world enforceability.
Our Proven Solution
We connect the legal and digital worlds through a hybrid structure.
- Hybrid Contract Design: Smart contracts handle capital pooling, premiums, and payouts while referencing the cryptographic hash of a corresponding legal policy.
- Legal-Tech Collaboration: We work with your legal team to ensure the policy document points directly to the on-chain contract address. This ensures both documents recognize each other as binding.
This “legal wrapper” gives your platform legal credibility and the trust required by institutional partners.
Challenge 3: Unbreakable Data Integrity with Oracles
Oracles link real-world events to smart contracts. If a single oracle or API is compromised, it can trigger false claims or block legitimate ones, putting your capital pools at risk. Oracle manipulation is one of the biggest technical threats in on-chain insurance.
Our Proven Solution
We design oracle architectures for resilience and redundancy.
- Primary Layer: We use Chainlink to collect data from multiple independent nodes, ensuring one bad actor can’t alter results.
- Fallback Layer: For complex claims such as security breaches, we enable a challenge process where a decentralized review council or a secondary oracle like API3 provides final verification.
- Redundancy: We add RedStone for frequent data updates to keep the system reliable during network delays.
This structure eliminates single points of failure and maintains integrity in every claims event.
Challenge 4: Mitigating Crypto Volatility
If an ETH-backed pool underwrites USDC policies, a sudden drop in ETH’s price can make the pool insolvent. Crypto volatility poses a unique solvency risk that traditional insurers rarely face. Without safeguards, a single market event can destabilize the entire platform.
Our Proven Solution
We embed financial risk management directly into smart contracts.
- Stablecoin Denomination: Policies and claims are priced in stablecoins like USDC or USDT to keep accounting consistent.
- Asset-Liability Matching: We align the asset with the insured risk like BTC policies backed by BTC pools, and fiat-equivalent coverage backed by stablecoins.
- Dynamic Re-Collateralization: Smart contracts continuously monitor collateral values. If ratios drop below 125%, the system can trigger margin calls or partial liquidations via decentralized exchanges to restore solvency.
This approach protects capital pools through volatility, preserving both liquidity and trust.

Tools & APIs for an On-Chain Insurance Platform Like Nayms
Building a regulated, blockchain-based insurance marketplace demands a layered architecture that unites smart contract engineering, compliance infrastructure, and secure data integration. Below is a breakdown of the essential tools and frameworks needed to develop such a platform.
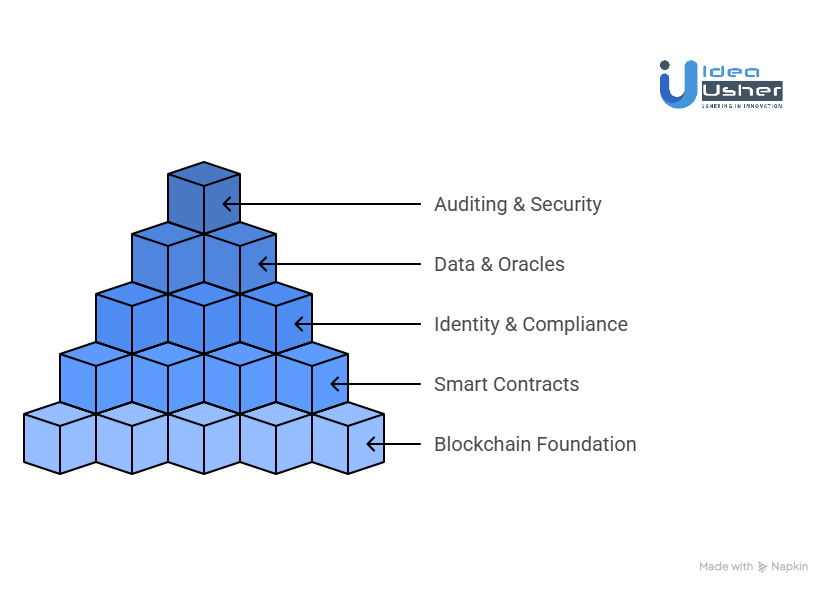
1. Blockchain Foundation
The blockchain serves as the settlement and verification layer of your platform. It must combine security, scalability, and flexibility to support complex financial contracts.
- Ethereum: A proven and secure choice for high-value insurance contracts where decentralization and trust are critical. However, transaction costs can be a limiting factor.
- Polygon, Avalanche, or Layer-2 Networks: These networks maintain Ethereum compatibility while significantly reducing gas fees and improving transaction throughput. They are ideal for handling marketplace activity and secondary token trading.
Recommended Approach: Deploy the core insurance contracts on Ethereum for maximum security and reliability, and use a cost-efficient Layer-2 for high-frequency trading and user interface operations.
Expert Insight: A well-designed multi-chain architecture balances cost, speed, and regulatory needs while maintaining seamless interoperability between layers.
2. Smart Contract Development
Smart contracts are the foundation of trust for on-chain insurance. They handle underwriting, claims, settlements, and fund management. Reliability and precision are non-negotiable.
- Languages and Frameworks: Use Solidity as the primary language and frameworks like Hardhat or Foundry for compiling, testing, and deploying contracts.
- Libraries: Employ OpenZeppelin Contracts for audited, standardized implementations of ERC-20 tokens (used for participation tokens) and essential security features such as Ownable and ReentrancyGuard.
- Oracles: Integrate Chainlink for decentralized data feeds and parametric triggers. RedStone or API3 can provide more flexible or specialized oracle solutions.
- Security Management: Utilize OpenZeppelin Defender to automate admin functions, manage access control, and monitor contract behavior in real time.
Critical Challenge: Translating traditional insurance logic, such as solvency tests, risk-sharing mechanisms, or pro-rata claim payouts, into secure, gas-optimized smart contracts requires close collaboration between legal, actuarial, and blockchain engineering teams.
3. Identity and Compliance
Compliance is not an afterthought. It is the bridge between your blockchain infrastructure and institutional trust.
KYC/AML Providers
Integrate APIs from Sumsub, Trulioo, or Persona to handle identity verification, liveness checks, and sanctions screening.
Permissioned Access
Implement a gateway smart contract that validates user eligibility through an on-chain allowlist before enabling actions such as investing, trading, or creating insurance programs.
4. Data and Oracle Architecture
Insurance depends on external data to determine when and how claims should be triggered. Reliable oracle integration ensures that smart contracts can respond to verified real-world events.
- Parametric Insurance: Use Chainlink oracles to feed trusted data, such as weather conditions, flight delays, or cyberattack metrics, directly into claims contracts for automatic payouts.
- Discretionary or Adjudicated Claims: For complex scenarios, such as assessing crypto asset hacks, use a hybrid model where an underwriter or approved reporter initiates a claim. The claim can then be reviewed by a decentralized oracle network or DAO during a verification period.
- Off-Chain Data Integration: Implement The Graph for querying on-chain event data to display pool performance, policy history, and investor portfolios on the front end.
Best Practice: Design a layered oracle system that applies decentralization where it matters most while retaining expert human oversight for nuanced claim decisions.
5. Auditing and Security
In on-chain insurance, a single vulnerability can destroy confidence and capital. Security must be treated as a continuous process, not a final step.
- Pre-Launch Audits: Engage independent security firms such as CertiK, OpenZeppelin Security, or ConsenSys Diligence to perform full audits of your contracts before deployment.
- Post-Launch Monitoring: Use OpenZeppelin Defender for continuous surveillance, alerting, and emergency controls. Smart contracts should include pause mechanisms and robust key management systems.
Conclusion
Nayms has shown how insurance and blockchain can truly work together to create trust, efficiency, and transparency. By entering this space early, your business could gain both a regulatory and a technical edge that will be hard for others to match. If your company wants to build a compliant and tokenized insurance marketplace like Nayms, Idea Usher can provide the full-stack solution from regulatory design to blockchain development and thorough smart contract audits.
Looking to Develop an On-Chain Insurance Platform Like Nayms?
At Idea Usher, we turn complexity into clarity. With over 500,000 hours of development experience and a team of former MAANG/FAANG engineers, we design and build financial ecosystems that are secure, compliant, and scalable.
We don’t just develop blockchain solutions, we architect complete on-chain infrastructures that combine:
- Jurisdictional and compliance strategy from the start
- Smart contract architecture designed for performance and trust
- Scalable, audited systems ready for real-world deployment
If you’re inspired by platforms like Nayms and ready to build your own compliant on-chain insurance marketplace, we’ll help you move from concept to market-ready reality.
Work with Ex-MAANG developers to build next-gen apps schedule your consultation now
FAQs
A1: An on-chain insurance platform runs fully on blockchain and lets users create and manage insurance programs through smart contracts. It can automate underwriting and claims while also allowing investors to provide capital in a transparent and traceable way that builds stronger confidence in every transaction.
A2: Nayms is different because it operates within full regulatory oversight under the Bermuda Monetary Authority, which gives it a real advantage over unregulated DAO-based models. It combines blockchain transparency with legal structure so institutions can safely participate and offer real-world insurance coverage
A3: A business could earn money by charging transaction fees and issuing policies through tokenized insurance pools. It can also generate income from premium collection and secondary trading, which may steadily increase as the platform gains more users and capital flow.
A4: Regulation is the backbone of trust and growth in this space. It helps platforms prove their credibility to investors and partners while ensuring every process remains compliant, enabling them to scale more quickly and confidently in global markets.