- What is Proof of Work (PoW)?
- How did it Start?
- Proof of Work Examples
- What is Proof of Stake (PoS)?
- How Businesses are Adopting POS and POW?
- Growth Statistics
- What is the difference between mining and forging?
- Proof of Stake Examples
- Proof of Stake vs Proof of Work: The Adoption of Blockchain
- How did PoS rise?
- Proof of stake vs Proof of work: What's a hybrid?
- What are the major differences between PoV and PoS in blockchain?
- Takeaway: What's the answer to the future?
- FAQ

In this crypto world, you will often hear the phrase: proof of stake vs proof of work. But many people may not be sure what they mean. Let’s face it, the terminology is quite complicated, but with some basic explanations and tons of examples, it shouldn’t be too hard to build your own understanding.
To understand the difference between Proof of Work and Proof of Stake, you must first understand how blockchains work.
Blockchains are decentralized networks. Therefore, different computers are in charge of validating transactions instead of a central authority. We call this mechanism consensus, and it is usually done by Cryptographic algorithms such as SHA or Scrypt.
PoW and PoS are two blockchain consensus algorithms used in many blockchain technologies.
The two most popular cryptocurrencies that use these two blockchain systems are Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Well, PoW is proven and, therefore, has many advantages over POS; there is no doubt about it. However, speed is the best advantage of POS. You can accept payments from the public directly on your website or smartphone. But this comes at a price; you cannot control the chain, and thus, something may break if you make a mistake or are not attentive enough.
On the other hand, PoW offers you real-time monitoring of your network and transactions; if any problem arises involving stolen credit cards, it will be instantly detected and stopped before it gets into circulation.
But we cannot explain the two in just a sentence. Let’s break down the Proof of stake vs. Proof of work phrase and understand each of them separately.
- What is Proof of Work (PoW)?
- How did it Start?
- Proof of Work Examples
- What is Proof of Stake (PoS)?
- How Businesses are Adopting POS and POW?
- Growth Statistics
- What is the difference between mining and forging?
- Proof of Stake Examples
- Proof of Stake vs Proof of Work: The Adoption of Blockchain
- How did PoS rise?
- Proof of stake vs Proof of work: What’s a hybrid?
- What are the major differences between PoV and PoS in blockchain?
- Takeaway: What’s the answer to the future?
- FAQ
What is Proof of Work (PoW)?
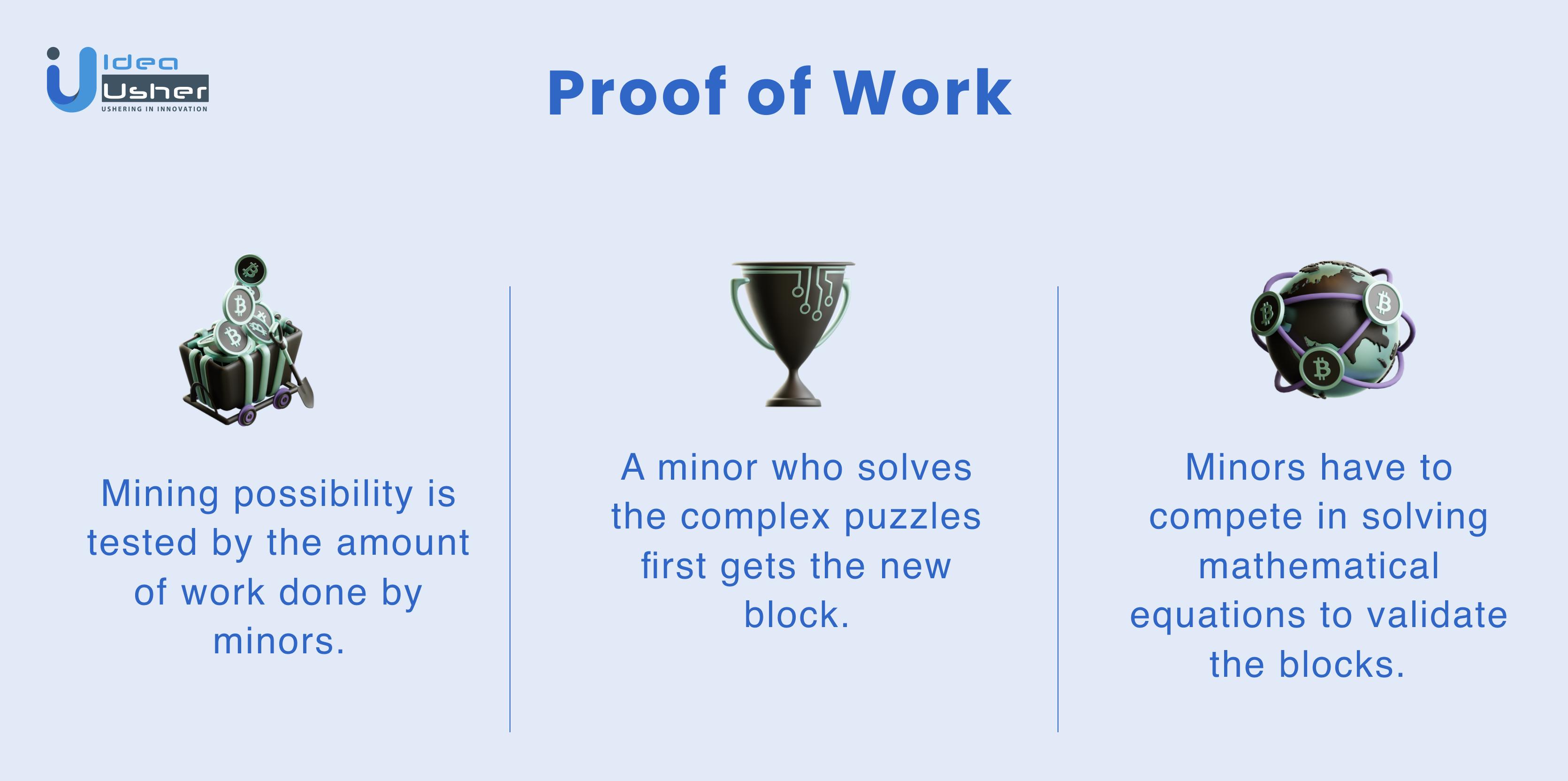
In a general sense, Proof of Work is a way to prove that you have done work. It’s used when someone asks for PoW in exchange for some service or exchange. There are many different kinds of proofs of work, but they all have one thing in common: they show somebody has performed some actions or calculated some data using the provided information.
How did it Start?
Ari Juels and Mark Jacobsson first coined the term ‘Proof of work’ in 1999. It was published in a document related to Bitcoin. In simple terms, it was a protocol designed to perform secure digital transactions without any need for third parties. It basically works with the puzzle-solving method. Minors compete in solving complex mathematical problems to generate new blocks or get new Bitcoins.
People often misunderstand Bitcoin as an immature and unstable currency system. They think it is a currency or a stock and, therefore, accept it as a form of payment without understanding that it is not. The precise relationship between Bitcoin and proof of work is something that people tend to get confused about.
So, let’s break it down: There is no fundamental relationship between Bitcoin and proof of work. Proof of Work is a method for selecting natural links among arbitrary data. That is exactly what Bitcoin does. It enables new ways to interact with the blockchain through its use as a data mover and shaper. In other words, Bitcoin does NOT replace proof of work but improves it.
Read more: How To Start Your Bitcoin Exchange app | Idea Usher
The definition of proof of work is something that someone can verify for themselves without the need for a third party to validate. This can be anytime someone puts work into a blockchain or on GitHub. Anyone can verify that a specific piece of software works by seeing how many other people are using it and providing feedback to the maintainers (the people who built the software).
You can submit requests to improve any software they use, whether they ask for a new feature or fix an existing one. This helps developers acquire gold stars for their projects and can be used as a competitive advantage if something gets patented (which it almost always does).
Proof of Work Examples
Proof of Work is an old and known method. Many fields utilize this method. Here are some of the examples:
Emails
An example of a ‘proof of work’ in an email is an attachment containing a lengthy piece of text. They use PoW to slow down the processing cycles. How? By providing hard mathematical problems to solve. This slow processing improves security. For example, spam emails.
A single ordinary computer can send millions of emails in a day at a fast speed. However, with spam emails, solving individual problems for each main could have a processing cost of $0.001/ mail. The huge cost of processing discourages people from sending bulk emails. In turn, it also reduces security issues.
Distributed Denial of Service Attack (DDoS)
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks have caused disruptions to websites and services. In this blog post, we’ll show you a proof of work (PoW) system that mitigates these attacks. A PoW is an algorithm that derives a set of collective solutions for a mathematical problem.
It acts as a kind of code farmer that solves problems in a distributed fashion so that a small number of participants can collectively solve larger problems. This system has been built and demonstrated in Google¹s Project Zero team and is now open source.
Proof of work is the process of obtaining a collective consensus on transactions conducted via computer programs. When a network of nodes blocks a transaction, it effectively creates a ‘guardian’ node and discards the attempted payment. Only the blockchain with that block includes the proof of work, which refers to the prior block on the network and identifies it as valid.
The DoS attacks are transmitted at high speed without needing any response from your side. PoW helps slow such attacks.
Cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrencies use Proof-of-work to mine new currencies. In blockchains, PoW gives miners a direct stake in the network and prevents double-spend attacks. By ensuring that a majority of new blocks include a sufficient number of headers, miners have a constant and predictable income. Since PoW is a consensus rule, PoW blocks contain a critical number of transactions called a Merkle root.
It is the original consensus algorithm that has been used by minors. Bitcoin users have largely been the main benefactors of this system. However, PoW consumes copious amounts of electricity by using land and CPUs. The PoW system is beneficial in many aspects of currency mining. But, bad for the environment. PoS was then introduced to cover PoW’s shortcomings.
What is Proof of Stake (PoS)?

PoS is short for proof of stake or stake block. What it means is a cryptographic proof-of-work system that establishes the legitimacy of blockchain networks. As the name suggests, PoS gives a stake to those who are actively using the blockchain ledger.
It prevents selfish mining and solves SHA256 exhaustion, which causes forgotten data in blocks to remain un-replayed for an extended period. Making a significant change in how information is stored and transferred safely within a cryptocurrency network. It relies on several technical solutions that are subject to change without notice.
Note: SHA256 is not some military code!
In fact, it is a member of the new SHA-2 cryptographic hash functions. The SHA abbreviation stands for Secure Hash Algorithm. It was first designed by the NSA (National Security Agency). Data encrypted with SHA256 flow one-way. Even supercomputers cannot trace the data back to the original data, making data super-secure.
In other words, Proof of stake is the process of rewarding miners without needing to own any actual hashing power. Instead of waiting for blocks to be mined, you stake your coins in the PoW blockchain and get paid in the staked coins when new blocks are found. When the reward for finding a block is lower than the cost of creating one, you can be assured that yours is the most likely to be included in a block. Thus rewarding miners without requiring them to have any centralized control over the network or exchange findings.
PoS is the process of incentivizing miners to create new coins by rewarding them with newly created currency. In a nutshell, it’s a way to incentivize miners to work on certain tasks without actually investing any resources in doing so. This allows us to work on projects without worrying about inflation or waiting for the blockchain to validate new transactions. This also means we can mine without worrying about connection issues, cheating devices, or other hacks that compromise your network security.
How Businesses are Adopting POS and POW?
Proof of Stake (PoS) and Proof of Work (PoW) are foundational consensus mechanisms within the realm of blockchain networks, shaping the landscape of Web 3.0. Their impacts on applications and businesses are substantial, as evidenced by the following key statistics and insights:
Proof of Work (PoW):
- PoW has historically served as the backbone of networks like Bitcoin, yet concerns regarding energy consumption and hardware upgrades have led to a decline in its popularity.
- Despite these challenges, PoW protocols are evolving to support Web 3.0 infrastructure, with active projects offering incentives to miners, contributing to the ecosystem’s growth.
Proof of Stake (PoS):
- PoS has emerged as a favored alternative due to its energy efficiency and scalability potential, finding adoption in major cryptocurrency projects such as Solana and Cardano.
- Ethereum’s transition to PoS through “The Merge” signifies a broader shift aimed at reducing carbon emissions and expanding adoption opportunities.
Adoption in Web 3.0:
- Web 3.0 businesses leverage both PoW and PoS to develop decentralized applications (dApps) and services, selecting consensus mechanisms based on factors like security, speed, and energy efficiency.
- The integration of these mechanisms into Web 3.0 fosters innovation in areas like decentralized finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and the metaverse.
Growth Statistics
the valuation of the global market for blockchain technology stood at USD 17.46 billion. Forecasts suggest an impressive expansion at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 87.7% from 2023 through 2030. This robust growth trajectory is fueled by the mounting necessity for transactions that are both secure and transparent across a multitude of industries. The blockchain framework, characterized by its decentralized and unchangeable ledger, guarantees both the integrity and clarity of transactional processes. This feature renders it highly attractive to critical sectors, including financial services, healthcare, and supply chain logistics. Consequently, enterprises operating within these spheres are progressively embracing blockchain methodologies to fortify security and enhance the transparency of their operational transactions.
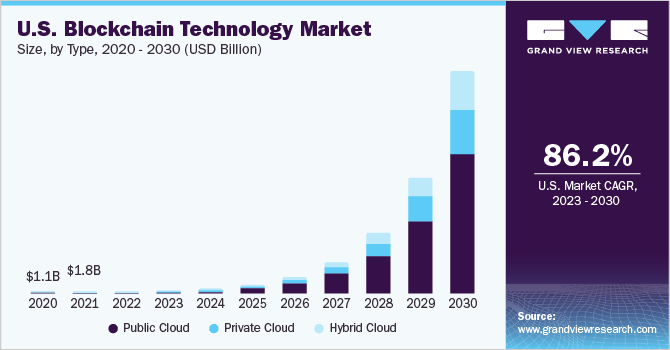
The proliferation of thousands of dApps across various blockchain networks reflects the robust adoption of PoW and PoS within the Web 3.0 ecosystem, fueling further expansion and innovation.
What is the difference between mining and forging?
We may use mining terminology while talking about PoS and PoW. But, when it comes to PoS, mining is not the exact method. ‘Mining’ does not happen in PoS. Forging occurs in a proof of stake system. Forging occurs when you get validation for a new block and earn a transaction fee for it.
So, the PoS blockchains need a minimum number of coins in your wallet to make transactions in the network. Once you have submitted the minimum amount of coins, the wallet freezes them. Next, the staking of the network happens. And if you are the next validator, you could stand a chance to earn the transaction fee.
Related read: How to create a crypto wallet app? | Idea Usher
Proof of Stake Examples
Proof of stake is the latest way of solving problems. However, unlike PoW, PoS is more focused on cryptocurrency mining solutions with fast speed and more security. PoW solved the complicated computational power that PoW requires. Let’s look at some examples of cryptocurrencies that use PoS:
Ethereum 2.0
Proof of stake is an Ethereum Improvement Proposal (EIP). Vitalik Buterin proposed it in 2016. The Ethereum community initially adopted it as a way to improve the performance of the network. It uses a modified version of the PoW algorithm called “sharding,” which cares more about holding onto hashing power and less about obtaining new nonce space cheaply.
As a side-effect, sharding also increases the number of transactions per second included in a block, reduces the time between block confirmation and payout, and increases carry chain security. It improves network decentralization by allowing any node on the network to validate the information contained in a block header without needing to be the owner of that data.
Tezos
The Tezos Network is a decentralized blockchain with an incentive mechanism built on top of it. This allows the network to reward validators with newly created tokens to secure and maintain the network. As more people join the system, their stakes are increased – incentivizing them to become active participants.
It is the perfect example of benefiting from the PoS system. The system also prevents holders from tampering with blockchain data or taking rewards away from participants without their consent. As a result, Tezos provides an elegant solution to cryptocurrency scalability while mitigating its risks.
Cosmos
If you thought blockchain was a dark period, wait until you hear about Cosmos. A blockchain company based in Colombia, Cosmos has successfully deployed a proof-of-stake (PoS) network for wider use than Bitcoin.
Cosmos is a cryptocurrency that aims to become the world’s first and biggest Proof of Stake (PoS) cryptocurrency. It is being developed by a team led by J. Paul Lang (a.k.a Jupiter bearing), who started the Ancora project.
In an interview with Forbes, CTO Marco Streng said his team’s work on Cosmos proves the viability of blockchain technology for everyday use. Though he didn’t disclose financials, he said he expects the network to be used by millions of people in the developing world who don’t have access to the banking system but are interested in moving money around.
Related Read: How to build a cryptocurrency exchange website? | Idea Usher
Proof of Stake vs Proof of Work: The Adoption of Blockchain

Technology is constantly changing our lives for the better. It is changing adoption rates and the buying experience, and it is even changing who we think should be using technology. Proof of stake vs. Proof of work did not become a debate until the latter came onto the scene. Yet, the crypto community has adopted both these systems in different ways.
The advent of mobile technology has fundamentally altered our relationship with technology. Whether you realize it or not, we are all more affected by mobile advertising now than ever before. Similarly, the way you perceive mobile advertising will directly impact whether or not you choose to use PoW or PoS adoption methods in your organization.
How did PoS rise?
Some of the old and well-established cryptocurrencies have adopted the proof of work system. Surprisingly, a tiny group of people in China have control over 50% of Bitcoins. So, you see, Proof of work is very well adopted in many countries. However, this centralization of crypto is unfair to other investors.
Proof of stake helps keep decentralized ethos in check and is also popular in vastly popular cryptos like Ethereum. The updated version of Ethereum has adopted the PoS system very well. But wait! Some cryptos are adopting hybrid systems. Read next about what the PoW/PoS hybrid system is.
Proof of stake vs Proof of work: What’s a hybrid?
Some kinds of blockchains combine both mechanisms to get the advantage of both. In fact, the primary objective of this hybrid mechanism is to combine the strengths of each system and cover the weaknesses that are identified.
Decred is one of the few cryptocurrencies that utilize this hybrid system to produce a robust consensus algorithm. Hopefully, many other cryptocurrencies will also lap up this new hybrid method in the future.
What are the major differences between PoV and PoS in blockchain?

Proof of Work (PoW) | Proof of Stake (PoS) |
| They don’t receive block rewards here. Instead, the network fee acts as a reward. | To add each blockchain, the minors have to compete in the puzzles, which are solved using computer processing power. |
| The new block validity in this is determined by the size of the stake (how many coins a person possesses) | Need only the initial investment in hardware. |
| Hackers would just need to have 51% of computational power to add malicious blocks. | Requires no competition as the user stake algorithm is used for choosing |
| The initial investment is made on two things: buying a stake and building a reputation. | Hackers need to own a minimum of 51%
Of cryptocurrency present on the network to get access ( Impossible to happen!) |
| Less energy-efficient and also less costly systems. More worked on and proven. | The newest ones are more energy-efficient and slightly more costly. They are new and, therefore, less proven systems. |
| Some specialized types of equipment are used to optimize the processing power of the system. | A very standard server-grade unit is more than enough for efficiency. |
| Bitcoin is the most popular example of a crypto that uses PoW consensus. The most used PoW function they use is SHA256. | So many new and well-known currencies use PoS, such as Tezos(XTZ), Cosmos(ATOM), and Cardano(ATA). |
| So many new and well-known currencies use PoS, like Tezos(XTZ), Cosmos(ATOM), and Cardano(ATA). | So many new and well-known currencies use PoS, such as Tezos(XTZ), Cosmos(ATOM), and Cardano(ATA). |
Also read: Which is better, Bitcoin vs Ethereum?
Takeaway: What’s the answer to the future?
PoW is the older and more secure system. POS is more expensive but may be available in your country. The recent crash of Bitcoin has thrown this debate into sharp relief. Is POS better than PoW? The answer is an unequivocal yes. While some argue that Bitcoin was doomed from the start due to its nature as a volatile exchange, others believe it is a diverse community with many opportunities to explore.
On the other side, the Proof of Work(PoW) system has also been proven to be one of the most secure ways of maintaining a distributed ledger. Thanks to the Proof of Work system, we can be confident that our Bitcoin will remain safely in our wallets until we are ready to spend it.
What do we conclude about each of them?
Proof of Work is the original and most secure method of validating transactions on a blockchain. Unfortunately, it is also the most expensive method. Proof-of-stake can be more easily implemented and, in some cases, may offer a better return than PoW. Both have their pros and cons.
Proof of stake is the new confirmed method; it is faster, less expensive, and more energy-efficient than the traditional PoW method. Proof of stake has a security risk, with a handful of owners trying to control a major portion of the network currency. However, with large and popular cryptocurrencies, the risk is negligible.
In conclusion, PoS is the latest trend, but that may not mean PoW will completely lose its power. It highly depends on the shift of trends in the crypto-community and the advancements made. And if you’re still stuck on the proof of stake vs proof of work debate (no worries, we will keep giving you more information!).
For more information on blockchain technology and how Idea Usher helps you with it, contact us.
FAQ
Q: Is proof of work better than proof of stake?
A: The superiority of proof of work (PoW) or proof of stake (PoS) depends on the specific use case and priorities of a blockchain network. PoW is praised for its security and proven track record, as demonstrated by Bitcoin’s resilience. It involves miners solving complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and secure the network. PoS, on the other hand, is lauded for its energy efficiency and scalability potential, as it doesn’t require the same computational power as PoW. Ultimately, the suitability of PoW or PoS depends on factors such as energy consumption, decentralization, security, and scalability needs.
Q: Which is more secure, proof of work or proof of stake?
A: The security of proof of work (PoW) versus proof of stake (PoS) is a subject of debate and depends on various factors. PoW is often considered more battle-tested and secure due to its extensive use in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, which has demonstrated resilience against attacks. PoS, however, can also achieve high levels of security through mechanisms such as slashing penalties and economic incentives to discourage malicious behavior. Both consensus mechanisms have their strengths and weaknesses, and the security of each ultimately relies on the design of the specific blockchain network implementing them.
Q: What are the downsides of proof of stake?
A: While proof of stake (PoS) offers advantages such as energy efficiency and scalability potential, it also has downsides. One major concern is the potential for centralization, as validators with more stake (wealth) have proportionally more influence over the consensus process. Additionally, PoS systems may face challenges related to initial coin distribution, as early adopters or large stakeholders may accumulate even more power over time. Moreover, PoS requires mechanisms to prevent or penalize malicious behavior, which can introduce complexities and potential vulnerabilities into the system.
Q: Which is better, PoS or PoW?
A: Determining whether proof of stake (PoS) or proof of work (PoW) is better depends on the specific needs and goals of a blockchain network. PoW is favored for its security and proven track record, particularly in the case of Bitcoin. It ensures network security through the expenditure of computational resources. However, PoW is criticized for its energy consumption and scalability limitations. PoS, on the other hand, offers potential advantages such as energy efficiency and scalability, but it may face challenges related to centralization and initial coin distribution. Ultimately, the choice between PoS and PoW depends on factors such as security, energy efficiency, scalability, and decentralization goals.