
In the ever-evolving landscape of the internet, staying up-to-date with the latest trends, technologies, and terminologies can be a challenging endeavour. One such conundrum that often perplexes both tech enthusiasts and casual users is the distinction between Web 3 vs Web 3.0 Are these terms interchangeable, or do they signify different facets of the digital realm?
Web 3, a term that has gained traction in recent years, refers to the next phase of the internet’s evolution. It represents a vision of a decentralized, user-centric internet where individuals have greater control over their data, digital identities, and online interactions. Web 3 envisions a departure from the centralized models of Web 2.0, embracing blockchain technology, decentralized applications (DApps), and cryptocurrencies.
On the other hand, Web 3.0, often referred to as the “semantic web” or the “read-write-execute” web, encompasses a broader vision of the internet. It emphasizes the transition from a web-primarily focused on human-readable content to a web where machines can understand, interpret, and execute data. Web 3.0 introduces machine learning, artificial intelligence, and advanced data semantics, enabling more intelligent and context-aware web applications.
In this blog post, we will delve into the nuances of both Web 3 vs Web 3.0, dissecting their core characteristics, technologies, and potential implications for various industries.
- History and Evolution of the Web: From Web 1.0 to Web 3.0
- Key Market stats of Web 3 and 3.0
- Web3 vs. Web 3.0: The Differences
- Similarities between Web3 and Web 3.0
- Challenges of Web 3.0 and Web3
- Business Implications of Web 3 and Web 3.0: Navigating the Next Digital Frontier
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
History and Evolution of the Web: From Web 1.0 to Web 3.0
To understand the distinctions between Web 3 vs Web 3.0, it’s essential to first take a step back and examine the evolutionary journey of the World Wide Web. This journey has seen remarkable transformations, shaping the digital landscape we navigate today.
Web 1.0: The Static Web
The inception of the World Wide Web, often referred to as Web 1.0, can be traced back to the early 1990s. During this phase, the internet primarily served as a repository of static web pages. These web pages contained text and simple graphics, and they were read-only in nature. Users could access information but had limited means to interact with it. This era was characterized by websites offering basic information and lacked the dynamic, interactive features we now take for granted.
Notable examples of Web 1.0 include early online directories like Yahoo! and static corporate websites that acted as digital brochures. The web was largely one-way communication, with content creators publishing information for users to consume.
Web 2.0: The Rise of Interactivity
The turn of the 21st century marked a significant shift in the web’s evolution, giving rise to Web 2.0. This phase introduced a fundamental change in how users engaged with the internet. Instead of passive consumers of information, users became active participants, contributing content and interacting with one another.
Key characteristics of Web 2.0 included:
- User-Generated Content: Platforms like Wikipedia, Blogger, and social media sites allowed users to create and share content effortlessly.
- Interactivity: Web 2.0 introduced interactive features such as comments, likes, and sharing, enabling user engagement and collaboration.
- Rich Multimedia: Websites began incorporating multimedia elements like images, videos, and animations to enhance user experiences.
- Dynamic Web Applications: The emergence of web applications like Gmail and Google Maps demonstrated the power of web-based software.
Web 2.0 gave birth to a new era of social networking, online collaboration, and information sharing. Popular platforms like Facebook, YouTube, and Twitter exemplified the shift towards user-centric, interactive web experiences.
Web 3: The Decentralized Web
As we fast forward to the present, the concept of Web 3 is making waves in the digital realm. Web 3 envisions a future where the internet operates on decentralized principles, empowering users to have greater control over their data, identities, and digital interactions.
Key aspects of Web 3 include:
- Blockchain Technology: Web 3 leverages blockchain and distributed ledger technology to create decentralized applications and services. These decentralized apps, known as DApps, operate on blockchain networks, offering transparency and security.
- Digital Ownership: In Web 3, users have ownership of their digital assets, including data, digital identities, and virtual assets. Blockchain ensures the authenticity and provenance of these assets.
- Cryptocurrencies: Web 3 embraces cryptocurrencies as a means of value exchange within decentralized ecosystems. These digital currencies facilitate trustless transactions and smart contracts.
- Privacy and Security: Web 3 emphasizes enhanced privacy and security through encryption and decentralized authentication, reducing reliance on centralized authorities.
Web 3 challenges the traditional paradigms of centralized internet giants that control vast amounts of user data. Instead, it envisions a web where individuals have sovereignty over their online presence and transactions, fostering trust and transparency.
Web 3.0: The Semantic Web
While Web 3 focuses on decentralization and user empowerment, Web 3.0 takes a broader perspective by introducing the semantic web. Often referred to as the “read-write-execute” web, Web 3.0 envisions a future where the internet becomes more intelligent and capable of understanding and processing data.
Key features of Web 3.0 include:
- Machine Learning and AI: Web 3.0 integrates machine learning and artificial intelligence to enable machines to comprehend and interpret data like humans. This enables advanced data analysis, context-awareness, and personalization.
- Contextual Understanding: In Web 3.0, web content is not just text and multimedia but also structured data with semantic meaning. This enables better search results, context-aware recommendations, and more sophisticated interactions.
- Interconnected Data: Web 3.0 emphasizes the interconnection of data across the web. Data is linked in meaningful ways, allowing machines to navigate and extract knowledge from the vast sea of information.
- Advanced User Experiences: Web 3.0 introduces smarter virtual assistants, predictive recommendations, and personalized services, enhancing user experiences.
Web 3.0’s vision is to create a more intelligent and intuitive web where information is not just presented but understood, making the internet a valuable tool for users in their daily lives.
In summary, the journey from Web 1.0 to Web 3.0 represents a remarkable evolution in the nature and capabilities of the World Wide Web. While Web 3 emphasizes decentralization and user empowerment, Web 3.0 adds a layer of intelligence and semantic understanding to the digital landscape. Understanding these phases is crucial to appreciating the distinctions
between Web 3 and Web 3.0 and their potential impact on our digital future.
Key Market stats of Web 3 and 3.0
In the ever-evolving landscape of blockchain technology, Web 3.0 has emerged as a game-changer, revolutionizing how we interact with the digital world. As we look forward to the future, understanding the market trends and statistics is crucial.
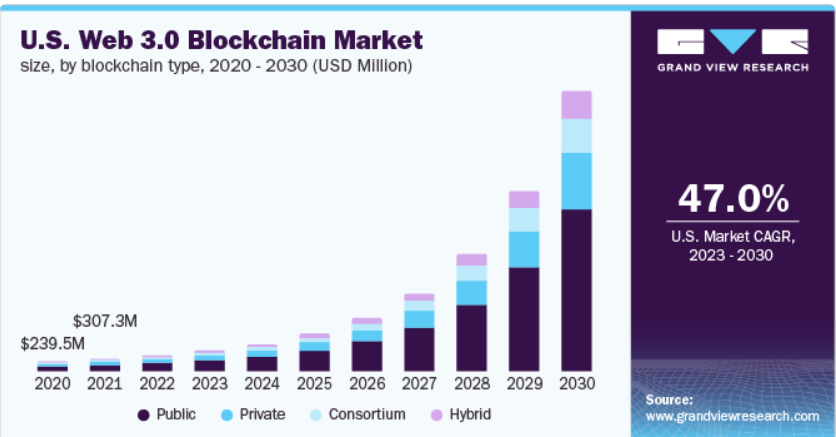
Source – Grandviewresearch.com
The Web 3.0 blockchain market is undergoing a remarkable transformation, poised for explosive growth in the coming years. In 2022, it stood at a valuation of USD 1.73 billion, and projections indicate a staggering compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 47.1% from 2023 to 2030.
1. Impressive Market Size in 2022
The global Web 3.0 blockchain market was nothing short of remarkable in 2022, boasting a staggering market size of USD 1.73 billion. This figure underscores the substantial investment and adoption of Web 3.0 technologies across industries.
2. Stratospheric Growth on the Horizon
The Web 3.0 blockchain market is not only sizeable but also poised for explosive growth. Projections indicate a staggering compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 47.1% from 2023 to 2030. This meteoric rise hints at the immense potential and demand for Web 3.0 solutions in the coming years.
3. Public Blockchain Dominance
In 2022, the public blockchain segment dominated the market, accounting for an impressive 56.0% of the global revenue. The appeal of public blockchains lies in their inclusivity, offering users worldwide the ability to participate in the network without restrictions. Security, transparency, and decentralization contribute to their allure.
4. Hybrid Blockchains on the Rise
While public blockchains take the lead, the hybrid blockchain segment is positioned for significant growth. Hybrid blockchains offer a unique blend of permission-based and permissionless systems, making them versatile for various applications. Users benefit from access through smart contracts, combining the best of both worlds.
5. BFSI Sector Leads the Way
Among end-use segments, the Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance (BFSI) sector led the pack in 2022, claiming over 35.0% of the global revenue. Web 3.0 blockchain technology provides solutions for scalability, transaction speed, and reduced costs in the finance industry. Additionally, it fosters decentralization, enhancing security and preventing cybercrimes.
6. Retail & E-commerce Revolution
Notably, the retail and e-commerce segment is gearing up for substantial growth in the coming years. Web 3.0’s promise of faster payments, reduced costs, increased transparency, and heightened security are driving factors. Moreover, distributed ledger technology fosters seamless collaboration within supply chains, benefiting retailers, importers, and distributors alike.
7. North America Takes the Lead
According to Report, Regionally, North America took the reins in 2022, commanding over 37.0% of the global revenue. This can be attributed to the widespread acceptance of Web 3.0 across various operating systems and the presence of major blockchain solution providers in the region.
8. Asia Pacific’s Ascension
The Asia Pacific region is poised to emerge as the fastest-growing market for Web 3.0 blockchain. Its rapid adoption of digitization in the banking and finance sectors, coupled with a thriving retail and e-commerce industry, positions it for remarkable growth.
In conclusion, the Web 3.0 blockchain market is not just a burgeoning industry; it’s a transformative force. With substantial investments, impressive growth projections, and diverse applications across sectors, Web 3.0 is set to redefine how we engage with technology. As we navigate this exciting landscape, staying informed about these key market statistics is crucial to unlocking the full potential of Web 3.0 blockchain technology.
Web3 vs. Web 3.0: The Differences
| Aspect | Web3 | Web 3.0 |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Web3 refers to the third iteration of the World Wide Web, focusing on decentralized technologies and applications. | Web 3.0 is often used interchangeably with Web3 and refers to the future vision of the internet, emphasizing advanced technologies like AI, IoT, and blockchain. |
| Key Technologies | Blockchain, cryptocurrencies, decentralized apps (dApps), smart contracts, decentralized finance (DeFi). | Artificial Intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), blockchain, augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and more advanced technologies. |
| Decentralization | Emphasis on decentralization, with a focus on eliminating intermediaries and giving more control to users. | Decentralization is a part of the vision, but it also encompasses other technologies and concepts to enhance the overall web experience. |
| Use Cases | Primarily associated with blockchain-based applications, digital currencies, and DeFi platforms. | Envisions a broader range of applications, including highly personalized and intelligent services, immersive experiences, and more. |
| Current State | Web3 is actively developing, with blockchain-based projects gaining popularity. | Web 3.0 is a long-term vision, and many of its components are still in the early stages of development. |
| Economic Models | Utilizes token-based economies and cryptocurrencies for incentives and governance in various platforms. | May include token economies but also explores new economic models enabled by advanced technologies like AI and IoT. |
| Governance Models | Often relies on decentralized governance mechanisms like DAOs (Decentralized Autonomous Organizations) | Governance models may evolve to incorporate AI-driven decision-making and decentralized protocols. |
| Privacy and Security | Focuses on improving privacy and security through blockchain encryption and decentralized data storage. | Continues to address privacy and security concerns but also explores new approaches and technologies to enhance them. |
| Scalability | Faces scalability challenges with blockchain networks and transaction processing. | Aims to address scalability issues with innovative solutions such as sharding and layer 2 scaling solutions. |
| User Experience | User interfaces can be complex, and interactions often require a learning curve. | Strives for a more intuitive and seamless user experience with the integration of AI and immersive technologies. |
Definition
Web3
Web3, also known as Web 3.0, is the third generation of the internet, marking a fundamental shift in how the digital world operates. It is primarily characterized by decentralization, blockchain technology, and user empowerment. At its core, Web3 aims to move control over digital assets, identities, and interactions from centralized entities, like tech giants, to individual users and decentralized networks. Blockchain plays a pivotal role in Web3, providing the infrastructure for decentralized applications (dApps), smart contracts, and decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms.
Web 3.0
Web 3.0 is a broader and more encompassing vision for the future of the internet. While decentralization remains a key component, Web 3.0 goes beyond this concept to emphasize the integration of advanced technologies. It envisions an intelligent web where machines have the capability to process and understand data in ways that resemble human cognition. This includes technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and more. Web 3.0 aims to create an internet that is not just decentralized but also highly intelligent and context-aware, capable of delivering personalized and immersive online experiences.
Key Technologies
Web3
Web3’s foundation is firmly rooted in blockchain technology. Blockchains are distributed ledgers that provide transparency, security, and immutability. They underpin decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contracts, enabling peer-to-peer transactions, decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, and other trustless interactions. Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum are often used as the native digital assets within Web3 networks.
Web 3.0
Web 3.0 incorporates a diverse array of advanced technologies that extend beyond blockchain. AI is a central pillar, enabling machines to analyze, interpret, and respond to data in sophisticated ways. IoT connects physical devices to the internet, creating a network of interconnected smart devices. AR and VR introduce immersive experiences, blurring the lines between the physical and digital worlds. While blockchain remains a component of Web 3.0, it collaborates with these technologies to create an intelligent and interactive web.
Decentralization
Web3
Decentralization is the fundamental principle of Web3. It seeks to disrupt traditional centralized systems and intermediaries. Blockchain technology is the driving force behind this decentralization, ensuring that digital interactions are trustless, transparent, and secure. Users gain greater control over their digital assets, data, and identities. Web3 aims to eliminate the need for intermediaries like banks or tech companies, allowing for peer-to-peer transactions and services.
Web 3.0
While decentralization remains a crucial aspect of Web 3.0, it doesn’t exclusively focus on this principle. Instead, it envisions a harmonious integration of decentralization with other advanced technologies. Web 3.0 recognizes that some centralized services, when combined with AI and IoT, can enhance user experiences and provide efficient solutions. It aims to strike a balance between decentralization and centralized systems where appropriate to deliver the most intelligent and seamless web experience.
Use Cases
Web3
Web3’s primary use cases are deeply intertwined with blockchain technology. It is renowned for blockchain-based applications, digital currencies, and DeFi platforms. These applications are transforming traditional finance, enabling peer-to-peer lending, decentralized exchanges, and even non-fungible tokens (NFTs). Additionally, Web3 extends to supply chain management, voting systems, and identity verification, all benefiting from its trustless and transparent nature.
Web 3.0
Web 3.0 envisions a significantly broader range of use cases that transcend finance. It seeks to revolutionize various aspects of our digital lives, offering highly personalized and intelligent services. This includes advanced virtual assistants that understand context and user preferences, immersive gaming experiences that blur the boundaries between the physical and digital realms, and applications that deeply comprehend user data to deliver tailored recommendations. Web 3.0 strives to create an internet that enhances nearly every facet of human interaction with technology.
Current State
Web3
Web3 is actively evolving and gaining momentum. Blockchain-based projects and DeFi platforms are experiencing widespread adoption. Developers are actively building decentralized applications across various sectors, and blockchain networks are reshaping traditional industries. While it’s not yet fully matured, Web3 is making significant strides in redefining how we engage with the internet.
Web 3.0
Web 3.0 represents a long-term vision for the future of the internet. While we are witnessing the emergence of AI and IoT applications, the complete realization of Web 3.0 is still in its infancy. It encompasses a futuristic perspective of the internet and is expected to unfold over several years. However, the integration of advanced technologies into our online experiences has already commenced, setting the stage for the intelligent web of tomorrow.
These detailed insights highlight the intricate differences and nuances between Web3 and Web 3.0, providing a comprehensive understanding of the two paradigms shaping the digital landscape.
Similarities between Web3 and Web 3.0
In the ever-evolving digital realm, the terms Web3 and Web 3.0 have emerged as key players, each representing a significant shift in how we interact with the internet. While they appear distinct in their focus and objectives, a closer examination reveals intriguing similarities that underscore their shared commitment to transforming the online landscape.
1. Technological Innovation
Both Web3 and Web 3.0 are characterized by their unrelenting pursuit of technological innovation. They represent successive phases in the evolution of the internet, each introducing groundbreaking technologies to redefine the digital experience.
Web3
At its core, Web3 harnesses the power of blockchain technology, cryptocurrencies, decentralized applications (DApps), and smart contracts. These innovations empower users by giving them greater control over their digital identities, assets, and interactions. The focus on decentralization and cryptographic security is a hallmark of technological innovation within Web3.
Web 3.0
Similarly, Web 3.0 pushes the boundaries of technology, albeit in a different direction. It integrates advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), machine learning, and augmented reality (AR) to create a more intelligent and context-aware web. This emphasis on AI-driven contextualization and data interpretation marks a significant technological leap.
2. User-Centric Approach
Both paradigms prioritize enhancing the user experience and shifting power dynamics away from centralized authorities.
Web3
In the realm of Web3, the user is firmly at the center. It empowers individuals with digital ownership, ensuring control over personal data and assets. Blockchain technology guarantees the authenticity and provenance of digital assets, aligning with the user-centric ethos.
Web 3.0
Web 3.0 shares this user-centric philosophy, albeit in a distinct manner. It seeks to create highly personalized and intelligent services, offering users a web that understands their needs and context. The focus is on providing more relevant, immersive, and convenient experiences.
3. Evolving Data Management
Both paradigms address the evolving nature of data management, albeit with different approaches.
Web3
Web3 addresses data management through decentralization. It relies on blockchain’s decentralized ledger to enhance data privacy and security. Users are encouraged to take control of their data, reducing reliance on centralized entities for data storage and authentication.
Web 3.0
Web 3.0 tackles data management by focusing on the semantic web. It adds meaning and context to data, allowing machines to interpret and process information like humans. This approach aims to make data more understandable and meaningful across the entire web.
4. Interconnected Ecosystems
Both Web3 and Web 3.0 recognize the importance of interconnected ecosystems.
Web3
Within Web3, interconnectedness thrives among decentralized networks and blockchain-based applications. The emphasis is on secure and transparent data sharing within these decentralized ecosystems.
Web 3.0
Web 3.0 envisions a highly interconnected web where data across the entire digital landscape becomes more accessible and meaningful for machines. This interconnectedness paves the way for smarter, context-aware services.
5. Embrace of Cryptocurrencies
Both paradigms incorporate cryptocurrencies into their frameworks, although with differing degrees of emphasis.
Web3
Cryptocurrencies play a central role in Web3 ecosystems, serving as a means of value exchange within decentralized networks and enabling smart contracts.
Web 3.0
While Web 3.0 explores advanced technologies, it may also incorporate cryptocurrencies, but they do not take center stage as in Web3.
6. Decentralization of Control
Web3
Web3 is often referred to as the “decentralized web” because it places a strong emphasis on decentralization. It leverages blockchain technology to create decentralized applications (DApps) and services. These applications operate on blockchain networks, ensuring transparency, immutability, and security. This decentralization shifts control from centralized authorities to individual users and decentralized networks.
Web 3.0
Web 3.0, while not solely focused on decentralization, also incorporates it as part of its vision. It envisions a web where control is distributed and not concentrated in the hands of a few entities. This decentralization extends to various aspects of Web 3.0, including data management and access.
7. Focus on Security and Privacy
Both Web3 and Web 3.0 place a significant emphasis on security and privacy, albeit with different approaches.
Web3
In the Web3 paradigm, security and privacy are paramount. Decentralized authentication methods and encryption technologies are employed to enhance user security and reduce reliance on centralized authorities. Blockchain’s cryptographic features contribute to the overall security of the ecosystem.
Web 3.0
While Web 3.0 enhances data processing capabilities, it also takes privacy and security seriously. Although not as deeply focused on these aspects as Web3, it explores new approaches and technologies to enhance security and privacy in the evolving digital landscape.
8. Economic Models
Both Web3 and Web 3.0 introduce new economic models, albeit with distinct characteristics.
Web3
Web3 utilizes token-based economies and cryptocurrencies for incentives and governance within various platforms. Tokens serve as a means of value exchange and play a vital role in powering decentralized networks and applications.
Web 3.0
While Web 3.0 may include token economies, it also explores new economic models enabled by advanced technologies like AI and IoT. These models may focus on creating value through data-driven insights and personalized services.
9. Governance Models
Both paradigms are evolving governance models, reflecting their commitment to decentralization and user empowerment.
Web3
Web3 often relies on decentralized governance mechanisms like DAOs (Decentralized Autonomous Organizations). These DAOs allow users to participate in decision-making processes and influence the direction of decentralized platforms.
Web 3.0
Governance models in Web 3.0 may evolve to incorporate AI-driven decision-making and decentralized protocols. These models aim to create more inclusive and community-driven governance structures.
10. Integration of Advanced Technologies
Lastly, both Web3 and Web 3.0 integrate advanced technologies into their ecosystems.
Web3
While the core of Web3 is blockchain and decentralized architecture, it can incorporate machine learning and AI technologies to enhance certain aspects of decentralized applications.
Web 3.0
Web 3.0 prominently incorporates machine learning and artificial intelligence. These technologies enable machines to comprehend and interpret data, leading to advanced data analysis and context-awareness, enriching the overall web experience.
In essence, the similarities between Web 3 vs Web 3.0 demonstrate a shared commitment to revolutionizing the internet. They both strive to enhance user control, security, and privacy while pushing the boundaries of technology. These parallels emphasize that while the paths they take may differ, their overarching goal is to create a more empowered, secure, and intelligent digital future.
Challenges of Web 3.0 and Web3
The advent of Web 3.0 and Web3 ushers in a promising era of technological advancement and innovation, but it is not without its share of potential challenges and concerns. In this rapidly evolving digital landscape, stakeholders must be proactive in addressing these issues to harness the full potential of these transformative paradigms. Here, we explore the key challenges associated with both Web 3.0 and Web3 and the imperative for collaborative solutions.
Web 3.0:
1. Complexity:
The vision of a highly intelligent and interconnected web in Web 3.0 demands sophisticated technologies and standards. Implementing these innovations can be intricate, necessitating concerted efforts in research and development.
2. Privacy and Security:
Web 3.0’s ambition to provide highly personalized experiences raises concerns about data collection and potential privacy breaches. A robust framework for security and privacy protection is paramount to build user trust.
3. AI Bias and Fairness:
The use of advanced AI systems in Web 3.0 may perpetuate biases inherent in training data. Ensuring fairness and impartiality in AI algorithms poses a significant ethical challenge.
4. Data Ownership:
Determining ownership and control of the vast amount of data generated in an interconnected web can be contentious. Establishing clear rules and regulations is crucial to resolve disputes.
5. Interoperability:
Making different devices, platforms, and technologies seamlessly work together in a Web 3.0 environment presents technical and logistical challenges. Standardization efforts are vital for smooth integration.
6. Digital Divide:
The introduction of resource-intensive technologies in Web 3.0 may exacerbate the digital divide, where some lack access to advanced technologies and high-speed internet. Bridging this gap is a pressing concern.
7. Ethical AI and Governance:
Crafting ethical guidelines for AI in Web 3.0 and establishing governance structures for decentralized systems is a complex endeavor that demands ethical foresight and inclusive decision-making.
Web3:
1. Scalability:
Many blockchain networks central to Web3 face scalability issues in terms of transaction processing and network congestion. While solutions like sharding and layer 2 scaling are in development, scaling remains a formidable challenge.
2. User Experience:
Current Web3 interfaces can be complex and unintuitive for mainstream users. Enhancing user experiences and making decentralized applications (dApps) more accessible is an ongoing priority.
3. Regulatory Uncertainty:
The regulatory environment for cryptocurrencies, token offerings, and DeFi projects is evolving and varies significantly across jurisdictions. This regulatory uncertainty poses challenges for Web3 projects seeking clarity and compliance.
4. Tokenomics:
Designing and managing token economies for dApps and blockchain platforms is complex. Ensuring tokens have real utility and value within their ecosystems is essential for sustainability and adoption.
5. Security:
Despite blockchain’s reputation for security, vulnerabilities in smart contracts have led to hacks. Ensuring the security of decentralized applications and platforms remains a continual focus.
6. Governance:
Developing effective governance models for decentralized networks and organizations, such as DAOs, is intricate. Achieving transparency and equitable decision-making is an ongoing challenge.
7. Adoption:
Expanding the adoption of Web3 technologies beyond the cryptocurrency sphere is a significant hurdle. Overcoming the network effects of existing centralized platforms requires strategic initiatives and user education.
Addressing these multifaceted challenges demands a collaborative effort among technologists, policymakers, industry leaders, and the wider community. By proactively addressing these concerns, we can pave the way for a future where the potential benefits of Web 3.0 and Web3 are fully realized, while mitigating associated risks and drawbacks.
Business Implications of Web 3 and Web 3.0: Navigating the Next Digital Frontier
The digital landscape is in a state of perpetual evolution, and businesses that fail to adapt risk becoming obsolete. As we explore the realms of Web 3 vs Web 3.0, it becomes evident that these paradigms are not merely technological novelties but carry profound implications for businesses across industries. Understanding these implications is essential for companies seeking to thrive in the next phase of the internet.
1. Decentralization and Disruption:
One of the fundamental shifts ushered in by Web 3 is decentralization. This concept challenges traditional business models built on centralized authority and control. Decentralized applications (DApps) and blockchain technology are poised to disrupt industries like finance, supply chain, and entertainment by eliminating intermediaries and promoting peer-to-peer interactions. Companies that embrace this decentralization can potentially reduce costs, increase transparency, and foster innovation.
2. Digital Ownership and Identity:
Web3’s focus on digital ownership and self-sovereign identity has profound implications for businesses dealing with customer data and authentication. Users are increasingly demanding control over their personal information, and companies that respect these principles will gain trust and loyalty. Implementing decentralized identity solutions and data ownership models can enhance customer relationships and compliance with evolving data protection regulations.
3. Cryptocurrencies and Smart Contracts:
Cryptocurrencies and smart contracts are integral to Web3 ecosystems. These technologies enable trustless transactions and automated agreements, revolutionizing payment systems and contract management. Businesses can leverage cryptocurrencies for international transactions, reducing fees and transaction times. Smart contracts offer opportunities for automation, streamlining processes, and reducing the risk of disputes.
4. Privacy and Security:
In an era marked by data breaches and privacy concerns, Web 3’s emphasis on privacy and security is a welcome shift. Decentralized architectures and cryptographic techniques enhance data protection. Businesses that prioritize user privacy and invest in robust security measures can gain a competitive edge by fostering trust and compliance.
5. Contextual Understanding and Personalization:
Web 3.0’s semantic web introduces the power of contextual understanding. Businesses can utilize this capability to provide highly personalized user experiences. Content recommendation, marketing, and customer support can be tailored with unprecedented precision, enhancing customer satisfaction and engagement.
6. Data-Driven Decision-Making:
Web 3.0’s capacity for data interpretation and context-awareness equips businesses with valuable insights. Data-driven decision-making becomes more sophisticated, enabling companies to make informed choices in product development, marketing strategies, and customer engagement. Understanding user behavior and preferences at a deeper level enhances competitive positioning.
7. Supply Chain Optimization:
Supply chain management stands to benefit significantly from both Web a3 vs Web 3.0. Decentralized supply chain networks can reduce inefficiencies, increase transparency, and mitigate fraud. Web 3.0’s contextual understanding can optimize logistics, inventory management, and demand forecasting, enhancing operational efficiency.
8. New Revenue Streams:
The innovative nature of Web3 and Web 3.0 opens doors to new revenue streams. Businesses can explore opportunities in tokenization, non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and blockchain-based services. Monetizing digital assets and offering unique experiences can diversify income sources.
9. Enhanced Customer Relationships:
The combination of decentralized identity, personalization, and secure communication in Web3 and Web 3.0 can transform customer relationships. Businesses can build trust by prioritizing user privacy, offering tailored experiences, and ensuring transparent, tamper-proof interactions.
10. Competitive Advantage:
Early adoption and adaptation to the principles of Web3 and Web 3.0 can confer a competitive advantage. Companies that harness these paradigms effectively can differentiate themselves in crowded markets, attract tech-savvy customers, and stay ahead of regulatory developments.
11. Emerging Technologies:
Web 3 and Web 3.0 are poised to intersect with emerging technologies like IoT, AI, and AR. Companies that strategically integrate these technologies can pioneer innovative solutions, improve operations, and create unique value propositions for their customers.
12. Risk Mitigation:
While the opportunities are vast, it’s essential to acknowledge potential risks and challenges associated with Web3 and Web 3.0. Companies must navigate regulatory uncertainties, address security concerns, and ensure compliance with evolving standards.
Conclusion
Web 3 and Web 3.0 mark a transformative era for businesses. Decentralization and semantic understanding of data offer unique opportunities. Companies must adapt to remain competitive.
Embracing self-sovereign identity, blockchain, and cryptocurrencies enhances trust and security. Smart contracts streamline operations, while personalization fosters customer loyalty. Decentralized networks optimize supply chains and create new revenue streams.
However, challenges like regulation and security require vigilance. Emerging technologies like IoT and AI will further innovate the landscape.
At Idea Usher, we specialize in web and app development, empowering your journey into Web 3 and Web 3.0. From decentralized applications to secure transactions and personalized user experiences, we have the expertise.
Our team crafts solutions with data security, privacy, and compliance in mind. Partner with Idea Usher to confidently embrace the future of digital business.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q. What is the main difference between Web 3 and Web 3.0?
A – Web 3, also known as the decentralized web, emphasizes decentralization, blockchain, and user ownership of digital assets. It focuses on shifting control from centralized authorities to individual users. In contrast, Web 3.0, or the semantic web, prioritizes the semantic understanding of data, machine learning, and advanced user experiences.
Q. How does Web 3 impact data privacy and security?
A – Web 3 places a strong emphasis on data privacy and security. It employs encryption and decentralized authentication methods to enhance user security and reduce reliance on centralized authorities. Users have greater control over their personal data and digital assets.
Q. What are the business implications of Web 3 and Web 3.0?
A. Web 3 and Web 3.0 offer significant business opportunities. Web 3 enables trustless transactions, smart contracts, and decentralized supply chains. Web 3.0 enhances user experiences with machine learning and semantic data understanding, leading to personalized services and improved customer relationships.
Q. How can companies prepare for the transition to Web 3 and Web 3.0?
A. Companies can prepare for this transition by staying informed about emerging technologies, investing in blockchain and AI capabilities, and exploring decentralized applications (DApps). Building partnerships with experts in web and app development is crucial to navigating this digital shift.
Q. What challenges are associated with Web 3 and Web 3.0 adoption?
A. Adoption challenges include regulatory uncertainties, security risks in decentralized networks, and the need for interoperability among different blockchain platforms. Additionally, businesses must adapt to evolving user expectations and data privacy regulations.








