- What Do We Mean by Digital Transformation in Banking?
- Key Market Takeaways of Digital Transformation in Banking
- Key Factors Behind the Digital Transformation in Banking
- Digital Technologies Utilized By Modern Banks
- Benefits of Digital Transformation in Banking
- How to Integrate Emerging Technologies for Digital Transformation in Banking?
- Case Study Digital Transformation in Banking: TPBank
- Conclusion
- Looking to Leverage Digital Transformation in Banking for Your Business?
- FAQs

In the rapidly evolving landscape of finance, the traditional paradigms of banking are undergoing a profound shift. With the advent of digital technologies, the financial industry is experiencing a transformative wave known as digital transformation. This paradigm shift is not only redefining the way banks operate but also revolutionizing the customer experience.
In this blog, we delve into the multifaceted realm of digital transformation within the banking sector. We unravel the myriad benefits that digitalization brings to financial institutions, as well as explore real-world use cases that highlight its transformative power. From enhancing operational efficiency to delivering personalized services, digital transformation is reshaping banking as we know it.
Join us on this exploration as we navigate through the innovative strategies and technological advancements driving the banking industry toward a digital future. Discover how embracing digital transformation is not just a choice for banks but a necessity to stay competitive and relevant in today’s dynamic market landscape.
- What Do We Mean by Digital Transformation in Banking?
- Key Market Takeaways of Digital Transformation in Banking
- Key Factors Behind the Digital Transformation in Banking
- Digital Technologies Utilized By Modern Banks
- Benefits of Digital Transformation in Banking
- How to Integrate Emerging Technologies for Digital Transformation in Banking?
- Case Study Digital Transformation in Banking: TPBank
- Conclusion
- Looking to Leverage Digital Transformation in Banking for Your Business?
- FAQs
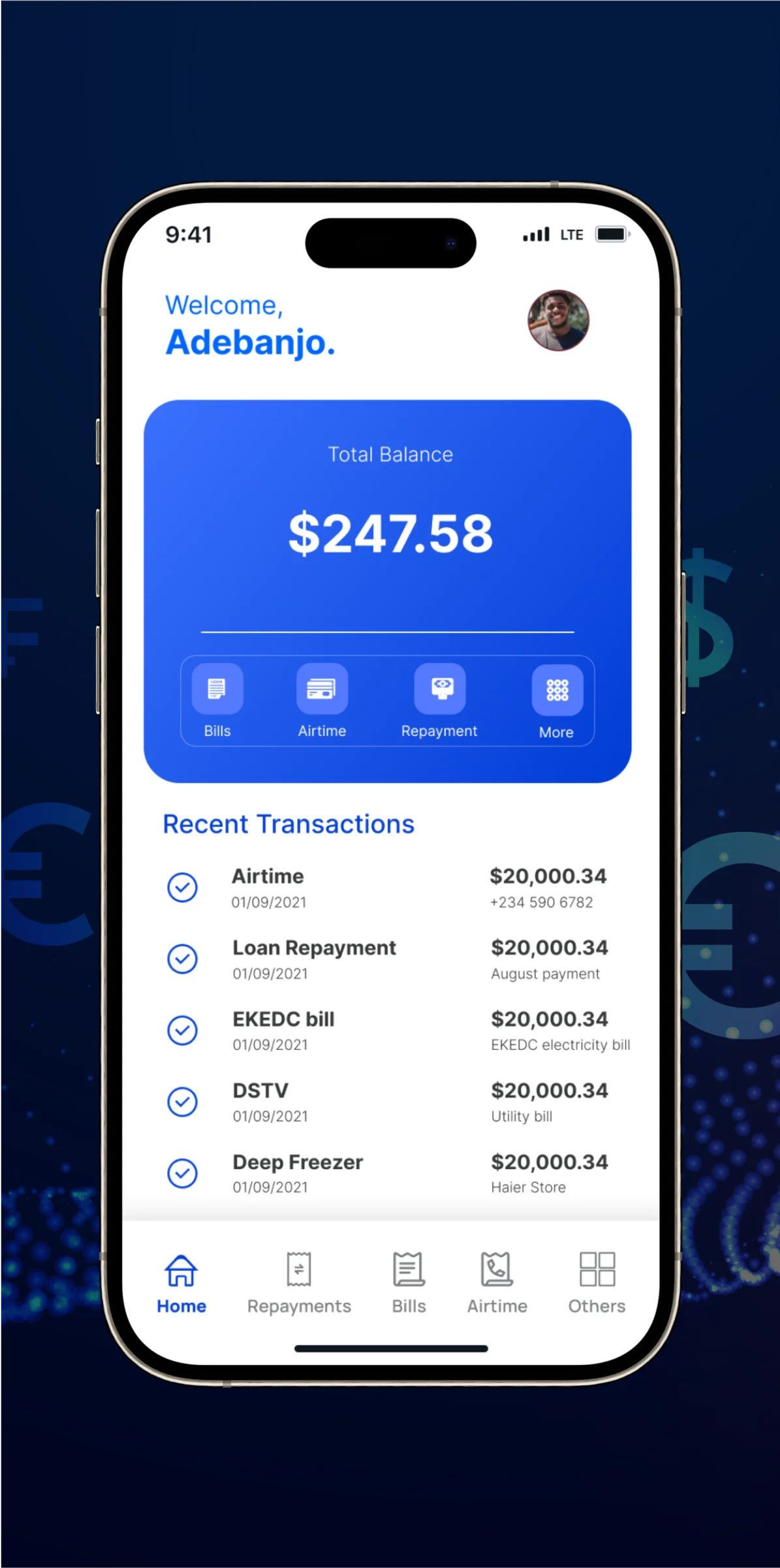
What Do We Mean by Digital Transformation in Banking?
Digital Transformation in Banking signifies the comprehensive integration of digital technologies across all facets of a bank’s operations, fundamentally altering its operational landscape and enhancing value delivery to customers. This paradigm shift entails moving from traditional banking practices towards modern, digitally-driven systems. Here are the key facets:
- Customer-Centricity: Banks leverage technologies such as AI and Machine Learning to analyze data, make predictions, and offer customer service through chatbots and online assistants. The aim is to personalize the customer journey and automate processes within a unified ecosystem.
- Integration and Inclusivity: Banks prioritize the development of robust digital banking software, emphasizing aspects like security, architecture design, technology stack, and seamless integration with third-party systems. Furthermore, the integration of blockchain technology enhances security and transparency.
- Operational Efficiency: Digital banking architectures, including layered and microservices-based approaches, play a pivotal role in enhancing operational efficiency. Additionally, the adoption of cloud computing significantly contributes to streamlining operations.
- Innovation: Banks drive innovation by implementing advanced technologies and introducing novel services such as online banking applications, robust data encryption software, virtual assistants, and KYC system software.
The overarching objective of digital transformation is to deliver superior customer experiences, drive operational efficiency, foster innovation, and create tangible business value.
Key Market Takeaways of Digital Transformation in Banking
Source: ResearchAndMarkets
Among the key segments contributing to this growth, retail banking is expected to achieve a CAGR of 13.2%, reaching US$21.9 billion by the end of the forecast period. Corporate banking, on the other hand, is anticipated to witness remarkable growth, with an estimated CAGR of 16.9% over the next eight years, underscoring the increasing importance of digitalization in this sector.
Geographically, while the United States currently holds a significant share of the digital banking market at US$5.2 billion in 2022, China is poised for rapid expansion. As the world’s second-largest economy, China is forecasted to reach a market size of US$9.3 billion by 2030, driven by a robust CAGR of 18.2% from 2022 to 2030.
Key market players are actively driving this transformation. Citibank has adopted a “Mobile First” strategy, prioritizing seamless mobile banking experiences for its customers. TD Bank has focused on upgrading its banking technology to enhance digital offerings, while BBVA offers “Do It Yourself” (DIY) transactions, granting customers greater control over their banking activities. J.P. Morgan, on the other hand, has prioritized accelerated product development to meet evolving customer needs in the digital era.
Key Factors Behind the Digital Transformation in Banking
Here are some key elements that are driving the digital Transformation in Banking,
1. Increased Demand from Tech-Savvy Generations
Modern consumers, particularly millennials and Gen Z, exhibit a preference for mobile banking and seamless digital experiences. This dynamic fuels the necessity for accessible banking solutions available 24/7 via smartphones and other devices.
Banks leverage AI and data analytics to offer personalized financial solutions, tailoring products and services based on individual financial goals and preferences.
2. Evolving Regulatory Landscape
Regulatory bodies are increasingly emphasizing Open Banking and APIs, enabling secure data sharing between banks and third-party providers. This regulatory shift encourages innovation and empowers customers to select the services they require, further propelling digital transformation in banking.
Banks prioritize creating omnichannel experiences, enabling customers to seamlessly transition between online, mobile, and in-person interactions. Integrated systems ensure consistent access to information across channels.
3. Rise of FinTech Companies
Disruptive FinTech startups are reshaping the traditional banking sector by offering innovative and user-friendly financial services. This competitive landscape urges traditional banks to adapt and innovate, prompting increased investment in digital transformation endeavors.
Banks focus on providing transparent information regarding fees, investments, and financial matters through user-friendly interfaces. Additionally, robust security measures, including multi-factor authentication, safeguard customer data.
4. Growing Cybersecurity Concerns
With the surge in digital adoption comes heightened cybersecurity threats. To maintain trust and protect customer data, banks must invest in robust security measures, a critical aspect of successful digital transformation efforts.
Upgrading outdated infrastructure is essential for handling the complexities of modern banking operations. Cloud computing and agile methodologies enhance scalability and efficiency.
5. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
These technologies are revolutionizing banking operations by automating tasks such as loan approvals, fraud detection, and personalized financial recommendations. AI-powered chatbots also enhance customer experiences by providing round-the-clock support.
Responsible utilization of consumer data enables banks to create targeted marketing campaigns and develop innovative financial products while addressing privacy concerns.
Digital Technologies Utilized By Modern Banks
Here are some of the digital technologies utilized by modern banks,
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML):
AI:
- Customer Service: Conversational AI agents powered by Natural Language Processing (NLP) can engage in natural, context-aware interactions with customers, resolving inquiries and providing personalized support.
- Data Analysis and Management: Deep learning algorithms can analyze vast, unstructured datasets to discover hidden patterns and trends. Knowledge graphs can connect entities and relationships within data, facilitating deeper insights and improved decision-making.
- Security: Anomaly detection systems leverage unsupervised learning models (e.g., autoencoders) to identify deviations from normal behavior in real-time, flagging potentially fraudulent activities.
ML:
- Fraud Detection: Supervised learning algorithms (e.g., Decision Trees, Random Forests) can be trained on historical data labeled as fraudulent and legitimate transactions, enabling them to identify and prevent fraudulent transactions in real time with high accuracy.
- Real-time Data Comparison: Online learning algorithms can continuously learn and adapt to evolving patterns in real-time data streams, enabling dynamic fraud detection and risk management.
Also read, “Artificial Intelligence (AI) In Mobile Phones: Benefits and Challenges“
2. Internet of Things (IoT):
Real-time Data Analysis:
- Sensor networks collect and transmit data via protocols like MQTT and LoRaWAN, enabling real-time insights into customer behavior and environmental conditions. Edge computing at the device level can perform pre-processing and filtering of data before transmission, optimizing bandwidth usage and reducing latency.
Contactless Payments:
- Near Field Communication (NFC) technology embedded in mobile wallets and wearables facilitates secure contactless payments through secure element chips with cryptographic capabilities.
Transformation of the Financial Ecosystem:
- Blockchain-based smart contracts can automate financial agreements and workflows based on predefined conditions, enabling real-time execution of financial transactions triggered by IoT sensor data.
Also read, “Top 10 IoT App Development Trends for Startups In 2024“
3. Blockchain:
Secured Data Transactions:
- Blockchain utilizes a distributed ledger technology (DLT) where transactions are cryptographically hashed and stored across a network of computers, ensuring immutability and tamper-proof record keeping.
Improved Interface:
- Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) built on blockchain platforms enable secure and standardized data exchange between banks and other financial institutions, facilitating interoperability and streamlining processes.
Transparency
- Blockchain provides an immutable audit trail of all transactions, fostering trust and accountability among participants in the network.
Also read, “Blockchain For Startups: Benefits And Use Cases“
4. Cloud Computing and APIs:
Cloud-driven Services:
- Public, private, or hybrid cloud infrastructure provides banks with on-demand access to scalable computing resources (e.g., virtual machines, containerized applications), enabling them to dynamically adapt to changing workloads and optimize resource utilization.
Open Banking APIs
- Standardized APIs, defined by specifications like the Open Banking Standard (OBS), enable third-party developers to securely access and utilize customer data (with explicit consent) to build innovative financial applications and services, fostering open innovation in the financial sector.
5. Big Data Analytics:
Transforming Customer Perception:
- Customer segmentation and profiling techniques are employed to group customers based on shared characteristics and behaviors, enabling hyper-personalized product offerings and marketing campaigns.
Analyzing Expenditures:
- Predictive analytics models (e.g., regression analysis) can predict future spending patterns and identify potential risks associated with customer behavior, allowing banks to offer tailored financial advice and personalized budgeting tools.
Also read, “Understand how to use blockchain data analytics for your business“
Risk Monitoring
- Credit scoring models (e.g., logistic regression) can assess the creditworthiness of loan applicants based on historical data and financial information, facilitating informed lending decisions and mitigating risk.
Feedback Management
- Sentiment analysis techniques can be applied to analyze customer feedback from various channels (e.g., social media, surveys) to identify trends in customer sentiment and areas for improvement.
6. Additional Technical Details:
- Cybersecurity and Authentication: Multi-factor authentication (MFA) utilizes various authentication factors (e.g., knowledge factors like passwords, possession factors like tokens, and inherence factors like biometrics) to improve security posture.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Software robots equipped with Optical Character Recognition (OCR) and screen scraping capabilities can automate repetitive tasks involving structured data and legacy systems integration.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): AR overlays digital information in the real world through devices like AR glasses, enabling visualizations of financial data or product information. VR creates immersive simulations for employee training or customer onboarding sessions.
- Regulatory Technology (RegTech): RegTech solutions leverage AI and Natural Language Processing (NLP) to automate regulatory compliance processes, such as Know-Your-Customer (KYC) verification and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) checks, reducing manual workload and ensuring adherence to regulations.
- Open-source Technologies: Adopting open-source software grants banks access to a wider talent pool of developers, fosters collaboration with the broader developer community, and enables faster adoption of new technologies and advancements.
Benefits of Digital Transformation in Banking
Here are the benefits of digital transformation in banking,
Investment Banking on Digital Platforms:
- Reduced operational costs: RPA bots automate repetitive tasks like back-office operations, data entry, and trade settlement, minimizing manual workload and associated costs. AI-powered algorithms can analyze market trends and execute trades based on predefined parameters, further streamlining investment processes.
- Faster transactions: Algorithmic trading utilizes sophisticated algorithms to analyze market data, identify trading opportunities, and execute trades at high speeds. Blockchain technology, with its distributed ledger capabilities, facilitates faster trade settlement and reduces clearing times.
- Centralized opportunities: Fractional shares allow investors to purchase portions of high-valued companies, lowering the barrier to entry for smaller investors. Robo-advisors, powered by AI, provide automated investment management services based on individual risk tolerance and financial goals. Micro-investing platforms enable investment in small increments, making it easier for individuals to begin investing with limited capital.
Compliance Advantages:
- Modern financial management systems:
- Auto auditing: These systems employ continuous transaction monitoring (CTM) and automated compliance checks, utilizing machine learning algorithms to identify potential regulatory violations in real-time.
- Standardized data: They utilize standardized data formats like XBRL (eXtensible Business Reporting Language) to facilitate consistent reporting and regulatory compliance across different jurisdictions.
- Shared data: Secure data platforms based on APIs and blockchain technology enable secure and efficient data exchange between banks and regulators, streamlining reporting and compliance processes.
Easier Acquisition of New Customers:
- Simplified acquisition: Digital onboarding utilizes electronic Know Your Customer (eKYC) and identity verification processes through biometrics and facial recognition, reducing time and hassle for new customers. Cloud-based account opening allows individuals to open accounts online seamlessly, eliminating the need for physical branch visits.
- Instant online payments: Real-time payment systems like Faster Payments (UK) and Immediate Payments (Australia) facilitate instant bank transfers and bill payments, offering greater convenience and flexibility for customers.
- Benefits for various businesses: E-commerce platforms can integrate digital payment gateways for secure and efficient online transactions. Service providers can offer subscription models with automated recurring payments. Retailers can leverage mobile wallets and contactless payment options to provide a frictionless checkout experience for customers.
Business Innovation and Adaptability:
- Social channels, shopping portals, and mobile apps: Banks utilize social media marketing to engage customers, provide financial education, and offer targeted promotions. Shopping portals with integrated payment solutions allow customers to compare prices and complete purchases seamlessly. Mobile banking apps offer a convenient and personalized way for customers to manage their finances on the go.
- Symbiotic relationship: Banking digitization empowers businesses by offering:
- Open Banking APIs: These APIs allow businesses to integrate financial services like account aggregation and payment processing into their platforms, creating a more comprehensive experience for their customers. Open Banking fosters innovation by enabling collaboration between banks and FinTech companies to develop new and unique financial products and services.
- Data-driven insights: Banks can leverage anonymized and aggregated customer transaction data to provide businesses with valuable insights into customer behavior and spending habits. This data can be used to personalize marketing campaigns, optimize product offerings, and improve customer engagement.
Enhanced Security Measures:
- Customer data security: Banks prioritize security through:
- Sophisticated software development services: These services employ secure coding practices, penetration testing, and vulnerability management to identify and mitigate potential security risks.
- Robust encryption: Data is encrypted both at rest and in transit using industry-standard algorithms like AES (Advanced Encryption Standard).
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA): MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide more than just a password to log in, such as a one-time PIN or fingerprint scan.
Personalized Offerings:
- Shift towards personalized banking: Machine learning algorithms analyze vast customer datasets to:
- Customer segmentation: Group customers based on shared characteristics and financial behavior to identify distinct customer segments.
- Predictive modeling: Predict future customer needs and preferences, allowing banks to offer hyper-personalized financial products and services, such as recommending suitable investment opportunities or personalized loan offerings.
- Benefits for customers: Personalized offerings provide:
- Increased relevance: Customers receive recommendations and financial products that are tailored to their specific needs and goals.
- Improved financial well-being: Personalized guidance and tools can help customers make informed financial decisions and achieve their financial objectives.
How to Integrate Emerging Technologies for Digital Transformation in Banking?
Here are some additional and latest digital transformation solutions you can leverage for your business, beyond those already mentioned:
1. Internet of Things (IoT) and Edge Computing:
- Integration Points:
- Predictive Maintenance: Implement sensor-based IoT solutions to monitor the health and performance of equipment in real time, enabling predictive maintenance and preventing costly downtime. This involves integrating sensors with edge computing devices that process data locally and send only relevant information to the cloud for analysis.
- Smart Buildings and Facilities Management: Utilize IoT sensors to automate building operations, optimize energy consumption, and enhance security. This involves connecting sensors to building management systems and utilizing edge computing for real-time data processing and control decisions.
- Connected Products and Personalized Services: Develop connected products that collect data on usage patterns and customer preferences, allowing for personalized services and improved user experience. This involves integrating sensors with mobile applications and leveraging data analytics to gain insights into customer behavior.
2. Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR):
- Integration Points:
- Remote Collaboration and Training: Utilize AR/VR for immersive remote collaboration and training experiences, improving communication and knowledge transfer across geographically dispersed teams. This involves developing AR/VR applications that simulate real-world scenarios and facilitate interactive learning experiences.
- Product Visualization and Customer Engagement: Enhance customer engagement and product visualization by allowing users to interact with virtual replicas of products in an AR/VR environment. This can be applied to various industries, such as retail, furniture, and automotive, allowing customers to virtually try products before making purchasing decisions.
- Marketing and Sales Enablement: Utilize AR/VR for interactive marketing campaigns and sales presentations, providing customers with a more immersive and engaging experience with your products or services. This can be applied to showcase product features, offer virtual tours of locations, or conduct interactive product demonstrations.
3. Low-code/No-code Development Platforms:
- Integration Points:
- Citizen Development and Democratization of Innovation: Empower non-technical users to create simple applications and automation using low-code/no-code platforms, fostering innovation and agility within the organization. This can be used to develop internal tools, automate workflows, or create simple customer-facing applications without relying solely on professional developers.
- Rapid Prototyping and Proof-of-Concept Development: Accelerate the development cycle and test new ideas quickly using low-code/no-code platforms. This allows businesses to build prototypes and proof-of-concept applications faster and with fewer resources, facilitating informed decision-making about potential digital solutions.
- Process Automation and Workflow Management: Utilize low-code/no-code platforms to automate repetitive tasks and streamline workflows across different departments. This can improve efficiency, reduce human error, and free up valuable resources for other activities.
4. Open Banking and APIs:
- Integration Points:
- FinTech Integration and Ecosystem Development: Open your banking infrastructure through APIs, allowing secure data sharing with FinTech companies. This fosters innovation and collaboration, enabling you to offer new and improved financial services to your customers through FinTech solutions.
- Personalized Financial Management Tools: Partner with FinTech companies to integrate their personalized financial management tools into your offering. This empowers customers to track their finances, analyze spending patterns, and set financial goals, increasing customer engagement and loyalty.
5. Hyperautomation:
- Integration Points:
- Intelligent Automation: Move beyond RPA by implementing intelligent automation solutions that combine RPA with AI and Machine Learning. This allows for automating a wider range of tasks, including more complex and cognitive processes, improving efficiency and decision-making capabilities.
- Hyperconnected Processes: Utilize hyper-automation to create interconnected and automated workflows across various departments and functions. This fosters seamless data flow, eliminates information silos, and breaks down barriers for a more unified and efficient operation.
6. Cybersecurity Mesh Architecture:
- Integration Points:
- Decentralized Security: Implement a cybersecurity mesh architecture that distributes security controls across different points in the network, rather than relying on a centralized approach. This provides more granular control and greater resilience against cyberattacks, protecting your business and customer data more effectively.
- Zero Trust Security Model: Adopt a zero-trust security model that assumes no user or device is inherently trustworthy. This requires continuous authentication and authorization checks, regardless of a user’s location or device, enhancing access control and reducing security risks.
7. Conversational AI and Chatbots:
- Integration Points:
- Omnichannel Customer Support: Implement conversational AI and chatbots to offer 24/7 customer support across various channels, such as websites, mobile apps, and messaging platforms. This enhances user experience, reduces support costs, and provides a consistent and personalized experience for customers.
- Lead Generation and Sales Qualification: Utilize AI-powered chatbots to qualify leads, answer basic customer queries, and schedule appointments, freeing up sales representatives to focus on closing deals. This improves lead conversion rates and optimizes sales processes.
Case Study Digital Transformation in Banking: TPBank
The banking industry is experiencing a significant shift, driven by the increasing adoption of digital technologies. This digital transformation compels banks to modernize their operations, products, and customer experiences to remain competitive. This case study examines the successful digital transformation journey of TPBank, a Vietnamese bank, highlighting the key technical details, strategies, benefits, and challenges encountered.
Challenges Faced by TPBank:
- Legacy Infrastructure: TPBank, like many traditional banks, relied on outdated systems hindering efficiency and agility. These systems often lacked the scalability and flexibility needed to support the demands of a growing digital customer base.
- Shifting Customer Preferences: Customers increasingly demand convenient and personalized digital banking experiences. Traditional core banking systems often struggle to integrate with modern digital channels, leading to a disjointed customer experience.
- Competition from FinTech Startups: Agile FinTech companies posed a threat with innovative digital products and services. These startups often leveraged cloud-based technologies and modern APIs to deliver faster and more efficient banking experiences.
TPBank’s Digital Transformation Strategy:
TPBank placed the customer at the core of its strategy, focusing on understanding and meeting their evolving needs. This involved conducting customer journey mapping, user experience research, and leveraging data analytics to personalize offerings.
The bank invested in building a robust digital infrastructure, including:
- Core Banking Modernization: TPBank migrated its core banking system to a modern, cloud-based platform. This provided greater scalability, flexibility, and integration capabilities with other systems.
- Mobile Banking App and Online Banking Platform Development: TPBank developed user-friendly mobile and online banking platforms offering a wide range of features, such as account management, bill payments, money transfers, and investment options. These platforms were built using modern development frameworks and APIs to ensure a seamless user experience.
- Advanced Analytics and Artificial Intelligence (AI) Implementation: TPBank leveraged AI and machine learning to personalize customer experiences, detect fraudulent activities, and automate routine tasks.
Benefits Achieved:
TPBank witnessed a significant surge in its customer base, acquiring over 5 million new customers in 2021 alone, attributed largely to its digital offerings.
TPBank placed the customer at the core of its strategy, focusing on understanding and meeting their evolving needs. Nam Nguyen, CEO of TPBank, emphasized this customer-centric approach, stating, “We put the customer at the heart of everything we do,”.
- Core Banking Modernization: TPBank migrated its core banking system to a modern, cloud-based platform from Temenos. This platform boasts 99.99% uptime and serves over 3,000 banks globally, highlighting its scalability and reliability, according to information on the Temenos website.
- Mobile Banking App and Online Banking Platform Development: TPBank developed user-friendly mobile and online banking platforms offering a wide range of features. Over 5 million users downloaded the TPBank mobile banking app within the first year of its launch.
- Advanced Analytics and Artificial Intelligence (AI) Implementation: TPBank leveraged AI and machine learning to personalize experiences, detect fraud, and automate tasks. Nguyen emphasized their commitment to AI adoption, stating, “AI is transforming the banking industry, and we are committed to being at the forefront of this innovation”.
- Enhanced Profitability: The bank’s digital transformation efforts led to improved operational efficiency and cost reduction. TPBank became the most profitable bank in Vietnam based on return on average equity, demonstrating the financial success of their digital transformation journey, as reported by Thanh Nien Newspaper in 2023.
Conclusion
Digital transformation is reshaping the banking landscape, driving efficiency, innovation, and customer-centricity. By embracing digital technologies, banks can stay ahead of the curve, deliver superior experiences, and unlock new opportunities for growth and differentiation in an increasingly digital world.
Looking to Leverage Digital Transformation in Banking for Your Business?
Are you interested in exploring digital transformation opportunities in banking? IdeaUsher can help you from mobile app to web app development. Our team of experts specializes in crafting tailored solutions to meet your specific needs and objectives. Contact us today to learn more about how we can empower your digital transformation journey.
FAQs
Q1: What are the objectives of digital transformation in banking?
A1: The objectives of digital transformation in banking include enhancing customer experience, improving operational efficiency, increasing agility and innovation, expanding market reach, and ensuring regulatory compliance. By embracing digital technologies, banks aim to modernize their operations, products, and services to meet the evolving needs and expectations of customers in an increasingly digital world.
Q2: What are the benefits of digital transformation?
A2: Digital transformation in banking offers numerous benefits, including improved customer experience through convenient and personalized services, enhanced operational efficiency and cost savings through automation and digitization, increased revenue and market share by attracting new customers and expanding into new markets, and better risk management and compliance through data analytics and regulatory technology solutions.
Q3: What is the impact of digital banking services?
A3: Digital banking services have a significant impact on both customers and banks. For customers, digital banking provides convenience, accessibility, and flexibility in managing their finances, enabling them to perform transactions, access account information, and engage with banking services anytime, anywhere. For banks, digital banking drives cost savings, operational efficiency, and revenue growth, while also enabling them to better understand customer behavior and preferences through data analytics.
Q4: What are the factors affecting digital banking?
A4: Several factors influence the adoption and success of digital banking, including technological infrastructure and capabilities, regulatory environment and compliance requirements, cybersecurity and data privacy concerns, customer preferences and behavior, competition from fintech startups and non-bank players, and organizational culture and change management capabilities. Banks must navigate these factors effectively to drive successful digital banking initiatives and remain competitive in the digital age.