Bitcoin has the potential to become a global currency. However, its limited transaction capacity has been a major barrier to its adoption for everyday purchases. On-chain transactions have been slow and expensive, making them impractical for many users. Luckily, a new solution called the Ledger Lightning Network promises to transform Bitcoin transactions. This second-layer protocol operates on top of the Bitcoin blockchain and creates a network of micropayment channels between users. The Lightning Network enables off-chain transactions, which significantly reduces the load on the main blockchain and promises near-instantaneous and ultra-low-cost Bitcoin transactions.
Several companies, such as Lightning Labs, Lightspark, and Cash App, are already reaping the benefits of these technologies by demonstrating the real-world applications of the Lightning Network. Read on to discover how these advancements can translate into advantages for your own business.
This blog explores the intricacies of the Lightning Network, including its technical aspects, benefits for businesses, and potential impact on the financial sector. By adopting the Lightning Network, businesses like yours can actually improve their operations and contribute to the broader adoption of Bitcoin.
Why Does BITCOIN Need Faster Transactions?
Transactions in Bitcoin are recorded on a transparent ledger called the blockchain, which is safeguarded by the collective participation of its network members and the meticulous process of validating transactions.
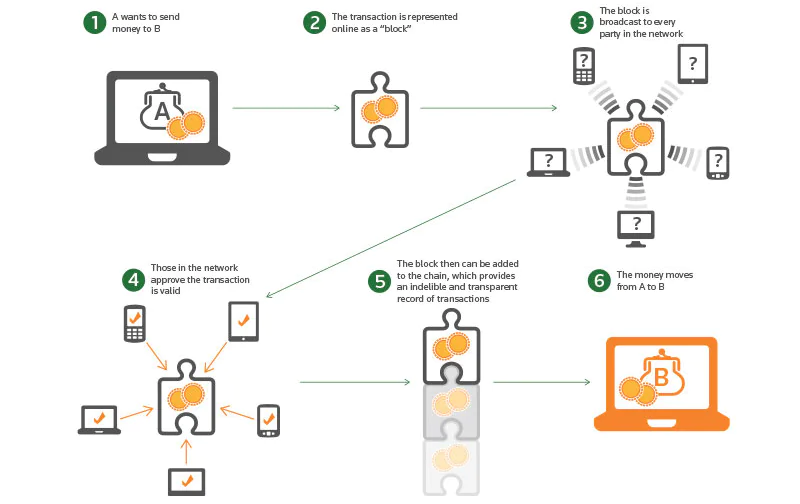
But why is it important to have faster Bitcoin transactions? Here’s why:
1. Efficiency:
Faster transaction speed results in a more efficient cryptocurrency. The faster a blockchain can process transactions, the smoother the transfer of data between parties and the quicker the validation of transactions.
2. Scalability:
Bitcoin has scalability issues. Although a single Bitcoin block can theoretically handle up to 4MB of data, real-world blocks typically handle around 1 MB to 1.5 MB. This means that a large number of transactions remain stuck in the mempool, which leads to significant delays.
3. User Experience:
Slow transaction times can be frustrating for users. Transactions with higher fees typically get confirmed faster by being included in the next block. On the other hand, transactions with lower fees can take longer to confirm.
What Is Lightning Network?
The Lightning Network simplifies how we handle cryptocurrency transactions. It is an innovative Layer-2 payment system that is still in development. It addresses a crucial issue in blockchain, which is the need for faster and more scalable transactions. It adds a layer above existing blockchains like Bitcoin that significantly reduces transaction times and costs, making transactions more efficient and accessible.
Traditionally, each blockchain transaction is recorded on the main blockchain, but the Lightning Network allows users to create direct payment channels between themselves. These channels act as private tunnels for off-chain transactions, enabling instant and secure exchanges of funds without the need for on-chain confirmation.
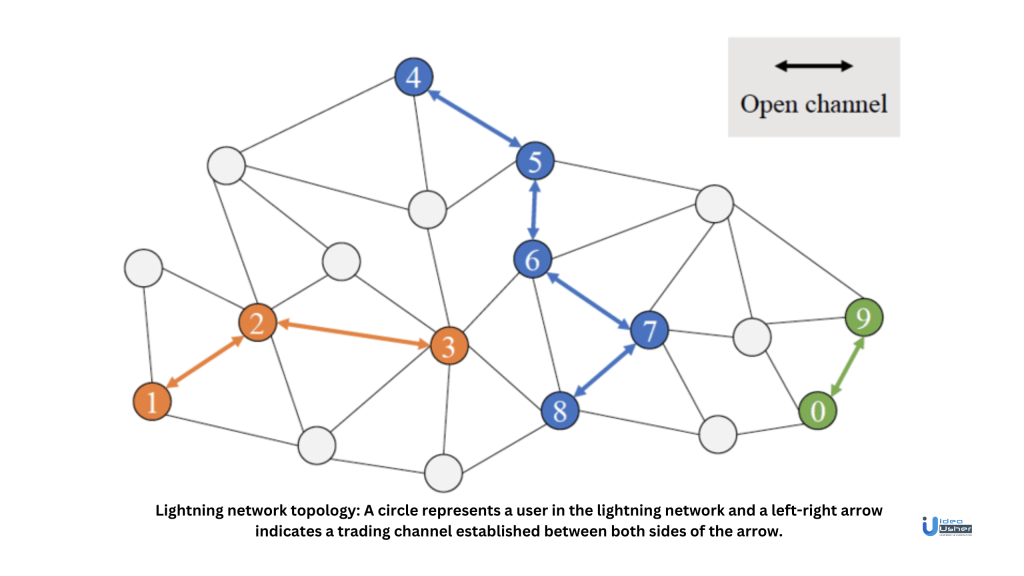
Lightning Network has a robust consensus mechanism known as the local two-party consensus. This mechanism ensures the integrity and security of transactions within payment channels. Moreover, it also eliminates the need for intermediaries by requiring mutual agreement for channel state updates that ensure direct and transparent transactions.
How Does The Lightning Network Work?
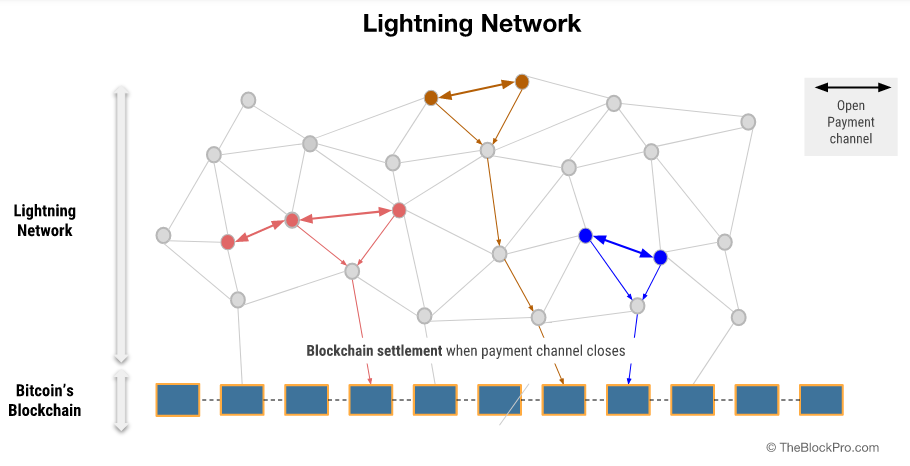
The Lightning Network tackles the limitations of Bitcoin’s on-chain transactions by establishing a network of payment channels. These channels operate off-chain, significantly boosting transaction speed and reducing costs. Here are the inner workings of this innovative system:
Step 1: Channel Creation:
It begins with two parties establishing a payment channel. This involves locking a predetermined amount of Bitcoin from both users’ wallets into a jointly controlled address on the Bitcoin blockchain. It is like a secure vault requiring keys from both parties for access and safeguarding the deposited funds.
Step 2: Off-Chain Transactions:
Once the channel is open, it transforms into a rapid exchange path for Bitcoin between the participants. Users can send and receive Bitcoin back and forth within this channel, bypassing the main blockchain entirely. These off-chain transactions within this channel occur under the radar of the main blockchain and are significantly faster and cheaper compared to traditional on-chain transactions that, too, without hefty fees.
Step 3: Keeping Track:
As transactions occur within the channel, the system keeps a running tally. Instead of recording every single transaction detail, the Lightning Network utilizes cryptography and employs unique codes called Hashes to represent the current balance without revealing the entire transaction history.
Step 4: Channel Closure:
Eventually, when users decide to conclude their transactions, they close the channel. This involves broadcasting a final settlement transaction on the Bitcoin blockchain. This transaction reflects the final balance for each party, similar to reconciling a shared account. The multi-signature address then releases the corresponding amount of Bitcoin back to each user’s respective wallet.
Step 5: Payment Routing:
The benefit of the Lightning Network lies in its ability to facilitate payments even between users who lack a direct channel (unconnected users), and this facility is achieved through a network of interconnected channels. Payment routing protocols act as intelligent navigators that find a path through networks to connect the sender and receiver, even if they aren’t directly linked.
Step 6: Dispute Management:
If there’s a disagreement, like when a node sends out wrong (possibly dishonest) transaction details, the process of finalizing the transaction is put on hold during a “dispute period.” During this time, nodes can question the proposed transaction. If another node provides a more up-to-date record of transactions, then all the funds that were set aside for the transaction are transferred to this second node.
Key Features Of The Lightning Network
Here are the six features of the Lightning Network that stand out:
1. Fast Transactions:
The Lightning Network excels in facilitating rapid transactions and provides a swift and cost-effective alternative to traditional Bitcoin transfers. With the capability to process transactions instantly, even in large volumes, it sets a new standard for efficiency in digital payments.
2. Scalability:
A standout advantage of the Lightning Network is its off-chain scalability, which alleviates the strain on networks like Bitcoin. By moving transactions away from the main blockchain and employing micropayment channels, it ensures smooth processing for transactions of any size.
3. Security And Privacy:
Security and privacy are important within the Lightning Network; thereby, it has the feature of multi-signature address and hash timelock contracts, which are the measures to safeguard transactions.
4. Network Of Nodes:
Lightning Network has a sturdy network of nodes that are essential for routing transactions and ensuring seamless fund transfers between users. These diverse nodes in operation benefit users from enhanced connectivity and reliability.
5. Bidirectional Payment Channels:
The Lightning Network’s bidirectional payment channels enable users to send and receive funds within the same channel, enhancing liquidity and flexibility. This innovative feature empowers users to conduct transactions efficiently and conveniently.
6. Cross-Blockchain Transactions:
In addition to its scalability and security features, the Lightning Network supports cross-blockchain transactions through atomic swaps. This groundbreaking functionality enables seamless interoperability between different cryptocurrencies and provides users with opportunities to manage their digital assets across multiple platforms.
Pros And Cons Of Ledger Lightning Network
The Lightning Network addresses the limitations of on-chain transactions. However, like any new technology, it comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Here are the both sides of the coin:
Pros:
- Faster Transactions: One of the most compelling advantages of the Lightning Network is its ability to allow near-instantaneous transactions. This is a significant improvement over on-chain transactions, which can take minutes or even hours to confirm.
- Reduced Fees: Due to the off-chain nature of transactions, the Lightning Network significantly reduces transaction fees compared to on-chain transactions. This opens the door for micropayments, previously deemed impractical due to high fees.
- Scalability: The Lightning Network offers a promising solution to Bitcoin’s scalability issues. By offloading a substantial portion of transactions off-chain, it allows the network to handle a much higher volume compared to its on-chain limitations.
- Enhanced Privacy: While not completely anonymous, transactions within a payment channel are invisible to the public ledger. Only the final settlement amount becomes visible on the blockchain, offering a degree of privacy for users.
Cons:
- Complexity: The Lightning Network introduces a layer of complexity compared to traditional Bitcoin transactions as it requires users to understand how to open and manage channels, which can be a barrier for some.
- Centralization Risks: The current design of the Lightning Network relies on intermediary nodes to route payments. This can lead to potential centralization risks if a limited number of nodes control a large portion of the network.
- Security Considerations: While the Lightning Network leverages the security of the Bitcoin blockchain, there are potential security risks associated with individual channels. Improper channel management or vulnerabilities in routing protocols could lead to loss of funds.
- Limited Adoption: The Lightning Network is still in its early stages of development and adoption. This can lead to challenges in finding suitable channels for transactions and limited merchant acceptance.
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT): The Foundation For The Lightning Network
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) is the foundational technology upon which the Lightning Network is built. It is a system that allows multiple participants, known as nodes, to access, verify, and record transactions in a decentralized manner without the need for a central authority or intermediary. This technology operates on a framework that ensures the security and integrity of the data across the network.
The Lightning Network, which is a “layer 2” payment protocol, uses this technology to enable fast transactions among participating nodes. With DLT, it creates a decentralized network of payment channels that enables off-chain transactions and multiple micro-transactions without clogging the main blockchain.
How Does Distributed Ledger Technology Enable The Lightning Network?
The Lightning Network relies on DLT to operate efficiently. Here is how it functions:
- Through its core features, such as decentralization and transparency, DLT establishes a secure environment conducive to trustless transactions within the Lightning Network.
- Both DLT and the Lightning Network share a peer-to-peer architecture and facilitate direct payments with minimal intervention from third parties.
- DLT plays a crucial role in enabling off-chain transactions within the Lightning Network, which allows it to manage numerous small payments without congesting the main blockchain.
- Here, the routing nodes are the integral components of the Lightning Network. It uses the DLT to create a network of paths for payments and improves overall payment flow and accessibility.
- Smart contracts – powered by DLT – further enhance the Lightning Network by enabling instant micropayments and increasing transaction volume while ensuring the safety and validity of each transaction.
Different Types Of DLTs
There are several types of Distributed Ledger Technologies (DLTs), each with its own unique features and use cases. Here are some of the most common types:
1. Blockchain:
Blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum are considered the pioneering architecture of DLT. It records data in chronologically ordered blocks. Each block is securely linked to the one preceding it, forming an immutable chain. This approach guarantees unparalleled security but can potentially result in slower transaction processing times due to the rigorous validation processes employed by miners or validators.
2. Consortium Blockchain:
This form of DLT is permissioned, meaning only approved participants can access the network. It provides enhanced control and potentially quicker transaction times compared to public blockchains. However, it compromises some aspects of decentralization inherent to DLT. Consortium blockchains are frequently employed in business scenarios where privacy, authority, and speed take precedence.
3. Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG):
Unlike blockchains, DAGs utilize a directed acyclic graph (like a directed flowchart) to structure data. This structure allows faster transaction processing compared to blockchains. However, DAGs might possess a slightly lower level of security compared to traditional blockchains due to their distinct validation mechanisms.
4. Tangle:
This is a specialized type of DAG employed by the IOTA cryptocurrency. Tangle takes an innovative step further by enabling transactions to validate other transactions, effectively eliminating the need for mining fees. This unique approach makes Tangle particularly well-suited for the Internet of Things (IoT) applications where frequent, low-value transactions are commonplace.
5. Sidechain:
Sidechains operate as independent blockchains tethered to the main blockchain (like Bitcoin). This configuration facilitates faster and more scalable transactions on the sidechain while still benefiting from the security of the main blockchain through a two-way peg. However, this setup introduces a degree of centralization, as permission might be required to access the sidechain.
6. Holochain:
This DLT breaks the conventional mold. Instead of a shared global chain, Holochain empowers each node (computer on the network) to maintain its own blockchain. This distributed approach promotes scalability and efficiency, making it suitable for applications that generate high volumes of data or necessitate complex interactions. However, ensuring consistency across all these individual chains can be a challenge.
7. Hashgraph:
This DLT utilizes a communication protocol. In this, nodes actively engage with each other to exchange transaction information so they can reach a consensus on the validity of transactions. This approach is known for its exceptional speed and security, making it a promising contender for applications demanding both attributes. However, Hashgraph is a relatively new technology, and its long-term viability compared to more established DLTs requires further observation.
Top 5 Real-World Sectors Using Specific DLTs For Operations
1. Supply Chain Enhancement:
DLTs are being utilized to boost transparency and efficiency in supply chain management. They provide a secure and unalterable record of product movement from origin to consumer, helping to prevent fraud and counterfeiting.
2. Healthcare Data Management:
In the healthcare sector, DLTs are being used for secure and efficient data management. They allow for the creation of a single, unchangeable record for each patient, improving data integrity and interoperability.
3. Identity Verification:
DLTs are being used for identity verification in various industries. They provide a secure and efficient means of verifying identities, reducing the risk of identity theft and fraud.
4. Voting Systems:
Some governments and organizations are exploring the use of DLTs for voting systems. They offer a transparent and secure way of recording votes, potentially reducing the risk of vote tampering.
5. Financial Transactions:
Many financial institutions are using DLTs to streamline and secure financial transactions. They offer a faster, more efficient alternative to traditional banking systems.
Apart from this, several other industries like aviation, education, insurance, manufacturing, transportation, utilities, music, and entertainment have also implemented DLTs for their day-to-day operations, such as managing intellectual property rights, tracking ownership, etc.
Choosing The Right DLT For Your Business
Selecting the appropriate Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) for your business depends on a variety of factors. Here are some points to consider:
- Business Requirements: Comprehend your business requirements and goals. Different DLTs offer different capabilities, so it’s crucial to select one that aligns with your business objectives.
- Scalability: Evaluate the scalability of the DLT. If your business is expected to expand rapidly, you’ll need a DLT that can scale accordingly.
- Security: Security is a vital factor. Ensure the DLT you select has strong security measures in place.
- Consensus Mechanism: Different DLTs employ different consensus mechanisms. Choose a DLT with a consensus mechanism that fits your business needs.
- Interoperability: If your business operates in a diverse technological environment, consider a DLT that offers interoperability with other systems.
- Community and Support: Consider the community and support available for the DLT. A strong and growing community can provide valuable resources and help.
- Cost: Lastly, consider the cost of implementing and maintaining the DLT. This includes not only the direct costs of the technology itself but also the indirect costs of training staff and integrating the DLT into your existing systems.
Based on these considerations, you can select a suitable DLT for your organization. To help you make effective decisions, here are some highlights of the above-mentioned DLTs:
| Feature | Structure | Security | Scalability | Speed | Decentralization | Consensus Mechanism | Use Cases |
| Blockchain | Chain of Blocks | High | Lower | Slower | Public or Private | Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS) | Asset tracking, Regulatory compliance |
| Consortium Blockchain | Permissioned Chain | High (permissioned) | Moderate | Moderate | Permissioned | Varies | Supply chain management, Trade finance |
| Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) | Directed Acyclic Graph | Moderate | Higher | Faster | Public or Private | Varies | Micropayments, Data streaming |
| Tangle (IOTA) | Directed Acyclic Graph | Moderate | Higher (feeless) | Fastest | Public | Varies | IoT micropayments |
| Sidechain | Separate Blockchain (attached) | High (main chain) | Higher | Faster | Partially | PoW or PoS on main chain | Faster payments |
| Holochain | Individual Chains per Node | Moderate | Highest | Fastest | Highest | Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) | High-volume data, Complex interactions |
| Hashgraph | Gossip Protocol | High | High | High | Public | Gossip about Gossip | Fast, Secure transactions |
Keep in mind that there’s no universal solution when it comes to DLT. It’s important to conduct your research and perhaps consult with a DLT expert at Idea Usher to ensure the best choice for your business.
Using Ledger With Lightning Network
The Lightning Network promises faster and cheaper transactions for Bitcoin users. While Ledger hardware wallets are renowned for their security, many users wonder if they can leverage this technology for their Lightning transactions. This section explores everything you need to know about using Ledger with the Lightning Network.
1. Compatibility Of Ledger With Lightning Network
The short answer is no. Ledger devices don’t currently support the Lightning Network directly. This is because Ledger prioritizes security above all else, and integrating the complexities of the Lightning Network directly into the hardware wallet could introduce potential vulnerabilities. However, Ledger users can still access the Lightning Network through third-party Lightning wallets that integrate with Ledger hardware wallets. These wallets allow you to sign Lightning transactions using the added security of your Ledger device while keeping your private keys offline. Here are some popular Ledger-compatible Lightning wallets:
- Electrum for desktop and mobile
- Wasabi for desktop
- Specter for desktop
- Apto for mobile
2. A Step-by-Step Process To Set Up Ledger For Lightning Transactions
The setup process will vary slightly depending on the specific Lightning wallet you choose. However, the general steps involve:
- Installing the chosen Lightning wallet on your computer or mobile device.
- Connecting your Ledger device to your computer or using the Bluetooth connection on your mobile wallet.
- Initializing the wallet and following the on-screen instructions to connect it to your Ledger device. This will typically involve verifying your Ledger’s screen and potentially entering your PIN.
- Lastly, fund your Lightning wallet by transferring Bitcoin from your Ledger wallet to your Lightning wallet address.
3. Payments With Lightning On Ledger
Once your Ledger and Lightning wallet are connected, you can send and receive Lightning payments:
3.1. Sending:
Within your Lightning wallet app, specify the amount you want to send and the recipient’s Lightning Network address (also known as a Lightning Invoice), and then confirm the transaction on your Ledger device.
3.2. Receiving:
Your Lightning wallet will generate a unique Lightning address. Share this address with the sender so they can send you Bitcoin through the Lightning Network. When a payment is received, the funds will be reflected in your Lightning wallet balance.
4. Types of Lightning Wallets And Their Advantages With Ledger
There are two main types of Lightning wallets:
4.1. Hardware Wallets:
These are physical devices like Ledger that offer the highest level of security for your private keys. Ledger integrates with third-party Lightning wallets, allowing you to sign transactions securely without compromising your private key on the connected device.
4.2. Software Wallets:
These are mobile or desktop applications that offer more features and potentially faster transaction processing compared to hardware wallets. However, they store your private keys on the device itself, which can be a security risk if compromised. The advantage of using a Ledger with a third-party Lightning wallet is the enhanced security it offers. By signing transactions on your Ledger device, you ensure your private keys never leave the secure hardware environment while minimizing the risk of theft or unauthorized access.
5. Finding Channels And Facilitating Payments
The Lightning Network relies on a network of payment channels. To make a payment, your Lightning wallet needs to find a route through these channels to connect you to the recipient. For that, your chosen Lightning wallet will typically handle finding the best route for your payment through existing channels. Additionally, some wallets allow you to open your own channels, which can improve liquidity and potentially reduce transaction fees. However, opening and managing channels can be a more advanced process.
6. Issues With Ledger And Lightning Network Transactions
Here are some common issues you might encounter and how to troubleshoot them:
- Connection Issues: Ensure your Ledger device is properly connected to your computer or mobile device via USB or Bluetooth.
- Verification Issues: Double-check that you’re verifying the transaction details displayed on your Ledger screen before confirming.
- Insufficient Funds: Verify you have enough balance in both your regular Bitcoin wallet and your Lightning wallet for the transaction.
- Outdated Firmware: Make sure your Ledger device and Lightning Wallet app are running the latest software versions.
If you encounter any persistent issues, consult the documentation for your chosen Lightning wallet or reach out to their support channels for further assistance.
When using the Lightning Network with Ledger, prioritize security. It is advisable to use only reputable third-party Lightning wallets that can integrate seamlessly with your Ledger device.
– Blockchain Expert, Idea Usher
Top 10 Companies Currently Using The Lightning Network
Here are the top ten companies currently using thee lightning network in their day-to-day operations:
1. Travala:
Travala is a platform for booking travel that accepts various cryptocurrencies, including Bitcoin, Ether, and several altcoins as payment. The Lightning Network’s integration with Travala is key in enabling faster and more affordable Bitcoin transactions, thereby offering its customers a smoother and more user-friendly experience. They provide over 3,000,000 travel products in more than 230 countries that can be purchased with BTC.
2. sMiles Bitcoin Rewards:
sMiles is a mobile app that rewards users with Bitcoin for completing a variety of simple tasks. After installing the app, users can select the tasks they want to complete and then earn Bitcoin instantly via a channel on the Lightning Network. This makes earning Bitcoin enjoyable and accessible to a broad range of users.
3. BitGild:
BitGild is an online retailer based in the Netherlands that allows customers to buy gold and silver using Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies. BitGild’s use of the Lightning Network allows the company to process Bitcoin payments almost instantly and with lower fees. This feature makes it a more convenient and cost-effective payment option.
4. Cash App:
Cash App is a mobile payment platform that introduced Lightning payments to its over 40 million users in 2022. It’s a unique business model that is fully enabled by Lightning, monetizing everyday activities while introducing new users to the world of crypto.
5. Lightning Labs:
Lightning Labs is a software development company that is building services based on the Lightning Network. They are working on making Lightning adoption easier and more accessible. Their open-source, scalable, and secure Lightning systems allow users to send and receive money more efficiently.
6. Lightspark:
Lightspark is a company focused on making Lightning adoption easier and more accessible. They are working on developing products and services that make Lightning easier to use and solve some of its outstanding issues.
7. McDonald’s (El Salvador):
In El Salvador, where Bitcoin is recognized as legal tender, some McDonald’s outlets do accept Bitcoin payments through the Lightning Network. This initiative is powered by OpenNode, a Bitcoin payment processor. It’s a pilot program that demonstrates the potential of cryptocurrency for quick and efficient transactions.
8. Shopify:
Shopify, a major e-commerce platform, has indeed partnered with Strike to enable merchants to receive Bitcoin payments via the Lightning Network. This integration provides faster transaction processing and potentially lower fees compared to traditional methods.
9. OpenNode:
OpenNode is a payment processor that enables Bitcoin and Lightning Network payments for businesses. Several online stores use OpenNode to accept these digital currencies. OpenNode powers instant settlement and lowest-cost payments.
10. Coinbase:
Coinbase has incorporated the Bitcoin Lightning Network to enable faster transactions. With layer-2 Lightning Network, users can transfer Bitcoin more swiftly and economically than transactions on the Bitcoin blockchain. At Coinbase, to use the Lightning Network, the recipient generates an invoice consisting of a long string of characters that Coinbase identifies as the transfer amount. This integration brings instantaneous transfers on the layer-2 Lightning Network to one of the largest Bitcoin exchanges in the world.
Conclusion
Upon conducting a thorough analysis of the Lightning Network, it is clear that this innovative technology has the potential to transform Bitcoin transactions as we know them. The Lightning Network is designed to address some of the most pressing issues affecting Bitcoin, including scalability, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. Additionally, with DLT, lightning networks even facilitate a decentralized approach to off-chain transactions, paving the way for lightning-fast and affordable payments. It can be confirmed that the Lightning Network represents a significant step forward for Bitcoin and the broader cryptocurrency ecosystem, and it opens up exciting new possibilities for individuals and businesses alike.
Want An Experienced Team For Blockchain Development?
At Idea Usher, we specialize in blockchain and cryptocurrency development and can effortlessly integrate Lightning Network into your existing systems.
Our team of experts has more than 1000 hours of coding experience and has completed over 800 successful projects. By partnering with us, you can benefit from faster settlements, lower fees, and an enhanced customer experience. If you’re not sure which technology is best suited for your project, our team can guide you through and help you ensure the future of payments for your business. Connect with us today!
Work with Ex-MAANG developers to build next-gen apps schedule your consultation now
FAQ
1. Can I use Lightning Network with Ledger?
While Ledger devices don’t directly support the Lightning Network, you can use your Ledger in conjunction with a Lightning-compatible wallet. This allows you to manage your keys securely while making fast, low-cost Lightning transactions.
2. Which wallet supports Lightning Network?
Several wallets support the Lightning Network, including Eclair, BlueWallet, and Zap. These wallets allow you to make fast, low-cost Bitcoin transactions using the Lightning Network.
3. Is Segwit a Lightning Network?
No, SegWit (Segregated Witness) and Lightning Network are different. SegWit is a protocol upgrade that changes the way data is stored, while the Lightning Network is a “second layer” solution built on top of the Bitcoin network for faster transactions.
4. Is a lightning wallet safe?
While Lightning wallets provide a convenient way to transact with Bitcoin, they may not be as secure as traditional Bitcoin software wallets or hardware wallets. This is due to the fact that your keys are actively present on the device running the Lightning node, which simplifies the process of signing channel openings and closures.

























