From logistics to health and fitness, the growing adoption of IoT has brought countless advantages to every industry.
The agriculture industry has also witnessed tremendous benefits from implementing and leveraging the power of IoT. The Internet of Things has simplified and made it easier for farmers to manage their crops and livestock efficiently.
From increasing productivity to optimizing resources, due to many IoT advantages, there has been a surge in demand for IoT across various aspects of the agriculture industry.
In this article, we will understand how IoT is transforming the agriculture industry with its potential benefits and applications. Also, we will delve into the development steps for implementing IoT in the agriculture industry.
What Is IoT In Agriculture?
Smart Agriculture or IoT in agriculture is the utilization of IoT-based sensors and devices to enhance the efficiency, productivity, and sustainability of crops.
There is the involvement of using connected devices, sensors, and data analytics for monitoring and managing various agriculture activities and processes. The primary intent of using IoT in the agriculture industry is to practice and implement source-efficient, data-driven farming solutions.
All IoT devices are interconnected through the internet to enable data exchange and accessibility over the Internet. The “Things” in IoT can be termed devices such as wearable devices, household appliances, and embedded sensors.
The data collected from IoT devices can be analyzed to improve efficiency, gain insights, automate tasks, and enhance overall functionality.
How IoT In Agriculture Works?
There is the involvement of various smart sensors, devices, and data analytics platforms to collect, transmit, and analyze data from agricultural operations.
Here’s a step-by-step process of IoT working in agriculture:
1. Sensing and Data Collection
Different environmental parameters such as temperature, humidity, soil moisture, light intensity, and weather conditions are collected with different IoT devices and sensors deployed to the farm. The IoT sensors can be placed in plants, animals, soil, weather stations, etc.
2. Data Transmission
The transmitted data can be collected through various communication protocols such as cellular networks, Wi-Fi, satellite connections, etc. The selection of sensors depends on the range of devices, the size of farms, and the availability of network infrastructure.
3. Data Storage and Cloud Platforms
The collected data can be stored on local servers or cloud-based platforms. However, there is a great level of data scalability and accessibility when opting for cloud storage instead of local servers for handling vast amounts of data generated by multiple farms.
4. Data Analytics
There is a utilization of sophisticated data analytics algorithms and tools for analyzing and processing information. The analytics can reveal data patterns and trends that can be used for optimizing agricultural processes and making informed decisions.
5. Decision Making and Automation
Data collected for different purposes, such as scheduling, irrigation activities, pest control, and other farming activities, can be automated for carrying out specific actions, such as activating machinery or adjusting irrigation systems.
6. Remote Monitoring and Control
Using real-time monitoring tools allows farmers to optimize resource usage even if they are not physically present on the farm and can better manage the operations of their farm remotely through mobile applications or web interfaces.
7. Integration with Farm Management Software
The farmers can perform seamless data sharing and streamline the decision-making process by integrating IoT devices and platforms with existing farm management software or agriculture-specific applications.
8. Data Security and Privacy
Major data security practices such as data authentication, encryption, and restricted control access are implemented to protect sensitive information collected by IoT sensors.
Applications of IoT in Agriculture With Examples
From indoor farming to livestock management, IoT is transforming the agriculture industry by simplifying and automating various agriculture activities. Here is a common application of IoT in agriculture with examples.
1. Robotics
There is a wide scope of robotics in the agriculture industry where farmers can use automated harvesters, tractors, and other machines and vehicles to operate without human effort.
Robotics in the farming industry can complete challenging, repetitive, challenging and labor-intensive tasks. Also, robotics can be used to perform various tasks such as weddings, planting, seeds, watering, etc.
Best Example: Bear Flag Robotics
A platform that provides robotic services to the farming industry. The platform enables farmers to control an entire fleet of tractors in an optimized and efficient way.
- Founded in: 2017
- Owner: John Deere
- Headquarters: Moline, Illinois, US
2. Greenhouse Automation
The use of IoT sensors enables farmers to get real-time and accurate information on greenhouse conditions such as temperature, lighting, soil conditions, humidity, etc, helping them to manage their greenhouse environment better.
In addition to the environmental data, farmers can adjust the conditions to match the given parameters, especially for improving greenhouse automation systems.
Best Example: Farmapp
The platform enables farmers to access food production management technologies with integrated pest management software-based services.
In addition, the platform provides a combination of fumigation and scouting apps with integrated IoT-based sensors for bringing automation to the agriculture sector.

- Founded in: 2014
- Owner: Jason Callison
- Headquarters: Victoria, Australia
3. Crop Management
Monitoring the health of crops and implementing effective solutions is another potential application of IoT in the agriculture industry. The farmers can monitor the crop growth and identify any anomalies to prevent any future diseases that can harm their crops.
Best example: Arable

A platform that enables farmers to manage their crops efficiently. The app platform helps farmers streamline the food supply chain, manage farm logistics, optimize water & nutrient availability, maximize crop yield & efficiency, etc.
- Founded in: 2014
- Owner: Adam Wolf
- Headquarters: San Francisco, US
4. Cattle Monitoring & Management
Similar to crop monitoring, IoT can also be implemented in cattle to monitor their health and low performance. Livestock tracking and monitoring can help farmers to identify sick animals and separate them from the herd and avoid contamination.
Best example: Cowlar

An IoT-based startup that facilitates farmers with nutrition insights, health, temperature, activity of each individual cow as well as collective information about the herd.
The platform connects all cattle with the help of IoT-based sensors within a 2-mile range that uses cellular connectivity for passing the cattle information to the farmers.
- Founded in: 2015
- Owner: Umer Adnan, Umer Ilyas
- Headquarters: Memphis, US
5. Agricultural Drones
Agriculture drones are another popular application of IoT in the agriculture industry. The drone utilizes infrared cameras, image processing, GPS, and ground control systems to facilitate effective solutions for crop management.
The farmers can leverage Drones-as-a-service (DaaS) to predict crop yield, diagnose pest infestation, and field supervision.
Best example: AgEagle
Researchers, agriculture engineers, and farmers can use drone-captured data with AgEagle to gain crop insight and develop effective solutions for crop management.
The platform facilitates farmers with a wide range of benefits such as cost savings, increased yield, season-long insights, improved crop planning, and high-level accuracy, current field data capturing, etc.
- Founded in: 2012
- Owner: Bret Chilcott
- Headquarters: Kansas, US
Advantages Of IoT In Agriculture
The IoT has impacted the agriculture industry in a variety of ways. Farmers are using IoT-based devices and sensors to transform the agriculture industry. Here are a few benefits of IoT in agriculture that can help you gain an insight into its future potential.
1. Accurate data analysis
The utilization of IoT-based solutions for the agriculture industry offers numerous practical applications such as weather forecasting, group data analysis, pest detection, etc. The farmers can make informed decisions based on accurate data analysis for enhancing productivity and promoting smart farm practices.
2. Increase in food production
The IoT-based tools allow farmers to automate their farming practices and improve efficiency by creating intelligent tools capable of predicting and measuring good agriculture practices.
Moreover, farmers can utilize IoT-based devices to understand better various environmental factors that influence their agricultural productivity.
3. Smart farming
The farmers can utilize smart farming to manage better and remotely control various aspects of the farm, such as soil and crop conditions which results in an overall improvement in the efficiency of the farming operations.
The collected data can be further monitored to determine the optimal time for watering the crops, pest removers, and pesticide applications.
4. Increased farm efficiency
The use of multiple IoT-based devices, such as irrigation devices, and soil measuring sensors, results in a significant increase in farm efficiency and productivity.
These IoT-based devices are capable of collecting and processing data for analyzing temperature conditions, soil quality, pest detection, crop health etc, enabling farmers to make informed decisions.
5. Real-time crop planning and forecasting
The IoT-based sensors and devices enable farmers to save time and money by implementing real-time crop planning and forecasting. Moreover, real-time data will help farmers to find the best time for harvesting their crops.
6. Drought monitoring
The Internet of Things often assists farmers in detecting water shortages even before facing a problem in real life. Additionally, some IoT-based systems provide data for the optimal location and times to irrigate crops to maximize their crop watering efforts.
7. Livestock tracking
IoT-based applications such as livestock GPS tools enable farmers to collect information about their kettles, well-being, health, and whereabouts, which helps farmers to prevent the spread of diseases and reduce labor expenditures.
The farmers can enjoy real-time visibility of livestock, providing greater control and insight into their agricultural operations.
8. Agricultural automation
The utilization of IoT in agriculture has an extreme potential to revolutionize a major aspect of the industry. Many IoT-based sensors, such as pressure sensors, light sensors, and others, simplify multiple farm processes by helping farmers with data collection and water monitoring, harvesting, etc.
How To Implement IoT In Agriculture?
The implementation of IoT in agriculture involves several key steps and careful consideration. Here is an overall process of leveraging IoT in agriculture.
1. Identify Farming Needs and Objectives
Define specific goals and challenges that you are facing in agriculture operations by determining various farming aspects such as optimizing resource utilization, improving water management, enhancing crop monitoring, health, etc.
2. Research and Select IoT Solutions
There are many IoT-based sensors and devices available in the market that can help farmers with data transmission, data analytics capabilities, and remote accessibility. Therefore knowing the exact farming requirements and objectives can help you select the right IoT solution for your crop.
3. Sensor Deployment and Data Collection
After defining project needs and selecting appropriate solutions, the next step is to set up IoT sensors and devices across a farm to collect relevant data. The data can be collected from different farming aspects such as weather stations, moisture sensors, livestock monitoring, and other data based on your agricultural needs.
4. Data Transmission and Connectivity
There is a requirement for a reliable communication channel between IoT devices and central hubs such as cloud platforms. Based on farm size and connectivity options, different options are available such as cellular, Wi-Fi, LoRa, etc.
5. Data Storage and Cloud Integration
Cloud-based platform is the best way to manage overall collected data due to its better scalability and remote accessibility. When using cloud-based services, consider focusing on data redundancy, data analytics capabilities, and scalability in addition to integration with farm management software.
6. Data Analytics and Insights
Data analytics is the best way to extract valuable information and make informed decisions about farm operations, livestock, health, resource, crop management, etc. Therefore consider using the best data analytical tool to operate your collected data overall efficiently.
7. Automation and Actuation
The next step is implementing an automation system to improve overall crop management activities with IoT-based devices and software. There is involvement in utilizing automated feeding systems for livestock and smart irrigation controllers when considering automation in the agriculture industry.
8. User Interface and Visualization
There is a requirement for a mobile app or web interface that will enable farmers to monitor, control and access their farm data in addition to accessing analytics and automated systems. Therefore, consider hiring an IoT development company that can help you deliver an effective software solution with software development.
9. Testing and Piloting
Before implementing an IoT system on a full scale, it is crucial to conduct a small-scale test to evaluate the effectiveness and reliability of the overall IoT infrastructure for your crop. Consider conducting various feedback tests and make necessary adjustments for improving the overall IoT infrastructure.
10. Scalability and Integration
After conducting successful tests, the next part is to deploy your IoT on all areas of the farm. Additionally, ensure you go through seamless integration with other farm management practices and processes to develop the best outputs.
11. Data Security and Privacy
Having total control over data, in addition to data security and privacy, is crucial for helping you to prevent unauthorized access or cyber threats. Therefore, try to implement best data practices such as access controls, encryption, and regular data backups.
12. Continuous Improvement
Regularly upgrading IoT system performance on a regular basis is crucial to meet the modern demands for an effective farming solution. You can partner with a reliable IoT development company that will monitor your IoT-based agriculture infrastructure and provide you with effective solutions for further upgrades and improvements.
IoT In Agriculture Tech Stack
The tech stack for IoT in the agriculture industry comprises hardware, software, and communication components for enabling farmers to improve their agriculture operations. Here is an overview of the typical IoT tech stack in the agricultural industry.
1. Sensors and Devices
There are various kinds of IOT-based sensors and devices that collect data from farm environments. The following sensors are used in the agriculture industry:
- Weather Stations: Gather data on temperature, humidity, wind speed, and other weather parameters.
- Livestock Monitoring Devices: Track the health, behavior, and location of animals.
- GPS Trackers: Monitor the movement of agricultural machinery or livestock.
- Crop Health Sensors: Detect plant diseases, nutrient deficiencies, and pest infestations.
- Smart Irrigation Controllers: Regulate irrigation based on environmental conditions.
2. Connectivity and Communication
The data collected by sensors must be transmitted to a central hub or cloud platform for processing and analysis. Communication & connectivity used in agriculture IoT includes:
- Wi-Fi: Suitable for short-range communication within farm buildings or areas with Wi-Fi coverage.
- Cellular Networks: Provide broader coverage, allowing data transmission from remote locations.
- Low-Power Wide-Area Networks (LPWAN): Such as LoRa or Sigfox, are ideal for long-range, low-power communication in rural areas.
- Satellite Communication: Used in extremely remote locations with limited terrestrial connectivity.
3. Edge Computing
Farmers can reduce latency and bandwidth usage by processing data locally before sending relevant information to the cloud for further analysis.
4. Cloud Platforms
Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure are commonly used cloud-based platforms. These platforms offer scalability, accessibility, and data analytics capabilities and help farmers store and manage vast amounts of data collected from multiple farms.
Conclusion
The Internet of Things has expanded its potential benefits among the various aspect of the agriculture industry. From managing agriculture resources to raising livestock, the integration of IoT in farming practices has already showcased their tremendous potential.
Due to the many possible benefits and applications of IoT in agriculture industries, entrepreneurs and investors can tap into the agriculture industry by offering innovative IoT solutions. However, IoT implementation requires expertise across programming, knowledge of IoT-based devices and sensors, and other important aspects.
Partnering with a reliable software development agency is a way to simplify IoT implementation in the agricultural sector and transform your innovative idea into reality.
Work with us if you are looking for an agency that can help you identify your project needs and delivers innovative solutions by leveraging the power of IoT in the agriculture industry.
Here is more information about IoT development services.
Get in touch with us today to understand more about how we can help your business grow.
Contact Idea Usher
Work with Ex-MAANG developers to build next-gen apps schedule your consultation now
Email:
Phone:
(+1)732 962 4560
(+91)859 140 7140
FAQ
Q. What is the future scope of IoT smart agriculture?
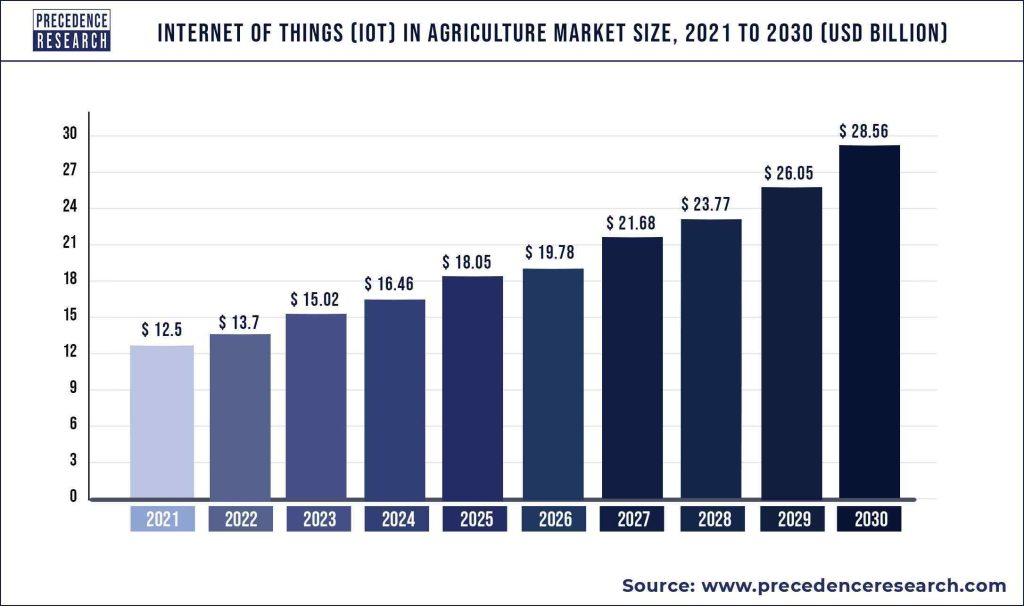
A. According to an analysis from Precedenceresearch.com, the Internet of Things (IoT) market for agriculture was valued at $12.5B in of 2021 and is expected to grow to approximately $28.56B between 2022 and 2030 at a CAGR of 9.62%.
Q. Which sensors are required for IoT applications in agriculture?
A. Temperature, depth, moisture, and humidity are some of the required sensors for IoT applications in agriculture.
Q. What are the benefits of IoT in agriculture?
A. Seamless data utilization, improved crop quality, livestock tracking, remote monitoring, drone monitoring, risk reduction, and business automation are some of the benefits of IoT in agriculture.
Q. What are the examples of IoT in agriculture?
A. Accurate data analysis, increase in food production, real-time crop planning and forecasting, drought monitoring, smart farming, increased farm efficiency, livestock tracking, and agricultural automation are some examples of IoT in agriculture.

























