Imagine what would happen if your valuable information, such as your credit card number or bank account number got into the wrong hands. What would happen if you faced a data breach? The thought of it is scary, right? Well, there are some techniques to help you avoid such circumstances. One of them is ‘tokenization.’ Its various types, including vault tokenization and vaultless tokenization, are instrumental in data security, helping us protect highly sensitive data.
How do they do it? We’ll discuss the details in this blog article. Here, we’ll elaborate on tokenization, its types, which type is better, and other relevant aspects. Let’s dive right into the details.
What is tokenization?
Tokenization is the process of converting highly sensitive data into non-sensitive data called ‘tokens.’ Tokens are sent to an organization’s internal systems for use after tokenization, while the initial data is securely held in a token vault.
Customers use payment cards for transactions daily, which must occur in a secure environment. The data these transactions carry is extremely valuable to attackers, thus becoming a prime target for attack. The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) lays down standards to secure cardholders’ data, which can be done through tokenization. It converts sensitive data, like card details, into a random number with the same format but no intrinsic value.
It is important to note that tokenization differs from encryption because they have different purposes and procedures.
Encryption changes a number mathematically, such as a card number or bank account number, but the new code still preserves the initial pattern. However, tokenization removes all sensitive information from the business systems, replaces it with a non-decipherable token, and stores the initial data in a secure cloud data vault.
You can decrypt the encrypted data using an appropriate key but cannot reverse tokens because of the absence of any mathematical relationship between the token and the initial number.
Marriott and its tokenization use
In 2018, Marriott announced one of the most significant data breaches in history.
The breach included:
- 383 million guest records
- 18.5 million encrypted passport numbers
- 9.1 million encrypted payment card numbers
- 385,000 valid card numbers
- 5.25 million unencrypted passport numbers
Could tokenization have prevented this data breach? Yes!
Marriott’s CEO, Arne Sorenson, stated in his testimony that they will now rely on encryption and tokenization tools to secure their data.
- Why tokenization? Because it swaps sensitive data like personally identifiable information (PII) with an indecipherable token.
- Why isn’t encryption enough? Because you can easily decrypt the encrypted data using the appropriate key.
Types of tokenization
There are two significant types of tokenization:
1. Vault tokenization
In vault tokenization, you maintain a secure database called tokenization vault database that stores the sensitive data along with its corresponding non-sensitive data. You can use this database containing sensitive and non-sensitive data to detokenize the newly tokenized data.
As the name suggests, de-tokenization is the reverse of tokenization. It refers to replacing the non-sensitive data with the sensitive data to retrieve the initial data.
2. Vaultless tokenization
As opposed to vault tokenization, vaultless tokenization does not use a vault to store data. Instead, it uses highly secure cryptographic devices for this purpose. This process is more efficient and safer than vault tokenization because of the absence of a database.
Secure cryptographic devices: Devices that use standard-based algorithms to convert sensitive data into non-sensitive data or to generate tokens.
You can use the tokens that the secure cryptographic devices generate for de-tokenization and obtaining original data without a vault database.
Vaultless tokenization falls under two classes:
| Anonymization | It de-identifies data and does not allow its re-identification. Re-identification refers to re-establishing a link between an individual’s identifiers and the information about them. |
| Pseudonymization | It also allows data de-identification, but this de-identification can be reversed. In other words, the link between an individual’s identifiers and their information can be re-established. |
How does vault tokenization work?
The below diagram and the steps that follow explain how vault tokenization works.
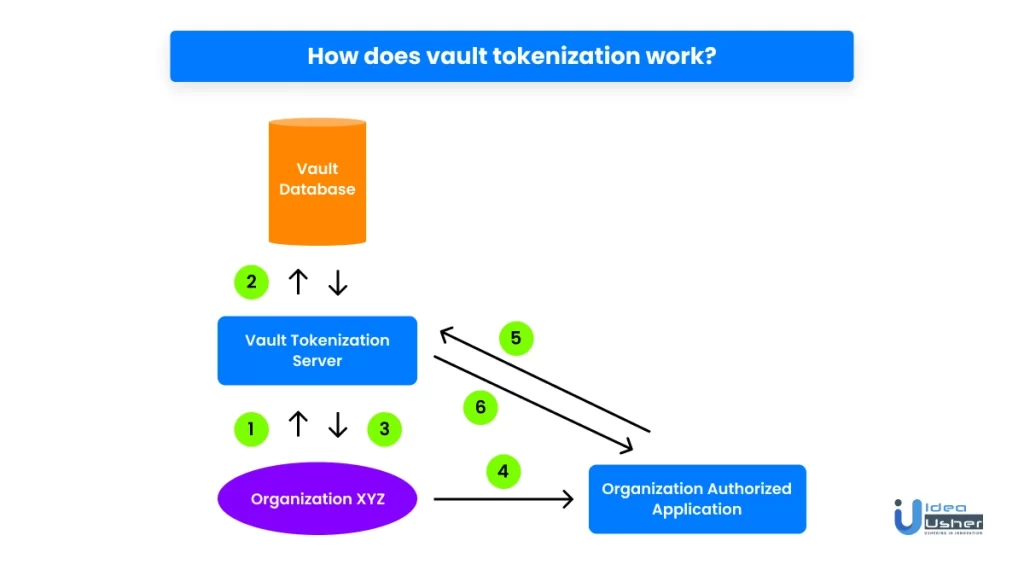
- The organization sends its original sensitive data to the vault tokenization server.
- Next, the vault tokenization server converts the sensitive data into non-sensitive data and saves its mapping in the tokenization vault database.
- Then, the organization receives the non-sensitive data back.
- For PCI DSS compliance, access control is necessary. As a result, whenever the organization requires the original data, it sends the non-sensitive data to the organization-authorized application.
- The application then passes the non-sensitive data to the tokenization server, which converts it into the original sensitive data with the help of the vault database.
- Lastly, the organization-authorized application receives the original data from the vault tokenization server.
How is the working of vaultless tokenization different from that of vault tokenization?
As explained earlier, vault tokenization uses a tokenization vault to store a mapping between the tokenized sensitive data and the corresponding token. In contrast, vaultless tokenization produces the token uniquely utilizing an algorithm. When the need for de-tokenization comes, the token can be easily utilized to determine the initial value without seeking it in a tokenization vault.
Both tokenization techniques allow the retention of the elements of the initial data. While vault tokenization allows the numeric card information token selection, vaultless tokens contain the alpha-numeric parts of the credit card primary account number.
Further, it is critical to highlight that the service provider does not maintain a library of the tokens that users generate. It is because vaultless tokenization does not require a database to store the tokens. The users can easily retrieve any previously tokenized data by giving their service provider the batch file containing the tokens.
Benefits of vaultless tokenization
Vaultless tokenization has several benefits, some of which are listed below:
1. Reduced latency
When the data size increases in vault tokenization, the vault database size also increases. It further increases the time taken for de-tokenization. Additionally, to provide vaulted customers with a highly available and fault-tolerant platform, vaulted data must be replicated between data centers, which can result in a recovery point objective (RPO)/recovery time objective (RTO) of several minutes in the event of a catastrophic outage.
On the contrary, vaultless tokenization reduces latency and results in a more responsive platform. As there is no token to replicate, the RPO/RTO drops to zero, thus increasing availability. Further, the absence of database reads or writes increases the platform’s responsiveness. This gain is minimal in a single API call, but when processing a larger batch file, the faster processing has a noticeable impact.
2. Greater security over token vaults
This technique is more secure than vault tokenization because it does not maintain a database to secure data. Instead, it uses secure cryptographic devices relying on standard-based algorithms for converting sensitive data into non-sensitive ones.
3. Lesser compliance scope and cost
As there is no need to maintain a tokenization vault, the costs of deploying this tokenization technique are significantly reduced. Compliance with PCI DSS is also more accessible, and the data can be secured more efficiently.
4. Smaller storage footprint of sensitive data
This type of tokenization has a smaller sensitive data storage footprint than vault tokenization. A lesser storage footprint ultimately leads to lesser hardware, software, power, and data center space costs, while also easing the strain on networks and backup windows.
5. Requires minimal to no architectural changes and works well with legacy systems
As this type of tokenization relies on standard-based algorithms and secure cryptographic devices, there is a minimal requirement for architectural changes. It is also advantageous as it works in tandem with legacy systems.
Vault tokenization vs. Vaultless tokenization: A comparison
| Vault tokenization | Vaultless tokenization | |
| Performance | Slow because of latency | Faster as there is lesser latency |
| Scalability | Difficult and expensive to create redundancy. Complex replication and powerful hardware are required. | Easier to create redundancy and replication is not required. Deployed with commodity hardware. |
| Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) | High TCO because of the above factors | Low TCO because of the above factors |
| PCI data protection | Fair- with the issues discussed above. | Excellent |
| PII data protection | Fair- more than one PII value will break this approach | Excellent |
| PHI (Personal Health Information) data protection | Not applicable | Excellent |
What is the future of vaultless tokenization?
Vaultless tokenization is a faster and more efficient data security solution than vault tokenization. It is ideal for:
- Individuals who want to keep their sensitive information secure from prying eyes
- Companies that want to make sure they have control over their assets (without having to worry about who holds them)
- Anyone who wants to be able to access their funds anywhere in the world with just one click
With the rise of cryptocurrency, it’s become more important than ever to be able to store your crypto safely and securely. Vaultless tokenization allows you to keep your digital assets on an open-source platform you and your company administer. You retain complete control over who can access your data and how it is used. It means that your crypto is safe from hackers, thieves, and other bad actors but also gives you complete visibility into how your money is being spent when necessary—so there are no surprises!
Tokenization in blockchain
So far, we’ve discussed tokenization outside the blockchain. But, with web3 blowing up, it is imperative to discuss tokenization in the blockchain. Blockchain tokenization divides asset ownership into several tokens. It is similar to NFTs, but tokenization also uses fungible tokens.
Types of blockchain tokenization
There are mainly three types of blockchain tokenization:
| NFT tokenization | NFTs are one of the most popular forms of tokenization today. They are digital data representing unique assets. These assets have no fixed value and can be used as proof of ownership, allowing people to trade different items or validate transactions. |
| Governance tokenization | This type of tokenization aims at the blockchain voting systems. It improves decision-making using decentralized protocols by allowing all stakeholders to vote, debate, and collaborate equally on-chain. |
| Utility tokenization | Utility tokens are established by following a specific protocol and giving access to particular services inside that protocol. They do not generate direct investment tokens but provide good platform activity for enhancing the system’s economy. |
Blockchain is a complex technology, and it might get overwhelming to understand its functioning. In such cases, it is advisable to consult experts who can guide you on how the technology can benefit you and how you can tokenize data for maximum advantage.
Idea Usher is a leading technology company providing blockchain, AI, IoT, and other web3 services. Our experts have a strong foundation in these technologies and years of experience delivering the best digital solutions to clients.
Contact us to understand how blockchain and tokenization can be helpful for your business.
E-mail: [email protected]
Phone Numbers : (+91) 946 340 7140, (+91) 859 140 7140 and (+1) 732 962 4560
Build Better Solutions With Idea Usher
Professionals
Projects
Frequently asked questions
Here are a few exciting FAQs about vaultless tokenization:
1. What is tokenization in encryption?
Tokenization and encryption are different terms. Encryption uses traditional methods to encode a given data that can be decrypted using an appropriate key. However, tokenization converts highly sensitive data into non-sensitive data called tokens. It replaces the sensitive data with a random set of characters without any intrinsic value.
2. What is vaultless tokenization?
Vaultless tokenization is a faster and more secure data protection technique that converts highly sensitive data into non-sensitive data using algorithms and does not require any vault database.
3. What are the benefits of tokenization?
Some critical advantages of tokenization include:
- Data breach risk reduction
- Greater customer trust
- Lesser red tape
- Greater efficiency
- Better regulatory compliance

























