In the dynamic realm of education, where traditional practices intersect with cutting-edge technologies, one innovation is generating significant interest: Virtual Reality (VR). As we progress further into the digital era, educators and technologists are increasingly captivated by VR’s potential to transform the teaching and learning experience.
The immersive nature of VR offers opportunities for experiential learning, allowing students to venture beyond the confines of classrooms into vibrant, interactive environments where subjects such as history, science, and art come to life. However, amidst the excitement, there are lingering questions: Is VR genuinely poised to revolutionize education, or is it simply a passing trend? This exploration delves into the possibilities, challenges, and implications of incorporating VR into education, aiming to provide insight into its potential to reshape the educational landscape.
What is VR Learning In Booming ?
VR Learning, also known as Virtual Reality Learning, refers to utilizing immersive virtual environments for educational purposes and facilitating interactive learning experiences. Below are some key aspects of VR Learning:
- Immersive Environment: VR technology enables students to enter computer-generated 3D worlds and interact with them using specialized devices like VR headsets.
- Real-world Simulation: VR can replicate real-life environments and scenarios, offering learners a safe and immersive platform to acquire and practice skills.
- Engagement: VR Learning has the potential to boost student engagement by introducing interactive and enjoyable learning experiences.
Applications: VR Learning finds applications across various educational domains. For instance, it’s utilized for immersive storytelling at San José State University, HVAC training at the Temperature Control Institute, and even in creating a VR chemistry lab at Morehouse College.
Key Market Takeaways for VR Education
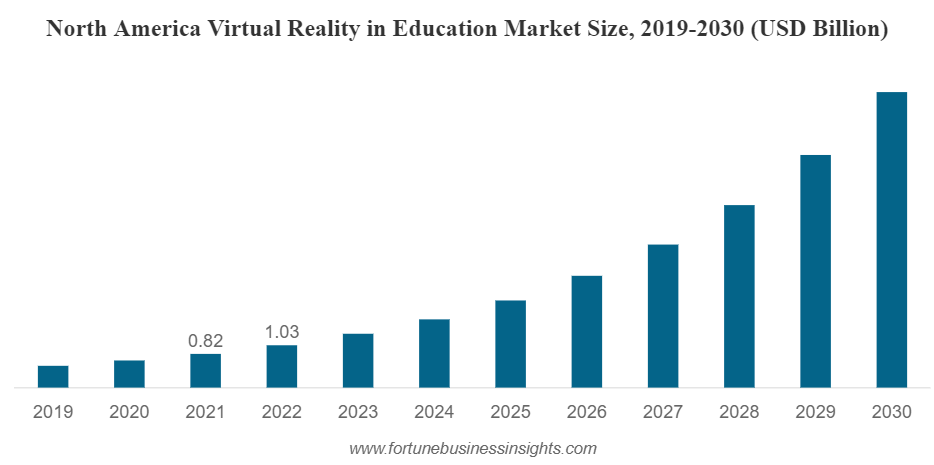
Source: FortuneBusinessInsights
By addressing common educational challenges such as Attention Deficit Disorders (ADD) and the limitations of traditional classroom learning, VR learning apps can help students overcome barriers to learning and unlock their full potential. Businesses that prioritize inclusivity and accessibility in their app development efforts stand to make a meaningful impact on education.
Leading companies such as Google LLC, EON Reality, and Schell Games are investing in VR education initiatives and developing innovative solutions to meet the growing demand. For example, Coursera launched VR technology courses in April 2023, aiming to enhance student learning experiences and provide certifications in collaboration with Meta’s Augmented Reality (AR) courses.
The VR education market is characterized by a diverse range of players, including technology giants like Google LLC and innovative startups like Veative Group and Alchemy Immersive. This diverse ecosystem fosters competition and drives innovation, leading to the development of advanced VR solutions tailored to the needs of educators and learners.
How Does VR Education Work?
VR education operates through a series of technical processes and components:
1. Content Creation:
- 360° Capture: Specially designed cameras capture real-world environments, providing a comprehensive spherical view.
- Post-processing: The captured footage undergoes editing, seamlessly stitching together multiple viewpoints and integrating interactive elements.
- Development: VR content is crafted using game engines like Unity or Unreal Engine, or through specialized VR authoring tools. This involves incorporating 3D models, animations, and interactive features.
2. Hardware and Delivery:
- VR Headsets: Devices such as Oculus Quest or HTC Vive offer stereoscopic visuals and head tracking, immersing users in the virtual environment.
- Immersive Classrooms: Projectors can create panoramic VR experiences on classroom walls, facilitating multi-user interactions without individual headsets.
3. User Interaction:
- Motion Controllers: Hand controllers enable users to manipulate virtual objects, navigate environments, and perform actions within the VR setting.
- Haptic Feedback: Advanced VR systems may utilize haptic feedback gloves or suits to provide users with tactile sensations, enhancing the immersive experience.
4. Educational Applications:
- Virtual Field Trips: Students can virtually visit historical sites, explore various ecosystems, or delve into the intricacies of the human body within a controlled environment.
- Interactive Learning: VR simulations offer engaging learning experiences where students can experiment with concepts and practice skills without real-world consequences.
- Visualizations: VR aids in visualizing complex concepts like molecular structures, historical events, or physiological processes, facilitating better understanding and retention of information.
How can Virtual Reality Improve Education?
While VR’s ability to engage and inspire students is readily acknowledged, its technical capabilities offer significant enhancements to the learning experience:
Knowledge Retention with Technical Finesse
Spaced Repetition Algorithms
Incorporating spaced repetition algorithms like the Leitner system into VR experiences enhances knowledge retention. These algorithms, based on the forgetting curve, present information at increasingly spaced intervals, optimizing memory retention over time. VR platforms can leverage machine learning to personalize these intervals, tailoring the learning experience to individual student needs.
Multisensory Learning with Haptic Feedback
VR environments are equipped with haptic feedback technology this can provide users with a tactile dimension to learning. By engaging multiple sensory channels, including touch, VR fosters deeper information processing and retention compared to traditional methods. Studies indicate that multisensory learning leads to enhanced comprehension and long-term memory encoding.
Personalized Learning through AI and Embodiment
Adaptive Learning with AI
AI-driven adaptive learning systems analyze student performance data to personalize the learning journey. By adjusting difficulty levels, providing tailored feedback, and offering alternative learning pathways, AI enhances engagement and comprehension. Virtual avatars or voice assistants guide students through personalized learning experiences, catering to diverse learning styles and paces.
Embodied Learning with Active Engagement
VR enables embodied learning experiences, allowing students to interact with virtual environments and manipulate objects. This active engagement promotes deeper understanding and knowledge application. Whether exploring historical sites or conducting virtual experiments, students gain practical insights and develop critical thinking skills through firsthand experiences.
Collaboration and Communication with Immersive Experiences
Multi-user VR Environments and Networked Learning
VR platforms create shared virtual spaces where students can collaborate, regardless of physical location. By working together on tasks and solving problems in immersive environments, students develop teamwork and communication skills. Networked learning connects students globally, fostering cultural exchange and preparing them for the interconnected world.
Real-time Communication with Spatial Audio
Spatial audio technology recreates real-world soundscapes within VR environments, enabling natural conversations and interactions. By replicating the direction and distance of sounds, spatial audio enhances immersion and facilitates effective communication. Whether engaging in group discussions or collaborative projects, students benefit from seamless communication in virtual spaces.
Also read, “Virtual Reality Meeting Platform Development : Complete Guide“
Skill Development and Assessment with Simulations and Immersive Testing
VR Simulations for Skill Development
VR simulations provide risk-free environments for students to hone practical skills. From conducting scientific experiments to practicing surgical procedures, VR offers hands-on learning experiences without real-world consequences. Integrated assessment tools provide real-time feedback, enabling students to track their progress and refine their skills iteratively.
Immersive Assessment Beyond Traditional Testing
VR-based assessments move beyond traditional testing methods to evaluate students’ comprehensive understanding and skills application. By simulating real-world scenarios, VR assessments measure critical thinking, decision-making, and problem-solving abilities in practical contexts. This holistic approach provides educators with deeper insights into students’ learning outcomes and areas for improvement.
How Virtual Reality Enhances Student Learning?
Virtual reality offers numerous benefits for students, with the primary advantages outlined as follows:
1. Enhanced sensory learning through multimodal interaction
VR goes beyond traditional text and lecture-based learning by engaging multiple senses simultaneously. By immersing students in virtual environments that stimulate sight, sound, and potentially touch, VR promotes neuroplasticity, leading to deeper understanding and improved knowledge retention.
Example: In a high school biology class, students can use VR headsets to explore the human body in 3D at a cellular level. They can virtually dissect organs, navigate through blood vessels, and manipulate cellular structures, enhancing their understanding of complex anatomy and physiology. This surpasses traditional 2D diagrams and static models, providing a spatially accurate and interactive learning experience.
2. Fostering spatial cognition through embodied interaction
VR allows students to physically interact with virtual environments, promoting embodied cognition. This hands-on approach helps students learn by actively engaging with the material, leading to a better grasp of complex spatial concepts such as molecular structures or historical battlefields.
Example: In a middle school math class, students can engage in a VR simulation where they explore a virtual world while solving mathematical problems integrated into the environment. Collecting virtual coins by solving equations or navigating through geometric shapes reinforces key math concepts and provides real-time feedback on their progress. The system can adapt difficulty based on individual performance, creating a personalized learning journey for each student.
3. Data-driven personalized learning via biofeedback integration
VR experiences can incorporate biofeedback sensors to track physiological responses like heart rate and brain activity. This data can be used to personalize learning, identifying areas of difficulty and providing real-time feedback to adjust instruction accordingly.
Example: An elementary school can take a virtual field trip to the Great Barrier Reef using VR headsets. Students can swim alongside virtual marine life, explore the reef ecosystem, and interact with educational hotspots that provide information about different species and conservation efforts. This provides an immersive and engaging experience that transcends geographical limitations compared to traditional field trips.
Also read, “Augmented Reality App Development: A Quick Guide“
4. Promoting empathy and social skills
Collaborative virtual spaces in VR enable students to work together on tasks, fostering important social skills like communication and collaboration. VR can also help develop empathy by allowing students to experience different perspectives and understand diverse viewpoints.
Example: In a high school history class, students can participate in a VR simulation of a historical event, like the signing of the Declaration of Independence. They can role-play different historical figures and engage in constructive discussions within the immersive environment. This fosters collaboration, communication skills, and critical thinking as students analyze the event from diverse perspectives.
5. Gamification and adaptive learning
VR experiences can be gamified with elements like points and leaderboards to increase motivation and engagement. Additionally, AI-powered adaptive learning algorithms can tailor content and difficulty levels to individual student performance, creating a personalized learning experience.
Example: A vocational training program can utilize VR to create a simulated laboratory environment for students to practice welding techniques. They can virtually operate welding equipment in a safe and controlled space, receive real-time feedback on their technique, and repeat the simulation as needed to improve their skills before transitioning to real-world practice.
6. Building future-ready skillsets through immersive simulations
VR provides realistic simulations of real-world scenarios, allowing students to practice and develop skills needed in the future workplace, such as surgical procedures or scientific experiments.
Example: VR experiences can be equipped with eye-tracking and motion tracking technology. This data can be analyzed to understand student engagement, identify areas of difficulty, and personalize instruction. Teachers can then adapt their teaching methods based on individual student needs, creating a more data-driven and effective learning approach.
How VR Can Enhance Learning in a Classroom Settings: A Case Study
Traditional classroom environments can often struggle to ignite student interest and effectively convey complex scientific concepts. Virtual Reality (VR) presents a captivating solution, offering immersive experiences that foster engagement and knowledge retention. This case study dives deeper into the 2018 implementation of VR at Lincoln High School in San Jose, California, focusing specifically on its impact on 8th-grade science education and exploring the technical aspects in greater detail.
Technical Considerations:
- VR Hardware: Lincoln High School utilized the Merge Cube, a cost-effective and portable VR system. It comprises a foam cube housing a smartphone, leveraging readily available mobile technology.
- VR Software: The chosen educational application, Visible Body: Human Anatomy Atlas, is a well-established resource in the field of medical visualization. It boasts a comprehensive library of 3D anatomical models and interactive functionalities.
- Technical Specifications:
- VR Platform: Merge Cube (smartphone-based)
- Operating System: Android or iOS (depending on the smartphone used)
- Connectivity: Bluetooth connection between the smartphone and the Merge Cube
- Application Features:
- Extensive library of 3D anatomical models, encompassing the entire human body and individual organ systems
- Interactive manipulation of organs for detailed examination through hand movements and spatial awareness
- Information overlays providing detailed anatomical descriptions and functionalities through a user-friendly interface
- Interactive quizzes and labeling exercises to assess understanding and reinforce learning
Implementation and Pedagogical Approach:
- Lesson Design: Teachers carefully integrated VR into the existing curriculum, ensuring alignment with learning objectives and building upon foundational knowledge. Pre-VR activities introduced key anatomical concepts, followed by VR-based exploration sessions where students actively interacted with the virtual human body. Post-VR activities solidified understanding through discussions, quizzes, and creative projects.
- Teacher Training: Lincoln High School invested in comprehensive teacher training to ensure effective VR integration. This included familiarization with the technology, pedagogical best practices for VR-based learning, and strategies for managing and optimizing classroom activities using VR.
Evaluation and Impact:
A multi-faceted approach was employed to assess the impact of VR:
- Quantitative Data: Standardized science test scores revealed a statistically significant improvement in students’ anatomical knowledge compared to previous years without VR.
- Qualitative Data:
- Classroom Observations: Teachers reported increased student engagement, active participation in discussions, and a deeper understanding of the material evidenced by insightful questions and problem-solving abilities.
- Student Surveys: Overwhelmingly positive student feedback highlighted increased interest in learning about the human body, appreciation for the interactive nature of VR lessons, and improved comprehension of complex anatomical concepts.
A Few Considerations:
Despite the success of the VR implementation, acknowledging challenges is crucial:
- Cost: While the Merge Cube offered a more affordable VR option, budget constraints remain a significant hurdle for widespread VR adoption in schools.
- Accessibility: Ensuring equitable access for all students requires addressing potential physical limitations and providing alternative learning opportunities for students who may not have access to VR technology at home.
- Technical Support: Ongoing technical support is essential to address hardware or software issues that might arise, requiring dedicated personnel or partnerships with technology providers.
- Curriculum Integration: Effective VR integration demands strategic planning, professional development for teachers, and potentially the creation of VR-specific learning materials to maximize its potential for learning and engagement.
Also read, “Virtual Reality Development: Strategies for Effective Planning and Execution“
What is a virtual field trip for education?
In recent years, education has undergone a remarkable transformation, propelled by advancements in technology. Among these innovations, Virtual Field Trips (VFTs) stand out as a compelling tool for educators seeking to enrich the learning experience. Leveraging Virtual Reality (VR) technology, VFTs offer students the opportunity to embark on immersive journeys to virtually any destination worldwide, transcending the confines of traditional classrooms. Let’s delve into the myriad benefits these virtual excursions bring to education.
Technical Aspects and Benefits:
VR Headsets: Opening Doors to New Worlds
VR headsets serve as the gateway to immersive learning experiences, providing students with a first-person perspective akin to physically being present in the environment. High-resolution displays and wide field of view ensure optimal visual fidelity, fostering a realistic sense of presence crucial for effective learning.
360° Video and Panoramic Images: A Window to Exploration
For those without access to VR headsets, 360° video and panoramic images offer an accessible alternative. Students can navigate these environments using simple controls, enabling them to explore destinations with ease. These immersive visuals capture the essence of a location, allowing students to delve into its intricacies and nuances.
Interactive Features: Engaging Minds Through Interaction
Interactive elements such as hotspots, 3D models, and gamification mechanics elevate engagement and facilitate deeper learning. Hotspots provide additional context when interacted with, while 3D models enable students to examine objects from all angles. Incorporating gamification elements like quizzes and challenges adds an element of fun, motivating students to actively participate in the learning process.
Accessibility and Cost-Effectiveness:
Overcoming Geographic Barriers
One of the most significant advantages of VFTs is their ability to transcend geographical limitations. Students, regardless of their location or physical abilities, can partake in these enriching experiences, leveling the playing field for all learners.
Cost-Effective Learning Solutions
Traditional field trips often come with logistical challenges and expenses. VFTs eliminate the need for travel, permission slips, and associated costs, making them a more budget-friendly option for schools with limited resources. By removing financial barriers, VFTs ensure equitable access to high-quality educational experiences for all students.
Immersive Learning and Engagement:
Stimulating the Senses
The sensory immersion offered by VFTs stimulates multiple senses, creating a truly immersive learning environment. High-resolution visuals combined with spatial audio transport students to distant locales, fostering a deep sense of presence and enhancing learning retention.
Fostering Active Learning
VFTs promote active engagement by encouraging students to explore, interact, and manipulate virtual elements. By empowering students to take control of their learning journey, VFTs foster critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and creativity.
Cultivating Emotional Connections
Beyond academic knowledge, VFTs have the power to evoke emotional responses and foster empathy. By experiencing historical events, cultural landmarks, or environmental phenomena firsthand, students develop a deeper understanding and appreciation for the world around them.
Examples and Future Applications:
Journeying Through Time: Virtual Museums
Virtual museums allow students to explore historical artifacts and artworks in unprecedented detail. By interacting with exhibits in 3D, students gain insights and perspectives that transcend traditional museum visits.
Reliving History: Immersive Reenactments
Through immersive historical reenactments, students can step into the shoes of historical figures and witness pivotal moments in time. By experiencing history firsthand, students develop a deeper connection to the past and a greater appreciation for its significance.
Exploring the Unseen: Virtual Dissections
Virtual dissections offer a safe and ethical alternative to traditional lab experiments. By dissecting virtual specimens in 3D, students gain a comprehensive understanding of biological structures and processes, without the need for physical specimens.
Top 10 VR Learning Apps in the USA
Here’re some interesting case studies of VR Learning apps in USA,
1. Apollo 11 VR
Cost: £7.99 on Quest.
Target audience: Students interested in space exploration and history.
- Learning objectives:
- Gain a first-hand understanding of the Apollo 11 mission and its significance.
- Experience the challenges and triumphs faced by the astronauts.
- Learn about the technology used in space travel.
- Strengths:
- Immersive and engaging experience that brings history to life.
- Combines original archival footage with 3D recreations for accuracy and emotional impact.
- Educational and inspirational for students of all ages.
2. Bodyswaps
Cost: Demos available on Quest.
Target audience: Students preparing for careers that require strong communication, teamwork, and leadership skills.
- Learning objectives:
- Practice and develop communication skills in realistic workplace scenarios.
- Improve teamwork and collaboration abilities through real-time interaction.
- Enhance leadership skills by observing situations from different perspectives.
- Strengths:
- Unique “bodyswapping” mechanic allows students to see themselves through others’ eyes.
- Provides opportunities to practice soft skills in a safe and controlled environment.
- Prepares students for real-world workplace challenges.
3. Wander
Cost: £7.99 on Quest.
Target audience: Students of all ages and subjects.
- Learning objectives:
- Explore different cultures and geographical locations virtually.
- Gain a deeper understanding of historical landmarks and events.
- Supplement classroom learning with immersive experiences.
- Strengths:
- Offers limitless exploration possibilities, allowing students to visit any place in the world.
- Integrates with Google Maps Street View for realistic and up-to-date visuals.
- Provides a valuable tool for remote learning and virtual field trips.
4. Engage
Cost: £4.99 per month.
Target audience: Educators and students of all ages and subjects.
- Learning objectives:
- Create and participate in immersive learning experiences.
- Facilitate interactive lessons, conferences, and private sessions.
- Collaborate and learn from others in a virtual environment.
- Strengths:
- Provides a platform for educators to design and host their own VR classes.
- Allows for multi-user interaction and collaboration between students and educators worldwide.
- Offers customization options for avatars, environments, and objects.
5. Tilt Brush
Cost: £14.99 on Quest.
Target audience: Students of all ages and those interested in art, design, and creative expression.
- Learning objectives:
- Explore 3D art creation using intuitive tools and a virtual canvas.
- Develop creativity and spatial thinking skills.
- Learn about color theory, composition, and other artistic concepts.
- Collaborate and create art with others in a virtual environment (Multibrush only).
- Strengths:
- Easy-to-use interface allows even beginners to create impressive 3D artwork.
- Offers a wide variety of brushes, colors, and effects to experiment with.
- Encourages creative expression and exploration in a unique medium.
- Fosters collaboration and social interaction in the Multibrush version.
6. ShapesXR
Cost: Free on Quest.
Target audience: Students interested in design, prototyping, and storytelling.
- Learning objectives:
- Learn the basics of 3D design and modeling in a virtual environment.
- Develop spatial reasoning and problem-solving skills.
- Create and iterate on design ideas quickly and easily.
- Collaborate with others on design projects in real-time.
- Strengths:
- User-friendly interface with an interactive onboarding process suitable for beginners.
- Allows rapid prototyping and visualization of design ideas in 3D.
- Enables real-time collaboration, fostering teamwork and communication.
- Free to use, making it accessible to a wider audience.
7. Ocean Rift
Cost: $9.99
Target audience: Students of all ages, particularly those interested in biology, marine life, and oceanography.
- Learning objectives:
- Explore the underwater world and its diverse ecosystems in a virtual environment.
- Learn about different marine animals, their habitats, and behaviors.
- Develop an appreciation for the beauty and fragility of the ocean environment.
- Strengths:
- Provides a fun and engaging way to learn about marine life.
- Offers 360° freedom of movement for a truly immersive experience.
- Showcases a variety of marine animals, including dolphins, sharks, and even dinosaurs.
- Can be used as a supplement to classroom lessons on biology or natural sciences.
8. ThinkLink
Cost: Free.
Target audience: Students and educators of all ages and subjects.
- Learning objectives:
- Create and share interactive multimedia content.
- Enhance presentations, assignments, and learning materials.
- Encourage critical thinking and engagement with information.
- Strengths:
- Versatile tool that can be used for various subjects and learning activities.
- Allows for the creation of interactive content that goes beyond static images and videos.
- Easy to use and share with students, fostering collaboration and communication.
- Free to use, making it accessible to a wide audience..
9. InMind VR 2
Cost: Free.
Target audience: Students interested in learning about the brain and its functions.
- Learning objectives:
- Explore the brain in a gamified and interactive way.
- Learn about different brain regions and their roles in various functions.
- Understand the process of brain development and maturation.
- Strengths:
- Makes learning about the brain fun and engaging, especially for younger students.
- Uses a game-based approach to encourage exploration and information retention.
- Provides a unique perspective on the brain through a virtual reality experience.
10. 4D Anatomy
Cost: Free
Target audience: Students studying anatomy, biology, and healthcare professions.
- Learning objectives:
- Gain a comprehensive understanding of human anatomy through interactive exploration.
- Examine the human body in detail from different angles and perspectives.
- Test knowledge and understanding through integrated quizzes.
- Strengths:
- Offers a highly detailed and interactive 3D model of the human body.
- Allows students to explore various anatomical structures and systems in depth.
- Includes quizzes to assess learning and reinforce knowledge retention.
Also read, “How to Develop a Virtual Reality Escape Game“
Conclusion
Virtual Reality (VR) holds immense promise for revolutionizing education, it’s essential to recognize that it’s not a one-size-fits-all solution. VR can certainly enhance learning experiences by providing immersive simulations and interactive environments, but its widespread adoption and integration into educational systems will require overcoming various challenges. These include accessibility issues, the need for specialized equipment, concerns about content quality and relevance, and the necessity for teacher training and support. However, with continued advancements in technology and a concerted effort from educators, developers, and policymakers, VR has the potential to significantly transform the way we teach and learn in the future.
Looking to Develop a VR Education APP for Your Business?
If you’re intrigued by the potential of Virtual Reality in education and seeking to explore its possibilities further, IdeaUsher is here to assist you. Whether you’re envisioning a mobile app or web app that leverages VR technology to enhance learning outcomes, our team of experienced developers can bring your ideas to life. With a focus on innovation and user-centric design, we’ll work closely with you to develop immersive educational solutions tailored to your specific needs. Contact us today to embark on your journey towards harnessing the power of VR in education.
Work with Ex-MAANG developers to build next-gen apps schedule your consultation now
FAQs
Q1: Is VR actually the future?
A1: Virtual Reality (VR) indeed holds significant potential to shape the future, especially in various fields such as education, healthcare, gaming, and entertainment. While it may not entirely replace traditional methods, VR technology offers immersive and interactive experiences that can enhance learning, training, and entertainment. With ongoing advancements in VR hardware, software, and content creation, it’s poised to become an integral part of our daily lives in the future.
Q2: Can VR be used for education?
A2: Absolutely. VR has already demonstrated its effectiveness as a valuable tool for education. By providing immersive simulations and interactive environments, VR can engage students in ways that traditional teaching methods cannot. It allows learners to explore historical landmarks, dissect virtual specimens, conduct scientific experiments, and more, all within a safe and controlled environment. VR promotes active learning, fosters critical thinking skills, and enhances retention, making it a powerful asset in educational settings.
Q3: What is the value of VR in education?
A3: The value of VR in education lies in its ability to create immersive learning experiences that transcend traditional classroom boundaries. VR enables students to interact with educational content in three-dimensional space, enhancing their understanding and retention of complex concepts. It caters to diverse learning styles, provides hands-on learning opportunities, and fosters engagement and motivation. Moreover, VR can bridge geographical barriers, allowing students to access educational resources and experiences regardless of their location.
Q4: How AI is going to shape the future of education?
A4: Artificial Intelligence (AI) is poised to revolutionize education by personalizing learning experiences, automating administrative tasks, and augmenting teaching and assessment processes. AI-powered adaptive learning platforms can tailor educational content to individual student needs, providing personalized instruction and feedback. AI-driven analytics can track student progress, identify areas for improvement, and inform instructional decisions. Additionally, AI-powered virtual tutors and chatbots can provide instant assistance and support to students, enhancing their learning experience both inside and outside the classroom. Overall, AI holds immense potential to improve educational outcomes, increase efficiency, and democratize access to quality education worldwide.