Logistics and the supply chain industry have been the backbone of global commerce. From seamless inventory management to timely delivery of goods, logistics are crucial in keeping economics and business running smoothly.
As the demand for the logistics industry is going further, businesses are looking for practical solutions that can help them resolve challenges in the logistics industry, such as data security, route optimization, and much more.
AI comes as an emerging solution that streamlines the entire logistic operations, such as cost reduction, improving productivity, efficient predictive analytics, reducing the error possibility, and much more.
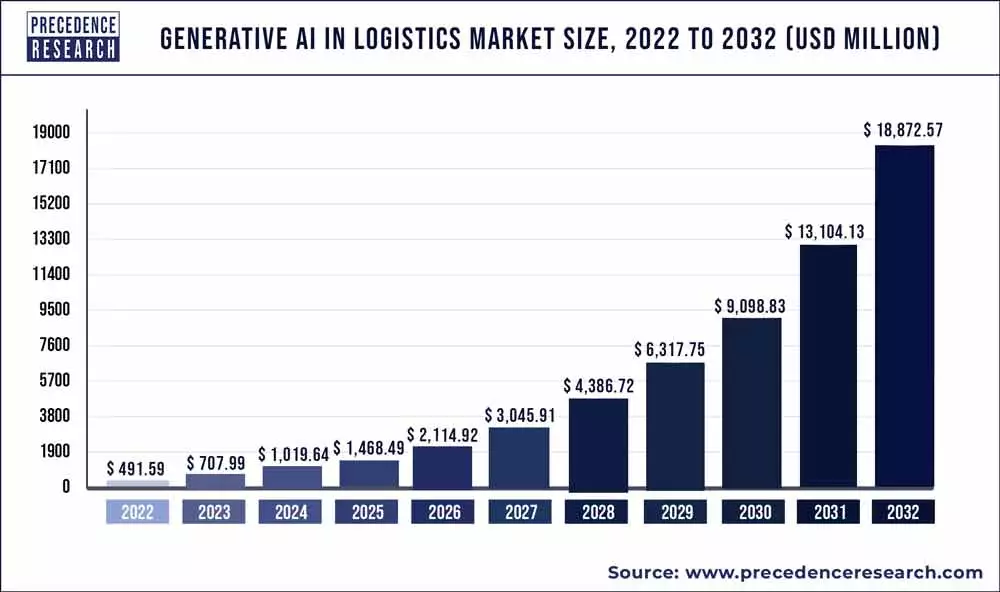
Source: Precedence Research
Many benefits of AI in logistics encourage companies to develop AI models for their logistic business operations, thus increasing the demand and global market of AI in logistics.
For the successful development of the AI model in logistics, we will explore development steps and tech stack. Also, we will find out how AI is improving the logistics industry with its potential benefits and use cases.
Use Case Of AI In The Logistics Industry
From smooth logistic operations to changing consumer demands. Machine intelligence or AI-driven supply chain management offers many use cases. Some of them have been mentioned below:
1. Autonomous Vehicles
Deliveries can be done in less time as the system can help businesses identify the best and fastest routes to destinations using AI systems in the trucking industry.
Moreover, ML usage can also reduce the possibility of package damage as the system can analyze the data and intelligently process actions, thus enhancing the experience and profitability.
Example: Autonomous truck platoon
The AI-based technique connects two or more trucks, where drivers control the first while the other trucks (powered by AI) follow them.
Truck platoon helps businesses save the expense on fuel by around 5 to 20%, depending on the speed, gap, number of vehicles, and location of a vehicle.
2. Delivery Drones
Useful machines for delivering products from one place to another, where a ground transfer is not safe, possible, reliable, or sustainable, Especially in the healthcare industry. The drones provide quick delivery for medicines that have short shelf life spans. Implementing drone delivery help business to reduce the cost needed to invest in storage facilities.
Example: Parcelcoptor
A joint project known as “Deliver Future” is a collaboration between DHL and GIZ on behalf of BMZ and Wingcopter. The drones deliver medicines to isolated areas in eastern Africa over a period of six months.
For Parcelcoptor, it took only 40 minutes for Parcelcopter 4.0 to fly 60 kilometers from the mainland to a remote island in Lake Victoria.
3. Predictive Analysis
Processing massive amounts of data with machine learning and other AI models helps logistics businesses ensure that errors occur by less than 1% with the efficient utilization of human labor.
Moreover, predictive analysis helps logistic businesses strategically plan shipments more simply and easily. Also, AI models predict demand based on historical data to help logistic businesses optimize inventory operations for efficient output.
Example: Maersk
A famous shipping and logistics company has developed an AI-powered virtual assistant, Captain Peter, who can provide quick and helpful responses to customer queries and suggest the most efficient shipping routes.
Also, the company has experienced improved demand forecasting using AI, allowing it to offer better customer satisfaction and smoother operations.
Maersks’ other platform, TradeLens, a cutting-edge blockchain-based platform, also utilizes AI for tracking and managing the shipping of goods across global supply chains, resulting in more transparency and efficiency.
4. Big Data
The massive amount of logistic data can only be handled effectively and meaningfully with the help of AI in logistics. Data analytics through AI can help logistic businesses stay ahead and be ready for predicted risks, such as bad weather, unexpected demands, operation failure, and much more.
Example: Speedy
A part of DPDgroup, where the company controls one-third of the courier, parcel, and express market in Bulgaria, with 16 million parcels handled annually.
The introduction of AI in logistics allowed Speedy to quickly identify and cancel unnecessary trips, which resulted in a hub-to-hub cost reduction of around 25%, as well as a 14% increase in fleet utilization. Also, AI helped speedy to cut costs by an estimated 7% to 9%.
5. Warehouse Robots
There is a crucial role for warehouse robots in the logistics industry. Warehouse robots are equipped with AI to automate inventory management, picking and packing, transportation, and even data analysis.
Example: Amazon Scout
In 2019, Amazon has unveiled a new robot called “Scout,” which is developed to deliver packages directly to customers’ homes. Scout is a six-wheeled small robot that can avoid obstacles and navigate sidewalks.
Also, Scout allows customers to place an order on Amazon and have it delivered within a few hours. The delivery robot could eventually reduce the need for human delivery drivers, improving Amazon’s operations efficiency even further.
6. Route Optimization
AI models help businesses to analyze existing routing and track route optimization. Route optimization uses shortest-path algorithms in graph analytics to identify the most efficient route for logistics trucks.
Therefore, the business can reduce shipping costs and speed up the process. For example, Valerann‘s Smart Road System is an AI web-based traffic management platform that delivers information about road conditions to autonomous vehicles and users.
Route optimizers are also effective tools for reducing corporate carbon footprint.
Example: DHL
A global transportation leader leverages the advantages of AI integration to recognize likely disruptions in the supply chain. DHL’s platform gathers insights from online discussions using natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning (ML).
Also, the platform identifies access problems, potential shortages, and supplier statuses with the help of Artificial Intelligence.
7. Back Office Operations
Companies in the logistics industry frequently face various back-office tasks requiring improvement, such as processing documents, managing schedules, tracking shipments, generating reports, and managing emails.
With the help of automation technologies like artificial intelligence, robotic process automation (RPA), and process mining, logistics companies can simplify these activities, such as tracking packages in the warehouse, scheduling transportation, and assigning employees to specific stations,
Example: UPS
UPS, a US-based parcel service, has developed an AI-based chatbot called UPS Bot that performs office tasks such as customer inquiries, shipment tracking, and rate quotes in an automated way. This helps UPS to optimize its processes and increase productivity.
The UPS Bot can make more conversational interactions and respond to customer queries in natural language, allowing its staff to focus on more complex tasks, improving efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Advantages Of Using AI In Logistics
Logistic businesses have witnessed rapid growth with the help of AI and machine learning for boosting management capabilities and organizing their business operations. Here are some benefits of developing an AI model in the logistics industry.
1. Enhanced Safety
The AI model in logistic business examines data for workplace safety and alerts manufacturers to any potential dangers with the help of intelligent planning and effective warehouse management.
Also, with AI, businesses can enhance safety by updating operations, recording stocking parameters, performing essential feedback loops, and preventative maintenance.
2. Timeless Delivery
The delivery process can be accelerated by automated technologies where there is the requirement of the least amount of effort for meeting delivery deadlines. Moreover, AI can assist logistics businesses to minimize their dependence on manual effort, which results in a safer, faster, and more efficient delivery process overall.
3. Reduced Operation Costs
Businesses can improve their operational costs by increasing speed and accuracy and bringing more productivity with the help of warehouse robots.
By utilizing many AI benefits, such as reducing the number of operational mistakes and workplace incidents, businesses can reduce operational costs.
4. Better Transportation Prediction
One of the major advantages of the logistics industry. There is the involvement of machine learning and AI algorithms to forecast the price variants in the current logistic market. AI algorithms help logistic businesses predict how much capacity will be available for modes, carriers, and lanes.
How Can Your Business Use AI For Logistics?
There are multiple ways AI can be used in businesses to enhance their operations. Some significant ways businesses can use AI for logistics are mentioned below.
1. Compare And Select
To select an appropriate AI solution, it is crucial to compare all the available options for developing an AI model that fits your business requirements. Consider focusing on various crucial aspects, such as integration with the existing system, technical capabilities, and vendor support.
Also, look for an AI development partner who can understand your required business operations and provide innovative solutions per your logistics needs.
2. Address Major Issues
Identify supply chain gaps for efficiently integrating AI into your logistics business. The process may involve addressing warehouse efficiency, equipment maintenance, and supply chain management.
After identifying the required areas of improvement, use AI to equip it with hassle-free functioning and better efficiency with AI’s major significant impacts.
3. Scale and Grow
It is a beneficial and strategic move to start AI development on a small scale and perform throughout testing to find the efficiency of the AI model.
After the successful output at a small scale during testing, you can take the AI model at a gradually large scale.
4. Train And Staff Support
AI can offer numerous benefits to the logistics industry, but your staff must have expertise and be ready to work. There is a possibility that your staff may find it challenging to work with AI models, which can be easily omitted by providing them with appropriate guidance.
Startups and enterprises need to offer general AI training for their employees to bridge any challenges and enable them to efficiently use AI models for maximizing profitable and beneficial outputs in the logistics business.
5. Plan AI Implementation
There is a requirement for careful AI implementation, which can be done by developing an appropriate AI model for your logistic business.
Consider qualifying various crucial aspects for successful AI implementation, such as scheduling, technology implementation, investment, budget, onboarding, and training strategy.
Also, identify appropriate metrics that can help you track progress for the successful implementation of an AI model.
How To Develop AI In Logistics?
The development of AI in logistics involves creating intelligence systems and algorithms for optimizing various crucial aspects and efficiency of logistic operations.
Here is a step-by-step detailed guide on developing AI for logistics.
1. Define Your Objectives
Create a detailed plan on how you will leverage the power of AI to fulfill the goals of your logistics business. You can Improve the various crucial aspects of logistic business, such as inventory management, demand forecasting, and warehouse automation.
2. Data Collection
Build the foundation of your AI model by gathering relevant data from various sources such as GPS devices, ERP systems, and historical records.
3. Data Preprocessing
A crucial step for removing noise and unnecessary data is cleaning, pre-processing, and transferring the data to ensure it is available in a usable format.
4. Select AI Techniques
The selection of appropriate AI techniques will help you develop a reliable solution for your logistic problems by selecting from common AI techniques, such as:
- Deep Learning: For image recognition, complex pattern recognition, and natural language processing.
- Machine Learning: For demand forecasting, classification tasks, and predictive analytics.
- Reinforcement Learning: For optimization problems like inventory management and route planning
5. Model Development
The preprocess data will help you develop and train your AI models by considering using popular machine learning libraries like Scikit-learn, PyTorch, and TensorFlow.
6. Testing and Validation
To ensure the AI model meets the essential criteria for your logistic business, such as reliability and accuracy, evaluate the performance of your AI using validation data sets.
7. Integration with Logistics Systems
Maximize the efficiency of your logistics system by integrating your AI model into the existing logistics workflows and systems. The integration process may involve creating API or custom interfaces for seamless communication between logistics software and the AI systems.
8. Continuous Learning & Deployment
There is a possibility that logistic data can change over time. Therefore, implement mechanisms for continuous learning and retrain your AI model.
Also, deploy your AI solution in a production environment in addition to monitoring the performance and addressing any issues that arise in the AI model.
9. Scale & Optimize
Scale your AI system as your logistics operations grow. The scaling of the AI model may involve deploying more powerful hardware or distributing workloads across multiple cloud services or servers.
To improve the performance and efficiency of the AI model, optimize your AI model continuously, which might involve exploring more advanced AI techniques or fine-tuning hyperparameters.
10. Feedback Loop
Make continuous improvements by establishing a feedback loop with logistics teams and gathering meaningful insights and feedback on the AI system’s performance.
11. Documentation and Training
Document the AI system’s algorithms, architecture, and data sources in addition to training logistics staff on effectively using and interpreting the AI-generated insights.
Tech Stack For Developing AI Model In Logistics
There is an involvement in combining various technologies and tools for analyzing and processing accurate data, optimizing routes, predicting demand, and more.
The specific tech stack selection will depend on your project’s requirements and your team’s expertise. Here’s a generalized tech stack for developing an AI model in logistics:
1. Programming Languages
- Widely used for data processing, machine learning, and scripting tasks: Python
- For statistical analysis and data visualization: R
2. Data Integration and ETL
- Apache NiFi
- Kafka
- Apache Spark
3. Machine Learning Frameworks
- TensorFlow
- PyTorch
- Scikit-learn
- XGBoost and LightGBM
4. AI Model Deployment
- Docker
- Kubernetes
- Cloud Services: AWS SageMaker, Google AI Platform, or Azure Machine Learning
5. Data Visualization
- Matplotlib and Seaborn for static plots
- Plotly and Bokeh for interactive visualizations
- Tableau or Power BI for creating dashboards
6. Data Storage and Processing
- Structured data: PostgreSQL, MySQL) for
- Unstructured or semi-structured data: MongoDB, Cassandra
- Warehousing: Amazon Redshift, Google BigQuery
7. Geospatial Analysis
- GeoPandas
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS) tools
8. Optimization Algorithms
- PuLP
- Gurobi
9. IoT and Sensor Integration
- MQTT or CoAP
- AWS IoT
- Azure IoT
10. Real-time Data Processing
- Kafka
- Flink
- Apache Storm
11. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- NLTK
- spaCy
12. Version Control and Collaboration
- Git for version control.
- Collaboration platforms like GitHub or GitLab
13. Security
- Encryption
- Authentication
- Access control
14. Monitoring
- Prometheus
- Grafana
15. Logging
- Elasticsearch
- Logstash
- Kibana
16. Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
- Jenkins
- GitLab CI/CD
17. Cloud Services
- AWS
- Google Cloud Platform
- Azure
Conclusion
The integration of artificial intelligence into logistics has demonstrated its capability to address various challenges and ultimately led to improved operational processes and enhanced customer experiences.
The AI can analyze vast real-time data, allowing accurate demand forecasting, inventory management, and route optimization. Moreover, the data-driven approach enables companies to make informed decisions, minimize environmental impact, and reduce cost and fuel consumption by optimizing transportation routes.
However, one should remember that adopting AI in logistics does not happen without challenges. Therefore, working with AI developers who have expertise in the logistics industry is a way to navigate any possible challenges and successfully adopt AI in the logistics business.
You can contact our team if you are looking for AI developers who can help you develop an appropriate AI model for your logistics business.
We will navigate any possible challenges through careful planning and commitment to facilitate a smoother journey toward AI adoption in your logistics business.
Work with Ex-MAANG developers to build next-gen apps schedule your consultation now
FAQ
Q. What are the challenges of AI in logistics?
A. Integrating AI into logistics involves several challenges that must be addressed, such as data security and the costs associated with setting up and maintaining the necessary infrastructure.
Q. How does AI impact the logistics industry?
A. AI can be employed in the logistics business to help companies analyze data and identify patterns for determining convenient transportation routes. Moreover, there are many ways AI can impact the logistics industry, such as identifying the most efficient routes for deliveries Red predicting weather conditions by utilising real-time data.
Q. What is the use case of AI in logistics?
A. There are many use cases of AI in logistics, such as route optimization, predictive maintenance, inventory management, warehouse automation, last-mile delivery, quality control, energy efficiency, customs and compliance, sustainability, supplier selection, cold chain monitoring demand forecasting, customer service, and risk management.
























