Virtual Reality (VR) has gained significant traction in sports training, catering to professional athletes and amateurs. This innovative technology offers a dynamic and immersive training environment that enables athletes to engage in endless practice scenarios. Its applications extend beyond just skill development, encompassing crucial safety and performance enhancement aspects.
In the context of safety, VR emerges as a vital asset. It allows athletes to refine their techniques while minimizing the risk of injuries. By immersing themselves in realistic training simulations, athletes can master their craft with reduced physical strain and potential harm.
Furthermore, VR serves as a powerful tool for enhancing skill development. Athletes can meticulously analyze game situations from a first-person perspective, gaining invaluable insights into their performance. This not only aids in technique refinement but also contributes to overall game strategy and decision-making.
In a broader sense, integrating VR into sports training fosters a holistic approach to athlete development. It empowers individuals to optimize their abilities, safeguard their well-being, and elevate their game to new heights, ensuring they are better prepared for the ever-evolving challenges of modern sports. Let’s understand this in depth.
Traditional Sports Training and Its Challenges
Traditional sports training has long been the foundation of athlete development, both for professionals and amateurs, but it comes with its set of challenges that need attention. While it has been the usual way of doing things for years, understanding its challenges is important.
1. Repeating Drills and Limited Scenarios
In the traditional world of sports training, athletes often find themselves doing the same drills and exercises over and over again. This repetitive nature can lead to getting stuck without much progress in skill development, as athletes may not encounter a wide range of situations they’d face in real games. This limitation makes it hard for them to adjust quickly during actual competitions.
2. Risk Of Injuries
Injuries are always a worry in traditional training methods. The physical demands of tough workouts and practice sessions can increase the chances of getting hurt, potentially keeping athletes on the sidelines for a long time. These injuries not only affect their performance but also can be bad for their health in the long run.
3. Lack of Realistic Game Situations
In traditional training, making the training feel like a real game can be hard. Athletes may struggle to recreate the pressure, noise from the crowd, and dynamic aspects of actual matches. This can lead to differences in performance when going from training to real games.
4. Limited Rehabilitation Integration
Rehabilitation within the traditional training setup often follows a simple path, with not much room for customization. Injured athletes may not have the chance to work with sport-specific elements during their recovery, which can slow down their return to top performance.
5. Mental Strength
Being mentally strong is really important in sports, yet traditional training might not prepare athletes well for high-pressure situations. Overcoming mental challenges, like feeling nervous or dealing with pressure from the crowd, can be hard when training environments lack the realism needed to help athletes get used to them.
Traditional sports training has its benefits, but it’s important to recognize its challenges. Embracing innovative approaches, such as virtual reality, can work together with traditional methods and address some of these difficulties, providing a more complete and effective path to developing athletes.
The Potential Of VR In Sports Training
VR in sports training is not a mere tool; it’s a transformational force that transcends boundaries and elevates athletes to new heights of performance while ensuring their safety throughout their journey. Here are some ways VR can contribute to sports training:
1. Safe And Controlled Environment
With VR, athletes can train without worrying about getting hurt. It’s like practicing in a safe bubble where they can improve without the risk of real-world injuries.
2. Skill Refinement
If a soccer player is working on their free-kick technique in VR, they can practice over and over, making every kick better, all without worrying about messing up in a real game.
3. Efficiency Redefined
In the VR world, athletes can practice specific skills without the need for long, tiring games. It’s like getting straight to the point and becoming better at what they do faster.
4. Realistic Scenarios
VR takes athletes into a world that feels just like the real thing. They can practice in situations that mimic actual games, making their training much more lifelike.
5. Total Immersion
In VR, athletes don’t just watch; they’re part of the action. It’s like being in the game, which makes training more engaging and helps them learn better.
6. Advancements
Modern VR technology is incredibly advanced. It can mimic how sports equipment behaves and recreate the excitement of a crowded stadium, making training super realistic.
7. Technique Development
VR allows athletes to practice their moves over and over, making them better and better. It’s like mastering a skill through endless repetition.
8. Injury Prevention
VR keeps athletes safe by letting them train without the risks of real-world practice. It’s like a protective shield, reducing the chances of getting hurt.
9. Psychological Preparation
VR prepares athletes for high-pressure moments, just like real games with huge crowds. It helps them get mentally ready to perform at their best.
10. Rehabilitation Integration
For injured athletes, VR can be part of their recovery plan. It helps them keep their skills sharp while they heal, potentially speeding up their return to the game.
11. Performance Elevation
VR empowers athletes to push their limits and become even better. It’s like having a personal coach that helps them reach new heights in their sport.
12. Training Redefined
VR isn’t just a tool; it’s the future of sports training. It’s a safe, dynamic, and immersive way for athletes to get ready for their games while prioritizing their well-being.
Market Insights For Virtual Reality
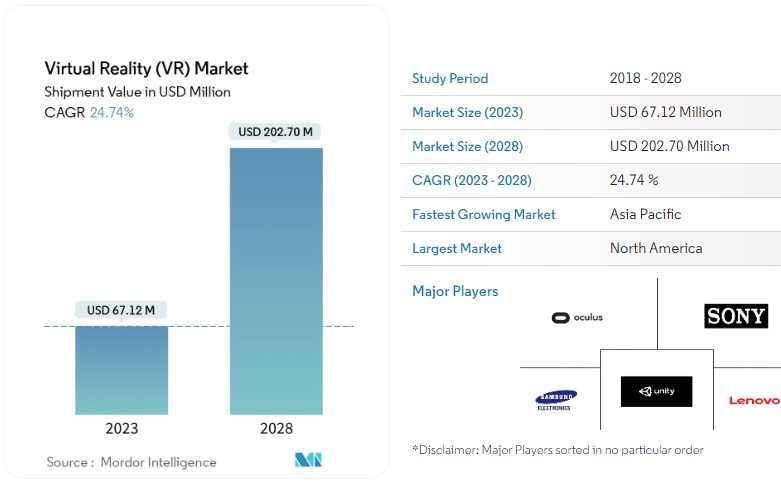
In accordance with a survey conducted by Mordor Intelligence, it is anticipated that the VR market’s shipment value will undergo substantial expansion, increasing from USD 67.12 million in 2023 to USD 202.70 million by 2028. This growth is projected to manifest at a remarkable Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 24.74% within the forecasted period spanning from 2023 to 2028.
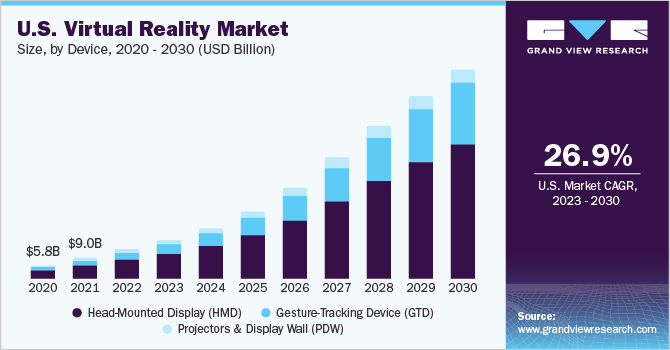
Furthermore, an alternative report suggests that the global virtual reality (VR) market was approximated at USD 59.96 billion in 2022, with expectations of continued growth at an impressive Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 27.5% from 2023 through to 2030.
Moreover, the worldwide virtual fitness market achieved a valuation of $14.9 billion in 2022, with estimations forecasting an impressive escalation to $250.7 billion by 2032. This substantial growth, marked by a robust Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 32.7% from 2023 to 2032, illustrates the sector’s tremendous potential and trajectory.
Business Opportunities In VR Sports Training
Virtual Reality (VR) in sports training isn’t just about refining skills; it’s also a gateway to promising revenue streams. Let’s explore the business opportunities that VR unveils:
1. Customized Training Platforms
Innovators can craft VR training platforms catering to both seasoned pros and budding athletes. These platforms offer a safe space for skill enhancement while ensuring technique precision.
2. Live Streaming Immersion
Entrepreneurs have the chance to revolutionize sports viewing by enabling fans to immerse themselves in live events via VR. This immersive experience promises to bring fans closer to the adrenaline-pumping action.
3. Commentary Enhancement
VR isn’t just for athletes; it can elevate the commentary game. By providing sportscasters with enhanced perspectives, it can fuel more insightful analysis and commentary.
4. Rehabilitation Revolution
VR plays a pivotal role in athlete rehabilitation. Businesses can develop programs that allow injured athletes to maintain their skills during recovery, ensuring a quicker return to peak performance.
5. Implementation Services
As the demand for VR training programs grows, an opportunity emerges for companies to offer specialized services for their seamless integration. This support can facilitate a smoother transition for businesses seeking VR’s advantages.
6. Diverse VR Experiences
Beyond sports training, VR opens doors to a multitude of experiences, from gaming to 3D entertainment. Businesses can tap into this diverse market to provide a range of engaging services.
These opportunities leverage VR’s immersive and realistic capabilities, making it not just a game-changer for athletes but also a fertile ground for innovative businesses. VR in sports training isn’t just a trend; it’s a doorway to a world of possibilities.
Key Considerations For The Development Of VR In Sports Training
1. Training Objectives
Begin by defining the specific skills and abilities you aim to enhance through VR training. Whether it’s improving kicking accuracy in soccer or honing basketball shooting skills, clarity on training objectives guides the entire development process.
2. User Demographics
Understand the target audience for your VR training program. Different age groups and skill levels require tailored experiences. For instance, programs for young athletes should prioritize engagement and simplicity, while those for professionals demand depth and realism.
3. Technological Resources
Assess the available VR hardware and software resources. The choice of technology impacts the complexity and quality of your VR experience. You can consider factors like headset capabilities, tracking systems, and graphical fidelity within your budget constraints.
4. Budget Allocation
Determine the budget allocated for VR development. Budget limitations may necessitate prioritization and trade-offs. It’s crucial to strike a balance between creating a compelling VR environment and staying within budgetary constraints.
5. Development Timeline
The timeline for VR development is another crucial factor. Be realistic about the time available for development. A longer time frame allows for more intricate details and fine-tuning, while shorter deadlines may require a more focused scope.
6. Safety Measures
Safety is paramount in VR sports training. Implement features to minimize the risk of injury, especially when users are fully immersed in the virtual world. Consider features like a guardian system to prevent collisions with real-world objects.
7. Interactivity And Feedback
Prioritize interactivity and real-time feedback. Athletes should be able to actively engage with the VR environment, receiving immediate feedback on their performance. This feedback loop is essential for skill improvement.
8. Realism And Immersion
Strive for a high level of realism and immersion in the VR experience. The more closely the virtual environment replicates real-world sports scenarios, the more effective the training will be. Attend details like physics, visuals, and sound to enhance immersion.
9. Customization
Allow for customization within the VR program. Athletes have unique needs and preferences, so provide options to adjust difficulty levels, training routines, and VR environments to cater to individual requirements.
10. Integration Of Technologies
You can consider integrating AI and data analytics to enhance the VR experience. AI can create realistic opponents or game scenarios, while data analytics can offer insights into an athlete’s performance.
11. User Experience
Put user experience at the forefront of development. Ensure that the VR system is user-friendly, intuitive to navigate, and engaging for athletes. A positive user experience is key to the success of your VR training program.
With this, you can develop a tailored VR sports training program that effectively enhances athletes’ skills, prioritizes safety, and aligns with budget and timeline constraints.
How To Develop VR For Sports Training?
Step 1: Understand The Sport And Training Objectives
To begin, it’s essential to define the specific training goals and objectives you aim to achieve using VR technology. You must gain a deep understanding of the sport you’re targeting and the specific training objectives you want to achieve. Whether it’s improving technique, strategy, or injury rehabilitation, clarity in your goals is essential.
Additionally, consider your target audience, whether it’s professional athletes, beginners, or a specific age group. Clear and measurable training goals, such as improving accuracy, speed, or decision-making, will serve as the foundation for your VR training program.
Step 2: Choose Appropriate Hardware And Software
Select the most suitable VR hardware and software components based on your project’s scope and budget. Choosing suitable VR hardware includes decisions regarding VR headsets, controllers, and tracking systems. Each VR hardware option comes with its own set of capabilities and limitations, so it’s essential to align your choices with the specific requirements of your project. VR headsets like Oculus Quest 2, HTC Vive, or Valve Index are popular choices. Furthermore, opt for a VR development platform or engine, such as Unity3D or Unreal Engine, that best suits your project’s needs and your development team’s expertise.
Step 3: Design The VR Experience
Create a VR environment that mirrors the real-world sports setting, focusing on realism and immersion. Make objects within the environment interactive, enabling athletes to engage with them naturally.
This stage involves the development of 3D models and animations for sports equipment, athletes, and training environments. To create an immersive experience, meticulous attention must be paid to developing realistic physics simulations that accurately mimic the behavior of sports equipment. High-quality audio recordings or syntheses are also crucial to replicate sports-related sounds and ambiance effectively.
Step 4: Develop The VR Experience
The design of interactive VR environments is paramount to engaging athletes effectively. Utilize your chosen VR development platform to build the VR sports training experience. This step will involve coding and programming to bring the virtual environment to life.
Users should be able to perform sports-specific actions seamlessly within the virtual environment, whether it’s throwing, kicking, or shooting. Implementing intuitive control schemes using VR controllers is essential to enable natural movements. It’s equally important to ensure the implementation of smooth locomotion techniques that prevent motion sickness, such as teleportation or incremental movement. In the end, you must ensure that interactions are fluid and user-friendly.
Step 5: Optimize For Realism And Immersion
Enhance the VR experience by paying attention to visual fidelity, audio quality, and realistic physics. Your primary focus should be on creating a hyper-realistic virtual environment that closely mirrors actual sports scenarios. This encompasses paying meticulous attention to visual fidelity, which involves optimizing textures, lighting, and animations.
Furthermore, enhancing the overall immersion involves incorporating haptic feedback and realistic sound effects to provide users with a heightened sense of presence within the virtual world.
Step 6: Implement Feedback Mechanisms
Integrate real-time feedback mechanisms into the VR training program. This may include performance evaluations, data tracking, and analytics to provide athletes with valuable insights into their progress.
The incorporation of real-time feedback mechanisms is pivotal to the effectiveness of VR sports training. Athletes benefit greatly from immediate performance evaluations during training. To achieve this, use data tracking and analytics to capture critical metrics, such as timing, body movements, and decision-making processes. Ensure that athletes receive instant feedback through visual cues, auditory signals, or haptic responses, enabling them to make rapid adjustments and improvements.
Step 8: Ensure Safety Measures
Prioritize user safety by implementing features that prevent collisions with real-world objects and reduce motion sickness. Implementing a guardian system, which sets virtual boundaries within the VR environment, ensures users remain within safe areas and minimizes the risk of accidents. Ongoing monitoring and management of potential health risks, such as motion sickness and discomfort, are also essential for a safe user experience.
Step 9: Customize For Individual Needs
Offer customization options within the VR training program to cater to individual athlete needs and skill levels. Allow users to adjust the training difficulty, modify training routines, and select specific sports scenarios. Customization empowers athletes to tailor their VR training experience to their unique requirements, thereby enhancing its effectiveness.
Step 10: User Interface (UI) Design
Creating an intuitive and user-friendly UI within the VR environment is vital for easy navigation and accessibility. Athletes should be able to access different training scenarios, adjust settings, and review feedback reports seamlessly. A well-designed UI ensures that users can maximize the benefits of the VR training program with minimal barriers to entry.
Step 10: Test Extensively
Conduct rigorous testing with athletes, coaches, or users from your target audience. Gather feedback and data on usability, effectiveness, and any issues encountered during training. Be prepared to make iterative improvements based on this feedback. Identify and address any issues, such as bugs, discomfort, or usability concerns, promptly. This iterative process allows for the refinement and continual improvement of the VR application to deliver an optimal user experience.
Step 11: Data Integration
Develop a robust system for collecting and analyzing training data to provide athletes and coaches with actionable insights. Data tracking allows for the monitoring of progress, identification of areas for improvement, and the customization of training programs based on individual performance data. The integration of data analytics enhances the overall effectiveness of the VR sports training program.
Step 12: User Onboarding And Training
For successful user adoption, provide comprehensive user onboarding materials and tutorials. These resources ensure that athletes can effectively utilize the VR system from the outset. Consider offering training sessions or workshops for coaches and trainers to maximize the benefits of VR training within a broader athletic development context.
Step 13: Deploy And Support
Upon completing the development and testing phases, deploy the VR sports training program to the intended audience. Whether the target users are individual athletes, sports teams, or training facilities, ensure a seamless deployment process. Additionally, provide ongoing technical support and updates to maintain the system’s functionality and address any emerging issues promptly.
Additional Technical Considerations:
14. Optimization For Performance
Implement optimization techniques to ensure that the VR application runs smoothly across various hardware configurations, enhancing the user experience.
15. Integration Of Biometric Data
Explore the integration of biometric sensors to capture and analyze athletes’ physiological data, offering deeper insights into performance and allowing for more tailored training regimens.
16. Multiplayer And Social Integration
Enable multiplayer functionality for remote training sessions and incorporate social features such as leaderboards and virtual coaches to enhance user engagement.
17. Artificial Intelligence And Machine Learning
Leverage AI and machine learning technologies to create adaptive training scenarios, intelligent virtual opponents, and personalized coaching based on performance data.
18. Content Updates And Expansion
Plan for regular updates to the VR training content to keep it engaging and relevant for evolving training needs and emerging sports trends.
19. Data Privacy And Security
Prioritize robust data privacy and security measures to protect user information and ensure compliance with relevant regulations.
20. Cross-Platform Compatibility
Consider cross-platform compatibility to reach a broader user base, accommodating various VR headset brands and models.
By following these steps and considering these additional technical details, you can successfully develop a VR sports training program that not only enhances athletes’ skills but also offers a safe, immersive, and highly effective training experience.
Tech Stack For The Development Of VR For Sports
1. Hardware
- VR Headsets (e.g., Oculus Quest 2, Oculus Rift, HTC Vive)
- VR Controllers
- Motion Tracking Sensors (e.g., Oculus Touch)
- High-Performance PCs or VR-Ready Laptops
- Haptic Feedback Devices (e.g., VR gloves)
2. Development Platform
- Unity3D or Unreal Engine for VR development
- VR-specific SDKs (e.g., Oculus SDK, SteamVR)
- 3D Modeling and Animation Software (e.g., Blender, Maya)
- Programming Languages (e.g., C#, C++, Python)
3. Content Creation
- 3D Modeling Software (e.g., Blender, Maya)
- Animation Software (e.g., Autodesk MotionBuilder)
- Audio Editing Tools (e.g., Audacity)
4. Interaction Design
- VR Interaction Frameworks (e.g., VRTK for Unity)
- Control Scheme Design
5. Realism and Immersion
- Realistic 3D Models and Textures
- Lighting and Physics Simulation
- Spatial Audio
6. Feedback Mechanisms
- Haptic Feedback Devices (e.g., Haptic gloves)
- Real-time Data Tracking and Analytics
7. Safety Measures
- Guardian System (for boundary safety)
- Motion Sickness Mitigation Techniques
8. Data Integration
- Database Systems (e.g., MySQL, MongoDB)
- Data Collection and Analysis Tools
- Integration with AI and Analytics Systems
9. Deployment and Support
- Internet Connectivity (for multiplayer features)
- Server Hosting (for online training sessions)
- Cloud Storage Solutions (e.g., AWS, Azure)
- VR Testing Devices and Software
- Quality Assurance (QA) Tools
Pros And Cons Of VR In Sports Training
VR in sports training presents an array of advantages but comes with hurdles such as cost, evolving technology, and the recognition that it complements rather than replaces traditional training methods. However, there are also a few disadvantages; let’s have a look at those:
1. Pros Of VR in Sports Training
1.1. Portable Training
VR transforms any space into a cutting-edge training arena, making it accessible in gyms, empty rooms, or remote locations. Athletes in various sports, from NASCAR to American football, can sharpen their skills without specialized equipment or venues.
1.2. Body-Safe Practice
VR enables athletes to engage with lifelike scenarios and potential hazards without risking physical harm. This is particularly valuable for contact sports like rugby and basketball, offering a way to maintain skills and positive sports psychology during injury recovery.
1.3. Ultra-Realistic Practice
VR’s hyper-realism lets athletes practice in ways unattainable in the real world. For instance, baseball batters can face hundreds of pitches in an hour without wearing out human pitchers. This lifelike setting enhances training, making it more natural and adaptable than traditional methods.
1.4. Data Collection
VR allows coaches to gather crucial metrics on timing, body movements, decision-making, and more. For example, baseball VR training provides insights into a player’s performance, aiding in skill enhancement and strategic decision-making. It also assists in tracking player engagement and workout effectiveness.
2. Cons Of VR In Sports Training
2.1. Costly Investment
One significant drawback lies in the cost factor. VR technology demands a substantial financial investment. The initial purchase of VR headsets, along with ongoing expenses such as system maintenance, software updates, and potential subscription fees, can strain the budgets of sports programs at various levels.
2.2. Evolving Technology
VR technology is continually advancing, necessitating regular updates and potential hardware replacements. Managing these technological shifts can be burdensome, particularly without dedicated IT support. Furthermore, extensive VR use may lead to adverse side effects, including headaches and nausea, underscoring the importance of maintaining balanced training schedules.
2.3. Simulation Limitations
While VR offers numerous advantages, it remains a simulation rather than a complete replacement for real-world gameplay. Critics argue that it should be viewed as a valuable tool for skill enhancement rather than a comprehensive substitute. VR undoubtedly contributes to physical and mental performance improvements, but it cannot fully replicate the dynamics of actual sporting events.
2.4. Technical Hurdles
Technical issues such as latencies and cybersickness can affect the overall user experience and potentially limit the effectiveness of VR-based training. These challenges can be frustrating for athletes striving for seamless and immersive training sessions.
2.5. Unsuitable For All Exercises
VR might not be suitable for all types of exercises or fitness techniques. Its effectiveness can vary depending on the specific sport or training regimen, and some athletes may find it less applicable to their needs.
2.6. Social Interaction Deficiency
Compared to real-world training, social interaction within VR environments can be less rewarding. This lack of genuine human interaction can impact athlete motivation and engagement levels, potentially leading to decreased enthusiasm during VR-based training.
6 Success Stories Of Athletes Using VR Training Regimen
1. Premier League Players
Numerous elite athletes from around the world, including those in the English Premier League, have embraced VR as a game-changing training tool. They leverage VR to meticulously analyze match footage within immersive environments. By recreating key moments from their games, these athletes gain valuable insights into their performance and identify areas for improvement. In one remarkable case, a Premier League goalkeeper incorporates VR into their warm-up routine, enhancing their reaction time and agility
2. Rehabilitation
VR has emerged as a vital component of the rehabilitation process for athletes recovering from injuries. The technology allows injured athletes to interact with their sport, such as soccer, within weeks post-surgery, including cases like ACL reconstruction. This innovative approach to recovery has yielded remarkable results, accelerating the return of athletes to peak physical condition
3. Karate Technique Training
A study compared VR with video training for the acquisition of a karate technique. Athletes were tasked with mastering the intricate Soto Uke technique while moving forward in Zenkutsu Dachi, all without the guidance of a trainer or partner. VR-based training was compared with traditional video-based training. The outcomes were striking, as all groups exhibited substantial improvement, with the VR-trained individuals showcasing significant progress after just four training sessions across various aspects of their technique.
4. Shooting Performance
Another compelling study focused on improving shooting performance through VR-based training. Athletes who underwent VRBI (Virtual Reality-Based Imagery) training exhibited remarkable advancements over a four-week period. Their improvements extended not only to their shot accuracy but also to their imagery skills, outperforming those in the VMBR + VM (Visualization, Motor Behavior Rehearsal, and Video Modeling) group.
5. Intel’s Training Program
Renowned tech giant Intel embarked on a transformative journey by incorporating VR into its training programs. The results were astounding, with an impressive 300% return on investment over five years. Trainees embraced VR-based training wholeheartedly, with a staggering 94% expressing their desire for more immersive virtual training experiences.
6. American Football
In American football, the adoption of virtual reality technology has witnessed a significant surge in popularity. According to a report authored by Jane Zorowitz for NBC Sports, several prominent NFL teams and collegiate programs have embraced this technology in their training regimens. Currently, a trio of NFL franchises, namely the Dallas Cowboys, New England Patriots, and San Francisco 49ers, along with an equal number of collegiate institutions—Auburn University, Vanderbilt University, and the University of Arkansas—are actively integrating VR technology into their training methodologies.
One of the standout advantages of this technology is its capacity to enable players to engage in practice sessions without the necessity of setting foot on an actual football field. This particular benefit carries significant weight, especially within the college sports landscape, where restrictions exist on the number of hours players can devote to practice and film study.
These compelling success stories underscore the profound impact of VR technology on the realm of sports training. It’s not merely about adopting innovative tools; it’s about leveraging these tools to create tangible differences in the way athletes prepare and ultimately excel in their respective sports. VR is a game-changer that continues to shape the future of athletic performance.
Best VR Sports Training Software In The Market
In VR sports training software, several top-notch platforms have emerged, each offering a unique blend of immersive experiences and performance-enhancing features. Let’s delve into the leading contenders:
1. STRIVR
STRIVR takes the lead with its impressive library of pre-designed VR training modules spanning a wide spectrum of sports, from baseball to soccer. Athletes can also customize their VR experiences, tailoring them to their specific training needs. What sets STRIVR apart is its unwavering commitment to realism. It harnesses real-world data and footage to create meticulously accurate simulations of sporting environments. Real-time feedback is another ace up STRIVR’s sleeve, enabling athletes to refine their techniques and amplify their performance. It’s no surprise that STRIVR boasts a clientele that includes prestigious professional sports teams like the NFL, NBA, and MLB, as well as esteemed educational and military institutions.
2. EON Sports
EON Sports, another frontrunner in the VR sports training arena, mirrors STRIVR’s comprehensive approach. With a diverse portfolio covering sports like football, tennis, and hockey, EON Sports empowers athletes with a selection of ready-made VR training modules while offering the flexibility to customize experiences. The platform’s hallmark lies in its captivating and immersive VR experiences. Leveraging high-quality graphics and sound, EON Sports creates an authentic training environment that engages athletes on a profound level. Like STRIVR, real-time feedback mechanisms guide athletes toward performance perfection. EON Sports is a favored choice among professional sports teams and esteemed academic institutions.
3. Virtua Tennis
For tennis enthusiasts seeking to up their game, Virtua Tennis delivers a compelling solution. This VR tennis game immerses players in a realistic training environment, complete with real-time physics and competitive gameplay. Athletes can refine their footwork, timing, and shot accuracy while practicing various strategies. Virtua Tennis supports multiple VR platforms, including Oculus Quest 2, HTC Vive, and Valve Index, making it accessible to a broad audience of tennis enthusiasts.
4. VR Golf
VR Golf steps onto the green with a realistic VR golf game. It offers golfers the opportunity to hone their swing mechanics and precision in a virtual setting. The game boasts real-time physics and provides players with the option to compete against others or the computer. With various courses and conditions to explore, VR Golf is an ideal platform for golfers looking to elevate their skills.
5. BoxVR
BoxVR enters the ring as a VR boxing game designed to enhance reflexes and hand-eye coordination. Offering a range of workouts, including cardio, strength training, and endurance training, BoxVR delivers a comprehensive full-body workout. Beyond physical fitness, it sharpens players’ coordination and reaction time.
6. Holofit
Holofit stands out as a versatile VR fitness platform encompassing workouts like yoga, Pilates, and strength training. It also offers a selection of sports simulations, including running, cycling, and rowing. Holofit redefines home workouts, providing users with a broad array of challenges and goals to stay motivated. It’s compatible with Oculus Quest 2, HTC Vive, and Valve Index.
In a dynamic VR sports training landscape, these platforms have carved their niches by delivering innovative technology, realism, and interactivity. The best choice for you depends on your sporting preferences and training objectives, but one thing is clear: VR sports training has arrived as a transformative force in athletic development.
The Future Of Sports Training
The future of sports training is poised for a remarkable transformation with the advent of Virtual Reality (VR). In the following discussion, we explore the potential long-term impacts and intriguing speculations regarding the evolution of VR in the realm of sports training:
1. Immersive Realism
As VR technology continues its relentless march forward, we anticipate a quantum leap in the realism of training environments. This evolution encompasses finer-tuned physics simulations, more stunning graphics, and increasingly immersive experiences.
2. Personalized Training
VR holds the promise of crafting highly personalized training regimens. Athletes may find themselves pitted against virtual opponents meticulously designed to mimic the unique playing style of their forthcoming real-world adversaries.
3. Injury Prevention
VR’s capabilities extend to injury prevention. Consider, for instance, soccer players practicing the art of heading the ball within the virtual realm, thereby reducing the risk of repeated head injuries during physical practice.
4. Mental Conditioning
The applications of VR in the psychological and sports training spheres are vast. Here, the control and manipulation of virtual scenarios grant athletes invaluable opportunities for mental resilience training, strategic planning, and honing their decision-making prowess.
5. Spectator Engagement
VR’s impact transcends athlete preparation; it also revolutionizes the spectator experience. Notably, events such as the EAFF E-1 Football Championship have introduced virtual reality viewing, ushering spectators into a more immersive and captivating world of sports.
6. Integration With Other Technologies
The future may witness VR seamlessly integrating with other cutting-edge technologies, including Artificial Intelligence (AI), biometrics, and data analytics. This integration promises a more holistic and data-driven approach to sports training.
7. Accessibility
As VR becomes increasingly affordable and accessible, it could soon emerge as a staple tool for sports training across all echelons, from grassroots youth leagues to seasoned professional teams.
In summation, the emergence of VR holds the potential to revolutionize sports training, offering a safe, engaging, and profoundly effective means of honing athletic skills. With the relentless march of technology, the role of VR in athlete preparation is on track to become even more integral, ushering in a new era of athletic excellence.
Conclusion
The future of sports training is undergoing an exciting and unprecedented transformation owing to the immersive potential of Virtual Reality (VR). It is imperative for athletes, coaches, and sports organizations to recognize the immense benefits that VR can bring to their training programs. VR offers many advantages, ranging from lifelike training environments to personalized skill development and injury prevention.
To fully capitalize on the potential of VR, there’s no better partner than Idea Usher. As a leading developer of VR projects, we are uniquely positioned to provide athletes and organizations with top-notch VR solutions. With our expertise, you can tap into the full spectrum of VR’s capabilities, ensuring that your training programs remain at the forefront of innovation.
As VR technology increasingly integrates into the sports training landscape, aligning with us guarantees access to safe, engaging, and highly effective training methods. The future of sports training is here, and we are your gateway to a more immersive and successful athletic journey. Don’t miss out on this transformative opportunity; collaborate with us as your trusted VR development partner today.
Work with Ex-MAANG developers to build next-gen apps schedule your consultation now
Contact Idea Usher at [email protected]
FAQ
1. How does VR benefit sports training?
VR confers a multitude of advantages for sports training. It affords athletes the privilege of immersive and authentic training settings. It advocates for secure and risk-mitigated training while proffering the capability for bespoke training regimens, instantaneous feedback, and the compilation of performance metrics for meticulous scrutiny.
2. What is the future of VR in sports training?
The outlook for VR in sports training appears auspicious. As technology continues its evolution, we anticipate more verisimilar training surroundings, the potential for tailor-made training regimes, harmonious integration with ancillary technologies like Artificial Intelligence and data analytics, and augmented accessibility as VR becomes increasingly economical.
3. What hardware and software is needed for VR sports training?
For VR sports training, obtaining crucial hardware components is imperative, including a VR headset and a robust computational system capable of proficiently running VR software. The selection of hardware profoundly shapes the user’s VR experience. In parallel, the development of VR sports training systems predominantly relies on game engines like Unity or Unreal Engine. These platforms empower developers with the essential tools for constructing three-dimensional environments and implementing gaming mechanics.
4. How is interactivity implemented in a VR sports training system?
Interactivity in a VR system transpires by coding objects within the environment to respond to the user’s actions, whether it involves swinging a tennis racket, hurling a football, or locomotion.
5. How is feedback provided in a VR sports training system?
The provision of real-time feedback to the user concerning their performance can be realized through a multifaceted system that employs visual cues, auditory responses, or haptic feedback.




















