- What Is Robotic Process Automation?
- Business Benefits Of Implementing RPA Solutions
- How to Choose the Right RPA Use Case?
- RPA Use Cases Acorss Industries
- Top RPA Trends To Look Out For In 2024
- How Businesses Across Industries Can Implement RPA Solutions?
- Conclusion
- How Idea Usher Can Help With RPA Implementation?
FAQ

Businesses across industries are increasingly recognizing the transformative potential of robotic process automation (RPA) in enhancing workplace productivity and efficiency. As organizations seek innovative solutions to streamline operations and reduce costs, RPA emerges as a powerful tool capable of automating repetitive, rule-based digital tasks.
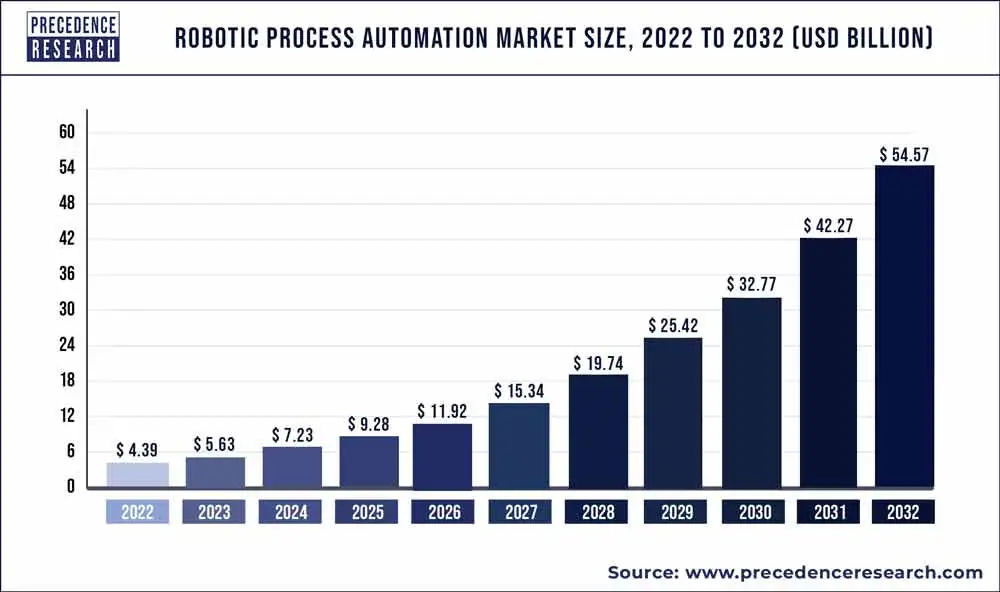
Source: PrecedenceResearch
As businesses continue to navigate through the complexities of digital transformation, the demand for RPA solutions is witnessing a remarkable surge, fueled by the need to automate repetitive tasks, optimize workflows, and enhance overall productivity.
One encouraging feature of RPA is its ability to help automate high-volume, repetitive, rule-based digital processes in a variety of sectors and roles. Any organization, regardless of sector or role, may use robotic process automation (RPA) to increase productivity in manual tasks.
This post will highlight popular RPA use cases by sector and function, providing insights into how RPA may considerably assist enterprises.
- What Is Robotic Process Automation?
- Business Benefits Of Implementing RPA Solutions
- How to Choose the Right RPA Use Case?
- RPA Use Cases Acorss Industries
- Top RPA Trends To Look Out For In 2024
- How Businesses Across Industries Can Implement RPA Solutions?
- Conclusion
- How Idea Usher Can Help With RPA Implementation?
FAQ
What Is Robotic Process Automation?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a cutting-edge technology designed to streamline and automate repetitive tasks within digital systems and software. By leveraging software robots, RPA simplifies the creation, deployment, and management of automated processes that mimic human actions. These virtual assistants are adept at tasks such as interpreting on-screen information, executing keystrokes accurately, navigating through various systems, extracting and processing data, and executing a myriad of predefined actions. Unlike their human counterparts, software robots operate at remarkable speeds and maintain consistency in their performance without the need for breaks or pauses, making them invaluable assets for optimizing efficiency in various industries.
At its core, RPA empowers organizations to automate mundane and time-consuming tasks, freeing up human resources to focus on more strategic and value-added activities. By automating routine processes, businesses can enhance productivity, reduce errors, and achieve significant cost savings. Furthermore, RPA implementation offers scalability, allowing organizations to adapt to fluctuating workloads and rapidly evolving business requirements with ease. Whether it’s data entry, invoice processing, customer service interactions, or any other repetitive task, RPA enables seamless integration with existing systems and workflows, without the need for extensive programming knowledge.
One of the key advantages of RPA lies in its ability to interact with a wide range of applications and systems, including legacy systems, web-based interfaces, and desktop applications. This versatility ensures that RPA solutions can be deployed across diverse environments, spanning multiple departments and functions within an organization. Additionally, RPA platforms often incorporate advanced capabilities such as machine learning and natural language processing, enabling software robots to adapt to dynamic scenarios and handle complex tasks with agility and precision.
Moreover, RPA promotes compliance and accuracy by enforcing standardized processes and reducing the risk of human error. By automating rule-based activities, organizations can ensure regulatory compliance and adherence to quality standards, thereby mitigating the potential for costly errors and penalties. Furthermore, RPA facilitates real-time monitoring and analytics, providing valuable insights into process performance and identifying opportunities for further optimization and refinement.
Robotic process automation revolutionizes the way businesses operate by offering a scalable, efficient, and reliable solution for automating repetitive tasks. By harnessing the power of software robots, organizations can streamline operations, drive innovation, and unlock new levels of productivity, ultimately gaining a competitive edge in today’s fast-paced digital landscape.
Business Benefits Of Implementing RPA Solutions
Robotic process automation enhances organizational profitability, flexibility, and responsiveness through streamlined workflows. It boosts employee satisfaction, engagement, and productivity by eliminating mundane tasks from their daily routines.
1. Accelerated Transformation
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) stands as a critical component in accelerating digital transformation initiatives, with 63% of global executives acknowledging its significance in this realm. By automating repetitive tasks and streamlining workflows, RPA enables organizations to adapt more quickly to evolving market trends and customer demands. This agility in transformation not only enhances competitiveness but also drives innovation, allowing businesses to stay ahead in today’s fast-paced digital landscape.
2. Substantial Cost Efficiency
RPA drives rapid and substantial improvements to various business metrics across industries
worldwide, resulting in significant cost savings, as evidenced by insights from IT Central Station regarding key drivers of time to value in RPA. These cost savings extend beyond operational efficiencies to encompass reductions in error rates, lower labor costs, and optimized resource allocation. By freeing up financial resources, organizations can reinvest in strategic initiatives, fueling further growth and innovation.
3. Enhanced Operational Flexibility
RPA enables organizations to enhance operational resilience by swiftly scaling up to match workload peaks and effectively responding to sudden spikes in demand, exemplified by its role in scaling COVID testing efforts. This adaptability ensures that businesses can maintain continuity and meet customer expectations even during periods of volatility or uncertainty. Additionally, by automating routine tasks, RPA reduces reliance on manual intervention, minimizing the risk of errors and downtime.
4. Higher Accuracy
RPA significantly improves accuracy in business processes, with 57% acknowledging its effectiveness in reducing manual errors, as per findings from Forrester regarding the impact of RPA on employee experience. By eliminating the potential for human error, RPA enhances data quality, compliance, and decision-making accuracy. This increased accuracy not only improves operational efficiency but also enhances customer satisfaction and trust, ultimately driving business growth and reputation.
5. Strengthened Regulatory Compliance
RPA plays a crucial role in enhancing compliance standards, with 92% of stakeholders affirming that it meets or exceeds expectations in this domain, as highlighted by insights from Deloitte’s 3rd Annual RPA Survey. By automating rule-based tasks and enforcing standardized processes, RPA ensures consistency and adherence to regulatory requirements. This proactive approach to compliance minimizes the risk of penalties, litigation, and reputational damage, safeguarding the long-term viability of the organization.
6. Amplified Workforce Productivity
Automation through RPA boosts productivity, with 68% of global workers expressing confidence that it will make them more productive, according to a UiPath survey of 4,500 global workers. By offloading repetitive and mundane tasks to software robots, employees can focus their time and energy on value-added activities that require human creativity and expertise. This not only enhances individual productivity but also fosters a culture of innovation and continuous improvement within the organization.
7. Optimized Utilization of Human Capital
Executives recognize that RPA enables employees to focus on more strategic tasks, with 60% agreeing that it empowers personnel to engage in high-value work, according to Forrester’s analysis of RPA’s impact on employee experience. By automating routine tasks, RPA frees up employees to pursue opportunities for professional development, collaboration, and innovation. This empowerment not only enhances job satisfaction and retention but also enables organizations to tap into the full potential of their human capital.
8. Enhanced Employee Satisfaction
RPA contributes to a positive work environment by increasing employee engagement, as highlighted by 57% of executives in Forrester’s examination of RPA’s impact on employee experience. By automating tedious and repetitive tasks, RPA reduces employee burnout and frustration, allowing them to focus on meaningful work that aligns with their skills and interests. This sense of fulfillment and purpose fosters a culture of positivity, teamwork, and continuous learning, driving organizational success and employee well-being.
How to Choose the Right RPA Use Case?
Use cases with process repeatability, rules-based judgments, duplicate data entry, common data format, and high frequency activities should be prioritized for automation. Such criteria prioritize which processes should be at the forefront of consideration for automation implementation.
1. Consistency in Execution
Ensuring the stability and predictability of the process is paramount for successful automation implementation. Processes earmarked for automation should demonstrate a steady pattern of execution, devoid of imminent modifications. This stability enables software robots to navigate through the workflow seamlessly, enhancing efficiency and reliability. A clear indication of a viable candidate is when users consistently interact with the same system interfaces, performing repetitive actions on standardized fields. While the data within these processes may vary, the underlying steps remain consistent, facilitating straightforward automation.
2. Decision-Making Based on Rules
The cornerstone of automation lies in processes governed by well-defined rules rather than intricate human judgment. These rules should be firmly established and resistant to frequent alterations, ensuring a stable foundation for automation. By adhering to predetermined criteria or geographical parameters, software robots can efficiently execute tasks with precision and consistency. Whether it’s routing inquiries or processing transactions, automation thrives on the clarity and stability of these decision-making frameworks.
3. Duplicate Data Entry
In the pursuit of system integration and efficiency, eliminating redundant data entry tasks is a perpetual goal for organizations. Automation serves as a potent remedy, bridging the gap between disparate systems and streamlining data entry workflows. By seamlessly navigating through various platforms and documents, software robots alleviate the burden of repetitive data input, allowing human resources to focus on more value-added activities. The telltale signs of a ripe automation opportunity often manifest in scenarios where data must be manually transferred or updated across multiple systems, highlighting the potential for significant efficiency gains.
4. Data Handling Capabilities
As automation technology evolves, so too does its ability to interpret and process diverse data formats. Beyond traditional digital data, modern RPA solutions excel at extracting insights from a plethora of sources, including emails, scanned documents, and web pages. While structured data remains the preferred terrain for automation, recent advancements in AI-driven capabilities enable robots to decipher contextual information with remarkable accuracy. This expanded scope empowers organizations to automate a broader range of tasks, even in scenarios where data may exhibit variability or anomalies.
5. Frequency of Task Execution
The frequency of a process’s occurrence serves as a pivotal determinant in its suitability for automation. Whether it’s a high-volume task executed hundreds of times daily or a routine procedure performed sporadically by numerous individuals, the cumulative time savings afforded by automation can be substantial. By identifying and prioritizing processes with high frequency and consistency, organizations can unlock significant efficiency gains across various business functions. This synergy between repeatability, consistency, and frequency underscores the transformative potential of automation in enhancing operational agility and competitiveness.
RPA Use Cases Acorss Industries
A. RPA Use Cases in Financial Services Sector
The financial sector is riddled with digital processes that can be optimized and automated, making it a natural fit for Robotic Process Automation (RPA). RPA technology offers numerous benefits for financial institutions, including increased efficiency, accuracy, and compliance across various functions. Below are some of the key areas where RPA is applied in the financial services sector:
1. Automating Reporting Tasks
RPA streamlines reporting tasks such as reconciliations, monthly closings, management reports, and mortgage processing. By automating these repetitive tasks, RPA frees up valuable human resources for more strategic endeavors and ensures error-free processes. Additionally, RPA can generate reports in real-time, providing stakeholders with timely and accurate information for decision-making purposes.
2. Accounts Payable and Receivable Processes
RPA enhances accounts payable and accounts receivable processes by automating invoice processing, payment reconciliation, and vendor management. This automation reduces manual errors, accelerates transaction processing, and improves cash flow management. Furthermore, RPA can integrate with existing financial systems, streamlining end-to-end processes and enhancing operational efficiency.
3. Fraud Detection and Payment Processing
RPA plays a crucial role in fraud detection, payment processing, and credit checks by analyzing large volumes of data in real-time. By automating these processes, RPA can identify suspicious transactions, patterns, and anomalies more efficiently than manual methods. Moreover, RPA can facilitate secure and seamless payment processing, reducing transaction times and enhancing customer satisfaction.
4. Loan Application Process
RPA streamlines the loan application process by automating data entry, verification, and approval workflows. This automation reduces processing times, minimizes errors, and improves the overall customer experience. Additionally, RPA can integrate with customer relationship management (CRM) systems to provide personalized loan offerings and recommendations based on individual financial profiles.
5. Wealth Management
In wealth management, RPA ensures error-free processes by automating tasks such as quality control management, compliance practices adherence, and investor data migration. This automation enhances data processing efficiency and accuracy, enabling wealth management firms to better serve their clients. Moreover, RPA can analyze market trends, investment portfolios, and risk profiles to provide personalized wealth management solutions and recommendations.
6. Private Equity
RPA addresses unique challenges in private equity, such as reconciling compensation structures, automating employee onboarding/offboarding, and facilitating merger and acquisition allocation processes. By automating these processes, RPA optimizes operational workflows and ensures compliance with regulatory standards. Additionally, RPA can analyze financial data, performance metrics, and investment opportunities to support strategic decision-making and portfolio management.
7. Insurance
Insurance companies leverage RPA to overcome challenges posed by legacy systems, siloed functions, and the need for superior customer experiences. RPA assists in tasks such as claims registration and processing, underwriting, regulatory compliance, policy servicing, and legacy application integration. This automation improves operational efficiency, reduces claims processing times, and enhances customer satisfaction. Moreover, RPA can analyze insurance policies, risk profiles, and market trends to optimize pricing strategies and mitigate risks.
Real-Life Use Case Example : JP Morgan Chase
JP Morgan Chase implemented RPA to streamline its mortgage processing. RPA bots are utilized to gather and validate customer information, assess eligibility, and process loan applications. This automation significantly reduced processing time, minimized errors, and improved overall efficiency in handling mortgage requests.
B. RPA Use Cases in Manufacturing
In the fast-evolving realm of manufacturing, the complex interaction between machinery and digital processes offers numerous automation possibilities with Robotic Process Automation (RPA). By smoothly incorporating RPA into their operations, manufacturing firms can reduce the likelihood of human errors and boost employee satisfaction by freeing them from repetitive tasks.
1. Invoice Processing
In addition to improving accuracy and efficiency, RPA in invoice processing offers manufacturers the advantage of real-time monitoring and analytics. By leveraging RPA bots to continuously analyze invoice data, companies can identify trends, optimize supplier relationships, and negotiate favorable terms. Furthermore, RPA enables seamless integration with Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, providing comprehensive insights into financial performance and facilitating strategic decision-making.
2. Purchase Order Processing
Beyond validation and execution, RPA empowers manufacturers to enhance collaboration and communication across departments involved in the procurement process. Through automated notifications and alerts, RPA ensures timely follow-up on purchase orders, reducing bottlenecks and preventing delays. Moreover, RPA-driven analytics enable proactive identification of potential supply chain disruptions, allowing manufacturers to implement contingency plans and maintain operational continuity.
3. Supply Chain Management
RPA not only streamlines operational tasks but also fosters innovation in supply chain management. By automating data analysis and scenario modeling, RPA enables manufacturers to optimize inventory levels, minimize carrying costs, and enhance resource allocation. Additionally, RPA-driven predictive analytics enhance forecasting accuracy, enabling manufacturers to anticipate market trends and adapt their supply chain strategies accordingly, thereby gaining a competitive edge in dynamic markets.
4. Accounts Payable Processing
In addition to expediting invoice approvals and payments, RPA enhances transparency and accountability in accounts payable processes. By maintaining a detailed audit trail of financial transactions, RPA ensures compliance with regulatory requirements and internal controls. Furthermore, RPA-driven insights into vendor performance and payment patterns empower manufacturers to negotiate favorable terms, optimize cash flow, and mitigate financial risks effectively.
5. Audits
RPA revolutionizes the audit process by providing continuous monitoring and real-time insights into key financial metrics. Through automated data validation and exception handling, RPA minimizes the risk of errors and fraud, ensuring the integrity of financial reporting. Moreover, RPA-driven analytics enable auditors to focus on high-risk areas and anomalies, facilitating more targeted and efficient audits. By incorporating RPA into audit procedures, manufacturers can enhance trust and credibility with stakeholders while driving operational excellence.
Real-Life Use Case Example: Tesla
Tesla utilizes RPA in its manufacturing processes to optimize production lines. Robots are programmed to perform repetitive tasks such as assembly, quality control inspections, and inventory management. By implementing RPA, Tesla has increased production speed, reduced operational costs, and enhanced product quality.
C. RPA Use Cases in Healthcare
In healthcare, smooth and efficient patient experiences are essential, relying heavily on streamlined processes. RPA is widely adopted to ensure the seamless delivery of healthcare services.
1. Utilizing RPA for Appointment Scheduling
In the healthcare sector, appointment scheduling is a critical aspect of ensuring efficient patient care delivery. Leveraging Robotic Process Automation (RPA) streamlines this process, automating appointment booking, rescheduling, and reminders. By implementing RPA in appointment scheduling, healthcare providers can optimize their scheduling workflows, reduce administrative burden, and enhance overall patient satisfaction.
2. Enhancing Patient Records and Data Management
Efficient management of patient records and data is essential for delivering quality healthcare services. RPA facilitates the automation of data entry, retrieval, and updating processes, ensuring accuracy and compliance with regulatory standards. By harnessing RPA for patient records management, healthcare organizations can improve data integrity, streamline workflows, and enhance patient privacy and security.
3. Optimizing Asset Tracking and Management with RPA
Effective asset tracking and management are crucial for healthcare facilities to ensure the availability of essential resources for patient care. RPA enables automated tracking of medical equipment, supplies, and inventory levels, minimizing stockouts and reducing operational costs. By implementing RPA in asset management, healthcare providers can enhance resource utilization, streamline procurement processes, and improve overall operational efficiency.
4. Facilitating Diagnostics and Data Analysis
RPA plays a significant role in accelerating diagnostics and data analysis processes in healthcare. By automating data extraction, analysis, and reporting tasks, RPA enables healthcare professionals to make timely and informed decisions. Leveraging RPA for diagnostics and data analysis enhances efficiency, accuracy, and scalability, ultimately improving patient outcomes and treatment effectiveness.
5. Strengthening Patient Outreach and Post-Treatment Care
Patient outreach and post-treatment care are critical components of comprehensive healthcare delivery. RPA facilitates automated communication channels for appointment reminders, follow-ups, and medication adherence support. By utilizing RPA for patient outreach, healthcare providers can enhance patient engagement, improve treatment adherence, and foster long-term patient relationships, leading to better health outcomes and satisfaction.
Real-Life Use Case Example: Mayo Clinic
Mayo Clinic utilizes RPA for appointment scheduling to improve patient experience and operational efficiency. RPA bots are programmed to handle appointment bookings, rescheduling, and cancellations across multiple platforms. This automation has reduced administrative burden, minimized scheduling errors, and ensured better utilization of staff resources.
D. RPA Use Cases in the Public Sector
In the public sector, efficiency is crucial for providing essential support to the public. However, time and budget constraints often hinder operations. Automation offers a solution by reclaiming time and resources, easing the burden on government organizations.
1. Enhanced Data Management and Analysis
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) offers significant potential for optimizing operations within the public sector, particularly in data capture and analysis, such as managing surveys and census data. RPA streamlines these processes by efficiently extracting relevant information and facilitating accurate analysis, ultimately enhancing decision-making capabilities. Furthermore, RPA can assist in data validation and cleansing, ensuring that the information collected is of high quality and reliability. By automating repetitive tasks associated with data entry and processing, organizations can allocate resources more effectively and focus on deriving actionable insights from the data.
2. Streamlined Automation of Legal Processes
Another critical application of RPA in the public sector lies in automating statutory processes, including regulatory compliance and documentation management. By leveraging automation, organizations can ensure adherence to legal requirements while minimizing manual errors, thereby enhancing compliance and operational efficiency. RPA can also facilitate the tracking and management of regulatory changes, ensuring that processes remain up-to-date and compliant with evolving regulations.
3. Efficient Content Transfer
RPA plays a crucial role in content migration tasks, involving the transfer of data between systems or platforms. Through automation, these processes can be expedited, leading to quicker and more seamless data transfers while reducing the burden on personnel and minimizing the risk of errors associated with manual migration. Additionally, RPA can help ensure data integrity during the migration process by automatically verifying and validating transferred data, thereby mitigating the risk of data loss or corruption.
4. Optimized Management in Registration Offices
In registration office operations, including processing and administrative tasks, RPA can significantly streamline workflows and improve service delivery. By automating routine tasks such as data entry, verification, and record maintenance, organizations can enhance efficiency and free up staff to focus on more complex or value-added activities. Moreover, RPA can facilitate seamless integration with existing systems and databases, reducing the need for manual data reconciliation and enhancing overall data accuracy and accessibility.
5. Streamlined Grant Processing, Permitting & Reporting
RPA also offers substantial benefits in streamlining grant application processing, permitting procedures, as well as reporting and compliance tasks within the public sector. By automating these processes, organizations can expedite the review and approval of applications, ensure timely and accurate reporting, and enhance overall compliance with regulatory requirements, leading to improved service delivery and stakeholder satisfaction. Additionally, RPA can enable organizations to gain real-time insights into their grant and permitting processes, allowing for more informed decision-making and resource allocation.
Real-Life Use Case Example: United States Internal Revenue Service (IRS)
The IRS employs RPA for tax return processing to enhance accuracy and expedite tax-related services. RPA bots are deployed to extract data from tax forms, perform validations, and process returns efficiently. This automation has helped the IRS to reduce processing time, mitigate errors, and improve taxpayer satisfaction.
E. RPA Use Cases in the Automotive
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) has emerged as a transformative technology across various industries, and the automotive sector is no exception. With its ability to automate repetitive tasks and streamline complex processes, RPA offers significant potential to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and drive innovation within automotive companies.
1. Supply Chain Management
RPA can be employed to streamline supply chain processes in the automotive industry by automating inventory management, order processing, and supplier communication. This can help in optimizing inventory levels, reducing lead times, and ensuring timely delivery of parts, ultimately improving overall efficiency and reducing costs. Additionally, RPA can assist in demand forecasting by analyzing historical data and market trends, enabling more accurate inventory planning and procurement decisions. Moreover, RPA can facilitate seamless integration between different systems and platforms used by suppliers and manufacturers, reducing manual errors and enhancing collaboration throughout the supply chain network.
2. Dealer Management
RPA can assist in automating various tasks related to dealer management, such as updating pricing information, managing sales leads, processing orders, and coordinating vehicle deliveries. By automating these processes, automotive manufacturers can enhance dealer satisfaction, improve sales performance, and ensure consistent customer experiences across different dealerships. Furthermore, RPA can analyze customer data to identify trends and preferences, enabling dealers to tailor their offerings and marketing strategies more effectively. Moreover, by automating routine administrative tasks, RPA allows dealer staff to focus on building relationships with customers and providing personalized assistance.
3. Customer Service and Support
RPA can be utilized to automate repetitive tasks in customer service and support, including responding to common inquiries, scheduling service appointments, processing warranty claims, and managing customer feedback. By automating these tasks, automotive companies can enhance customer satisfaction, reduce response times, and free up human agents to focus on more complex issues. Moreover, RPA can analyze customer interactions and feedback to identify areas for improvement in products and services, enabling continuous enhancement of the customer experience. Additionally, RPA can facilitate seamless communication between different departments within the organization, ensuring that customer inquiries are resolved promptly and efficiently.
4. Production Line Optimization
RPA can play a significant role in optimizing production line efficiency by automating tasks such as data entry, quality control checks, inventory management, and equipment monitoring. By integrating RPA with manufacturing systems, automotive companies can minimize downtime, improve production throughput, and ensure consistent product quality. Moreover, RPA can analyze production data in real-time to identify inefficiencies and bottlenecks, enabling proactive decision-making and continuous improvement initiatives. Additionally, RPA can automate maintenance scheduling and predictive maintenance tasks, ensuring that equipment is serviced and repaired before failures occur, further minimizing disruptions to production.
5. Compliance and Regulatory Reporting
RPA can assist automotive companies in automating compliance-related tasks, such as collecting and analyzing data for regulatory reporting, ensuring adherence to industry standards, and monitoring changes in regulatory requirements. By automating these processes, companies can reduce the risk of compliance violations, avoid penalties, and streamline reporting efforts. Moreover, RPA can track changes in regulations and automatically update internal policies and procedures accordingly, ensuring ongoing compliance with evolving regulatory requirements. Additionally, RPA can generate audit trails and documentation to demonstrate compliance to regulatory authorities, simplifying the audit process and reducing the burden on internal compliance teams.
6. Finance and Accounting
RPA can streamline finance and accounting processes in the automotive industry by automating tasks such as invoice processing, expense management, financial reporting, and reconciliation. By automating these repetitive and time-consuming tasks, automotive companies can improve accuracy, reduce processing times, and free up finance professionals to focus on more strategic activities. Furthermore, RPA can analyze financial data to identify cost-saving opportunities, optimize budget allocation, and mitigate financial risks. Additionally, RPA can facilitate seamless integration between different financial systems and applications, ensuring data consistency and eliminating the need for manual data entry and reconciliation.
Real-Life Use Case Example: Ford Motor Company
Ford Motor Company utilizes RPA for inventory management within its automotive manufacturing facilities. RPA bots are deployed to track inventory levels, manage parts procurement, and optimize supply chain operations. This automation has enabled Ford to minimize stockouts, reduce inventory holding costs, and improve production efficiency.
G. RPA Use Cases In Energy & Utilities
To maintain high-quality service while navigating these challenges,companies face constant pressures to adapt to environmental shifts and regulatory demands. There’s a growing need to streamline operations and free up human resources for more strategic tasks.
1. Contact Center Processes
RPA plays a crucial role in streamlining contact center operations within the Energy & Utilities sector. By automating repetitive tasks such as data entry, information retrieval, and customer query handling, RPA enhances efficiency and reduces response times, leading to improved customer satisfaction. Moreover, RPA can assist in categorizing and prioritizing incoming queries, ensuring that urgent matters are addressed promptly while also providing agents with relevant information to offer personalized assistance. Additionally, RPA can integrate with existing customer relationship management (CRM) systems, enabling seamless access to customer data and history, thus empowering agents to deliver more effective solutions and support.
2. Virtual Agents
The deployment of virtual agents augmented by RPA technology significantly enhances customer support services. These automated agents assist in addressing common inquiries and troubleshooting, thereby supplementing human agents and ensuring round-the-clock availability for customers. Virtual agents powered by RPA can utilize natural language processing (NLP) algorithms to understand and respond to customer queries, providing accurate and consistent assistance across multiple channels, including web chat, email, and social media platforms. Furthermore, RPA enables virtual agents to access and update relevant customer information in real-time, ensuring a seamless experience for customers as they interact with automated systems.
3. Metering
RPA facilitates the automation of metering processes, enabling the seamless collection and analysis of data from various meters. This automation ensures accuracy and timely insights for energy consumption monitoring and management, thereby optimizing resource allocation and enhancing operational efficiency. Moreover, RPA can perform advanced analytics on metering data, identifying usage patterns, anomalies, and potential areas for optimization or cost savings. By leveraging machine learning algorithms, RPA can predict future energy demands based on historical data, enabling utilities to proactively adjust supply and distribution strategies to meet customer needs efficiently.
4. Statements and Billing
RPA streamlines statements and billing processes by automating tasks such as invoice generation, validation, and distribution. By minimizing errors and expediting the billing cycle, RPA improves accuracy and efficiency in financial transactions within the Energy & Utilities sector. Additionally, RPA can integrate with billing systems and financial software, enabling seamless data exchange and reconciliation between different departments. This integration reduces manual intervention, streamlines workflows, and enhances auditability and compliance with regulatory requirements.
5. Customer Account Management
RPA enhances customer account management by automating tasks such as account updates, service activations, and disconnections. This automation not only improves operational efficiency but also enhances customer satisfaction by ensuring timely and accurate account management services. Furthermore, RPA can automate the processing of customer requests, such as address changes, meter installations, or service upgrades, reducing turnaround times and enhancing the overall customer experience. Additionally, RPA can generate personalized communications, such as welcome messages, service notifications, or renewal reminders, based on customer profiles and preferences, fostering stronger relationships and increasing customer loyalty.
6. Technician Dispatch and Reporting
In technician dispatch and reporting, RPA optimizes scheduling, route planning, and reporting processes. By automating these tasks, RPA enables swift response to service requests and efficient utilization of resources, ultimately enhancing the overall efficiency of field operations. Moreover, RPA can integrate with geographic information systems (GIS) and asset management systems, providing technicians with real-time visibility into customer locations, equipment status, and work orders. This integration improves response times, reduces travel distances, and minimizes downtime, resulting in cost savings and improved service levels. Additionally, RPA can generate automated reports on technician performance, service completion rates, and equipment maintenance activities, enabling management to monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) and make data-driven decisions to optimize field operations.
Real-Life Use Case Example: Enel
Enel, a multinational energy company, utilizes RPA for monitoring and maintenance of its energy grid infrastructure. RPA bots are deployed to collect and analyze data from sensors and IoT devices, detect anomalies, and trigger alerts for preventive maintenance. This automation has improved grid reliability, reduced downtime, and optimized asset management for Enel.
H. RPA Uses Cases In Telecoms
By leveraging RPA, telecom companies can gain a competitive edge and stay ahead of the curve. RPA presents an opportunity for these firms to modernize and meet evolving customer demands swiftly
1. Automating Network Management Tasks
In the realm of network management, Robotic Process Automation (RPA) offers transformative capabilities. Automated processes can continually monitor network performance metrics, such as latency, bandwidth usage, and packet loss. When predefined thresholds are met or exceeded, RPA can promptly trigger alerts and actions, ensuring swift responses to potential issues. Moreover, RPA can streamline the provisioning and de-provisioning of network resources. This includes tasks such as setting up new customer accounts, allocating IP addresses, and configuring network settings. By automating these processes, telecom companies can enhance operational efficiency and scalability.
2. Efficient Customer Onboarding and Offboarding Processes
Automation plays a crucial role in ensuring a seamless experience for customers during onboarding and offboarding processes. RPA can automate the creation and verification of customer accounts across various systems, including billing platforms, CRM databases, and provisioning systems. This ensures consistency and accuracy of customer data while expediting the account setup process. Additionally, RPA facilitates the generation of personalized welcome messages and service activation notifications for new customers, fostering positive initial interactions. Similarly, during offboarding, RPA automates account closure tasks, such as cancelling services, processing refunds, and updating billing records, streamlining the process for both customers and service providers.
3. Optimizing Data Transformation Procedures
In the realm of data transformation, RPA offers significant benefits by automating the extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL) processes. Automated processes can extract data from diverse sources, including billing systems, CRM databases, and network logs, ensuring timely availability of data for analysis and reporting purposes. Through standardized transformation processes, RPA ensures consistency in data formats and structures, facilitating seamless integration with downstream systems and applications. Moreover, RPA can implement data quality checks and validation rules to identify and rectify errors or inconsistencies in the data, ensuring its reliability and accuracy for decision-making purposes.
4. Streamlining Debt Collection Operations
RPA is instrumental in streamlining debt collection processes within the telecom industry. By automating the generation and delivery of payment reminders, escalation notices, and collection letters, RPA enhances the efficiency of debt recovery efforts. Moreover, RPA can integrate with predictive analytics models to prioritize collection efforts based on customer behavior, payment history, and propensity to pay. This data-driven approach enables telecom companies to optimize their debt collection strategies and improve overall financial performance.
5. Enhancing Expense Management and Control
Expense control is another area where RPA can deliver substantial benefits to telecom companies. Automated processes can capture and categorize expense data from various sources, such as receipts, invoices, and expense reports, reducing manual data entry errors and accelerating processing times. Furthermore, RPA enforces expense policies and compliance rules through automated validation checks, flagging exceptions and discrepancies for review and approval. By providing real-time visibility into expense trends, variances, and cost-saving opportunities, RPA enables proactive expense management and decision-making, ultimately driving operational efficiency and financial sustainability.
6. Improving First Call Resolution Strategies
In customer support operations, RPA plays a pivotal role in improving First Call Resolution (FCR) rates and enhancing the overall customer experience. By deploying virtual assistants or chatbots, telecom companies can automate responses to common customer inquiries and troubleshooting steps, providing immediate assistance without the need for human intervention. Additionally, RPA automates the retrieval and presentation of relevant customer information and account details to support agents during customer interactions, reducing handling times and improving accuracy. By leveraging historical call data and customer interactions, telecom companies can identify patterns and root causes of recurring issues, enabling proactive measures to prevent future incidents and improve FCR rates over time.
Real-Life Use Case Example: TelecomTech Solutions
TelecomTech Solutions implemented RPA to automate its network management tasks. By leveraging RPA bots, the company automated the monitoring of network performance metrics and streamlined the provisioning of network resources, leading to faster response times to potential issues and improved scalability. This initiative not only optimized operational processes but also allowed TelecomTech Solutions to meet evolving customer demands swiftly, gaining a competitive edge in the dynamic telecom market.
I. RPA Use Cases in Finance and Accounting
The finance department gains substantial advantages with RPA integration. By automating tedious back-office tasks like invoicing and reporting, RPA alleviates manual burdens and enhances efficiency. Explore various use cases below for how RPA optimizes finance and accounting processes.
1. Streamlining Expense Reimbursement
RPA can streamline the expense reimbursement process by automating the validation of expense reports, checking for policy compliance, and initiating reimbursement transactions without human intervention. Additionally, it can automatically categorize expenses, flagging outliers or non-compliant items for review by finance personnel. Moreover, RPA can integrate with existing ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems to ensure seamless data flow and real-time updates on reimbursement status for employees. This integration can extend to mobile applications, allowing employees to conveniently submit expenses on-the-go, while RPA manages the processing in the backend, enhancing user experience and efficiency.
2. Enhancing Financial Planning and Analysis (FP&A)
RPA can assist in data collection, consolidation, and analysis for FP&A activities. It can automate the extraction of financial data from multiple sources, generate reports, and even perform basic analysis tasks, freeing up finance professionals to focus on strategic decision-making. Furthermore, RPA can continuously monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) and provide timely alerts or insights based on predefined thresholds or trends, enabling proactive management of financial performance. By leveraging machine learning algorithms, RPA systems can evolve to identify new patterns or correlations in financial data, providing deeper insights and foresight for decision-makers.
3. Optimizing Accounts Payable Processes
RPA can automate the entire accounts payable process, from invoice receipt and data entry to invoice approval and payment processing. This helps in reducing errors, accelerating invoice processing times, and improving vendor relationships. Moreover, RPA can dynamically update payment schedules based on cash flow forecasts or supplier agreements, optimizing working capital management and cash utilization. Additionally, RPA can implement intelligent invoice routing based on predefined rules or historical data, ensuring that invoices are directed to the appropriate department or individual for review and approval, further streamlining the process.
4. Improving Accounts Receivable Management
Similarly, RPA can be utilized to automate accounts receivable processes such as invoice generation, payment reminders, and reconciliation of payments received, leading to faster cash collection cycles and improved cash flow management. Additionally, RPA can analyze customer payment behavior patterns and tailor collection strategies accordingly, minimizing overdue receivables and reducing the risk of bad debts. Furthermore, RPA can integrate with customer relationship management (CRM) systems to provide a comprehensive view of customer interactions and payment histories, enabling finance teams to make data-driven decisions regarding credit terms and collection priorities.
5. Managing Accounting Changes Efficiently
During periods of accounting standard changes or system migrations, RPA can assist in data migration, validation, and reconciliation tasks. It can ensure accuracy and consistency throughout the transition process, minimizing disruptions to financial operations. Furthermore, RPA can provide audit trails and documentation for regulatory compliance purposes, facilitating smoother audits and inspections by internal or external stakeholders. By leveraging natural language processing (NLP) capabilities, RPA systems can also assist finance teams in interpreting and implementing new accounting standards or regulations, reducing the burden of manual interpretation and ensuring compliance.
6. Automating Account and Bank Reconciliations
RPA can automate the reconciliation process between accounting records and bank statements by matching transactions, identifying discrepancies, and flagging exceptions for further review by finance staff. Moreover, RPA can reconcile accounts on a more frequent basis, enabling real-time visibility into cash positions and reducing the risk of fraud or errors going undetected for prolonged periods. Additionally, RPA can implement self-learning algorithms to improve reconciliation accuracy over time, adapting to changes in transaction volumes or patterns without manual intervention, thereby enhancing efficiency and reliability.
7. Efficient Reporting Automation
RPA can automate the generation and distribution of financial reports, regulatory filings, and management dashboards. It can extract data from various systems, consolidate information, and format reports according to predefined templates, saving time and reducing the risk of errors. Additionally, RPA can generate ad-hoc reports or analyses in response to specific inquiries or requests from management, enhancing decision-making agility and responsiveness. Furthermore, RPA can leverage advanced analytics techniques such as predictive modeling or scenario analysis to provide forward-looking insights in financial reports, empowering stakeholders to anticipate market trends or business risks proactively.
8. Enhancing Back Office Operations through Automation
Beyond specific tasks, RPA can automate various back-office processes such as data entry, data migration, compliance checks, and routine administrative tasks, enhancing overall operational efficiency within the finance function. Furthermore, RPA can facilitate cross-functional collaboration by integrating with other business systems or departments, enabling seamless information sharing and workflow coordination. Additionally, RPA can implement role-based access controls and encryption protocols to ensure data security and compliance with privacy regulations, mitigating the risk of data breaches or unauthorized access to sensitive financial information.
Real-Life Use Case Example: American Express
American Express utilizes RPA for automating accounts payable processes to streamline invoice processing and payment reconciliation. RPA bots are deployed to extract data from invoices, validate against purchase orders, and initiate payment approvals. This automation has improved accuracy, reduced processing time, and optimized cash flow management for American Express.
J. RPA Use Cases in Human Resources (HR)
In today’s dynamic business landscape, HR faces the imperative of agility and scalability to address key challenges like talent acquisition, employee experience enhancement, and retention of top performers. To meet these demands, HR departments can leverage RPA solutions to streamline operations and adapt quickly to changing needs, ensuring optimal efficiency and effectiveness. Explore below for inspiring RPA use cases tailored to HR functions.
1. Analytics and Reporting on Expenditure
RPA can be programmed to extract data from various sources including ERP systems, procurement databases, and expense management tools. Once collected, the data can be cleansed, categorized, and analyzed to identify spending trends, anomalies, and cost-saving opportunities. RPA bots can then generate customized reports and dashboards tailored to the specific needs of HR managers and executives. Additionally, RPA can automate the distribution of these reports on a scheduled basis, ensuring that stakeholders receive timely insights into spending patterns.
2. Administration of Learning and Development
RPA bots can not only handle administrative tasks but also assist in identifying training needs through analysis of employee performance data and skill gaps. They can automate the process of scheduling training sessions based on employee availability and preferences, as well as managing registration and attendance tracking. Moreover, RPA can integrate with learning management systems (LMS) to automatically update employee records upon completion of training modules and certifications, ensuring accurate tracking of learning progress.
3. Position Management
RPA can streamline the entire lifecycle of position management, from creating job postings and screening applicants to managing internal transfers and promotions. Bots can be programmed to scrape job boards for relevant openings, pre-screen candidates based on predefined criteria, and schedule interviews with hiring managers. Additionally, RPA can facilitate the approval process for new positions, automatically updating organizational charts and HR systems with changes in position status.
4. Automation of Travel and Expense Handling
RPA can automate the end-to-end process of travel and expense management, starting from travel request submission to expense reimbursement. Bots can extract data from travel booking platforms and expense reports, validate expenses against corporate policies, and route them for approval. They can also integrate with corporate credit card systems to reconcile expenses in real-time, minimizing manual intervention and reducing the risk of errors or fraud.
5. Streamlining Payroll Processes
RPA bots can handle complex payroll calculations, including overtime, bonuses, and deductions, with speed and accuracy. They can integrate with time-tracking systems to capture employee hours worked and automatically apply relevant pay rates. Moreover, RPA can ensure compliance with tax regulations by automatically withholding the correct amount of taxes based on employee information and jurisdictional requirements. Additionally, bots can generate payroll reports for audit purposes and seamlessly integrate payroll data with accounting systems.
6. Validation and Importing of Payroll Batches
RPA can automate the process of importing payroll data from disparate sources such as timesheets, attendance systems, and HR databases. Bots can validate the imported data against predefined rules and conduct reconciliation checks to identify discrepancies or anomalies. They can also handle exceptions by flagging errors for review and resolution by HR or payroll administrators. Furthermore, RPA can streamline the process of data entry by automatically populating payroll forms and templates with validated information.
7. Employee Benefit Invoice Reconciliation:
RPA bots can compare invoices from benefit providers against employee enrollment data to ensure accuracy and completeness. They can reconcile discrepancies such as mismatches in coverage levels, changes in employee status, or billing errors. Additionally, RPA can automate the approval workflow for benefit invoices, routing them to designated stakeholders for review and authorization. By automating the reconciliation process, RPA helps HR departments save time and resources while minimizing the risk of overpayments or underpayments for employee benefits.
8. Efficient Onboarding of New Hires
RPA can orchestrate a seamless onboarding experience for new employees by automating the execution of various tasks across multiple systems. Bots can generate offer letters, initiate background checks, and facilitate the completion of required paperwork such as tax forms and employment agreements. Additionally, RPA can provision access to IT systems and applications based on predefined role-based permissions, ensuring that new hires have the necessary tools and resources from day one. Moreover, bots can send personalized welcome emails and notifications to new employees, guiding them through the onboarding process and providing relevant information about company policies, benefits, and culture.
9. Maintenance of Employee Data
RPA can maintain the accuracy and integrity of employee master data by automating data entry, validation, and synchronization processes. Bots can extract employee information from various sources such as HRIS, payroll systems, and onboarding platforms, ensuring consistency across all systems and databases. They can also perform data quality checks to identify duplicates, inconsistencies, or missing information, prompting HR administrators to take corrective actions as needed. Additionally, RPA can update employee records in real-time to reflect changes such as promotions, transfers, or terminations, ensuring that HR data remains up-to-date and reliable for reporting and analysis purposes.
10. Creation of User Credentials
RPA can streamline the provisioning of user accounts and credentials for new employees, contractors, and temporary staff across multiple systems and applications. Bots can automate the creation of accounts based on predefined templates and access permissions, ensuring consistency and security in user provisioning processes. Additionally, RPA can enforce password policies and authentication requirements to enhance cybersecurity posture and mitigate the risk of unauthorized access. Furthermore, bots can integrate with identity and access management (IAM) systems to automatically assign role-based permissions and entitlements, reducing the burden on IT administrators and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
11. Automated Access Termination
RPA can play a critical role in offboarding processes by automating the deprovisioning of access rights and user accounts for departing employees. Bots can revoke access privileges across various systems and applications, including email accounts, network drives, and enterprise software platforms. They can also archive or transfer files and documents associated with departing employees to ensure continuity of operations and data security. Additionally, RPA can generate audit trails and compliance reports documenting access termination activities for regulatory purposes. By automating access termination procedures, RPA helps organizations mitigate the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Real-Life Use Case Example: IBM
IBM employs RPA for streamlining employee onboarding processes to enhance HR efficiency. RPA bots are used to automate tasks such as employee data entry, document verification, and provisioning access to internal systems. This automation has accelerated onboarding timelines, minimized errors, and improved the overall employee experience at IBM.
K. RPA Use Cases in CRM
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) can be effectively utilized in various aspects of Customer Relationship Management (CRM) to automate repetitive tasks, streamline processes, and improve overall efficiency. Here are some specific use cases for RPA in CRM:
1. Customer Support Automation
RPA can assist in managing customer support inquiries by automating tasks such as logging support tickets into CRM systems and triaging and routing customer complaints to the appropriate departments or agents. It can also help in generating automated responses to common queries or FAQs and updating customer profiles with relevant information from support interactions. Furthermore, RPA bots can be programmed to analyze historical support data to identify trends and patterns, enabling more proactive support measures. Additionally, by integrating with natural language processing (NLP) capabilities, RPA can understand and respond to customer inquiries more effectively, providing a more seamless support experience.
2. Customer Account Management
RPA bots can help in managing customer accounts by automating tasks like creating and updating customer profiles with new information and verifying and validating customer data across different systems. Additionally, they can generate reports on customer activity or engagement and send automated reminders for upcoming renewals or account reviews. Moreover, RPA can be leveraged to analyze customer behavior and preferences based on historical data, enabling personalized account management strategies. By integrating with predictive analytics tools, RPA can anticipate customer needs and recommend tailored solutions or offers, enhancing overall account management efficiency and effectiveness.
3. Order Tracking and Processing
RPA can streamline order tracking and processing workflows by automatically updating order status in the CRM system based on inputs from various sources such as emails and tracking systems. It can also check inventory levels and initiate reorder processes when necessary, as well as process routine orders without human intervention and send automated order confirmations and tracking information to customers. Furthermore, RPA bots can be configured to identify and address order discrepancies or exceptions, reducing manual intervention and minimizing processing errors. By integrating with machine learning algorithms, RPA can continuously improve order processing accuracy and efficiency over time.
4. Data Transfers and Integration
RPA bots can facilitate data transfers and integration between different CRM systems and other applications by extracting data from various sources such as emails, spreadsheets, and databases. They can also transform and standardize data formats for consistency, load data into CRM systems or other databases, and synchronize data between CRM platforms and other business systems such as ERP or marketing automation tools. Additionally, RPA can automate data validation and reconciliation processes, ensuring data integrity and reliability across systems. By leveraging robotic data automation techniques, RPA can handle large volumes of data transfers efficiently and securely, supporting seamless data integration across the organization.
5. Compliance Monitoring and Reporting
RPA can assist in ensuring compliance with regulations and internal policies by automating routine compliance checks on customer data and interactions. It can also generate compliance reports and audit trails, notify relevant stakeholders about potential compliance issues or anomalies, and assist in the documentation and tracking of regulatory requirements related to customer interactions. Moreover, RPA can be integrated with advanced analytics tools to identify compliance risks and trends proactively, enabling timely corrective actions. By implementing automated compliance monitoring workflows, organizations can mitigate compliance-related risks and enhance regulatory compliance posture effectively.
Real-Life Use Case Example: Salesforce
Salesforce utilizes RPA for customer relationship management (CRM) to automate data entry and update processes. RPA bots are deployed to sync customer data from various sources, update records, and ensure data consistency across the CRM platform. This automation has improved data accuracy, enhanced sales productivity, and enabled better customer insights for Salesforce users.
L. RPA Use Cases in Supply Chain & Logistics
For supply chain businesses, RPA offers transformative automation solutions, enhancing efficiency from invoice management to inventory tracking. Unlock the potential of your operations with tailored automation ideas. Streamline processes and boost productivity across the supply chain with RPA integration.
1. Shipment Scheduling and Tracking
RPA can automate the process of scheduling shipments by extracting data from various sources such as emails, spreadsheets, and ERP systems. It can also identify optimal shipping routes based on factors like cost, transit time, and carrier preferences, streamlining the scheduling process for maximum efficiency. Additionally, RPA can integrate with GPS tracking systems to monitor shipment progress in real-time, providing timely updates on delivery status and potential delays. By automating these tasks, organizations can reduce manual errors, minimize delays, and improve overall supply chain visibility.
2. Invoice Processing and Credit Collections
RPA can automate the extraction of invoice data from emails, PDFs, or other documents and input it into accounting or ERP systems. It can intelligently classify invoices based on predefined criteria, routing them to the appropriate departments or stakeholders for approval. Furthermore, RPA can analyze historical payment data and customer creditworthiness to prioritize collections efforts effectively. By automating invoice processing and credit collections, organizations can accelerate cash flow, reduce Days Sales Outstanding (DSO), and enhance overall financial performance.
3. Order and Inventory Processing
RPA can automate the processing of orders received through different channels by validating order details, updating inventory levels, and generating order confirmations. It can also perform data reconciliation across disparate systems to ensure inventory accuracy and prevent discrepancies. Additionally, RPA can automate order fulfillment processes, such as picking, packing, and shipping, further streamlining operations and improving order accuracy. By leveraging RPA for order and inventory processing, organizations can enhance order fulfillment efficiency, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction.
4. Capturing, Researching, and Closing Out Loads
RPA can capture load information from various sources such as emails, portals, or EDI messages and input it into transportation management systems (TMS). It can then analyze historical shipment data and carrier performance metrics to optimize load assignments and minimize transportation costs. Additionally, RPA can automate load closure processes by validating delivery confirmations, reconciling invoices, and updating relevant systems accordingly. By automating load capture, research, and closure tasks, organizations can optimize transportation operations, improve cost control, and enhance supply chain visibility.
5. Procurement and Inventory
RPA can assist in procurement processes by automating tasks such as vendor selection, RFQ (Request for Quotation) generation, and purchase order processing. It can also monitor supplier performance and inventory levels in real-time, triggering automated replenishment orders when stock levels reach predefined thresholds. Furthermore, RPA can streamline the procurement approval process by routing purchase requests to the appropriate stakeholders for review and authorization. By leveraging RPA for procurement and inventory management, organizations can optimize sourcing decisions, reduce procurement cycle times, and minimize stockouts.
6. Order and Inventory Tracking
RPA can track orders and inventory movements across the supply chain by integrating with warehouse management systems (WMS) and ERP systems. It can provide real-time visibility into order status, shipment locations, and inventory levels through customized dashboards and alerts. Additionally, RPA can automate the generation of shipment notifications and delivery confirmations, keeping stakeholders informed throughout the order fulfillment process. By implementing RPA for order and inventory tracking, organizations can enhance supply chain transparency, improve decision-making, and optimize inventory management practices.
Real-Life Use Case Example: DHL
DHL employs RPA for shipment tracking and logistics management to optimize supply chain operations. RPA bots are utilized to track shipments in real-time, update delivery statuses, and proactively identify potential delivery issues. This automation has improved transparency, reduced manual intervention, and enhanced overall efficiency in DHL’s logistics operations.
M. RPA Use Cases In Retail
The prosperity of retail businesses relies on satisfied, returning customers, necessitating efficient digital processes. Addressing customer inquiries, marketing to potential customers, and managing inventory are crucial tasks for ensuring success. Therefore, the retail sector presents ample opportunities for leveraging RPA assistance.
1. Demand-Supply Planning
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) plays a crucial role in demand-supply planning within the retail industry. By harnessing data from diverse sources including sales records, market trends, and external factors like weather forecasts, RPA facilitates accurate demand forecasting and supply chain management. Automation of these processes enables the creation of precise demand forecasts and supply plans, which consider factors such as seasonality, promotions, and regional variations. Moreover, RPA bots dynamically adjust inventory levels and reorder points based on real-time sales data, ensuring optimal stock levels and minimizing the risk of stockouts or overstocking. Integration with Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems and supplier databases further streamlines procurement processes by automating purchase order generation and managing supplier relationships efficiently.
2. Product Categorization
In the realm of product categorization, RPA leverages machine learning algorithms to automatically classify products based on attributes such as size, color, brand, and type. This automation not only standardizes product descriptions and attributes across various platforms but also enhances search relevance and simplifies product discovery for customers. RPA continuously updates product categorization by analyzing sales data and customer feedback, ensuring that product catalogs remain organized and up-to-date. By automating this process, retailers mitigate the risk of manual errors and inconsistencies, thereby fostering a more efficient and user-friendly shopping experience.
3. Inventory Management
RPA streamlines inventory management processes by automating tasks such as stock reconciliation, shelf replenishment, and inventory audits. Integration with Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) or barcode scanning systems allows RPA bots to track inventory movements in real-time and trigger automatic replenishment orders as stock levels reach predefined thresholds. These bots optimize inventory allocation across multiple locations or channels, minimizing carrying costs and maximizing sales opportunities. By providing visibility into inventory levels and trends, RPA enables retailers to make data-driven decisions to optimize their supply chain and improve customer satisfaction.
4. Call Center Processes
In call center operations, RPA handles repetitive customer inquiries such as order status checks, product returns, and account inquiries, thereby reducing the workload on call center agents. Integration with Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems allows RPA bots to access customer data and transaction history, providing personalized assistance and recommendations. Automation of support ticket creation and inquiry routing ensures that inquiries are directed to the appropriate agents based on skill level, availability, and workload. By automating routine tasks, RPA empowers call center agents to focus on resolving complex issues and delivering high-quality customer service, ultimately leading to increased customer satisfaction and retention.
5. Marketing Automation
RPA revolutionizes marketing efforts by automating the creation and scheduling of email marketing campaigns, including list segmentation, content personalization, and A/B testing. By analyzing customer data and behavior, RPA identifies opportunities for targeted marketing campaigns such as cross-selling, upselling, and re-engagement campaigns. Bots monitor social media channels for brand mentions or relevant keywords, facilitating timely responses and customer engagement. By automating repetitive marketing tasks, RPA allows marketers to focus on strategy development, creative content creation, and campaign performance analysis, thereby driving business growth.
6. Sales Analysis
RPA empowers retailers to collect, consolidate, and analyze sales data from various sources, including point-of-sale systems, e-commerce platforms, and CRM systems. Customized reports and dashboards generated by RPA provide insights into sales performance, product trends, and customer behavior. By identifying patterns and correlations in sales data, RPA uncovers actionable insights and optimization opportunities such as pricing adjustments or product promotions. By automating sales data analysis, retailers make data-driven decisions to enhance sales effectiveness, optimize inventory management, and improve customer satisfaction.
7. Supply Chain Management and Logistics
In supply chain management, RPA automates end-to-end processes including order processing, shipment tracking, inventory management, and vendor management. Integration with third-party logistics providers and transportation management systems optimizes route planning, reduces transportation costs, and enhances delivery efficiency. RPA bots monitor inventory levels and demand forecasts to proactively identify potential supply chain disruptions and implement corrective actions. By automating supply chain management tasks, RPA enhances visibility, reduces lead times, and improves overall operational efficiency.
8. Customer Support
RPA transforms customer support operations by automating common inquiries such as order status checks, product returns, and account inquiries through self-service portals or chatbots. Integration with knowledge bases and CRM systems equips RPA bots with relevant information and suggested responses, facilitating efficient customer assistance. Automation of routine tasks allows timely escalation of complex issues to human agents, ensuring swift resolution and optimal resource utilization. By automating customer support, RPA reduces response times, enhances first-contact resolution rates, and improves overall customer satisfaction.
9. Fraud Detection
RPA enhances fraud detection capabilities by analyzing transactional data in real-time to identify suspicious patterns, anomalies, or deviations from normal behavior. Integration with fraud detection algorithms and machine learning models enables continuous learning and adaptation to new fraud patterns. Bots flag potentially fraudulent transactions for further investigation by human analysts and trigger automated responses such as transaction blocking or account suspension. By automating fraud detection processes, RPA helps retailers minimize financial losses, protect customer data, and uphold trust and credibility with customers.
Real-Life Use Case Example: Walmart
Walmart employs RPA for order management processes to enhance efficiency in its retail operations. RPA bots are utilized to automate order processing, track shipments, and manage inventory across distribution centers and retail stores. This automation has helped Walmart to improve order accuracy, reduce fulfillment times, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Top RPA Trends To Look Out For In 2024
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) continues to evolve, driven by advancements in technology, changes in business needs, and lessons learned from implementation experiences.
1. Hyper Automation
Hyperautomation refers to the use of advanced technologies like RPA, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and process mining to automate as many business processes as possible. This trend involves end-to-end automation, intelligent decision-making, and the integration of various automation technologies. Organizations adopting hyperautomation aim to streamline operations, enhance agility, and improve customer experiences through the seamless orchestration of automated workflows across the enterprise. By leveraging a combination of RPA, AI, and other digital tools, businesses can achieve higher levels of efficiency, scalability, and innovation while staying competitive in rapidly evolving markets.
2. Intelligent Process Automation (IPA)
IPA combines RPA with AI technologies such as natural language processing (NLP), machine learning, and cognitive automation to automate more complex tasks that involve decision-making and unstructured data processing. IPA enables greater efficiency, accuracy, and adaptability in automating business processes. By incorporating AI-driven capabilities into RPA workflows, organizations can automate tasks that require contextual understanding, reasoning, and learning from data patterns. This enables them to tackle a broader range of use cases, drive deeper insights, and deliver enhanced value across diverse business functions, from customer service and finance to supply chain management and human resources.
3. Process Discovery and Mining
Process discovery and mining tools help organizations identify and analyze their existing business processes to uncover automation opportunities. These tools analyze user interactions with software systems to identify repetitive tasks, bottlenecks, and inefficiencies that can be automated using RPA or other automation technologies. Through process discovery and mining, organizations gain visibility into their operations, identify optimization opportunities, and prioritize automation initiatives based on their potential impact on efficiency, cost savings, and customer satisfaction. By leveraging data-driven insights, businesses can accelerate their automation journey and achieve tangible results more quickly and effectively.
4. Cloud-Based RPA
Cloud-based RPA solutions offer scalability, flexibility, and ease of implementation compared to on-premises solutions. With the increasing adoption of cloud technologies, organizations are leveraging cloud-based RPA platforms to automate their business processes and reduce infrastructure costs. Cloud-based RPA solutions enable organizations to rapidly deploy and scale automation initiatives without the need for extensive IT infrastructure investments. By leveraging the scalability and agility of the cloud, businesses can accelerate time-to-value, optimize resource utilization, and adapt to changing business requirements more efficiently. Additionally, cloud-based RPA platforms often provide built-in security features and compliance controls to ensure data protection and regulatory compliance.
5. RPA Analytics and Insights
Analytics and reporting capabilities within RPA platforms provide valuable insights into automation performance, process efficiency, and ROI. Advanced analytics tools help organizations monitor automation workflows, identify optimization opportunities, and make data-driven decisions to improve automation outcomes. By analyzing key performance indicators (KPIs) such as bot utilization, cycle times, and error rates, businesses can assess the impact of automation on productivity, cost savings, and customer satisfaction. Additionally, RPA analytics enable continuous improvement by identifying areas for optimization, refining automation strategies, and maximizing the value of RPA investments over time.
6. Industry-Specific RPA Solutions
RPA vendors are increasingly developing industry-specific solutions tailored to the unique needs and requirements of various verticals such as healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and retail. These specialized RPA solutions incorporate industry-specific processes, regulations, and compliance standards to deliver targeted automation benefits. By addressing industry-specific challenges and use cases, these solutions enable organizations to accelerate the adoption of RPA, achieve faster time-to-value, and realize industry-specific benefits such as improved patient care, regulatory compliance, supply chain efficiency, and customer experience. Industry-specific RPA solutions empower businesses to optimize processes, mitigate risks, and drive innovation within their respective sectors.
7. RPA Governance and Compliance
As RPA deployments scale across organizations, there is a growing focus on governance, risk management, and compliance (GRC) to ensure that automation initiatives adhere to regulatory requirements and industry standards. Establishing robust governance frameworks and compliance controls is essential for mitigating risks and maintaining the integrity of automated processes. By implementing governance best practices such as role-based access controls, audit trails, and change management processes, organizations can ensure transparency, accountability, and compliance throughout the automation lifecycle. Additionally, ongoing monitoring and risk assessment help organizations identify potential issues, address compliance gaps, and optimize automation processes to align with business objectives and regulatory requirements.
How Businesses Across Industries Can Implement RPA Solutions?
Implementing Robotic Process Automation (RPA) solutions in businesses involves several steps to ensure successful deployment and integration. Here’s a general guide on how businesses can implement RPA solutions:
1. Identify Suitable Processes
Begin by collaborating with various departments and teams to identify a wide range of processes that could benefit from automation. Encourage brainstorming sessions to uncover hidden opportunities for RPA implementation across different business functions. Prioritize processes based not only on their repetitive nature but also on their potential impact on business goals and objectives. Consider leveraging process mining techniques to gain insights into process efficiency and identify bottlenecks ripe for automation.
2. Assess Feasibility and ROI
Conduct a comprehensive analysis of each identified process to assess its suitability for automation. Engage stakeholders from finance, IT, operations, and other relevant departments to gather insights into process complexity, transaction volumes, and potential cost savings. Utilize business process modeling tools to simulate the impact of automation on key performance indicators (KPIs) such as cycle time, error rates, and resource utilization. Ensure that the projected ROI aligns with the organization’s strategic objectives and investment criteria.
3. Select the Right RPA Tool
Take a holistic approach to selecting the most suitable RPA tool for your organization’s needs. Evaluate RPA vendors based on criteria such as ease of use, scalability, security features, and compatibility with existing IT infrastructure. Consider conducting proof-of-concept (POC) projects with multiple RPA tools to assess their performance in real-world scenarios. Engage with industry experts and consult peer reviews to gain insights into each tool’s strengths and limitations. Ultimately, choose a tool that offers the best balance of functionality, flexibility, and value for your organization.
4. Design Automation Workflows
Invest time upfront to meticulously design automation workflows that capture the nuances of each business process. Collaborate closely with subject matter experts (SMEs) and RPA developers to map out process steps, decision points, and exception handling logic. Leverage process modeling techniques such as swimlane diagrams and flowcharts to visualize workflow dependencies and streamline automation design. Incorporate feedback from end-users to ensure that the automated workflows align with their operational needs and preferences.
5. Develop and Test RPA Bots
Adopt an agile approach to RPA bot development, breaking down automation workflows into manageable tasks or user stories. Encourage cross-functional collaboration between RPA developers, business analysts, and quality assurance (QA) testers to iterate rapidly and address any issues early in the development cycle. Leverage version control systems and automated testing frameworks to maintain code quality and ensure consistency across multiple bot deployments. Implement robust logging and monitoring mechanisms to track bot performance and identify opportunities for optimization.
6. Deploy RPA Bots
Establish clear deployment procedures and governance protocols to ensure a smooth transition from development to production. Conduct comprehensive regression testing in a staging environment to validate bot functionality and integration with upstream and downstream systems. Coordinate with IT operations teams to schedule bot deployments during off-peak hours and minimize disruption to business operations. Implement rollback procedures and contingency plans to mitigate risks associated with bot failures or unexpected outcomes. Provide training and documentation to end-users to facilitate adoption and ensure successful bot utilization.
7. Provide Training and Support
Offer a variety of training resources and learning opportunities to support employees in adapting to the new RPA-driven workflows. Develop customized training modules tailored to different user roles and proficiency levels, covering topics such as bot interaction, exception handling, and troubleshooting. Establish a dedicated support team or helpdesk to address user inquiries, technical issues, and enhancement requests in a timely manner.
Conclusion
The adoption of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) presents a multitude of benefits for businesses seeking to streamline operations, enhance efficiency, and drive productivity. By automating repetitive and rule-based tasks, RPA enables organizations to reallocate human resources to more strategic and value-added activities, thereby accelerating processes and reducing operational costs.
Partnering with a specialized RPA development company offers numerous advantages in navigating the complexities of RPA implementation and maximizing its benefits. RPA experts possess deep domain knowledge and technical expertise essential for identifying automation opportunities, designing tailored solutions, and ensuring seamless integration with existing systems.
Collaborating with an RPA development company also accelerates the implementation timeline, allowing businesses to realize the benefits of automation more rapidly. By leveraging established methodologies and best practices, RPA experts streamline the deployment process, minimizing disruptions to daily operations and maximizing return on investment.
How Idea Usher Can Help With RPA Implementation?
Idea Usher can significantly aid in RPA (Robotic Process Automation) implementation through a variety of benefits and services:
1. Expertise and Experience
Idea Usher brings a team of experienced professionals who are well-versed in RPA technologies and implementation strategies. This expertise ensures smooth execution and minimizes implementation risks.
2. Customized Solutions
Idea Usher understands that every organization has unique processes and requirements. They tailor RPA solutions to fit the specific needs of each client, ensuring maximum efficiency and effectiveness.
3. Cost Efficiency
By automating repetitive and mundane tasks, RPA reduces the need for manual labor, leading to cost savings in the long run. Idea Usher helps organizations identify areas where automation can yield the highest return on investment and implements solutions accordingly.
4. Increased Productivity
RPA streamlines workflows and accelerates processes, allowing employees to focus on more strategic tasks that require human intervention. Idea Usher’s solutions enhance overall productivity by freeing up valuable time and resources.
5. Accuracy and Compliance
RPA ensures a higher level of accuracy in performing tasks compared to manual intervention, reducing the risk of errors and compliance issues. Idea Usher implements RPA solutions with stringent adherence to industry regulations and standards.
6. Scalability and Flexibility
Idea Usher designs RPA solutions that are scalable and flexible, capable of accommodating changes in business requirements and adapting to evolving technologies. This scalability ensures that the automation remains effective and relevant in the long term.
7. Continuous Support and Maintenance
Idea Usher provides ongoing support and maintenance services to ensure the smooth functioning of RPA systems. This includes troubleshooting, performance optimization, and updates to keep the automation solution up-to-date.
This case study describes how we effectively integrated RPA technologies for our client’s organization.
Contact us today to learn more about how we can assist you with RPA solutions.
FAQ
Q. What is RPA, and how can it benefit business?
A. RPA stands for Robotic Process Automation, which involves the use of software robots or “bots” to automate repetitive tasks within business processes. These bots can mimic human actions in interacting with digital systems, such as entering data, triggering responses, and communicating with other systems. RPA can benefit our business by increasing efficiency, reducing errors, improving compliance, and freeing up human resources to focus on higher-value tasks.
Q. What are some typical use cases for RPA for businesses?
A. Some typical use cases for RPA in our business include automating data entry tasks, processing invoices, reconciling accounts, updating customer records, generating reports, and managing email communication. Additionally, RPA can be applied in areas such as customer service, HR operations, supply chain management, and regulatory compliance.
Q. How difficult is it to implement RPA in our existing systems and processes?
A. The difficulty of implementing RPA depends on factors such as the complexity of our processes, the availability of suitable RPA tools, and the level of expertise within our organization. Generally, RPA implementations can range from relatively simple to more complex projects. Starting with a proof of concept (POC) can help assess feasibility and identify potential challenges before scaling up.
Q. How long does it take to see a return on investment (ROI) from an RPA implementation?
A. The time it takes to see ROI from an RPA implementation can vary depending on factors such as the scope of automation, the efficiency gains achieved, and the costs involved in implementing and maintaining the RPA solution. In many cases, organizations can start realizing benefits relatively quickly, often within months, especially when focusing on high-impact processes and continuously optimizing automation over time.











Gaurav Patil