The Internet of Things has enabled firms to incorporate intelligent systems into their functions. As a result, entrepreneurs wish to know more about real-world IoT examples and how they can scale their businesses.
IoT has changed the economic and technological landscape by integrating intelligent systems into day-to-day processes. It has shown time and again that its capability cannot be underestimated. From smart homes to smart cities to smart businesses, it has facilitated growth in every sector.
This blog discusses real-world IoT examples and their use cases.
What is IoT?
Before delving into real-world IoT examples, it is essential to understand the term “IoT”. IoT, or the Internet of Things, is a network of interconnected devices sharing information via the internet. With the help of low-cost computing, the cloud, big data, analytics, and mobile technologies, physical objects have become capable of sharing information with minimal human intervention. Everyday objects are embedded with chips, making them intelligent to transmit data and communicate with each other.
Overview of the significance of IoT in 2024
In 2023, the impact of the Internet of Things (IoT) is nothing short of transformative, touching upon diverse aspects of our daily existence, such as commerce, travel, healthcare, and beyond. This comprehensive overview delves into key dimensions, shedding light on the intricacies that define IoT’s profound influence in the current year.
1. Explosion of Data and Devices
The year 2019 witnessed approximately 3.6 billion actively connected devices, a number that has skyrocketed with the advent of 5G and the widespread adoption of edge computing. This surge not only amplifies the volume of interconnected devices but also intensifies the flow of data traffic, ushering in an era of extensive connectivity and information exchange.
2. AI and IoT Working Hand in Hand
At the forefront of IoT’s evolution stands the pivotal role of Artificial Intelligence (AI). The close relationship between AI and IoT is extracting meaningful insights from the massive datasets amassed by IoT devices, thereby enhancing their value for businesses. AI’s contributions span diverse realms, encompassing data preparation, discovery, real-time analytics, and predictive capabilities.
3. Voice User Interface (VUI) as a Game-Changer
Smart devices are advancing with the rise of Voice User Interfaces (VUI). Digital assistant devices like Alexa, Siri, and Google Assistant emerge as central hubs, steering the course for the next phase of intelligent devices. The integration of voice commands for setup, configuration changes, and result retrieval establishes a seamless and user-friendly interaction model.
4. Appeal for Investments
The undeniable impact of IoT acts as a magnet for venture capitalists, propelling investments into projects spanning hardware, software, and services. Projections indicate that the expansion of the IoT Market indicates a surge from USD 1.02 trillion in 2023 to USD 2.06 trillion by 2028, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.12% over the forecast period from 2023 to 2028, underscoring the financial community’s recognition of IoT’s potential as a transformative force.
5. Exponential Growth in IoT Devices
A numerical indication of the widespread impact of IoT is the increasing number of connected devices. According to Statista, the current count has reached an impressive 15.14 billion connected IoT devices as of 2023, illustrating the substantial growth of interconnected technologies.
What are the Components of IoT?
Here are the fundamental components that constitute the Internet of Things (IoT):
1. Sensor and Devices
Sensors and devices are the basis of IoT. These tools systematically collect data from the surrounding environment. They can be simple, like temperature sensors, or more complex, like cameras and GPS devices. These devices act as data collectors, diligently capturing information from their surroundings.
2. Connectivity
Following data collection, the transition to the cloud requires a reliable Connectivity framework. This stage involves various methods for transferring data, including cellular networks, satellites, WiFi, Bluetooth, or direct internet connection via Ethernet. Each method serves as a channel for seamless communication.
3. Data Processing
The cloud becomes the central hub for intricate Data Processing. Here, the software conducts analyses, from basic checks like validating temperature thresholds to more complex tasks like using computer vision for object identification. This phase transforms raw data into meaningful insights.
4. User Interface
The ultimate distribution of refined information occurs through the User Interface. This could be alerted through emails, texts, or notifications, as well as visual dashboards. Users, armed with real-time data, may also have interfaces allowing them to proactively interact with the system.
What are the Benefits and Challenges of IoT?
The domain of the Internet of Things (IoT) constitutes a dynamic landscape, presenting an array of advantages while concurrently introducing intricate challenges that warrant meticulous consideration. Delving into the complexities of this transformative technology reveals detailed benefits and obstacles with which businesses contend.
1. Advantages of IoT
1.1. Enhanced Operational Efficiency through Automation
IoT’s capacity for automating and streamlining processes emerges as a key advantage. Consider sensors meticulously monitoring machinery, proactively identifying issues before they escalate. This not only mitigates maintenance costs but also contributes to heightened operational uptime.
Example: Manufacturing facilities employ IoT sensors to optimize production, curb downtime, and enhance overall operational efficiency.
1.2. Informed Decision-Making with Data Analytics
The substantial data generated by IoT devices serves as a valuable resource for informed decision-making. By closely examining this data, enterprises gain profound insights into customer behavior, market trends, and operational details. This knowledge empowers strategic decisions related to product development, resource allocation, and market positioning.
Example: Retailers leveraging IoT data analytics to discern consumer preferences, tailoring marketing strategies and inventory management accordingly.
1.3. Cost Reduction through Automated Processes
A notable benefit of IoT is its ability to reduce costs by automating manual and repetitive tasks. By decreasing the need for human involvement in everyday operations, businesses can streamline processes, achieve cost efficiencies, and enhance their overall financial performance.
Example: Smart offices employing IoT-driven automation for energy management, optimizing lighting and climate control to reduce utility expenses.
2. Challenges of IoT
2.1. Ensuring Optimal Performance
Achieving top-notch performance for IoT devices presents a significant challenge. Ensuring these devices operate seamlessly and at high performance, especially in varied environments, demands ongoing innovation and robust technological solutions.
Example: Wearable devices face challenges in maintaining consistent performance across various user activities and environments.
2.2. Prioritizing Security and Privacy Measures
Ensuring the security of the vast amounts of data collected and exchanged by IoT devices is a top priority. The potential vulnerabilities in IoT networks require strong security measures to prevent cyber threats and safeguard user privacy.
Example: IoT-enabled healthcare devices requiring stringent security protocols to safeguard sensitive patient data.
2.3. Managing the Scale-Up Complexity
As the Internet of Things (IoT) network grows with an increasing number of devices, handling and integrating this expanding network becomes a growing challenge. Achieving smooth communication and compatibility among diverse devices requires advanced infrastructure and strategic planning.
Example: Smart cities grappling with the integration of numerous IoT devices for traffic management, public safety, and utilities.
2.4. Addressing Interoperability Challenges
Connecting different IoT devices, each using different protocols and standards, poses a significant challenge. Achieving universal interoperability requires collaborative efforts to establish cohesive communication channels.
Example: Home automation systems are struggling to synchronize IoT devices from different manufacturers, hindering a seamless user experience.
2.5. Navigating the Complexity of Big IoT Data
Dealing with the large amount of data produced by IoT devices brings the challenge of efficient management. Businesses face obstacles in fully harnessing the potential of these extensive datasets, from storing the data to conducting real-time analysis.
Example: Industrial IoT setups wrestling with processing and analyzing extensive data streams from sensors on manufacturing floors.
2.6. Capital Investment Dilemma
The adoption of IoT solutions involves a substantial financial commitment, acting as a potential barrier for businesses, particularly smaller enterprises. The initial investment required for infrastructure, devices, and training can be a critical factor in the decision-making process.
Example: Small businesses are hesitant to embrace IoT due to concerns about the upfront costs and uncertainties surrounding the return on investment.
Top 10 real-world IoT examples
Today IoT applications in gyms or hospitality have gained traction. However, there are countless use cases for this smart technology.
The following list discusses the top 10 real-world IoT examples:
1. Smart Homes
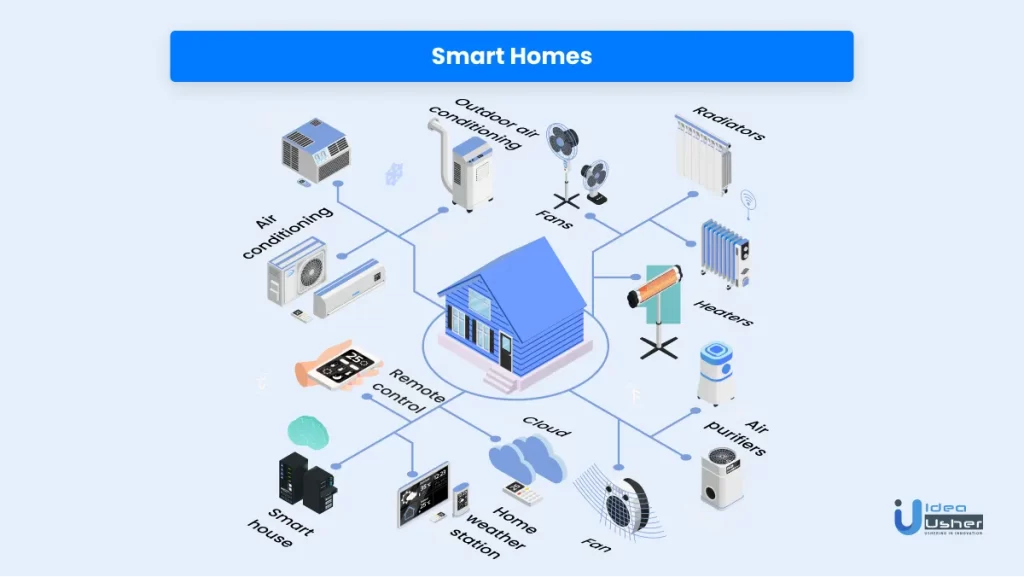
Simply put, a smart home is a home having interconnected devices. The devices are ‘smart’ and can communicate using the internet. They can monitor energy usage and provide safety, security, entertainment, and other daily activities.
The sensors fitted in these devices detect the changes in the environment or the instructions given via remote signals and help the devices function accordingly. These smart home devices can be controlled using a remote control or an IoT app installed on the user’s smartphone.
A smart home is equipped with a range of IoT devices. Some examples include:
a. Smart TV
A smart TV connects to the internet and provides additional services like on-demand video and music streaming. It also has voice or gesture recognition features.
b. Smart lighting
You can remotely control smart lights like Hue from Philips via remote control or a smartphone. Smart lights also detect human presence in the room and adjust the lighting accordingly.
c. Smart thermostats
Smart thermostats like Nest allow users to schedule, monitor, and remotely control room temperature.
d. Smart locks
Smart locks grant or deny entry to visitors. They also detect when the house owner is nearby and unlock the door for them.
2. Smart Cities

A smart city uses Information and Communication Technology (ICT) to improve the quality of life of its citizens. It allows remote monitoring and managing of devices to generate valuable insights. It uses this information to improve public utilities, infrastructure, etc.
The UN estimates that the global urban population will reach 6.7 billion by 2050. As more and more people move towards cities, it becomes essential to look for ways to manage the cities better. Smart cities do precisely that.
A smart city incorporates IoT in the following use cases:
a. Smart transportation
The public transport system is connected and shares real-time data in a smart city. Public vehicles like buses share their location, and the bus stops update this data. This information lets the passengers get an accurate idea of the waiting time.
b. Smart waste management
The sensors fitted in the garbage cans detect the waste in the can. After reaching a certain threshold, the sensor transmits the signal to the waste management authority. This authority sends the notification to the waste collection truck driver. The driver can then go and empty the garbage can. Thus, this leads to a better waste management system.
c. Smart lighting
The street lights are interconnected and fitted with sensors that detect the luminance in the surrounding, movement of people and vehicles on the road, etc. The sensors then control the street lights by dimming or brightening them.
d. Air quality monitoring
Smart cities have air quality monitoring devices that detect pollutants present in the air. They display this information on a screen to inform the users about the pollution level in their surroundings. Paris, London, Copenhagen, New York, and San Francisco have already become smart cities.
3. Traffic management
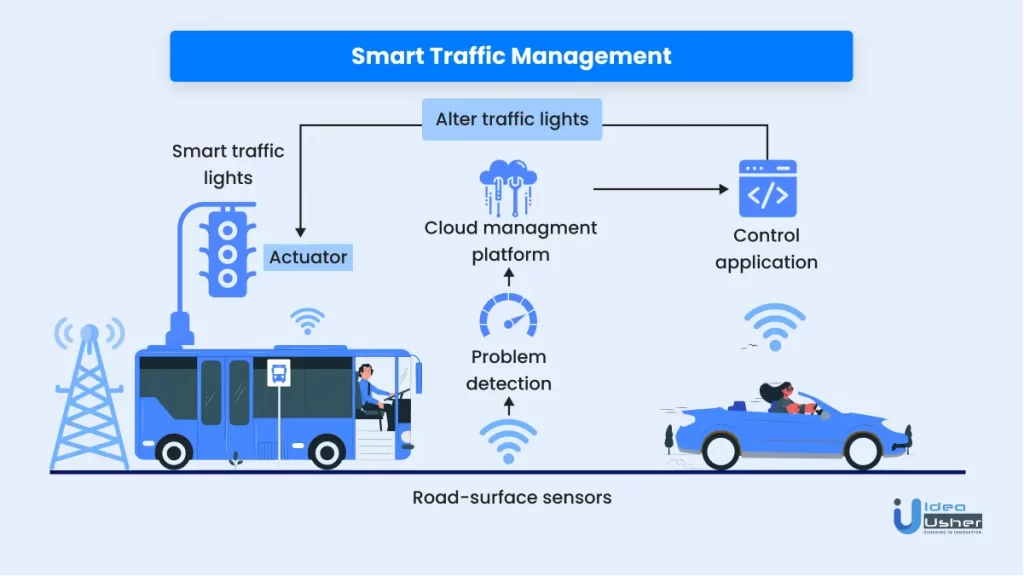
Smart cities are very closely linked with smart traffic management. A city cannot function smoothly without a proper traffic control system. With the number of road vehicles increasing, better and effective traffic control becomes essential.
Better traffic control leads to smoother traffic flow and fewer idle vehicles stuck in traffic jams. It eventually leads to shorter run times, efficient use of fuel, and lesser pollution.
IoT is used in traffic management in the following ways:
a. Traffic Lights
The traffic signals are equipped with sensors that detect the heat and moisture in the environment and the visibility index. These sensors transmit this information to the traffic lights and adjust their brightness based on the weather and road visibility.
b. Road accident prevention
IoT helps prevent road accidents by informing the drivers about the road conditions in advance. Thus, the driver moves cautiously, reducing the possibility of a road accident. Even if an accident occurs, the information quickly reaches the traffic control authorities and the nearby hospital leading to a quick resolution of the issue.
c. Better parking
IoT sensors in the parking lots inform the drivers about the unoccupied spaces so they can directly proceed towards those spaces. This system leads to lesser congestion in the parking lots and quicker parking of vehicles.
4. Smart cars
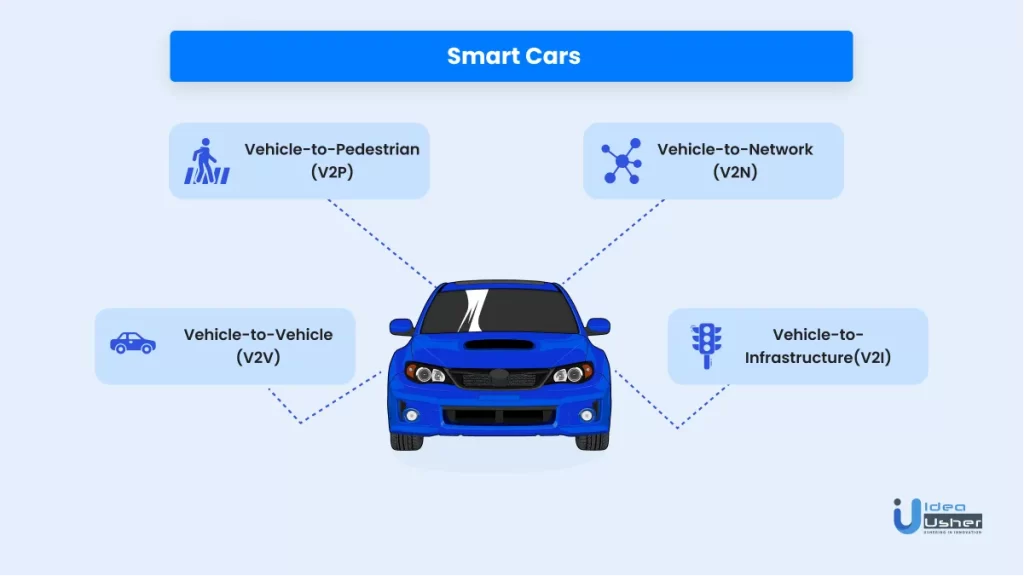
For intelligent traffic management to function, we also need smart cars. A smart car has IoT features to connect to other vehicles and traffic systems.
They work on an IoT network called CV2X (Cellular Vehicle to Everything). CV2X can take any of the following forms:
a. Vehicle to Vehicle (V2V)
V2V connection enables the vehicles to interconnect. They share data like speed, location, and dynamics. This connection prevents road accidents and allows emergency vehicles to navigate easily.
b. Vehicle to Infrastructure (V2I)
V2I connects the vehicles to the road infrastructure. This connection lets drivers get data about road conditions, traffic signals, toll booths, etc. Thus, the roads have smoother traffic flow, and the drivers do not have to wait in long queues at toll booths, parking lots, etc.
c. Vehicle to Pedestrians (V2P)
This connection informs the pedestrians about any vehicle coming their way. Similarly, it alerts the drivers about any pedestrians that might come their way, thus avoiding a collision.
d. Vehicle to Network (V2N)
The cars connect to the centralized cloud network and get updates about weather conditions, traffic situations, etc. The drivers also use V2N to use GPS or give voice commands for music while driving.
5. Industrial IoT (IIoT)
Industrial IoT refers to the implementation of IoT in industrial settings. IIoT enables industries to improve their efficiency and operational reliability by focusing on machine-to-machine communication, big data, and machine learning.
Businesses use IIoT to monitor and control processes, equipment, and infrastructure. This monitoring includes checking the activity or status of machines remotely. IIoT is also used to monitor the environmental conditions inside a factory.
IIoT has the following use cases:
a. Predictive quality
IoT extracts insightful data about product quality from industrial units. This data is analyzed and used to improve product quality for customer satisfaction.
b. Asset condition monitoring
IIoT provides information about the condition of the industrial equipment, like temperature, vibration, and error codes. This data helps determine the asset performance.
c. Predictive maintenance
IoT helps detect faults and breakdowns in the machinery before they impact production. It increases equipment lifespan, worker safety, and supply chain optimization.
6. Agricultural IoT
Smart agriculture refers to the integration of IoT in farming. By implementing agricultural IoT, farmers make informed decisions and improve almost every aspect of their work, like livestock husbandry and crop farming.
Intelligent farming helps the farmers decide the best time to harvest plants, creating fertilizer profiles based on the soil chemistry and detecting soil nutrients and moisture levels.
IoT is used in agriculture for the following purposes:
a. Precision agriculture
Precision farming refers to using information generated by sensors to make quick and precise decisions. This technique includes many applications like livestock monitoring, vehicle tracking, irrigation management, field observation, and more.
b. Weather conditions monitoring
IoT sensors are placed across the field to detect weather conditions. These sensors provide real-time weather data like humidity, rainfall, temperature, etc. The farmers use this data to choose suitable crops for the weather.
c. Greenhouse automation
Sensors placed inside the greenhouse provide real-time information about the conditions of the greenhouse, like temperature, lighting, humidity, etc. Additionally, the weather station is connected to the greenhouse to control the environmental conditions directly. Thus, it eliminates the need for human intervention.
d. Agricultural drones
One of the most significant developments in the agricultural sector is the introduction of agricultural drones. These drones assess crop health, monitoring, planting, spraying, and field analysis.
7. Construction management

Construction is a slowly evolving sector known to run overtime and over budget often. Using IoT in this sector helps in project progress tracking. IoT also helps in optimal resource utilization and expense planning.
Additionally, IoT syncs the devices, equipment, materials, and personnel to a central server that monitors their activity in real-time. It ensures that they adhere to the policies while also maintaining their safety.
IoT in the construction industry has the following use cases:
a. Site monitoring
IoT helps construction managers have real-time updates about the employees and machines working on the site.
b. Machine Control
The sensors installed on the machines instruct them to function in a certain way with minimal human intervention.
c. Construction safety
You can enhance safety at the construction site by implementing IoT and other technologies like AI.
d. Fleet management
IoT fleet management solutions optimize transit routes and maintain vehicles.
e. Project management
IoT solutions help construction project managers keep the project on track regarding time and cost.
8. Environmental monitoring
Environmental monitoring is one of the most important applications of IoT. IoT sensors detect the level of pollutants present in the air and water. This information is used to maintain cleanliness and promote sustainability.
Environmental monitoring also includes indoor environments and closed spaces. In such areas, the sensors send the information to the cloud, informing the authorities about the triggers and concerns. The authorities thus take appropriate action to improve the environmental condition.
Environmental monitoring comprises air quality monitoring, water quality monitoring, toxic gas detection, smoke detection, etc.
You can use IoT to monitor the environment to:
- Analyze what is happening in an area over a time period
- Identify issues with habitat and resources that need attention
- Create a baseline against which you can track future behavior
9. Smart energy management
Energy management using IoT focuses on energy conservation by connecting appliances to an internet-enabled hub that monitors and controls energy flow.
IoT energy management provides many benefits like reduced energy spending, minimized carbon emission, compliance with regulations, optimized asset maintenance, process automation, etc.
Energy management systems uses IoT in the following areas:
a. Smart meters
Smart meters provide real-time energy availability and consumption data. Utility providers use this data to distribute energy to maximize benefits and reduce outages. This information also allows customers to be more energy-conscious and modify energy usage.
b. Smart grids
IoT-enabled smart grids enable energy suppliers to meet the growing energy demands. They use this technology to identify load distribution and improve reliability. Smart grids give energy suppliers greater control over the power infrastructure and resources.
c. Oil and gas
The oil and gas industry uses intelligent energy management systems to optimize production and ensure safe extraction and delivery. The companies get better insights into infrastructure health to detect and fix problems at the earliest.
10. IoT in Healthcare (IoMT)
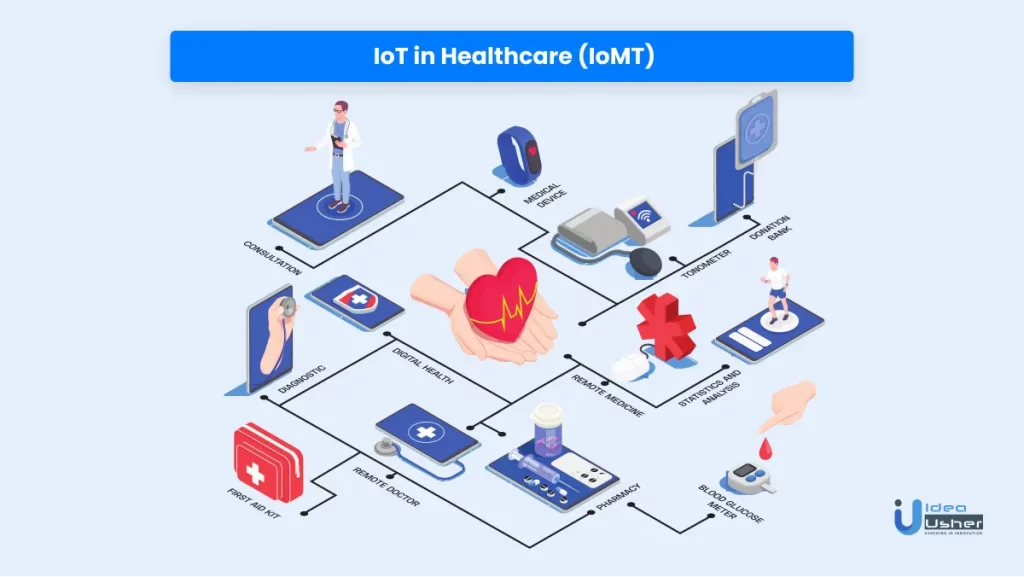
The healthcare sector has applied IoT very successfully. Also known as the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT), this technology enables medical devices and machines to collect, analyze and send data using stable internet connectivity.
IoMT provides various benefits like accessibility, cost cuts, quick implementation, improved efficiency, remote care, mHealth (care of patients’ health using mobile apps), etc. It is applied in hospitals, at home, and on the body. It has significantly improved the patient experience as they gain convenience, engagement, and reduced medical visits.
IoMT has the following use cases:
a. ER medical treatment
IoMT reduces the Emergency Room (ER) wait times. The sensors capture real-time hospital bed availability to speed up the admission process. They also track the hospital’s blood supply and other kinds of biomaterials.
b. Insurance procedures
Intelligent devices like wearables, biosensors, and mobile apps record the patient’s data and suggest which processes are ideal for each patient. Insurance firms use this data to process the claims better by reducing unnecessary exploratory operations.
c. Pharmacy inspection
IoT helps in improving pharmaceutical inventory management. The RFID tags and barcodes provide real-time insight into the flow of inventory.
Future Trends and Developments in IoT
The future of the Internet of Things (IoT) shows great potential to transform various industries. Here are some of the new trends in IoT that offer a glimpse into the exciting possibilities that await us:
1. Digital Twins
Digital twin technology is swiftly reshaping diverse industries, from engineering to healthcare and beyond. These digital replicas of physical assets enable optimized performance monitoring and control, fostering unprecedented efficiency.
In healthcare, digital twins can predict the outcomes of new medications and treatments, providing a revolutionary approach to precision medicine. Pharmaceutical companies leverage this technology for simulations that enhance drug development.
2. AI’s Integration
The increased number of IoT devices has ushered in an era of data abundance. This surplus of information empowers businesses to make data-driven decisions. By integrating artificial intelligence into IoT systems, businesses can automate operations, elevating the quality of their products and services.
Companies now have comprehensive insights into personnel, productivity, and product/service quality. This wealth of data serves as the backbone for crafting advanced AI models that enhance operational efficiency.
3. Sensor Technology
The continual enhancement of innovative sensor technologies is anticipated to substantially boost the capabilities of IoT devices. This ongoing development holds the potential to unlock advanced functionalities, expanding the horizons of what IoT devices can accomplish
4. 5G
The advent of 5G networks is a game-changer for IoT. The increased speed and efficiency of data transfer between devices lay the groundwork for seamless connectivity, unlocking new possibilities in real-time communication and interaction.
5. Automotive Industry
IoT is not just about self-driving cars but extends to revolutionizing vehicle maintenance. Connected cars communicate with manufacturers, enabling proactive maintenance and ensuring vehicles operate at optimal efficiency. The automotive industry is at the forefront of leveraging IoT for a holistic transformation.
6. Chip-Level Innovation
Innovations at the chip level are propelling the performance and capabilities of IoT devices. These advancements translate into more efficient and powerful devices across various sectors, from smart gadgets to industrial machinery.
7. Healthcare Operations
The influence of IoT on healthcare goes beyond monitoring. It optimizes healthcare operations, leading to more patient-centric care. From remote patient monitoring to the seamless integration of health data, IoT is streamlining processes for improved healthcare outcomes.
8. Security
As the Internet of Things (IoT) network grows, prioritizing the security of devices becomes crucial. With a notable increase in connected devices, it is essential to establish strong security measures to protect against potential threats and breaches.
9. User-Centric Interfaces
The future of IoT centers on reshaping user experiences. Emerging interfaces and interaction patterns are providing users with a more intuitive and seamless connection to their devices. From utilizing voice commands to incorporating gesture controls, the manner in which we engage with IoT is undergoing a transformative evolution.
10. Connectivity Technologies
The development of new connectivity technologies is redefining how IoT devices communicate. From low-power, wide-area networks to mesh networks, these technologies enhance the reliability and reach of IoT connections.
11. Manufacturing Industries
In manufacturing, IoT is not just about automation; it’s about optimizing production processes and revolutionizing supply chain management. Connected devices on the factory floor enhance efficiency, reduce downtime, and contribute to more agile and responsive manufacturing.
Wrapping up
The internet of things is a concept that is gaining a lot of attention today. With the world becoming more technologically advanced, businesses are ready to make the most of any innovation that helps them grow. IoT is one of them.
The global IoT market is expected to grow from USD 478.36 billion in 2022 to USD 2,465.26 billion by 2029. This growth proves that IoT is worth investing in. Businesses can take inspiration from the real-world IoT examples mentioned above and use IoT to their advantage.
To integrate IoT into your business, you need expert guidance and consultation. Idea Usher has been in the business of providing IoT services for many years. With an international presence, we aim to serve clients across countries with cutting-edge digital solutions.
Get in touch with us and see your business boom with IoT.
Frequently asked questions
Here are some interesting FAQs about real-world IoT examples.
Q. How do IoT devices communicate with each other?
A. IoT devices are connected through an IP network to the internet. They connect to the internet via ethernet or Bluetooth.
Q. Which technologies does Idea Usher use to provide IoT services?
A. Idea Usher’s experts have experience developing IoT apps for Android and iOS platforms. They use channels like WiFi, WiFi Direct, Bluetooth Low Energy, Bluetooth 2.0, iBeacon, Zigbee, and NFC.
Q. What is the future of IoT?
A. The future of IoT looks promising. The industrial internet will advance through increased network agility, integrated AI, and the capacity to deploy, automate, and secure diverse use cases.











Mayank Sharma