Web3 applications bring together smart contracts, wallets, front-end interfaces, and off-chain services into a single user experience, which makes architecture decisions critical from the start. Choices around contract design, data flow, state management, and integrations directly affect scalability, security, and usability. These considerations sit at the core of building a Web3 app on Base, where efficiency and composability need to be balanced across the entire stack.
Developing on Base introduces specific architectural patterns around transaction handling, gas optimization, and interaction with Ethereum-compatible tooling. While Base offers faster settlement and lower costs, applications still need a well-structured tech stack that connects on-chain logic with off-chain services, indexing layers, and front-end frameworks. Early decisions around architecture shape how easily the app can evolve as usage grows.
In this blog, we explain how to build a Web3 app on Base by breaking down the recommended architecture, core technology stack, and system design considerations involved in launching a scalable and production-ready decentralized application.

What is a Web3 App?
A Web3 app is a blockchain-based application that operates in a decentralized environment using smart contracts rather than centralized servers. This model allows users to directly access digital services while maintaining ownership of their data, identity, and assets, enabling transparent and trustless interactions such as payments, governance, trading, or gaming.
When deployed on Base, a Layer 2 blockchain built on Ethereum by Coinbase, a Web3 app gains improved scalability through faster transaction speeds and lower gas fees. At the same time, it continues to benefit from Ethereum’s security, making decentralized applications more efficient and suitable for real-world use.
Why Businesses Should Build a Web3 App on Base?
This section outlines key reasons businesses choose Base for building secure, scalable Web3 applications with low transaction costs. It highlights the platform’s growing ecosystem and developer adoption.
1. User Adoption for Low Transaction Costs
Base lowers transaction fees versus Ethereum, enabling high-activity Web3 apps like micro-payments, rewards, subscriptions, and asset transfers without high costs. This efficiency supports scaling user engagement and predictable expenses.
- Optimistic rollup architecture for lower gas fees: Base processes transactions off the Ethereum mainnet and submits them in batches, reducing computational costs while preserving security. This directly lowers per-transaction fees for end users.
- Layer 2 execution with Ethereum: Transactions execute on Base but ultimately settle on Ethereum, ensuring cost efficiency without compromising trust or data integrity.
- Cost-efficient on-chain interactions for consumer-facing apps: Lower execution costs make it practical to move more logic on-chain, enabling richer features without financial friction.
2. Ethereum-Level Security Without Mainnet Complexity
Security is vital for businesses in Web3. Base inherits Ethereum’s security but reduces the operational challenges of building on the mainnet. This enables deployment of reliable apps with lower protocol risks.
- Ethereum-backed settlement layer: Final transaction validation occurs on Ethereum, ensuring data immutability and resistance to tampering.
- Proven OP Stack infrastructure: Base is built on battle-tested rollup technology that is already supporting large-scale blockchain applications.
- Compatibility with audited Ethereum smart contract standards: Businesses can rely on widely used, security-reviewed contract libraries instead of custom logic.
3. Faster Development, Quicker Launch
Base is fully EVM-compatible, allowing teams to use familiar Ethereum tools, frameworks, and libraries. This eliminates the need for training on new languages or rebuilding infrastructure, shortening development cycles and cutting costs.
- Full EVM compatibility: Existing Ethereum contracts can be deployed on Base with minimal or no code changes.
- Support for Solidity-based smart contracts: Development teams can continue using the most widely adopted smart contract language.
- Seamless integration with Ethereum developer tools: Tooling for testing, deployment, and monitoring remains consistent across environments.
4. Wallet Login and Ownership UX
Web3 apps on Base use wallet-based authentication instead of traditional logins, enabling self-sovereign identity and reducing data storage risks. This gives users full control over their assets, access rights, and digital identities.
- Native support for Ethereum wallets: Users can authenticate and transact using wallets they already trust and use.
- On-chain identity and permission logic: Access rules can be enforced transparently through smart contracts rather than centralized databases.
- Smart contract-based access control: Permissions, subscriptions, and roles are verifiable and tamper-proof.
5. Bridging Web2 and Web3 Experience
Base enables businesses to create Web3 apps that feel familiar to Web2 users. By combining low fees, fast transactions, and modern frontend frameworks, companies can onboard non-crypto users without friction while still delivering decentralized benefits.
- Fast transaction: Users experience near-instant confirmations, similar to traditional applications.
- Support for modern frontend stacks: Teams can build intuitive interfaces using popular Web frameworks.
- Lower onboarding friction for new Web3 users: Reduced fees and simplified flows make it easier for first-time users to engage.
Type of Web3 App You Can Build on Base
Base is best suited for Web3 applications that require frequent user interactions, low transaction costs, and Ethereum-level security. If your product needs scale, usability, and real business adoption, the following app categories are ideal for building on Base.
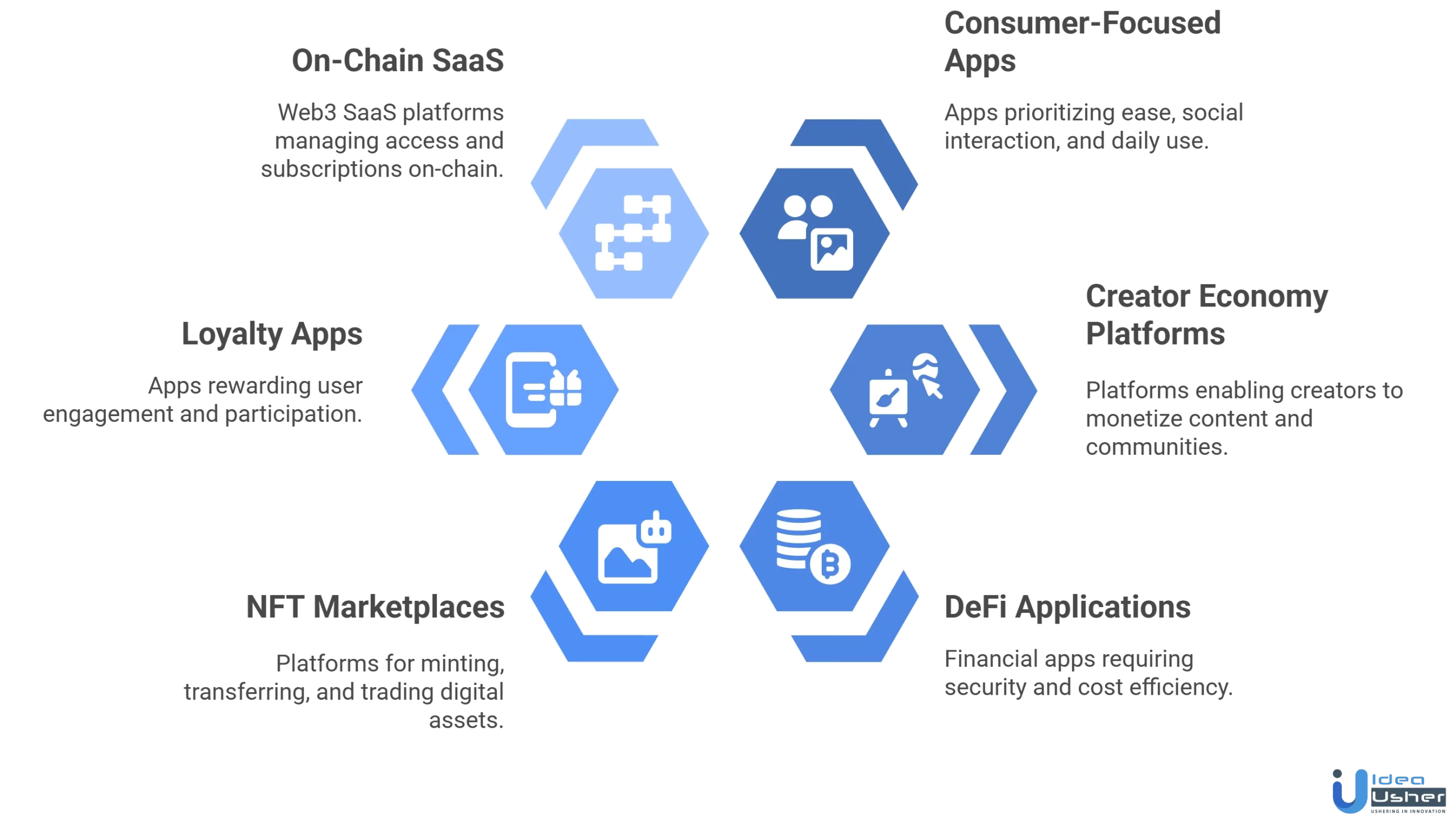
1. Consumer-Focused Web3 Apps
Consumer-facing Web3 apps benefit from Base’s low fees and quick confirmations, essential for frequent blockchain interactions. They prioritize ease, social interaction, and daily use while maintaining on-chain ownership and logic.
Example: Apps like Friend.tech demonstrate how social interactions, access communities, and creator-fan links can be built on Base without friction for non-technical users.
2. Creator Economy and Monetization Platforms
Base is an ideal foundation for creator platforms where earnings depend on frequent, low-value transactions. Creators can monetize content, communities, and access directly, without losing a significant portion of revenue to gas fees.
Example: Platforms like Zora enable creators to mint, distribute, and monetize digital content on Base efficiently, extending to subscription apps, fan clubs, and token-gated communities.
3. DeFi and Financial Web3 Applications
Financial applications require both security and cost efficiency. Base allows DeFi apps to execute complex logic while maintaining Ethereum-grade trust guarantees, making it suitable for lending, trading, payments, and yield-based products.
Example: Protocols like Aerodrome Finance show how decentralized exchanges and liquidity platforms work well on Base. They also suit payment rails, treasury tools, and financial automation.
4. NFT Marketplaces and Digital Asset Platforms
NFT platforms rely on high transaction volumes for minting, transfers, and marketplace activity. Base makes these operations affordable while remaining compatible with Ethereum NFT standards.
Example: Bright Moments is a digital art platform that goes beyond simple NFT trading by combining curated collections, on-chain minting, community ownership, and cultural storytelling.
5. Loyalty, Rewards, and Engagement Apps
Web3-powered loyalty apps benefit from Base’s ability to handle frequent reward issuance and redemption. Tokens or NFTs can represent points, tiers, or benefits, while smart contracts ensure transparency and automation.
Example: Projects like Mint.fun showcase how engagement-driven Web3 experiences foster user participation, and similar methods suit brand loyalty, referral, and community incentives.
6. On-Chain SaaS and Subscription-Based Apps
Base is well-suited for Web3 SaaS platforms where access, subscriptions, or usage rights are managed on-chain. Smart contracts control permissions and billing, while off-chain services handle performance-heavy operations.
Example: Platform like Collectify, a no-code Web3 utility platform that allows users to create and manage on-chain components such as token launches, NFT minting, airdrops, and allowlist contracts.

Key Market Takeaways of Web3 Apps
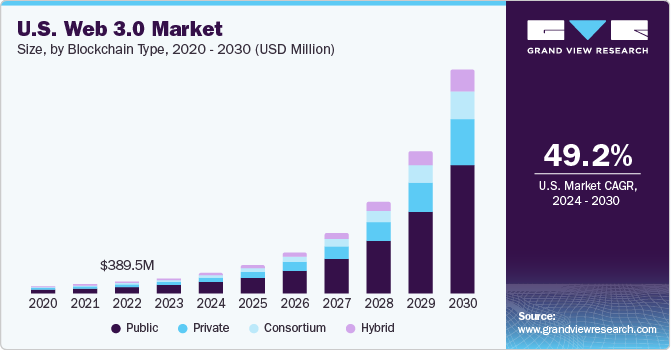
The global Web 3.0 market size was estimated at USD 2.25 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 33.53 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 49.3% from 2024 to 2030, reflecting strong investor confidence and broad industry adoption. This rapid expansion is driven by increasing enterprise interest, decentralized finance growth, and mainstream blockchain integration across sectors.
Rapid Enterprise Adoption in Web3 Apps
Web3 is no longer confined to experimental pilots. Enterprises are increasingly deploying production-grade Web3 applications as part of their core digital strategy, driven by the need for transparency, automation, and user-owned data.
- Shift from proof-of-concept to real-world deployments: Companies are moving beyond testnets and launching live Web3 apps that handle real users, assets, and transactions, raising expectations around performance and reliability.
- Demand for predictable costs and scalability: Enterprise adoption places pressure on blockchain infrastructure to deliver low fees, stable throughput, and minimal latency, influencing architecture decisions from the start.
- Growing emphasis on security and compliance readiness: As Web3 apps integrate with financial workflows and user data, enterprises prioritize secure smart contracts, audited infrastructure, and scalable Layer-2 solutions.
Overall, these market trends indicate that Web3 applications are entering a mature growth phase driven by enterprise adoption, scalable infrastructure, and real-world use cases. As expectations around performance, cost efficiency, and compliance rise, Web3 platforms must be designed for production from day one.
Core Architecture Layer of Web3 App on Base
The core architecture layer of a Web3 app on Base defines how smart contracts, blockchain infrastructure, and user interactions function together. It highlights the technical foundation enabling scalability, security, and decentralized performance.

1. Blockchain & Execution Layer (Base L2)
The Blockchain & Execution Layer powers on-chain activity in Base, an Ethereum Layer 2 using Optimistic Rollups that scales transactions and relies on Ethereum for finality. Offloading computation cuts costs and increases throughput, ideal for frequent interactions, microtransactions, and high-performance platforms.
Key responsibilities
- Smart contract execution on Base: Runs app logic on Base to reduce congestion and gas fees while ensuring trustless execution.
- Final settlement on Ethereum: Transactions settle on Ethereum for strong decentralization and security guarantees.
- Low fees and high throughput: Optimized batching supports high user activity at minimal cost.
- Inherited Ethereum security: Posts proofs to Ethereum, maintaining proven network security without added trust risks.
Why it matters: This layer ensures trustless execution while keeping costs low, making consumer and creator-facing apps economically viable.
2. Smart Contract Layer (On-chain Logic)
The Smart Contract Layer defines the core business logic of Web3 apps on Base, where rules, permissions, and value flows are enforced through Solidity smart contracts. Running on Base ensures low execution costs while maintaining full Ethereum compatibility, enabling secure and scalable on-chain systems.
What lives here
- Token contracts: Standardized token implementations such as ERC-20, ERC-721, and ERC-1155 that represent currencies, digital assets, memberships, or access rights within the application.
- Payment and monetization logic: Smart contracts that handle subscriptions, one-time payments, tipping, revenue distribution, and automated payouts without manual intervention.
- Access control and permissions: On-chain rules that define who can interact with specific features, content, or assets based on ownership, roles, or token holdings.
- Governance rules: Contracts that manage voting, proposals, and protocol upgrades, enabling decentralized decision-making within the platform.
- Creator revenue splits and royalties: Automated logic for splitting income among creators, collaborators, and platforms, ensuring transparent and tamper-proof revenue distribution.
Core characteristics
- Deterministic and immutable: Once deployed, smart contracts execute exactly as written, ensuring predictable outcomes and resistance to manipulation.
- Transparent business logic: All rules and transactions are publicly verifiable on-chain, increasing trust among users, creators, and partners.
- Programmatic trust without intermediaries: Trust is enforced by code rather than institutions, enabling direct interactions between users and platforms.
3. Protocol & Middleware Layer
The Protocol & Middleware Layer connects blockchain data with application logic, making on-chain information easy to access and use. It abstracts direct blockchain interactions to ensure fast performance and a smooth user experience as activity scales.
Typical components
- RPC providers (node access): Provide reliable connections to the Base network, allowing applications to send transactions and read on-chain data without running their own nodes.
- Indexers for fast data retrieval: Organize and store blockchain data in queryable formats, enabling instant access to balances, transaction history, and contract state.
- Event listeners and transaction: Monitor smart contract events and transaction statuses in real time, keeping application state synchronized with on-chain activity.
- SDKs and protocol integrations: Simplify interactions with smart contracts and external protocols by offering standardized libraries and APIs for developers.
Why this layer is critical:
Direct blockchain reads are slow, resource-intensive, and not designed for real-time user interfaces. The Protocol & Middleware Layer transforms raw on-chain data into application-ready information, enabling Web3 apps on Base to scale, remain performant, and deliver seamless user experiences.
4. Off-chain Services & Infrastructure Layer
The Off-chain Services & Infrastructure Layer manages functions not needing on-chain execution, like data storage and real-time processing. This boosts performance, cuts costs, and supports scalable user experiences while keeping key logic on-chain.
Common responsibilities
- User profiles and metadata: Stores dynamic user information, preferences, and application-specific metadata that would be inefficient or costly to maintain on-chain.
- Notifications and emails: Manages real-time alerts, transactional messages, and engagement communications triggered by on-chain or off-chain events.
- Analytics and dashboards: Aggregate and visualize application activity, user behavior, and performance metrics for creators, operators, and enterprises.
- AI or recommendation engines: Power personalized content discovery, rankings, and intelligent features that require computation beyond blockchain capabilities.
- File storage pointers: Maintains references to decentralized storage systems such as IPFS or Arweave, keeping large files off-chain while preserving verifiable links.
Architecture principle: A hybrid Web2 and Web3 architecture keeps applications fast and scalable while ensuring decentralization is applied where it delivers the most value. By combining off-chain infrastructure with on-chain guarantees, Web3 apps on Base achieve both performance and trust.
5. Identity & Wallet Layer
The Identity & Wallet Layer enables user authentication through cryptographic wallets instead of traditional logins. It links identity, permissions, and asset ownership directly to on-chain accounts, supporting secure and self-sovereign access.
This layer typically includes:
- Wallet-based login: Allows users to access the application using their crypto wallets, eliminating the need for passwords or centralized credentials.
- Signature-based authentication: Verifies user intent and identity through cryptographic signatures, ensuring secure and permissionless access to application features.
- Session management: Maintains authenticated sessions to support smooth user experiences without requiring repeated wallet confirmations for every action.
- Account abstraction support: Enables advanced account features such as gas sponsorship, batched transactions, and improved onboarding for non-technical users.
Key advantage: Users retain full control over their identity and assets without depending on centralized accounts or password-based systems. This layer empowers trustless participation while improving security, portability, and user ownership across Web3 applications on Base.
6. Application & Frontend Layer
The Application & Frontend Layer delivers the user interface for Web3 apps on Base, translating on-chain processes into intuitive experiences. It ensures smooth interactions, usability, and engagement comparable to modern Web2 applications.
Built with components such as:
- Web or mobile frameworks: Power responsive interfaces across browsers and devices, ensuring accessibility and consistent user experiences.
- Web3 libraries for wallet interaction: Enable secure connections to user wallets, allowing applications to read account data and request transaction approvals.
- State management for on-chain and off-chain synchronization: Keeps the application interface in sync with blockchain state and off-chain services, ensuring accurate and real-time updates.
Built with components such as:
- Displaying balances, NFTs, and activity: Presents on-chain assets, transaction history, and platform activity in a clear and user-friendly manner.
- Triggering smart contract interactions: Allows users to initiate transactions such as payments, minting, staking, or voting through intuitive UI flows.
- Handling transaction feedback and UX flows: Manages confirmations, pending states, success messages, and error handling to guide users through blockchain interactions smoothly.
7. Governance, Security & Monitoring Layer
The Governance, Security & Monitoring Layer protects the stability and reliability of Web3 apps on Base by overseeing smart contracts, infrastructure, and operations. It ensures systems remain secure, upgradable, and well-governed as platforms scale.
This layer typically covers:
- Smart contract audits: Independent security reviews that identify vulnerabilities, logic flaws, and potential attack vectors before and after deployment.
- Upgrade mechanisms: Controlled contract upgrade paths that allow systems to evolve while maintaining security, transparency, and backward compatibility.
- Governance voting systems: On-chain mechanisms for proposals and voting, enabling decentralized or stakeholder-driven decision-making.
- Monitoring and alerting: Real-time tracking of contract activity, transactions, and anomalies to detect issues and respond quickly.
- Compliance and access policies: Permissioning and policy enforcement for enterprise or private applications, supporting regulatory and operational requirements.
This layer ensures that Web3 applications on Base are not only functional at launch but remain secure, adaptable, and resilient as usage, complexity, and value grow over time.

Recommended Tech Stack for Building Web3 Apps on Base
The recommended tech stack for building Web3 apps on Base combines scalable blockchain tools, smart contract frameworks, and modern frontend technologies. It ensures efficient development, secure execution, and seamless user experiences across decentralized applications.
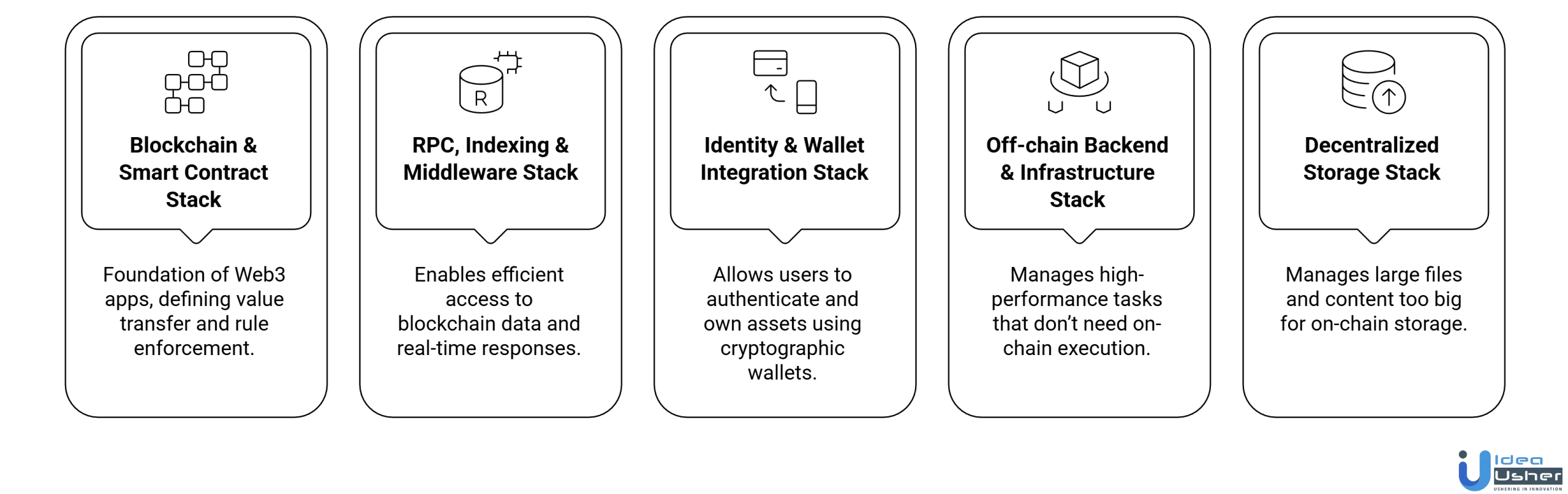
1. Blockchain & Smart Contract Stack
The Blockchain & Smart Contract Stack is the foundation of Web3 apps on Base, defining value transfer, rule enforcement, and trust. It combines low transaction costs with Ethereum-level security, enabling scalable, production-ready applications.
| Component | Description | Benefits to Build Web3 App on Base |
| Base Network (EVM-Compatible Execution Layer) | Programming language used to write smart contracts deployed on the Base network. | Enables deterministic, low-cost execution of application logic with full EVM compatibility. |
| Solidity | Primary programming language used to write smart contracts that run on Base and define on-chain logic. | Enables low-cost, deterministic execution of business logic while maintaining Ethereum compatibility. |
| Ethereum Standards (ERC-20, ERC-721, ERC-1155) | Widely adopted token standards for fungible tokens, NFTs, and multi-token assets. | Ensures seamless interoperability across the Ethereum ecosystem while benefiting from Base’s scalability. |
| Hardhat / Foundry | Development and testing frameworks for compiling, testing, debugging, and deploying smart contracts. | Allows faster development and safer deployments to Base with robust testing and simulation tools. |
| OpenZeppelin | Audited smart contract libraries providing reusable components for tokens, access control, and upgrades. | Reduces security risks and accelerates production-ready smart contract development on Base. |
By combining standardized smart contracts with battle-tested development tools, this stack enables teams to build secure and scalable Web3 applications on Base while maintaining full compatibility with the broader Ethereum ecosystem.
2. RPC, Indexing & Middleware Stack
The RPC, Indexing & Middleware Stack enables Web3 apps on Base to access blockchain data efficiently and deliver real-time responses. It abstracts technical complexity, ensuring fast, Web2-like performance on decentralized infrastructure.
| Component | Description | Benefits to Build on Base |
| RPC Providers | Infrastructure services that provide programmatic access to Base nodes for reading data and submitting transactions. | Enables reliable interaction with the Base network without maintaining node infrastructure. |
| Blockchain Indexing Services | Systems that organize on-chain data into structured, queryable formats. | Allows fast data retrieval and real-time application updates on Base. |
| Event Listeners & Transaction Monitoring | Services that track smart contract events and transaction status changes. | Keeps the application state synchronized with the Base blockchain activity. |
| Middleware APIs & SDKs | Developer libraries and APIs that abstract low-level blockchain interactions. | Reduces development complexity and speeds up Web3 app implementation on Base. |
This stack transforms raw blockchain data into application-ready information, allowing Web3 apps on Base to scale smoothly while delivering fast, reliable user experiences.
3. Identity & Wallet Integration Stack
The Identity & Wallet Integration Stack enables users to authenticate, sign actions, and own assets on Base using cryptographic wallets instead of traditional logins. It supports secure, user-owned identity with smooth onboarding and scalable access.
| Component | Description | Benefits to Build on Base |
| Wallet Connectors | Tools that connect browser and mobile wallets to the application interface. | Enables seamless user onboarding and broad wallet compatibility on Base. |
| Wallet Providers | User-facing wallets such as MetaMask that manage keys and sign transactions. | Allows users to securely control assets and interact with Base without centralized accounts. |
| Signature-Based Authentication | Uses cryptographic message signing to verify user identity and intent. | Eliminates passwords, reduces attack surfaces, and improves security. |
| Session Management | Maintains authenticated sessions after wallet connection to reduce repeated signature prompts. | Improves UX while preserving wallet-based security. |
| Account Abstraction Tooling | Smart account features that support gas sponsorship and batched transactions. | Lowers onboarding friction and enables user-friendly experiences on Base. |
This stack empowers users to control their identity and assets directly while giving developers the flexibility to design secure, scalable, and intuitive authentication flows for Web3 applications on Base.
4. Off-chain Backend & Infrastructure Stack
The Off-chain Backend & Infrastructure Stack manages high-performance tasks that don’t need on-chain execution, improving speed and scalability. It powers modern Web3 experiences on Base while keeping critical logic and value flows on-chain.
| Component | Description | Benefits to Build on Base |
| Backend Frameworks | Server-side frameworks used to build APIs and application services. | Enables fast data processing and business logic without adding on-chain costs. |
| Databases | Store user profiles, metadata, preferences, and application state. | Keeps applications responsive while avoiding expensive on-chain storage. |
| Queue & Messaging Systems | Handle asynchronous tasks such as notifications, indexing jobs, and background processing. | Improves scalability and ensures smooth user experiences during high activity. |
| Analytics & Monitoring Services | Track user behavior, application performance, and engagement metrics. | Helps teams optimize product decisions and improve platform growth on Base. |
| AI & Recommendation Engines | Power personalization, content discovery, and intelligent features. | Enhances user engagement without burdening on-chain execution. |
This stack ensures that Web3 applications on Base can operate at scale, deliver real-time experiences, and evolve rapidly, while still relying on blockchain layers for trust, security, and ownership.
5. Decentralized Storage Stack
The Decentralized Storage Stack manages large files and content too big for on-chain storage. Base smart contracts handle ownership, while decentralized systems store data, ensuring scalability and verifiability. It’s vital for Web3 apps with media, documents, NFTs, and creator content.
| Component | Description | Benefits to Build on Base |
| IPFS | Distributed file system used to store and retrieve content via content-addressed hashes. | Enables scalable, censorship-resistant storage without high on-chain costs. |
| Arweave | Permanent storage network designed for long-term data persistence. | Ensures critical content remains available indefinitely, ideal for NFTs and records. |
| Metadata Hosting | JSON metadata files describing assets, content, or profiles. | Keeps NFTs and digital assets interoperable across Base and Ethereum ecosystems. |
| On-chain Storage Pointers | Smart contract references linking on-chain records to off-chain files. | Preserves trust and data integrity while minimizing gas usage on Base. |
This stack allows Web3 applications on Base to handle rich content efficiently while maintaining transparent links between on-chain ownership and off-chain data.
Web3 App Development Process on Base
Building a Web3 app on Base demands a structured approach balancing on-chain trust, off-chain performance, and scalability. Here is a proven process to develop production-ready Web3 apps on Base.
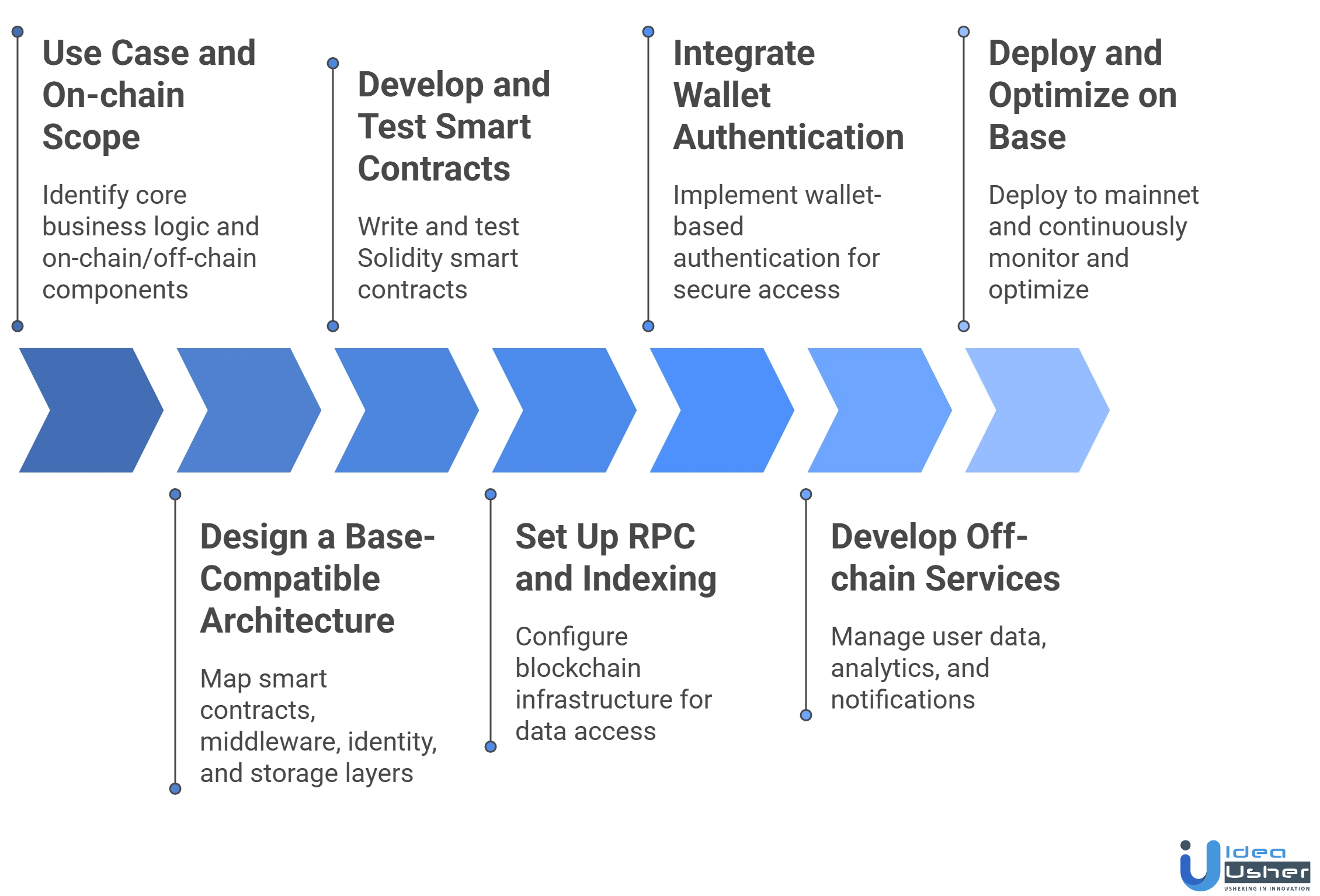
1. Use Case and On-chain Scope
This step identifies the core business logic and determines which components must operate on-chain versus off-chain. Clear scoping ensures trust-critical functions run on Base while optimizing performance, cost efficiency, and long-term scalability.
2. Design a Base-Compatible Architecture
The application architecture is designed around Base’s Layer 2 execution model, mapping smart contracts, middleware, identity, and storage layers into a cohesive system that ensures Ethereum compatibility, modularity, and smooth interaction between on-chain and off-chain components.
3. Develop and Test Smart Contracts
Solidity smart contracts are developed to handle core logic such as asset ownership, payments, and permissions. Rigorous testing on local and Base test networks validates correctness, security, and edge cases before mainnet deployment.
4. Set Up RPC and Indexing
Blockchain infrastructure is configured to enable efficient data access, event tracking, and transaction monitoring. This layer ensures the application can read blockchain state in real time and remain responsive as on-chain activity scales.
5. Integrate Wallet Authentication
Wallet-based authentication is integrated to manage user identity, signatures, and sessions without passwords. This step ensures secure access, seamless transaction approvals, and a frictionless onboarding experience aligned with Web3 principles.
6. Develop Off-chain Services
Off-chain services are developed to manage user data, analytics, and notifications, while decentralized storage handles large files and metadata. This hybrid setup balances performance with decentralization and verifiable on-chain ownership.
7. Deploy and Optimize on Base
The application is deployed to Base mainnet with continuous monitoring for transactions, performance, and anomalies. Ongoing optimization improves gas efficiency, user experience, and infrastructure scalability as adoption grows.

How Does Base Support Low Gas Fees When Building a Web3 App?
Base supports low gas fees by using Layer 2 scaling on Ethereum, batching transactions, and optimizing execution costs for Web3 apps. This approach improves affordability and performance while maintaining network security.
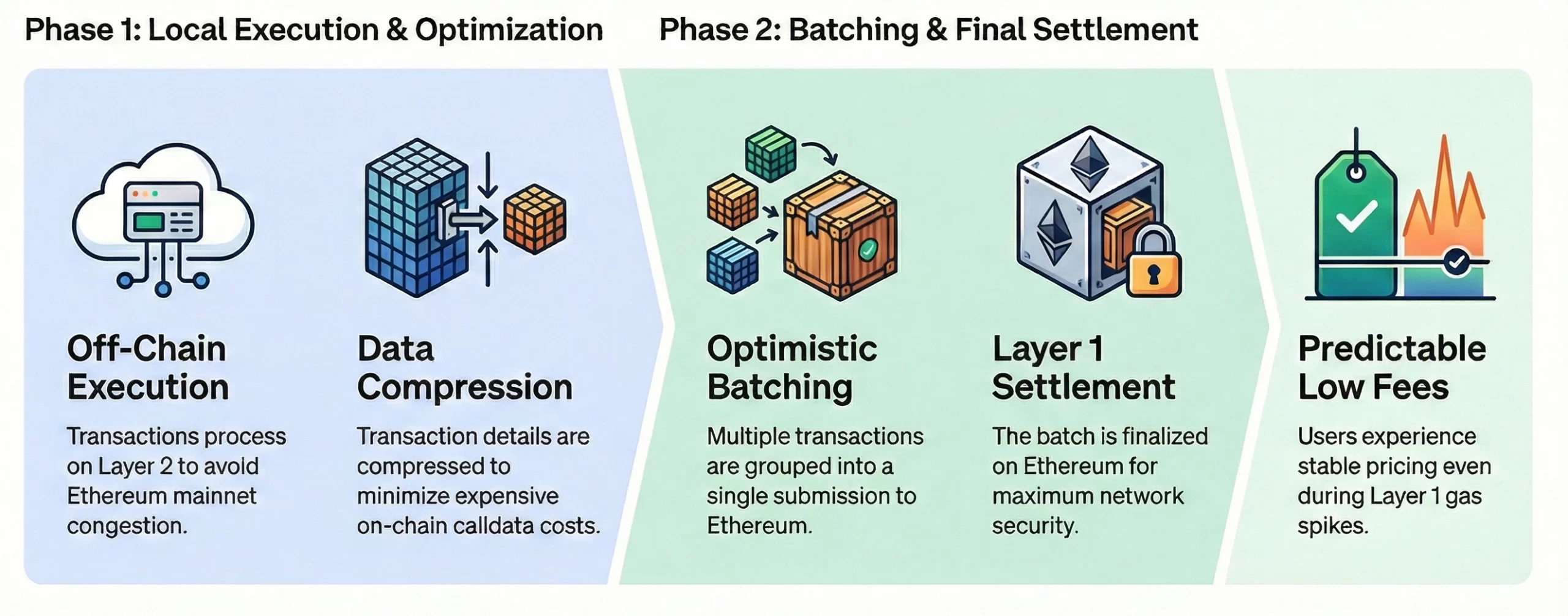
1. Lower Costs with Layer 2 Execution
Base operates as an Ethereum Layer 2 network that executes transactions off the Ethereum mainnet. By moving computation away from Layer 1, Base significantly reduces gas costs while still relying on Ethereum for final settlement and security.
2. Batching and Optimistic Rollups
Base uses Optimistic Rollup architecture to batch multiple transactions into a single submission to Ethereum. This spreads the cost of mainnet settlement across many transactions, lowering the average gas fee per user interaction when building and running Web3 apps.
3. Efficient Data Posting to Ethereum
Instead of posting full transaction execution details on-chain, Base submits compressed transaction data to Ethereum. This data optimization minimizes calldata costs, which directly contributes to lower gas fees for developers and end users.
4. Ethereum Security, Lower Gas Fees
When building a Web3 app on Base, developers benefit from Ethereum’s security guarantees without paying full Layer 1 gas fees for every transaction. This makes frequent actions such as minting, transfers, and interactions economically viable for consumer-scale applications.
5. Predictable Fees for Frequent Transactions
Base offers a more stable fee environment by executing transactions at the Layer 2 level and batching settlements to Ethereum. This predictability allows developers to design Web3 apps with frequent interactions, microtransactions, and consistent user experiences without exposure to volatile Layer 1 gas spikes.
Top Web3 Apps Built on Base
Top Web3 apps built on Base demonstrate how scalable Layer 2 infrastructure enables efficient decentralized finance, social, and consumer applications. These platforms highlight real-world adoption through low fees, speed, and Ethereum compatibility.
1. Aerodrome Finance
Aerodrome Finance is a decentralized exchange and liquidity hub focused on efficient token swaps, deep liquidity, and on-chain governance. By building on Base, it benefits from low gas fees, faster execution, and scalability while retaining Ethereum-level security.
2. MoveUP

MoveUP is a move-to-earn Web3 platform that rewards real-world physical activity using tokens and NFTs. Base enables MoveUP to handle frequent user transactions cost-effectively, ensuring smooth reward distribution, fast confirmations, and an accessible user experience.
3. Virtuals Protocol
Virtuals Protocol is an on-chain platform for creating, launching, and managing tokenized AI agents. Building on Base allows the protocol to deploy complex smart contracts efficiently, reduce operational costs, and scale AI interactions without high transaction fees.
4. Matcha
Matcha is a decentralized exchange aggregator that sources liquidity across multiple protocols to deliver optimal trade execution. Base enhances Matcha’s performance by lowering swap costs and speeding up transactions while maintaining seamless access to Ethereum’s DeFi ecosystem.
5. Alien Base

Alien Base is a decentralized trading platform offering token swaps, liquidity pools, and advanced DeFi features. By leveraging Base, it achieves faster transaction speeds, lower costs, and the scalability required to support active traders and liquidity providers.
Conclusion
Building a Web3 App on Base requires thoughtful planning across architecture, security, and scalability. By selecting the right tech stack and structuring smart contracts carefully, you create a foundation that supports performance and long term growth. A well designed Web3 App on Base benefits from low fees, fast transactions, and seamless integration with the Ethereum ecosystem. When these technical choices align with your product goals, development becomes more efficient and predictable. The result is an application that delivers value to users while maintaining reliability, transparency, and user trust over time.
Develop High-Performance Web3 Apps on Base with Us!
IdeaUsher can full-stack Web3 applications on Base with audited smart contracts, scalable backend services, and responsive frontends. Our approach combines efficient indexing, caching layers, and clean on-chain event models to keep apps fast, observable, and secure.
With a proven track record of 500,000+ development hours and experienced ex-MAANG/FAANG engineers, we deliver architectures that support growth, maintainability, and long-term performance.
Explore our portfolio showcasing a wide range of blockchain products built with a focus on security, scalability, and real-world usability.
Work with Ex-MAANG developers to build next-gen apps schedule your consultation now
FAQs
A strong architecture includes smart contracts on Base, a frontend using wallet connections, and a backend for indexing, analytics, and off-chain business logic. Add secure key management, role controls, and monitoring to support production reliability.
Common choices include Solidity with Hardhat or Foundry, React or Next.js for the frontend, and Node.js for APIs. Use indexers like The Graph or custom event listeners, plus a database for user and transaction data.
Use Base testnet for contract testing, run unit and integration tests locally, and verify contracts on block explorers. Add simulations for edge cases like reverts and failed transfers, then complete audits before mainnet deployment.
To scale, use RPC providers, caching, and indexing to reduce latency. Add observability for contract events, backend performance, and user flows. A reliable CI/CD pipeline, alerts, and incident handling are key for long-term stability.