- Traditional KYC
- Centralized KYC
- The Issues In Centralized KYC Systems
- How Can Blockchain Help In the KYC Process?
- Applications Of Blockchain In KYC
- Benefits Of Using Blockchain in the KYC Process
- How Does A KYC Blockchain Application Work?
- Advantages Of Blockchain Technology In The KYC Process
- Key Consideration In Implementing Blockchain-Based KYC Solution
- How To Implement Blockchain Technology In KYC?
- Required Tech Stack For Blockchain KYC
- 10 Use Cases Of KYC Implementation On Blockchain
- Conclusion
- How Idea Usher Can Help?
- FAQ

Financial institutions rely heavily on Know Your Customer (KYC) processes to combat money laundering. The global e-KYC market is booming, expected to reach a staggering $1.57 billion by 2027, reflecting the industry’s focus on KYC.
However, despite these investments, traditional KYC processes remain riddled with inefficiencies. They often prioritize data collection, leaving limited resources for crucial tasks like risk assessment and ongoing monitoring. This imbalance, coupled with the tedious and repetitive nature of KYC, creates a frustrating experience for both institutions and customers.
Enter blockchain technology, a potential game-changer for KYC. This blog dives deep into blockchain KYC, exploring its significance, functionalities, and implementation. We’ll uncover how blockchain can transform and secure KYC processes, addressing current challenges and paving the way for a smoother, more customer-centric approach.
- Traditional KYC
- Centralized KYC
- The Issues In Centralized KYC Systems
- How Can Blockchain Help In the KYC Process?
- Applications Of Blockchain In KYC
- Benefits Of Using Blockchain in the KYC Process
- How Does A KYC Blockchain Application Work?
- Advantages Of Blockchain Technology In The KYC Process
- Key Consideration In Implementing Blockchain-Based KYC Solution
- How To Implement Blockchain Technology In KYC?
- Required Tech Stack For Blockchain KYC
- 10 Use Cases Of KYC Implementation On Blockchain
- Conclusion
- How Idea Usher Can Help?
- FAQ
Traditional KYC
Traditional KYC refers to the standard procedure used by financial institutions and other organizations to verify the identity of their clients or customers. The primary goal of traditional KYC is to ensure that individuals engaging in financial transactions or accessing certain services are who they claim to be, thereby mitigating the risk of fraud, money laundering, and other illicit activities.
The traditional KYC process typically involves three main elements:
1. ID Verification (IDV)
This includes verifying the identity of an individual through the submission of original documents, scanned copies, or photographs. The documents may include passports, birth certificates, social security cards, or driver’s licenses. The verification process may involve a superficial check, and in some cases, documents are cross-referenced with databases, such as credit history databases.
2. Client Identification Program (CIP)
Organizations implement various means to check documents against state and corporate blacklists. The methods can vary, ranging from analyzing documents to utilizing fingerprints or facial scans. There is no standardized approach, and organizations choose the means of control based on their capabilities and jurisdictional requirements.
3. Video Identification
Some traditional KYC processes incorporate video identification methods, such as video calls through platforms like Zoom, Skype, etc. This is an attempt to address the challenge of remote identification.
One of the key drawbacks of traditional KYC is its decentralized nature, where each organization or government agency independently conducts identity verification. This leads to redundancy, increased time and resource consumption, and potential security risks as personal data is transferred at each verification point, susceptible to interception or hacking. Thus, new-day technology has prompted a reconsideration of traditional KYC methods in favor of more streamlined and secure digital identity verification processes.
Centralized KYC
Central Know Your Customer (CKYC), an initiative established by the Government of India, redefines the KYC process. This centralized repository ensures that once an individual completes the KYC process with a financial entity, be it a bank, mutual fund, or insurance company, there’s no need for redundant processes. CKYC stands out by consolidating all KYC data onto a unified platform.
CKYC serves as a defense against financial fraud, including money laundering and unauthorized fund usage. Its centralized nature enhances oversight and control. Financial institutions reap the benefits of streamlined operations as CKYC eliminates the redundancy of KYC processes. This not only reduces operational costs but also eases the burden of document maintenance. CKYC introduces a revolutionary concept — a single KYC applicable across various financial services. This simplifies the customer experience and accelerates service accessibility.
The Issues In Centralized KYC Systems
Centralized KYC systems, while designed to enhance identity verification, struggle with significant challenges that impact their effectiveness. A critical analysis of these limitations reveals the need for innovative solutions in financial security. Here are the limitations:
1. Lack of Standardization
Navigating through repetitive KYC processes becomes a hassle for users due to the absence of standardized procedures. Each bank or financial service provider operates with unique specifications, requiring users to adapt to varying requirements during the KYC process. This lack of uniformity not only consumes more time and effort for users but also adds complexity to the overall experience.
2. Enclosed Data Silos
The confined nature of centralized KYC systems creates isolated data silos, hindering Financial Institutions (FIs) from obtaining a comprehensive view of consumer expenses across different platforms. This fragmented data limits FIs’ ability to fully understand customer financial behaviors, resulting in incomplete insights that may impact decision-making and risk assessment.
3. Fraudulent Data Misidentification
The inherent structure of centralized systems makes them susceptible to misidentifying fraudulent data, compromising the accuracy of identity verification processes. The lack of flexibility in adapting to evolving fraud techniques may lead to false positives or negatives, raising concerns about the system’s reliability and effectiveness in detecting fraudulent activities.
4. Customer Tracking Challenges
Seamlessly tracking customers across various platforms poses a substantial issue for centralized KYC systems. The inability to follow customers efficiently across different services and institutions creates gaps in understanding customer behavior and interactions. This limitation may impact the system’s ability to provide a comprehensive and accurate overview of customer activities.
5. Risk of Fake Data Entry
Users pose a risk by entering falsified information into the system, challenging the integrity of the KYC process. The centralized model’s susceptibility to inaccurate data entry raises concerns about the reliability and authenticity of the information collected during the KYC process. Ensuring the accuracy of entered data becomes crucial for maintaining the effectiveness of identity verification.
6. Processing Time Inefficiencies
The centralized model often leads to delays in KYC checks, contributing to inefficient processing times. Complicated processes within the centralized KYC model can result in extended waiting periods for users, potentially impacting their experience and the overall efficiency of the verification system. Simplifying these processes is essential for improving efficiency and enhancing the user experience.
These challenges not only escalate the costs associated with KYC processes but also contribute to an upswing in money laundering instances.
How Can Blockchain Help In the KYC Process?
Blockchain technology within the banking sector offers innovative models for both intra- and inter-bank verification and update processes.
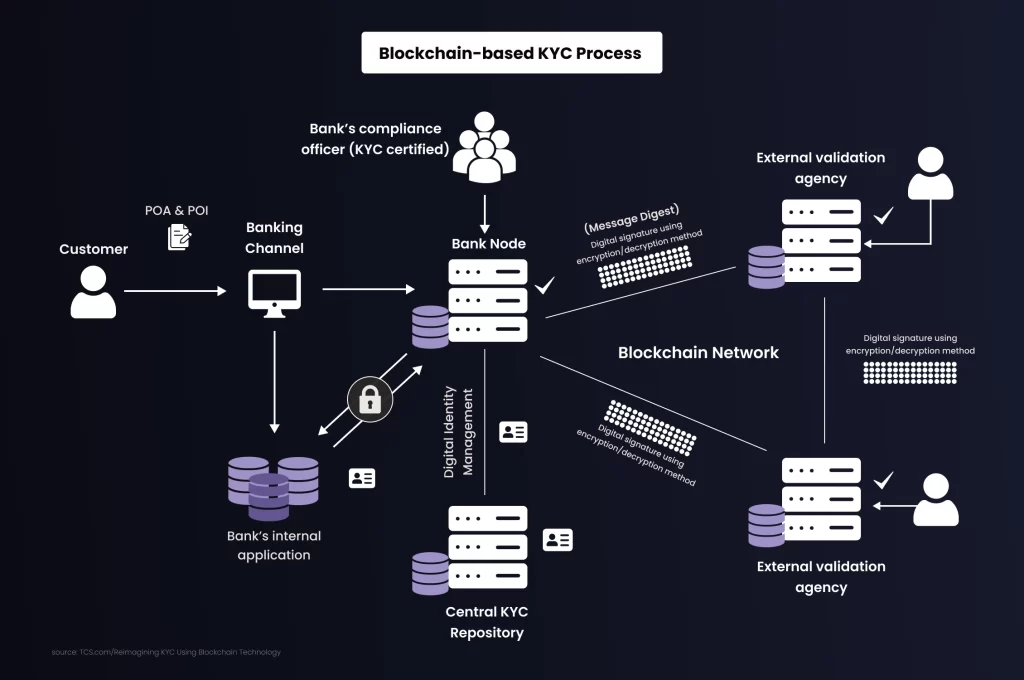
1. Intra-Bank Applications
Banks can use blockchain technology to deploy powerful intra-bank applications within their banking groups. This approach drastically reduces the time and effort expended in repetitive effort. When a new service request necessitates additional customer information that is not available in the ledger, the model empowers the bank to seamlessly update the ledger. External agencies then revalidate the updated information, essentially translating into a streamlined re-KYC process.
2. Inter-Bank Applications
In inter-bank applications, participating banks collaborate to establish a consensus on the validation process, building trust and integrity. Bank A takes on the role of the originating bank, conducting the initial KYC verification for a customer. When the customer engages with Bank B for services, Bank B can securely request and receive KYC documents from Bank A through the blockchain platform. This ensures a secure inter-bank document transfer mechanism, enhancing overall process efficiency, standardizing KYC processes, and facilitating near-real-time customer validations.
3. Centralized Blockchain-Based KYC
Another groundbreaking approach involves linking banks to a centralized KYC repository, similar to the existing KYC registry system. In this setup, customer data and documents find a place in the distributed ledger. The bank conducting the KYC process stores all relevant details and generates a unique KYC number. When another bank seeks to perform due diligence on the same customer, it can utilize the unique KYC number to access the central registry and seamlessly download comprehensive customer details.
Blockchain, through these dynamic models, not only addresses the challenges of redundancy and inefficiency in KYC processes but also introduces trust, security, and streamlined collaboration among financial institutions. The adoption of blockchain technology represents a pivotal step toward redefining how banks approach and execute KYC procedures, promising a future of heightened efficiency and enhanced customer experiences.
Applications Of Blockchain In KYC
In the Know Your Customer (KYC) process, blockchain offers diverse applications that redefine identity verification, data security, and financial services. Here are some of the applications of blockchain in KYC:
1. Identity Verification
Blockchain KYC utilizes a secure digital ledger to verify identities, streamline cross-border payments, and enhance fraud prevention, ensuring a secure and transparent identity validation process.
2. Data Security and Protection
Blockchain KYC stands out for its robust data security. Access to data is restricted to authorized parties, providing effective safeguards for sensitive information.
3. Financial Services Integration
KYC guidelines in financial services align with broader Anti-Money Laundering (AML) policies, emphasizing identity verification, suitability assessment, and risk management.
4. Anti-Money Laundering (AML) Policy
The KYC process plays a pivotal role in comprehensive Anti-Money Laundering (AML) policies adopted by financial institutions.
5. Electronic KYC (e-KYC)
Governments globally are digitizing KYC processes through e-KYC, enhancing convenience and transparency in the verification process.
6. Banking System Integration
Banks can choose private or public blockchains for KYC operations, offering tailored solutions for enhanced efficiency.
Benefits Of Using Blockchain in the KYC Process
Blockchain technology in Know Your Customer (KYC) offers a multitude of benefits that reshape the traditional KYC paradigm. Here are the distinctive advantages that lead Blockchain to the forefront of KYC innovation:
1. Enhanced Data Quality
Blockchain ensures the integrity of KYC data by tracking and monitoring all alterations in real-time. This transparency safeguards data quality and authenticity, setting a new standard for reliability.
2. Accelerated Turnaround Time
Financial Institutions (FIs) gain direct access to KYC data through Blockchain software solutions, streamlining data gathering and processing. The result is a significantly lowered turnaround time, expediting customer onboarding.
3. Streamlined Processes, Reduced Manual Labor
By eliminating paperwork from the KYC process, Blockchain reduces the need for manual labor. This streamlining enhances operational efficiency, allowing institutions to focus resources on value-driven tasks.
4. Operational Efficiency Amplified
Blockchain’s impact extends to the early stages of the KYC procedure, speeding up onboarding processes and diminishing KYC and regulatory compliance costs. This operational efficiency translates into a more agile and cost-effective workflow.
5. Immutable Security
The immutable and unchangeable nature of records in the Blockchain makes fraud almost impossible. Security is elevated to unprecedented levels, instilling confidence in KYC processes.
6. Redundancy Eliminated
Blockchain facilitates the sharing of KYC information among financial institutions, eliminating redundancy. Customers no longer need to undergo the KYC process with each institution they engage with, enhancing convenience.
7. Standardized Processes
Blockchain’s standardization capabilities bring uniformity to KYC processes, reducing the likelihood of errors. This standardization fosters efficiency and consistency across the KYC landscape.
8. Unique Identification Solutions
In regions lacking a system for unique documented identification, Blockchain steps in by providing a unique identification for each individual. This feature is particularly valuable, as it addresses identity challenges in various jurisdictions.
How Does A KYC Blockchain Application Work?
Adding Blockchain technology to the KYC process brings a big change, making it more efficient and secure. Here are the detailed steps of this transformation:
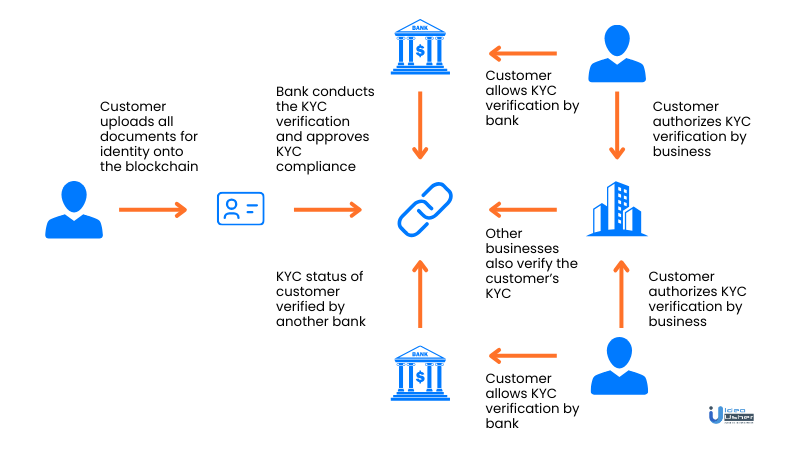
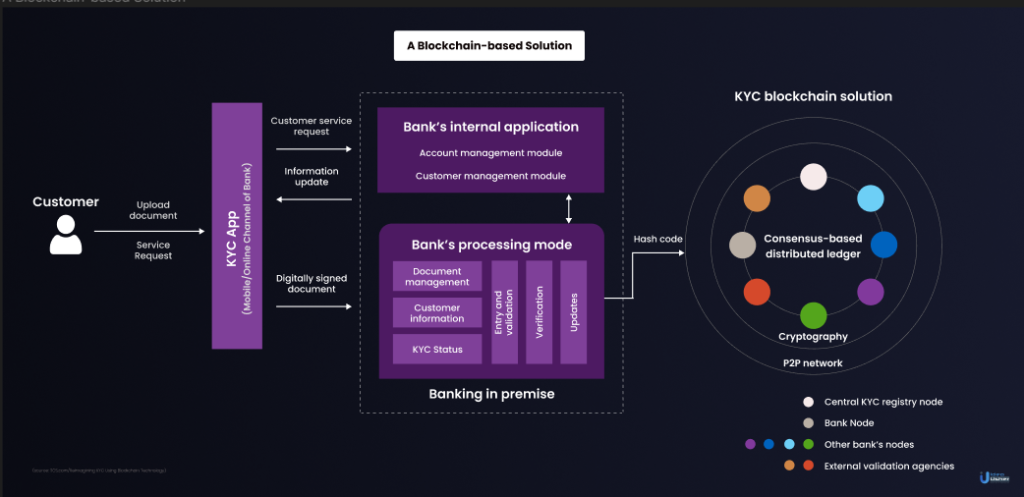
Step 1: Building a Secure Profile
Users initiate the KYC process by constructing a profile on the KYC Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) system. Financial Institutions (FIs) deploy a cutting-edge Blockchain-based KYC platform, streamlining the one-time setup with user identity documents. The uploaded data, stored through various options like a centralized, encrypted server, FIs’ private server, or the DLT platform, becomes accessible for verification purposes.
Step 2: Transactional Transparency with Financial Institutions 1 (FI1)
As users engage in transactions with FI1, they grant access to their profile. FI1 meticulously verifies KYC data, saves a copy on their server, and uploads a ‘Hash function’ on the DLT platform. The KYC digital copies, embedded with a matching Hash Function, ensure data integrity. Any attempt to alter KYC data triggers alerts across the blockchain, maintaining a vigilant network of financial institutions.
Step 3: Seamless Interactions with Financial Institutions 2 (FI2)
When users perform KYC for FI2, access is granted to their profile. FI1’s review of the KYC data and its Hash Function ensures consistency. Matching Hash Functions signify uniformity, while discrepancies prompt FI2 to manually validate KYC documents, ensuring accuracy and reliability.
Adaptive Changes and Smart Contracts
In the cases where users update their documents, smart contracts come into play. As users submit new documents to FI1, smart contracts automatically broadcast changes across the blockchain, employing a new Hash Function. This decentralized approach ensures swift updates, enhancing accessibility for all participating FIs.
Advantages Of Blockchain Technology In The KYC Process
The desire for blockchain adoption among financial firms has been notable for securities cleansing and settlement. However, the decentralized technology extends beyond routine fintech applications. Blockchain’s integration into Know Your Customer (KYC) processes presents an opportunity to improve transparency, collaboration, and efficiency within regulated sectors.
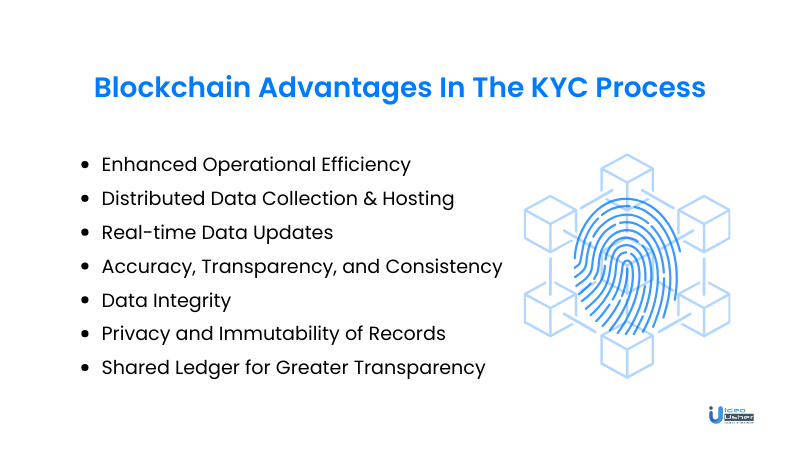
1. Enhanced Operational Efficiency
Leveraging scalable digital processes and secure user information sharing on a permissioned network, blockchain significantly diminishes the time and effort demanded in the initial stages of KYC. This streamlined approach reduces the customer onboarding process duration and cuts down regulatory and compliance costs.
2. Distributed Data Collection & Hosting
Blockchain’s influence in KYC establishes a decentralized system for data accessible only to authorized parties. Granting users control over data access ensures security, eliminating instances of unauthorized entry.
3. Real-time Data Updates
KYC transactions, when completed by a Financial Institution (FI), trigger real-time updates on a distributed ledger. This system empowers other participating institutions with access to dynamically updated information, coupled with notifications for any document additions or modifications.
4. Accuracy, Transparency, and Consistency
KYC Blockchain systems introduce transparency and immutability, empowering FIs to validate data and its trustworthiness on the Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) platform. This decentralized KYC process facilitates secure and timely access to updated user data, minimizing the time and effort required for information gathering.
5. Data Integrity
Blockchain employs cryptographic techniques to secure and validate data changes in real-time. Each block in the chain contains a unique identifier (hash) of the previous block, creating a secure and tamper-evident record. This ensures that any alteration to the data is immediately detected and can be traced back to its source.
6. Privacy and Immutability of Records
Blockchain’s decentralized and cryptographic nature ensures that once data is added to the blockchain, it becomes tamper-resistant and immutable. Private user data is stored securely, and the cryptographic hashes prevent unauthorized access or alterations. This not only enhances user privacy but also establishes a reliable and unchangeable record of each user’s KYC information.
7. Shared Ledger for Greater Transparency
The shared ledger architecture of Blockchain allows all authorized participants in the network to view transactions in real-time. This transparency promotes trust among financial institutions and regulatory bodies. Smart contracts, self-executing contracts with coded rules, further enhance transparency by automating certain KYC processes, ensuring adherence to predefined rules without the need for intermediaries.
8. Streamlined Compliance and Cost Savings
Blockchain’s immutable and transparent nature simplifies compliance processes. Auditors and regulatory bodies can efficiently verify transactions and ensure adherence to compliance standards. Smart contracts play a crucial role in automating compliance checks, reducing the need for manual intervention. The efficiency gains from streamlined compliance not only ensure adherence to regulations but also result in substantial cost savings for financial institutions.
Key Consideration In Implementing Blockchain-Based KYC Solution
Implementing blockchain-based Know Your Customer (KYC) solutions requires careful consideration of key factors to ensure optimal performance and adherence to industry standards. Here are essential considerations for organizations looking to adopt best practices:
1. Decentralized Identity Solutions
Exploring decentralized identity solutions on the blockchain is basic. These solutions enhance privacy, security, and customer control over sensitive information. Consider adopting a self-sovereign identity system for a more secure and streamlined KYC process.
2. Regulatory Compliance
Ensuring compliance with regulations such as GDPR and AML/KYC laws is paramount. Alignment with these standards not only ensures legal soundness but also builds trust and credibility in the regulatory landscape.
3. Collaborate with Industry Partners
Collaboration with industry partners is crucial for standardizing blockchain-based KYC solutions. This cooperative approach facilitates knowledge sharing and resource pooling, enhancing the overall effectiveness of the KYC process.
4. Smart Contracts Integration
Integrating smart contracts automates aspects of the KYC process, reducing human error and ensuring strict adherence to predefined rules. This step brings efficiency and reliability to the KYC verification process.
5. Data Security
Security is a top priority. Employ robust security measures, including encryption, to safeguard sensitive customer information. This approach prevents unauthorized access and potential data breaches, instilling confidence in the security of the KYC process.
6. Focus on User Experience
While improving security and efficiency is important, organizations must prioritize a positive user experience. Designing a simple and intuitive user interface ensures that the KYC process is user-friendly, minimizing the burden on customers and increasing overall satisfaction.
How To Implement Blockchain Technology In KYC?
We consulted our experts to offer insights on the implementation of blockchain technology in the KYC process and the value that a dynamic Blockchain development company like Idea Usher can bring to your organization.
1. Smart Blockchain Development
In this phase, we’re building applications using blockchain technology. The focus is on creating a decentralized, secure system for handling KYC data. As blockchain developers, we dive into the intricacies of blockchain architecture, ensuring data integrity and security through distributed ledger technology.
2. Integration with Existing Systems
Our role here is to seamlessly blend blockchain with existing KYC processes in financial institutions. This involves understanding APIs, data structures, and encryption methods. The goal is to enhance security, minimize redundancy, and boost operational efficiency without disrupting the current workflow.
3. Customized Solutions for Unique Needs
Each institution has distinct KYC requirements. As developers, we create blockchain applications to meet these specific needs. This involves understanding the unique workflows of different entities and creating flexible blockchain solutions that align with their individual demands.
4. Continuous Maintenance and Upgrades
Blockchain systems, like any technology, need regular maintenance. As developers, we engage in ongoing updates and enhancements, ensuring that the KYC solutions remain secure, efficient, and up-to-date. This includes addressing any vulnerabilities, optimizing performance, and integrating the latest blockchain advancements.
5. Ensuring Regulatory Compliance
Understanding the regulatory landscape is crucial. Here, we embed features into blockchain applications to guarantee compliance with regulations like GDPR and AML/KYC laws. This requires a deep understanding of legal frameworks and the ability to implement technical solutions that align with these regulations.
6. User-Centric Interface Design
Creating a user-friendly interface is a technical challenge, and thus, focusing on designing interfaces that are not only visually appealing but also intuitive for end-users. This involves employing UX/UI design principles and optimizing the interaction between users and the blockchain application.
Required Tech Stack For Blockchain KYC
The implementation of blockchain technology in KYC involves a specific tech stack. Here are some key components of the tech stack:
| Component | Examples |
| Blockchain Platforms | Ethereum, Hyperledger Fabric, Corda |
| Smart Contracts | Solidity (for Ethereum), Chaincode (for Hyperledger Fabric), Java/Kotlin (for Corda) |
| Decentralized Identity Solutions | uPort, Sovrin |
| Consensus Mechanisms | Proof of Work (Ethereum), Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (Hyperledger Fabric), Notary (Corda) |
| Data Encryption | AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), SHA-256 (Secure Hash Algorithm) |
| User Interface (UI) Development | React, Angular, Vue.js |
| Backend Development | Node.js, Python, Java |
| Database | MongoDB, PostgreSQL, CouchDB |
| Web3 Libraries | Web3.js (for Ethereum), Hyperledger Composer (for Hyperledger Fabric), |
| Integration Tools | Docker, Kubernetes |
| Security Auditing Tools | MythX (for Ethereum), Hyperledger Caliper (for Hyperledger Fabric) |
10 Use Cases Of KYC Implementation On Blockchain
Here are some cases where blockchain technology has been applied to the KYC process:
1. IBM Blockchain Trusted Identity
IBM’s Trusted Identity project integrates blockchain and artificial intelligence, adhering to the standards set by the Decentralized Identity Foundation and the World Wide Web. This decentralized platform aims to give individuals more control over their digital identity, allowing selective sharing and decentralized management. Currently, in the alpha stage, it serves as a foundational element for potential commercial solutions.
2. ASEAN Association Project
Led by OCBC Bank, HSBC Singapore, and MUFG, in collaboration with IMDA, the ASEAN Association Project pioneers the application of blockchain to KYC procedures in Southeast Asia. Leveraging IBM technologies, the project streamlines KYC processes, offering a corporate solution tailored to the banking sector.
3. uPort
Uport introduces an open identification infrastructure designed for user-friendliness and operates on the Ethereum blockchain. Users can create accounts, verify identities, request and send credentials, sign transactions, and securely manage keys through uPort’s mobile-centric platform.
4. Cambridge Blockchain
Cambridge Blockchain, recognized as the first blockchain startup invested in by PayPal, introduces a Digital Identity System. Operating under KYC regulations such as GDPR, the blockchain-based system ensures secure and compliant management of user data.
5. IBM, Deutsche Bank, HSBC, Cargill, and MUFG Collaboration
This collaborative effort focuses on establishing a secure, efficient, and decentralized mechanism for collecting, validating, storing, sharing, and refreshing KYC information. Aligned with the Monetary Authority of Singapore’s vision, the initiative enhances transparency in KYC processes performed by participating banks.
6. 26 French Companies
Limited information is available about the involvement of 26 French companies in a trial of an innovative Blockchain KYC procedure. The trial included collaboration with five banks, including BNP Paribas, emphasizing advancements in KYC practices.
7. HSBC
A global banking giant, HSBC embraces blockchain technology for its KYC process. The implementation signifies a commitment to enhancing efficiency and security in identity verification processes.
8. BNP Paribas
As the largest banking group in Europe, BNP Paribas participated in a trial of an innovative Blockchain KYC procedure. The trial aimed to explore the potential of blockchain in optimizing KYC practices.
9. Merehead
Merehead, a technology company specializing in fintech and blockchain, developed a blockchain solution for KYC applications. Offering services like product design and software development, Merehead contributes to the evolution of KYC processes through innovative blockchain solutions.
10. KYC-Chain
KYC-Chain provides a white-label B2B Ethereum solution designed for streamlined KYC processes. The platform designates “trusted custodians” responsible for checking, authorizing, and issuing digital documents. It supports basic KYC templates and sanctions checking.
Conclusion
The potential of blockchain technology to revolutionize the KYC process is evident, offering solutions to current inefficiencies and transforming it into a more secure and streamlined system. By utilizing blockchain’s distinct features like immutability, transparency, and decentralization, we can improve data integrity, minimize redundancy, and enhance the overall customer experience. Incorporating blockchain into KYC signifies more than a technological upgrade; it represents a strategic shift toward a resilient and efficient financial ecosystem. As we move deeper into this technology, it becomes apparent that blockchain KYC is not merely a possibility but an imminent reality in finance.
How Idea Usher Can Help?
With our expertise in developing blockchain and fintech projects, we can significantly enhance your business growth. We can help you implement blockchain technology in your KYC processes, making them more secure, efficient, and customer-friendly. Our advanced solutions can transform your data integrity, reduce redundancy, and improve customer experience. With our services, you can strategically move towards a more robust and efficient financial ecosystem. Whether you’re looking to upgrade your existing systems or build new ones, Idea Usher’s innovative solutions can pave the way for your business to thrive in the digital age. Let’s collaborate today!
Contact Idea Usher at [email protected]
FAQ
Q. What is Blockchain KYC?
Blockchain KYC involves utilizing a secure, public digital ledger to authenticate identity, facilitate cross-border payments, and prevent fraud. It ensures a decentralized and tamper-resistant record, offering heightened security and transparency in identity verification processes.
Q. How can Blockchain reshape outdated KYC processes?
Blockchain holds transformative potential for outdated KYC processes. Enabling efficient outsourcing and decentralization of personal data empowers individuals to maintain full control. This not only streamlines the KYC workflow but also enhances data security and user privacy.
Q. What are the problems with the current KYC system?
The way we currently check people’s identities in the financial system has some problems. It takes a lot of time and effort, there’s a risk of making mistakes, and we end up doing the same work more than once. This causes issues for both the banks and the people going through the process, making it less than ideal.
Q. How can Blockchain solve the issues with the current KYC system?
Blockchain technology effectively addresses challenges in the current KYC system by providing a decentralized, tamper-resistant ledger for personal data. This ensures data integrity, reduces redundancy, and minimizes the risk of errors, resulting in a more efficient and secure KYC process.
Q. What is the process of using Blockchain for KYC?
Applying Blockchain to KYC involves multiple stages within a Distributed Ledger Technology. From identity verification to data decentralization, each step utilizes the unique features of Blockchain to enhance the security, transparency, and efficiency of the KYC process.











Rebecca Lal