Health problems rarely present with clear warning signs. Often, they develop slowly between doctor visits, checkups, or missed follow-ups. People may sense that something is off, but without real-time data, it’s hard to pinpoint. This uncertainty can lead to anxiety and delay, making early intervention harder.
That’s why people started using health monitoring apps to track metrics such as heart rate, sleep patterns, blood pressure, glucose levels, and activity without waiting for a clinic visit. As wearables and smartphones became more common, individuals began monitoring their health regularly, gaining real-time insights into stress levels, hydration, and ECG readings.
Over the years, we’ve developed numerous health monitoring solutions that leverage AI-driven analytics and IoT-enabled devices. As we have this expertise, we’re sharing this blog to outline the key steps to develop a health monitoring app, including essential features and cost considerations. Let’s dive in!
What is a Health Monitoring App?
A health monitoring app is a digital tool that tracks and manages health metrics, including heart rate, physical activity, and sleep patterns. It collects data from wearable devices and sensors, processes it to provide real-time feedback, and securely stores it for long-term analysis.
These apps often offer personalized insights that help users improve their health and well-being, while enabling healthcare providers to monitor patient conditions remotely and facilitate timely interventions when necessary.
Key Features of a Health Monitoring App
Key features of a health monitoring app include real-time tracking of vital signs like heart rate, sleep, and activity levels. Users can log health metrics manually or sync with devices to monitor trends over time.
1. Personal Health Dashboard
The personal health dashboard is where users can quickly understand their daily health status by bringing together key metrics such as steps, heart rate, sleep, and calories in a clear visual format.
For example, the Apple Health app provides a simple, customizable dashboard where users can track all of their health data in one place, helping them stay aware of their overall well-being.
2. Activity and Fitness Tracking
Activity and fitness tracking lets users monitor how much they move during the day, automatically recording steps, distance, and active time using phone sensors or connected wearables.
The Fitbit app is a great example, letting users set daily step goals and track real-time progress, encouraging healthier movement habits.
3. Vital Signs and Health Data Logging
Vital signs and health data logging enable users to record measurements such as heart rate, blood pressure, glucose, and weight in one place. The MySugr app helps people with diabetes log their blood glucose levels and sync them with devices such as glucose meters, enabling them to understand trends and share data with their healthcare providers during medical visits.
4. Medication Reminders & Routine Management
Medication reminders help users consistently follow treatment schedules, with alerts for medications, dosages, and timing.
The Medisafe app is an example, providing users with timely reminders for medications and health routines such as blood pressure checks, reducing missed doses and supporting long-term care.
5. Symptom and Health Journal
The symptom and health journal lets users note how they feel each day, logging symptoms, mood changes, or triggers.
The CareClinic app allows users to log their symptoms, medications, and mood, aligning these with health data timelines and helping users and clinicians understand what happens between appointments.
6. Personalized Insights & Recommendations
Personalized insights turn collected data into meaningful guidance, such as highlighting better sleep after active days or flagging unusual readings early.
Sleep Cycle app, for example, offers personalized insights by analyzing sleep patterns and providing tips to improve sleep based on daily activity levels and sleep quality.
7. Reminders, Alerts, and Goal Tracking
Reminders, alerts, and goal tracking keep users engaged with their health plan by notifying them of tasks, appointments, and upcoming measurements.
The Garmin Connect app allows users to set health goals, such as increasing daily steps or improving sleep, and provides visual progress toward those goals, encouraging long-term habit building.
Key Market Takeaways for Health Monitoring Apps
Source: GrandViewResearch
The growing popularity of wearable devices, which can include smartwatches and fitness trackers, has further contributed to the growth of the health monitoring app market. These devices seamlessly integrate with apps to provide comprehensive data on physical activity, heart rate, sleep patterns, and other health metrics. For example, Fitbit and Garmin have formed partnerships with various health monitoring apps to offer integrated tracking solutions.
Other popular health monitoring apps include MyFitnessPal, Lose It!, Calm, and Headspace. These apps often partner with healthcare providers, insurance companies, and wearable device manufacturers to offer additional features and benefits. For instance, MyFitnessPal has partnered with Under Armour to provide integrated tracking and rewards, while Calm has partnered with healthcare providers to offer their app as a benefit to their employees.
Work with Ex-MAANG developers to build next-gen apps schedule your consultation now
Understanding the Business Model of Health Monitoring Apps
Let’s explore some popular revenue models for health monitoring apps,
1. Freemium Model
The Freemium Model offers a low barrier to entry by providing a basic version of the app for free. However, converting free users to paying subscribers can be challenging. MyFitnessPal is a prime example, offering a free version with limited features while enticing users to upgrade to Premium for personalized meal plans and macronutrient tracking. The Premium subscription starts at $7.99 per month.
2. Subscription Model
Subscription Model provides a consistent revenue stream by charging app users a recurring fee for access to the app’s full features. Fitbit Premium is a popular example, offering advanced analytics, coaching, and exclusive features. The Premium subscription costs $9.99 per month.
3. In-App Purchases
In-App Purchases offer flexibility by allowing users to purchase additional features or content as needed. Apple Health provides various in-app purchases, such as personalized health reports, which can cost $4.99.
4. Advertising
Advertising can also be a significant revenue source for apps with large user bases. Lose It! incorporates ads but offers an ad-free subscription option for $3.99 per month.
How Does a Health Monitoring App Work?
A health monitoring app collects data from sensors like heart rate monitors or accelerometers, processes it in real-time on your device, and securely transmits it to the cloud for analysis. Advanced algorithms then create insights by tracking patterns and anomalies in the data.
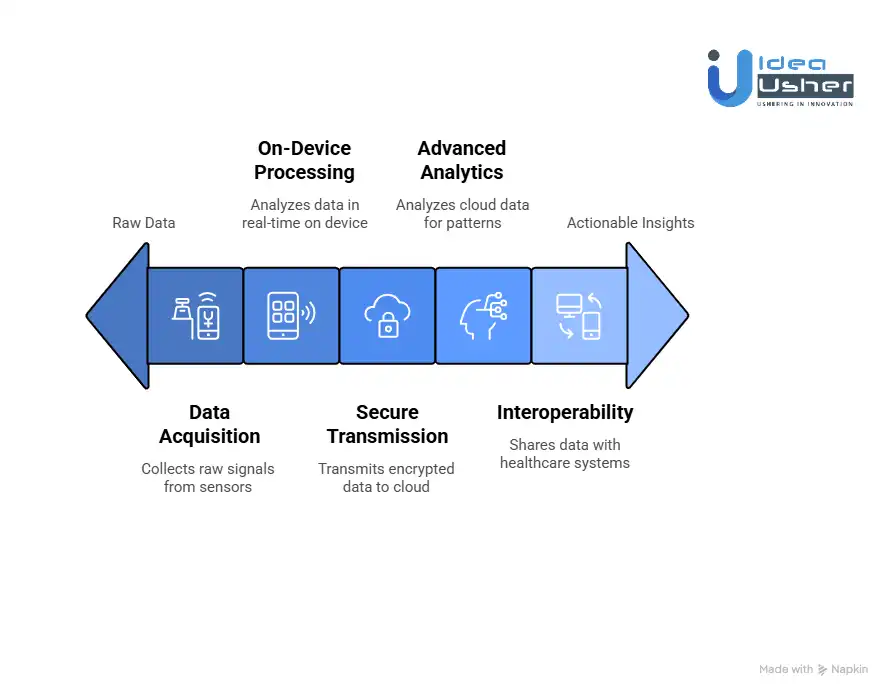
1. Data Acquisition & Validation
It starts with raw signals from the physical world.
The Hardware Link:
Your smartwatch’s optical heart rate sensor, also known as PPG, emits light into your skin and measures the reflected light modulated by blood flow. The accelerometer tracks micro movements. These sensors generate a continuous stream of raw data.
The First Technical Hurdle: Noise
This raw data is messy. A heart rate spike could be atrial fibrillation, or it could be you typing vigorously. This is where Sensor Fusion comes in. The app does not trust a single source.
It uses algorithms to cross-reference the heart rate with accelerometer data, including whether there was movement, skin temperature, and even time of day, to clean the signal and determine context. This step is what separates clinical-grade data from fitness tracker estimates.
2. On-Device Processing & Immediate Intelligence
Privacy by Design
For critical real-time alerts, speed and privacy are paramount. The data does not need to travel to a server.
Edge AI in Action:
Lightweight machine learning models built with frameworks like TensorFlow Lite or Core ML run directly on your smartphone or wearable. They analyze the cleaned sensor data in milliseconds.
Real World Example: Fall Detection
The on-device AI analyzes the accelerometer and gyroscope patterns. A specific sequence of acceleration forces followed by no movement triggers a high-confidence fall event.
The app can then immediately vibrate, sound an alarm asking for a response, and if none is given, automatically place a call to emergency contacts, all without the data ever leaving the device. This ensures zero latency and maximal privacy for sensitive events.
3. Secure Data Transmission & Cloud Storage
The Encrypted Journey
For long-term trend analysis and backups, data needs to be stored securely in the cloud.
The Secure Tunnel:
When your phone syncs, data is encrypted end-to-end using protocols like TLS 1.3 before it leaves your device. It travels through a secure tunnel to compliant cloud servers, such as AWS GovCloud or Google Cloud Platform, with a HIPAA BAA.
Structured for Meaning:
Here, the data is transformed from simple time series numbers into structured meaningful information. A raw number becomes:
{ “type”: “heart_rate”, “value”: 72, “unit”: “bpm”, “patient_id”: “xyz”, “timestamp”: “2026-01-31T10:30:00Z” }.
4. Advanced Analytics & Predictive Modeling
The Proactive Brain
This is where the app evolves from a tracker to a health guardian.
Cloud-Based AI: In the secure cloud, more powerful algorithms analyze aggregated and anonymized data. They look for patterns invisible to the human eye.
Creating Clinical Insight:
This AI builds a personalized baseline, often referred to as a digital twin, for the user.
It then performs anomaly detection. Instead of just showing “Your resting heart rate is 5 BPM higher today,”
it can correlate it with poor sleep data from the previous two nights and elevated stress markers to generate an insight such as “Your elevated resting heart rate may be linked to cumulative fatigue. Consider a recovery day.”
Predictive Triage:
In advanced systems, if the model detects patterns strongly associated with worsening heart failure, such as gradual weight increase from a smart scale combined with declining oxygen saturation and increased nocturnal heart rate, it can flag the patient for early proactive intervention from their care team. This may help prevent a hospital readmission.
Stage 5: Interoperability & Action
Data is powerless if it is trapped in an app. Its true value is realized when it reaches the right person at the right time.
Speaking the Language of Healthcare:
To share data with a doctor or hospital, the app uses the HL7 FHIR standard, also known as Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources. The backend acts as a translator, converting its internal data format into standardized FHIR resources, such as an Observation resource for a blood pressure reading.
Secure Clinical Integration:
Through a secure API, this FHIR data is sent to the hospital’s Electronic Health Record system. Now, the doctor can view the patient’s last 30 days of home vitals alongside lab results during a telehealth visit.
Consent Driven Sharing:
Crucially, all sharing is governed by granular, and user managed permissions. Using an OAuth 2.0-like framework, the patient can grant their cardiologist read-only access to heart data for three months without exposing mental health journal entries. The system enforces this by using short-lived, scoped access tokens.
Developing a Health Monitoring App: A Detailed Guide
To develop a health monitoring app, start by defining the medical conditions and health goals you want to track. Next, select reliable, FDA-cleared data-collection devices and integrate them with secure, compliant systems.
Over the years, we’ve successfully built a wide range of Health Monitoring Apps, and here’s the approach we take.
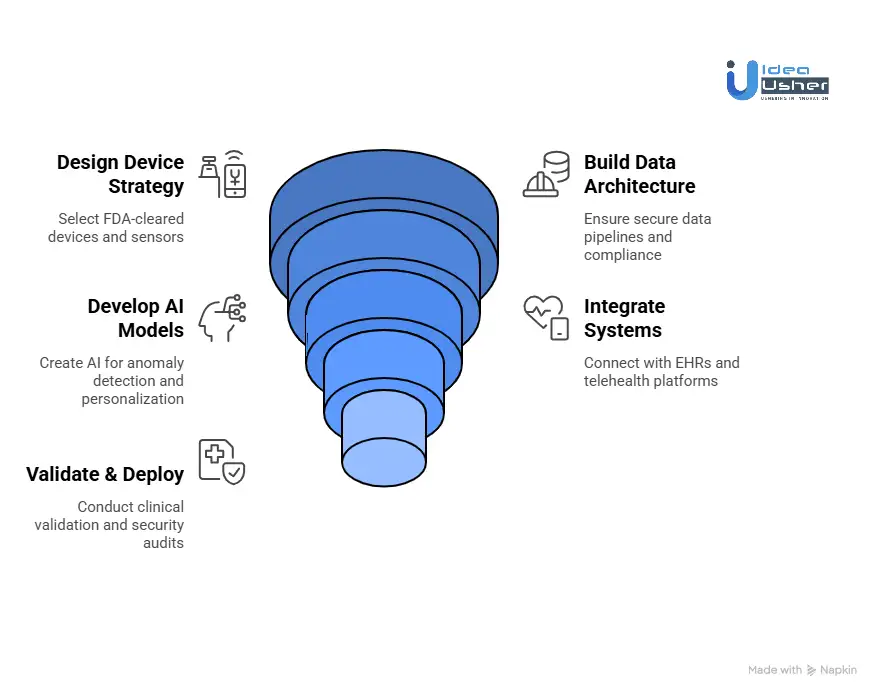
1. Define Use Case & Risks
We start by identifying the medical conditions the app will monitor and the health goals it aims to achieve. This includes setting alert thresholds and defining the escalation process for healthcare providers or caregivers. By understanding the clinical use case, we ensure the app is both functional and effective in meeting user needs.
2. Device Strategy Design
We select FDA-cleared or medical-grade devices and design a multi-sensor data collection strategy to ensure the app captures accurate health data from multiple devices, such as heart rate monitors and glucose meters. This helps us ensure the app collects precise, relevant health information for comprehensive monitoring.
3. Data Architecture & Compliance
Our team ensures secure data pipelines are in place and implements HIPAA, GDPR, and other healthcare regulations to protect user data and maintain compliance with industry standards. We prioritize both security and privacy to foster user trust and protect sensitive health information.
4. AI & Intelligence Development
We build AI models to detect anomalies in health data, personalizing health baselines for each user to deliver tailored alerts and recommendations aligned with their specific health needs. This allows us to deliver real-time, actionable insights to improve health outcomes.
5. System Integration
We integrate the app with existing healthcare systems, including EHRs and telehealth platforms, ensuring seamless data flow and providing healthcare providers with relevant information to improve decision-making. This integration enables seamless communication between the app and healthcare ecosystems, enhancing collaboration.
6. Validation & Deployment
Before launch, we conduct clinical validation and performance testing to ensure the app meets healthcare standards. Security audits are performed, and once ready, we deploy the app for real-world use with confidence in its performance and security. Our deployment process ensures the app is both reliable and ready for scaling.
Cost of Developing A Health Monitoring App
The cost of developing a health monitoring app largely depends on features compliance and data complexity. We follow a cost effective approach for our clients by aligning technical depth with real clinical value and long term scalability.
| Component | Cost Range | Scope |
| Research and Development | $2,000 – $8,000 | – NLP Model Selection: Choose an appropriate pre-trained model like BERT or GPT to avoid the need for training from scratch.- Data Acquisition: Basic data collection and preparation, including cleaning and labeling datasets.- Customization: Minor adjustments or fine-tuning to ensure the model meets the app’s requirements. |
| Front-End Development | $1,500 – $7,000 | – UI Design: Create a simple, intuitive user interface that allows users to interact with the NLP system, whether through text input or other forms.- Integration: Connect the front-end with the NLP backend for seamless processing of user requests and outputs. |
| Back-End Development | $3,000 – $15,000 | – Model Deployment: Deploy the selected NLP model on a cloud platform or local server.- API Development: Create APIs to facilitate communication between the front-end and the NLP model.- Data Management: Set up basic data storage solutions for handling user data and model interactions. |
| App Features | $2,000 – $20,000 per feature | – Text Analysis: Implement features like sentiment analysis or topic modeling.- Natural Language Generation (NLG): Simple features to generate short human-like text responses.- Speech Recognition/Synthesis: Basic real-time speech processing capabilities (if needed). |
| Testing and Quality Assurance | $1,000 – $4,000 | – Manual Testing: Test the app manually to identify bugs and issues in functionality and user experience.- Automated Testing: Implement basic automated testing to streamline quality checks, focusing on key NLP functions. |
| UI/UX Design | $500 – $3,000 | – User Experience (UX): Design a user journey that is easy to navigate and provides a smooth interaction with NLP features.- User Interface (UI): Focus on making the interface visually appealing, responsive, and consistent with the app’s branding. |
| Overall Cost Estimate | $10,000 – $100,000 | Total cost of developing the NLP app based on the complexity, features, and development scope. |
While the general factors influencing app development costs apply to health monitoring apps, several unique aspects can affect their specific cost:
Data Privacy and Security
Ensuring stringent measures to protect sensitive health data requires additional resources and expertise. Compliance with regulations like HIPAA or GDPR can increase development time and costs.
Integration with Medical Devices
Integrating with wearable devices, medical sensors, or other health-related hardware can introduce complexities and increase development time.
Algorithm Complexity
Developing accurate algorithms for data analysis, personalized recommendations, or predictive analytics can require specialized expertise and computational resources.
Regulatory Compliance
Adhering to healthcare-specific regulations, such as FDA clearance or CE marking, can involve additional documentation, testing, and certifications, increasing costs.
What Level of Data Accuracy Is Required for Health Monitoring Apps?
The required level of data accuracy for a health monitoring app depends on the decisions the app is intended to support. Wellness-focused apps typically use approximate data to show trends, while clinical monitoring apps must closely match validated medical devices.
Diagnostic apps should meet very high accuracy thresholds because users and clinicians may rely on them for urgent medical decisions.
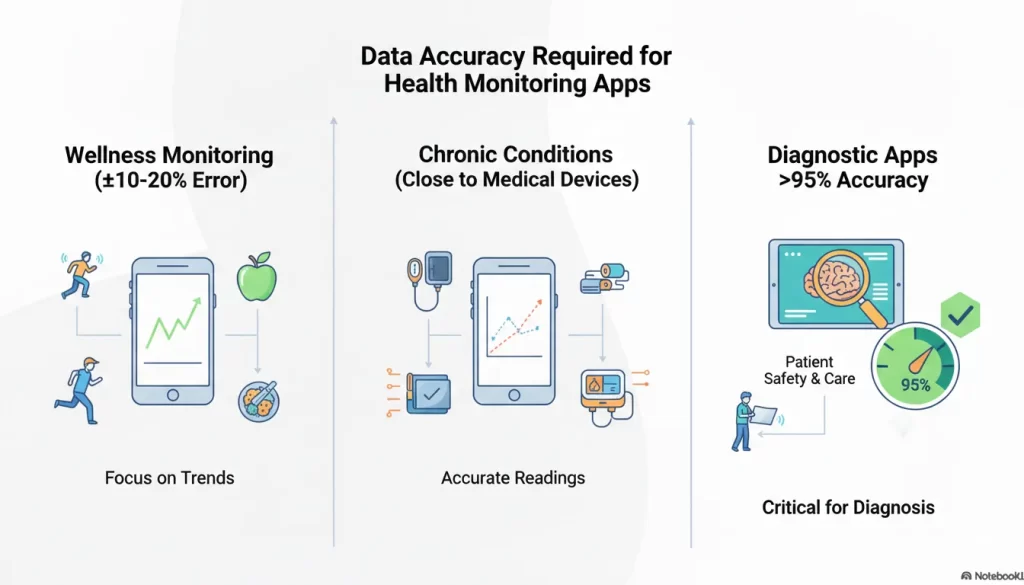
1. Wellness and Lifestyle Awareness
Accuracy Standard: ±10-20% margin of error is often acceptable.
What This Means: If the app shows 10,000 steps, the actual count could reasonably range from 8,000 to 12,000. A sleep stage analysis may align with clinical sleep studies at roughly sixty to seventy percent.
The Legal Shield
These apps must include clear disclaimers stating they are for wellness and informational purposes only and are not medical devices. Users generally understand that this data shows trends and patterns rather than precise clinical measurements.
Example App: Fitbit
Fitbit tracks activity, sleep trends, and general wellness insights. The data helps users understand habits over time and meets expectations for informational accuracy.
2. Chronic Condition Management
Accuracy Standard: Data must align closely with validated medical devices.
For Example,
- Blood Pressure: Should meet standards like the AAMI/ESH/ISO Universal Standard (mean error ≤5 mmHg, standard deviation ≤8 mmHg).
- Heart Rate/ECG: For atrial fibrillation detection, accuracy must match FDA-cleared pulse oximeters or ECG patches (sensitivity & specificity >90%).
The Regulatory Gate
This level typically requires FDA 510 (k) clearance or CE marking for a Class IIa or IIb medical device. You must demonstrate that your software output is as safe and effective as an existing predicate device.
Patients and clinicians may rely on this data to adjust treatment. An inaccurate glucose or blood pressure reading can directly lead to harmful decisions.
Example App: Omada Health
Omada Health supports chronic condition management, including diabetes and hypertension, with clinically validated devices and care programs. Its data helps guide treatment decisions.
3. Diagnostic and Acute Care
Accuracy Standard: This tier requires diagnostic-grade precision across the full Software-as-a-Medical-Device workflow, including sensors, algorithms, and decision logic.
- Key Metrics: High Sensitivity (correctly identifying those with the condition) and Specificity (correctly identifying those without it). Often targets are >95%.
- Validation: Requires large-scale clinical trials to prove statistical significance.
The Legal Responsibility
These products are fully regulated medical devices. FDA De Novo classification or Pre-Market Approval may be required, and liability exposure is substantial.
Users may seek urgent or emergency care based on app outputs. Accuracy at this level can directly affect patient outcomes and safety.
Example App: AliveCor Kardia
AliveCor Kardia provides FDA-cleared ECG analysis to detect conditions such as atrial fibrillation. The app delivers diagnostic-grade outputs for clinical follow-ups.
What Determines Whether an App Qualifies as a Medical Device?
A health monitoring app usually qualifies as a medical device when its intended use goes beyond general wellness and starts supporting diagnosis, treatment or disease prevention. Regulators will primarily assess the claims you make and how users or clinicians may rely on the output in real-world decisions.
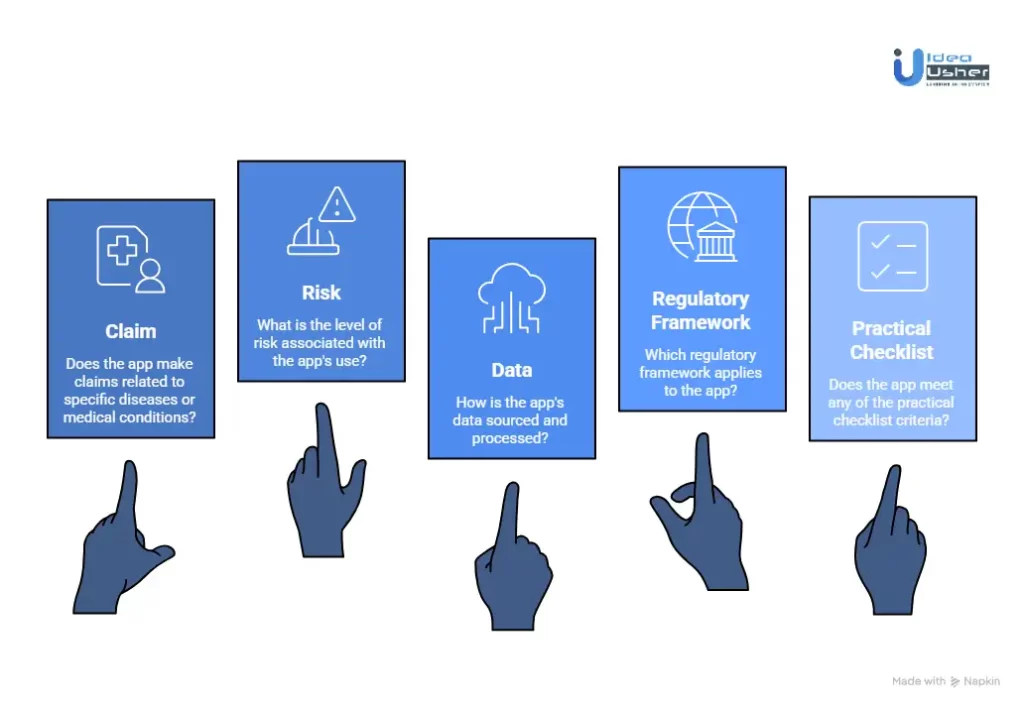
1. The Claim It Makes
This is about the language you use in marketing, labeling, and within the app itself.
| Likely a GENERAL WELLNESS APP | Likely a REGULATED MEDICAL DEVICE |
| Helps you understand your sleep patterns. | Aids in the screening for sleep apnea. |
| Promotes relaxation and mindfulness. | Provides a therapeutic intervention for Generalized Anxiety Disorder GAD. |
| Tracks heart rate during workouts. | Analyzes heart rhythm for possible atrial fibrillation AFib. |
| Logs dietary intake for general awareness. | Calculates insulin bolus doses for diabetics. |
The Litmus Test: Are you making a claim associated with a specific disease or medical condition? If yes, you’re in medical device territory.
2. The Level of Risk to the User
Regulators use a risk-based classification (Class I, II, III in the US). Higher risk = stricter scrutiny.
- Low Risk (May be exempt or Class I): An app that helps manage known migraines by logging triggers (symptom tracking).
- Moderate Risk (Likely Class II): An app that uses the phone’s camera to analyze a skin lesion and provides a risk assessment for melanoma. (This is SaMD – Software as a Medical Device).
- High Risk (Class III): An app that drives a connected insulin pump, automatically calculating and delivering doses.
3. The Source and Processing of Data
How the app handles data is a major clue.
- Wellness Path: Uses data only from manual entry (e.g., logging food, mood) or from sensors for general wellness purposes (step counting, estimated calorie burn).
- Medical Device Path: Integrates with a regulated medical device (e.g., a continuous glucose monitor or an ECG chest strap). Or it uses algorithms to analyze sensor data (such as camera or microphone inputs) to generate a specific clinical output.
Key Regulatory Frameworks & Their Triggers
U.S. FDA
Governed by the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. The FDA has a clear Digital Health Policy and Software Precertification Program. They focus on functionality that could pose a risk if it failed.
EU MDR/IVDR
The Medical Device Regulation (MDR) is stringent. It defines a medical device broadly and has specific rules for software. Rule 11 of the classification system is dedicated to software.
Other regions, including Health Canada, the UK’s MHRA, and Australia’s TGA, have similar but distinct criteria. Global compliance is a layered challenge.
Practical Checklist: Questions to Ask
Answering “YES” to any of these strongly indicates you’re building a medical device:
- Diagnosis/Detection: Does the app provide a specific diagnosis or detect a named disease/condition?
- Treatment/Therapy: Does it suggest or control a treatment protocol (e.g., medication dosage, physiotherapy exercises for a specific injury)?
- Clinical Decision Support: Is it intended to inform clinical decisions? Would a doctor or patient rely on its output to make a care decision?
- Connected Hardware: Does it work with an FDA/CE-cleared hardware device to display or analyze its data?
- Algorithmic Output: Does it use proprietary algorithms to transform sensor data into a new clinical parameter (e.g., calculating blood pressure from a PPG signal)?
The Consequences of Misclassification
| If You Under-Classify (Wellness, but it is Medical) | If You Over-Classify (Medical, but it is Wellness) |
| FDA warning letters or invalid CE marking | Unnecessary regulatory costs |
| Fines and financial penalties | Longer time to market, often extending beyond a year |
| Forced removal from app stores | Complex quality system requirements, such as ISO 13485 |
| Product seizure by regulators | Ongoing post-market surveillance obligations |
| Reputational damage and loss of user trust | Increased operational overhead |
| Exposure to liability and legal claims | Reduced product agility and slower iteration cycles |
The Grey Zone & The “Breakthrough” Opportunity
Some apps live in a grey zone (e.g., mental health apps for “stress” vs. “PTSD”). The regulatory landscape is evolving. Engaging in Pre-Submission meetings with the FDA or consulting with a Notified Body (for CE marking) early is not just advisable—it’s critical for de-risking your project.
Tech Stacks Required to Develop a Health Monitoring App
Developing a health monitoring app requires the integration of various technologies to ensure seamless functionality, data processing, and a user-friendly interface. By using the right tech stacks, businesses can build apps that meet the growing demand in the healthcare industry.
1. Front-End Development
For the app’s interface, using languages such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript is crucial. These technologies help in building the visual aspects of the app, ensuring that app users can navigate smoothly. Frameworks like React, Angular, and Vue.js are popular choices among companies, as they allow for dynamic and responsive designs. Incorporating UI libraries such as Material UI, Bootstrap, and Foundation ensures that health-related icons, progress bars, and data visualization components are integrated effectively into the app, improving user experience.
2. Medical Device Integration
Connecting the app with wearable devices and medical sensors is essential for real-time health tracking. Protocols like Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), ANT+, and Wi-Fi facilitate this communication between devices and the app. Additionally, businesses can leverage SDKs provided by manufacturers of medical devices, such as fitness trackers and other health-related hardware, to integrate these technologies directly into the app.
3. Healthcare Data Standards
Ensuring that the app adheres to healthcare data standards is critical for interoperability with other systems. HL7 FHIR allows for smooth data exchange between healthcare systems. DICOM is another important standard for handling medical imaging data, ensuring that the app can process and store information effectively.
4. Biometric Data Processing
Accurate biometric data processing is a key feature of health monitoring apps. Algorithms that analyze heart rate variability detect sleep stages, and assess gait patterns can provide users with valuable insights into their health. Open-source libraries can help companies process specific biometric data, reducing development time and cost.
5. Health-Related APIs
To offer additional value, businesses can integrate APIs from popular fitness trackers like Fitbit, Garmin, and Apple HealthKit. These APIs allow the app to gather health data directly from users’ devices. In addition, incorporating medical databases such as Mayo Clinic API and WebMD API can provide users with up-to-date health information. Integrating with EHRs further enhances the app’s ability to deliver comprehensive health insights.
6. Health Data Visualization
Specialized libraries for health data visualization play a vital role in displaying metrics like heart rate, blood pressure, and sleep patterns. By presenting this data clearly and engagingly, businesses can enhance user engagement and help individuals better understand their health status.
7. Health-Related Machine Learning Models
AI-powered machine learning models are transforming the health app industry. By using these models, companies can predict disease onset based on collected data and offer personalized recommendations tailored to users’ health profiles. This creates a more proactive and customized healthcare experience, leading to better outcomes for users.
Latest Technologies That Can Enhance a Health Monitoring App
The integration of advanced technologies into health monitoring apps is crucial for improving user engagement and enhancing health outcomes. Three recently developed technologies that can significantly enhance these applications are wearable health devices, AI, and telemedicine solutions.
1. Wearable Health Devices
Wearable health devices have transformed health monitoring by providing real-time data collection on vital signs such as heart rate, activity levels, and even sleep patterns. Companies like Fitbit and Apple have developed devices that seamlessly connect with health apps, enabling users to track their wellness and share data with healthcare providers. According to recent studies, the use of wearables has led to a 30% increase in user engagement with health management, allowing for proactive interventions and improved health outcomes.
2. Artificial Intelligence
AI is playing a really important role in health monitoring apps by offering personalized insights and predictive analytics. AI algorithms analyze data from wearables and user inputs to identify trends and recommend lifestyle changes. For instance, IBM Watson Health uses AI to process large datasets, providing actionable health insights that help users manage chronic conditions effectively. Research indicates that AI-driven health monitoring can improve patient adherence to treatment plans by up to 50%, significantly enhancing overall health management.
3. Telemedicine Solutions
Telemedicine solutions have gained prominence in health monitoring apps, allowing healthcare providers to remotely monitor patients’ health conditions. This technology enables real-time data transmission from wearable devices to healthcare professionals, facilitating timely interventions. Companies like Teladoc Health have successfully integrated telemedicine into their platforms, enabling healthcare providers to conduct virtual consultations and monitor chronic conditions without requiring frequent hospital visits. Statistics show that telemedicine can reduce hospital readmissions by approximately 20%, highlighting its effectiveness in managing patient health remotely.
Top 5 Health Monitoring Apps in the USA
Here are five of the top health monitoring apps in the USA:
1. MyFitnessPal
MyFitnessPal is a leading calorie-counting and nutrition-tracking app that was founded in 2005. With over 200 million downloads, it has become a staple for individuals looking to manage their diet and exercise. The app boasts a comprehensive food database and community support features, making it user-friendly and engaging. In 2023, MyFitnessPal generated approximately $310 million in revenue, capturing over 40% of the health app market share. The app collaborates with various fitness trackers and wearable devices, enhancing its functionality and user experience. Its acquisition by Under Armour in 2015 for about $475 million further solidified its position in the health and wellness sector.
2. Fitbit
Fitbit, established in 2007, is renowned for its wearable devices and the accompanying app that tracks a wide range of health metrics, including steps, heart rate, and sleep patterns. The application has millions of active users and integrates seamlessly with Fitbit devices, providing personalized health insights. Fitbit has formed strategic partnerships with healthcare providers and insurance companies to promote wellness initiatives. In 2021, Fitbit was acquired by Google for $2.1 billion, which has allowed it to leverage Google’s technology and data analytics capabilities to enhance its health monitoring offerings.
3. Headspace
Founded in 2010, Headspace is a meditation and mindfulness app that has attracted millions of users globally. The app offers guided meditation sessions aimed at reducing stress and improving mental well-being. Headspace has successfully partnered with various corporate wellness programs and healthcare providers to promote mental health awareness. The company has raised over $75 million in funding, reflecting its growth and commitment to enhancing mental health through accessible resources.
4. HealthTap
HealthTap, launched in 2010, is a telemedicine app that connects users with healthcare professionals for virtual consultations. It offers a nice range of medical services, including prescription refills and lab test ordering, and has millions of users. HealthTap collaborates with healthcare providers and insurance companies to enhance access to medical care. The company has secured over $100 million in funding, emphasizing its role in the telehealth market and its mission to improve healthcare accessibility for users.
5. Sleep Cycle
It’s a sleep-tracking app that was founded in 2009. The app uses sound technology to analyze users’ sleep patterns and wake them during their lightest sleep phase. With millions of downloads, Sleep Cycle is recognized for its effectiveness in improving sleep quality. The app collaborates with various wearable device manufacturers to enhance its functionality. The company has raised around $10 million in funding, showcasing its dedication to advancing sleep health and wellness to various health goals. Here are five of the top health monitoring apps in the USA:
Conclusion
Health monitoring apps offer individuals greater control over their health, enabling them to track metrics, manage conditions, and make informed choices. These apps can improve health outcomes and quality of life by providing personalized insights and reminders. Healthcare businesses can benefit from developing health monitoring apps by attracting new patients, gaining valuable data insights, and improving patient care. By investing in these apps, businesses can enhance their services, improve outcomes, and generate new revenue.
Looking to Develop a Health Monitoring App?
At Idea Usher, we specialize in crafting innovative health monitoring solutions that empower individuals to take control of their well-being. With over 500,000 hours of coding experience in the field, our team of experts is well-equipped to design and develop cutting-edge apps tailored to your specific needs. From tracking vital signs and activity levels to providing personalized insights and reminders, we utilize advanced technologies to create intuitive and effective health monitoring solutions. Let us help you create an app that promotes healthier lifestyles and improves overall patient outcomes.
Work with Ex-MAANG developers to build next-gen apps schedule your consultation now
FAQs
Q1: How to make a health monitoring app?
A2: Developing a health monitoring app requires careful planning, design, development, and testing. Key considerations include defining the target audience and app features, designing an intuitive UI, choosing suitable technology, integrating with hardware devices, developing algorithms for data analysis, ensuring data security, conducting thorough testing, launching the app, and ongoing maintenance. By addressing these aspects, people can create a successful health-monitoring app that provides valuable insights and helps users improve their well-being.
Q2: What are the features of a health tracker app?
A2: Health tracker apps provide numerous features that assist users in monitoring and managing their overall health. Common functionalities include tracking physical activity, monitoring heart rate, utilizing GPS for tracking movement, and logging nutritional intake. These apps may also offer medication reminders, analyze health data, and integrate with various devices for a more holistic approach. While the specific features may differ across apps, their primary goal is to equip users with essential tools to effectively track and enhance their well-being.
Q3: How much does it cost to develop a health app?
A3: The expense of developing a health app can fluctuate a lot based on factors such as complexity, platform, development resources, and regulatory requirements. While basic apps may be more affordable, complex apps with advanced features can be more costly. It’s essential to obtain accurate cost estimates from multiple developers to ensure you’re getting a fair price for your project.
Q4: How long does it take to develop a health monitoring app?
A4: The development time for a health monitoring app can vary on factors such as complexity, platform, development resources, and regulatory requirements. While simple apps might be developed in a few months, more complex ones can take up to a year or longer. Allocating sufficient time and resources is crucial for successful development, testing, and ongoing maintenance.
























