
Smart contracts are programs or snippets of code that are stored on a P2P network and run when a given set of conditions are satisfied. Smart contracts are generally used to replace or substitute the middlemen. It regulates the outcome of a situation based on parameters that are based on the participants’ inputs. This guarantees that there is no interference in the transaction and also keeps the process transparent for everybody.
Smart contracts allow transactions and agreements to take place among parties. Especially those who want to remain anonymous and do not want the involvement of centralized authority over it.
So now that you understand what is a smart contract in blockchain, let’s look at how it actually works, its benefits, applications and how it can be deployed.
How do Smart Contracts Work?
In the year 1994, Nick Szabo wrote the first smart contract. He was also the founder of a company called “Bit Gold”, this was 10 years before Bitcoin was first made. In fact, Szabo is often rumored to be the real Satoshi Nakamoto, the anonymous inventor of bitcoin, which he has denied.
In a smart contract, there are various terms and conditions which should be satisfied by the participants in order for the transaction to take place. There are various “if/then…when” rules and stipulations that need to be followed. These rules govern the outcome(s) of the contract. It should also consider all exceptions and define a framework accordingly.
Traditional Contract Vs. Smart Contracts:
Here is how a traditional contract works:
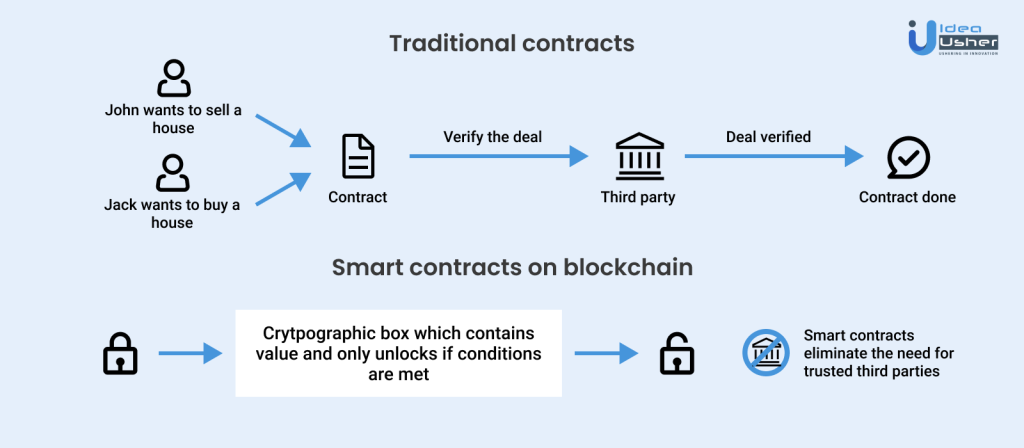
- Nature of a traditional contract: a traditional contract works in a fairly simple manner. Most of the time there are more than one party involved. A contract is established between them, with set terms and conditions and generally, a centralized authority keeps watch over it as a trusted third party.
- How it works: When the terms of the contract are satisfied it results in the necessary outcome. For example in the infographics shown above; it shows how John wants to sell his house, and Jack wants to buy one. The contract is set and watched over by a centralized authority like the Government, or the bank.
- Outcome: When the set conditions are met like the payment is made by Jack, John verifies the transaction. And then the ownership of the house is transferred to Jack.
- Vs. smart contract: Whereas this entire contract can be simplified by using blockchain technology. The terms can simply be uploaded into the contract and when the transaction is made by Jack, the exact amount of money enters John’s bank account from a given bank account. It acts as a trigger and transfers the ownership of the house to Jack. This eliminates the need for a third party to be involved.
The steps followed by the smart contract are as follows:
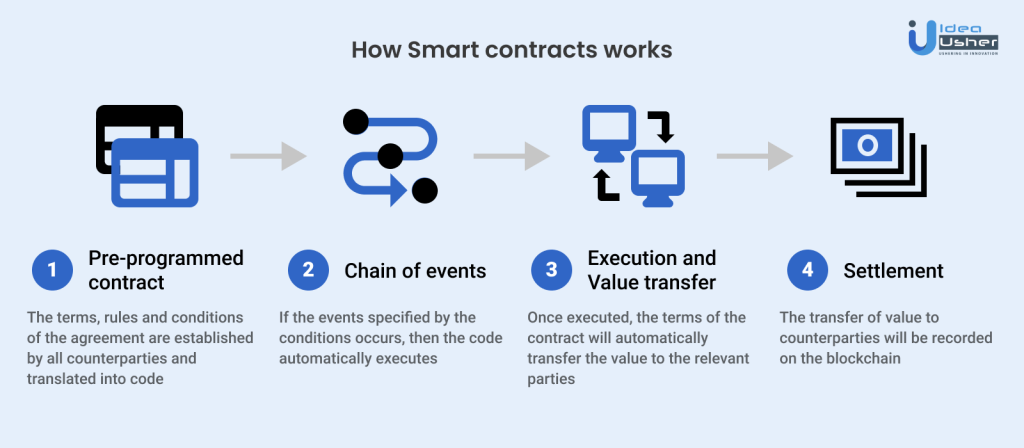
- Pre-defined Contract: The terms and conditions to be satisfied are uploaded in the contract.
- Events: The contract sets definite parameters, if the parameters are satisfied by the participants, it acts as a trigger of execution.
- Execution: The smart contract determines the outcome of the situation according to the parameters satisfied.
- Settlement: The settlement takes place between various parties involved in the contract.
The contracts need to be embedded in a particular P2P network which is generally the Ethereum network. ETH network is chosen because it has a lot of miners. This makes the network faster and more secure compared to bitcoin which has relatively fewer miners.
What are Proof-of-Work and Proof-of-Stake?
However other P2P networks are also used such as Polkadot, Cardano, Solana, etc. networks like Cardano are given preference because they use a proof-of-stake model rather than a proof-of-work model.
- Proof-of-work(PoW): Multiple computers compete with each other to solve a problem faster. The one who gets it done earlier wins and gets rewarded a small amount of the native currency, in this case, ETH.
- Proof-of-stake(PoS): This model allows the system with the most amount of the native currency to solve the problem. This makes sure that energy is spent more efficiently and also, everybody gets to participate at their own level.
Smart Contracts lie at the heart of Proof of Stake. The shift from PoW to PoS will make the trustworthy and secured code execution faster and more efficient. This is the reason why ETH is working on ETH 2.0 which will use a PoS model instead of a PoW model.
Benefits of Smart Contracts:
There are various benefits of a smart contract including and not limited to:
1. Speed, Efficiency, and Accuracy:
Smart contracts are executed immediately after the conditions are satisfied. There are no errors or hardcopy documents that need to be filed, recorded, or submitted. Everything is done digitally and recorded in the blockchain itself. This results in high speed, efficient processing, and 100% accuracy.
2. Trust and Transparency:
Since there are no middlemen involved in the process, the entire transaction remains transparent and the records are sent to every participant separately. There is no question of any authority or participant altering the records for their own benefit. This makes the process inherently trustworthy and transparent.
3. Security:
All transactions on the blockchain are recorded and encrypted. This makes the system incredibly hard to hack. Every single block on the blockchain is connected to the block previous to it. This requires the hackers to alter the entire chain in order to change a single record. Moreover, even if they are able to do that. The same record is kept in all the systems across the blockchain so, we can just restore the original copy by overwriting the corrupted one.
4. Savings:
Since there is no need for middlemen in a smart contract. This results in a lot of savings as intermediaries are often the most expensive part of the transaction.
Applications of Smart Contracts:
There are various applications of smart contracts, here are some of them:
1. International Payments:
International payments can be simplified and made more secure with the use of blockchain technology and smart contracts.
The use of smart contracts will definitely make it easier to liquidate assets, in return, making the traders and investors earn in a more efficient manner.
Since there is no paperwork involved the scope of errors becomes zero. Moreover, every single transaction is recorded in a transparent manner.
2. Supply Chain Management:
The efficiency of a supply chain can be improved drastically using smart contracts and blockchain technology. It can be used to track individual items in the supply chain with great visibility.
Using smart contracts will help in reducing theft and loss of items. And also cut down the cost of verification and tracking of items in the supply chain.
3. Insurance:
Smart contracts can help the insurance holders claim their policy in case they need to. The conditions of the policy will be uploaded on the contract. If the user satisfies all the terms. Their payment would be processed immediately.
This makes it easier for both the insurance company and the policyholder to verify/ claim the policy in case they need to.
How to Deploy Smart Contracts:
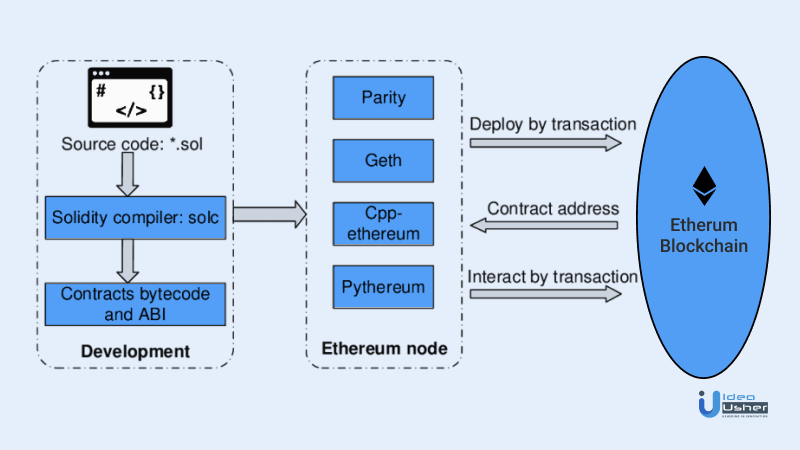
This infographic shows the exact procedure of deploying a smart contract. The source code is written by the blockchain developer. Which uses a solc compiler. Then the code is embedded into the ETH blockchain.
There are various components in the ETH node as well like Parity, Geth, Cpp-ethereum, Pyethereum, etc. Parity for example is an Ethereum client that is integrated directly into your web browser.
Conclusion:
Now that you understand what is a smart contract in blockchain and how they work, you must be convinced that they are an essential part of the future of our economy. It can provide a base for necessary automation and decentralization.
This also means faster international trade and the democratization of data. With the arrival of Web3.0, the metaverse, and the advent of blockchain technology. A decentralized future is almost certain. If you want to know more about blockchain you can click here.
FAQ Section:
1. Who writes smart contracts?
Nick Szabo was the first person to write a smart contract in 1994. Nowadays blockchain developers and programmers write smart contracts on the ETH network.
2. Which smart contract is the best?
ETH smart contracts are the best so far, however, there are others like Polkadot, Cardano, Solana, etc which are also substantially good.
3. Are smart contracts reversible?
No, smart contracts are irreversible.







Ronit Banerjee