Sustainability is no longer optional, and it now shapes regulation, investment strategy, and enterprise infrastructure. The challenge is that most climate participation still feels out of reach because the systems behind it are fragmented and difficult to navigate. Traditional carbon markets were built for institutions, not for the scalable digital access modern platforms require.
That is why the demand for carbon credit and ESG token exchanges is steadily increasing. Tokenization enables automated verification, transparent audit trails, real ownership attribution, on-chain ESG scoring, and secure transactions at scale. Markets that once moved slowly can finally operate with liquidity, measurable trust, and real-time compliance.
Over the past decade, we’ve built multiple carbon credit solutions powered by blockchain ecosystems and IoT-based environmental data infrastructure for real-time monitoring and verification. With that experience, we’re sharing this blog to walk you through the key steps required to develop a carbon credit and ESG token exchange. Let’s get started.
Key Market Takeaways for Carbon Credit and ESG Token Exchange
According to PSMarketResearch, the voluntary carbon credit market was valued at about USD 78 billion in 2024 and is forecast to reach roughly USD 600 billion by 2032, growing at an annual rate of around 29.2 percent. This surge reflects stronger regulation, greater investor attention to climate risks, and increasing demand for transparent, traceable environmental assets. As markets mature, tokenization is helping convert credits into programmable, fractional, and globally tradable instruments that are easier to track, retire, and verify.
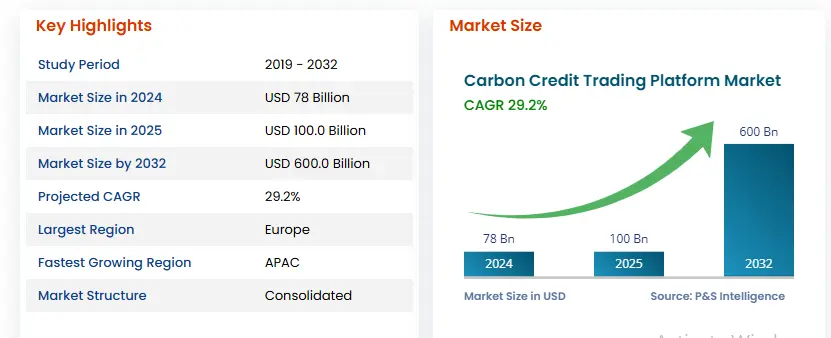
Source: PSMarketResearch
Interest in carbon and ESG token exchanges is rising because they help address long-standing challenges such as fragmented registries, slow settlement, and concerns about double-counting.
Tokenized credits include key details like vintage, project type, standard, and retirement status, making transactions more transparent and efficient. This structure also supports new ESG financial products, including carbon baskets, tokenized offsets, and automated retirement systems for companies with net-zero targets.
Both traditional and Web3-native platforms are shaping the sector. Xpansiv’s CBL marketplace plays a major institutional role, supporting bulk trading across registries such as Verra and Gold Standard. Meanwhile, KlimaDAO offers a decentralized model, using its KLIMA token and carbon pools to issue on-chain credits.
Strategic partnerships, including the initiative between S and P Global Commodity Insights and JPMorgan’s Kinexys, are advancing tokenization by linking registry-verified carbon credits to shared blockchain infrastructure for standardized reporting and smoother global transfers.

What Is a Carbon Credit and ESG Token Exchange?
A carbon credit and ESG token exchange is a blockchain-based marketplace where carbon credits and sustainability-linked digital assets can be securely tokenized, traded, and verified in real time. It creates transparency, prevents double-counting, and automates settlement through smart contracts, making environmental markets more efficient, trustworthy, and accessible for companies, investors, and regulators.
Understanding Carbon Credits
A carbon credit represents one tonne of carbon dioxide (or an equivalent greenhouse gas) either prevented from being released or actively removed from the atmosphere.
Carbon markets operate across two major frameworks.
Compliance Markets
Governments create a legal emissions limit and companies must stay within it. Firms that emit less than their allowance can sell their unused credits, while those exceeding limits must purchase more. Systems like the EU ETS and California’s program have turned emissions reduction into an economic incentive.
Voluntary Markets
These markets are driven by corporate net-zero strategies, ESG commitments, and consumer expectations rather than regulation. Credits originate from verified projects such as:
- Reforestation and ecosystem restoration
- Clean energy installations
- Methane and industrial leakage prevention
This is the space where tokenization is rapidly emerging to enhance traceability and confidence.
What Are ESG Tokens?
While carbon credits measure emissions impact, ESG tokens expand the concept to include measurable environmental, social, and governance performance.
They can represent:
- Real-time sustainability metrics verified through IoT devices and trusted data oracles
- Fractionalized green bonds or social impact securities, allowing smaller investors to participate
- Governance and stewardship rights that tie token ownership to voting or decision-making within sustainability initiatives
This represents a shift from static reporting to dynamic, data-driven value creation.
How Does a Carbon Credit and ESG Token Exchange Work?
A carbon credit and ESG token exchange works by turning verified environmental assets into secure digital tokens on a blockchain. These tokens can then be traded instantly through smart contracts, giving buyers clear ownership and full transparency. Once a token is retired, the system permanently records the action, so the impact may be audited and trusted.
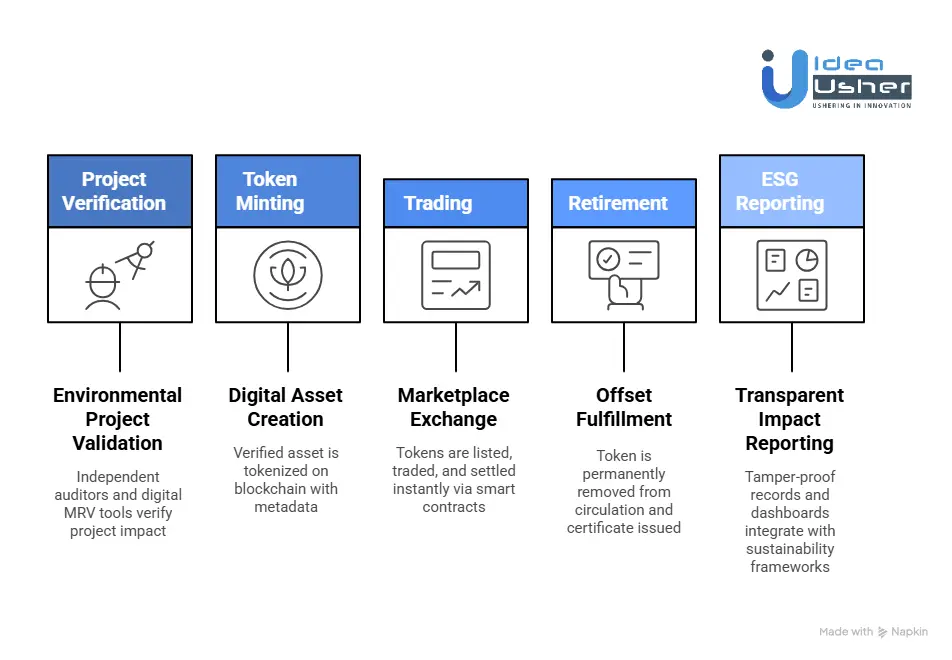
Step 1: Project Verification
Before any asset becomes digital, the underlying environmental project must prove that its impact is real.
How this phase works:
- Traditional Certification: The project, such as a forest restoration program or methane reduction facility, undergoes review from established bodies like Verra or Gold Standard. Independent auditors assess methodology, calculate emissions impact, and issue official serial numbers.
- Digital MRV (Measurement, Reporting, Verification): Emerging platforms now enhance this validation with real-time data from IoT sensors, satellite imagery, and drone monitoring. These tools continuously track performance and feed future metadata.
- Oracle Validation: A decentralized oracle network verifies the authenticity of the collected data and prepares it for the blockchain.
This step ensures that only credible environmental outcomes enter the digital market.
Step 2: Token Minting
Once verified, the environmental asset receives a digital counterpart on the blockchain.
Process overview:
- Preventing Duplication: Before a token is created, the original carbon credit is either locked or permanently marked as tokenized in the legacy registry.
- Smart Contract Minting: The system issues a corresponding on-chain asset, typically using widely adopted token standards such as ERC-1155 or ERC-721.
- Metadata and Logic: Each token includes permanent details like origin, methodology, geographic region, issuance year, and embedded rules for how the token can be used or retired.
The result is a tamper-proof digital representation of a verified climate asset.
Step 3: Trading
Once tokenized, the asset becomes tradable in a transparent and efficient digital marketplace.
Key functions:
- Discovery and Listing: Buyers filter listed tokens by factors such as region, project type, price, and impact score.
- Fractional Participation: Credits can be divided into smaller units, enabling participation from retail buyers and smaller organizations.
- Instant Settlement: Smart contracts facilitate real-time transfers of ownership and payment. No intermediaries. No multi-week settlement delays.
- Secondary Market Access: These tokens can also be traded on compatible decentralized exchanges, expanding liquidity beyond the primary marketplace.
This step transforms environmental assets from a niche commodity into a predictable and accessible financial instrument.
Step 4: Retirement
A carbon credit has value only when it offsets emissions. Retirement is the moment the asset fulfills that purpose.
How retirement works:
- The holder initiates a retirement transaction on-chain.
- The token’s smart contract permanently removes it from circulation.
- A public retirement certificate is generated and timestamped on the blockchain.
- Optional registry synchronization updates legacy systems with final status.
- The retiring organization receives a verifiable digital proof of offset.
This step ensures that each tonne of carbon is claimed only once.
Step 5: ESG Reporting
The lifecycle concludes with reporting and insight generation that is backed by verifiable data.
Output includes:
- A complete tamper-proof record of all offsets and transactions.
- Automatic integration with sustainability platforms and reporting frameworks like CDP, GRI, SASB, and TCFD.
- Dashboards that visualize the environmental impact, offset volume, costs, trends, and progress toward internal climate targets.
At this stage, the exchange becomes more than a marketplace—it becomes a transparent system of record for a company’s ESG and climate strategy.
How to Develop a Carbon Credit and ESG Token Exchange?
To build a carbon credit and ESG token exchange, you start by linking verified registries and MRV feeds, so every asset is measurable and trusted. Then you design token standards and a secure trading engine that can automate compliance and retirement. We have built several fractional real estate token platforms, and this same workflow has proven reliable.
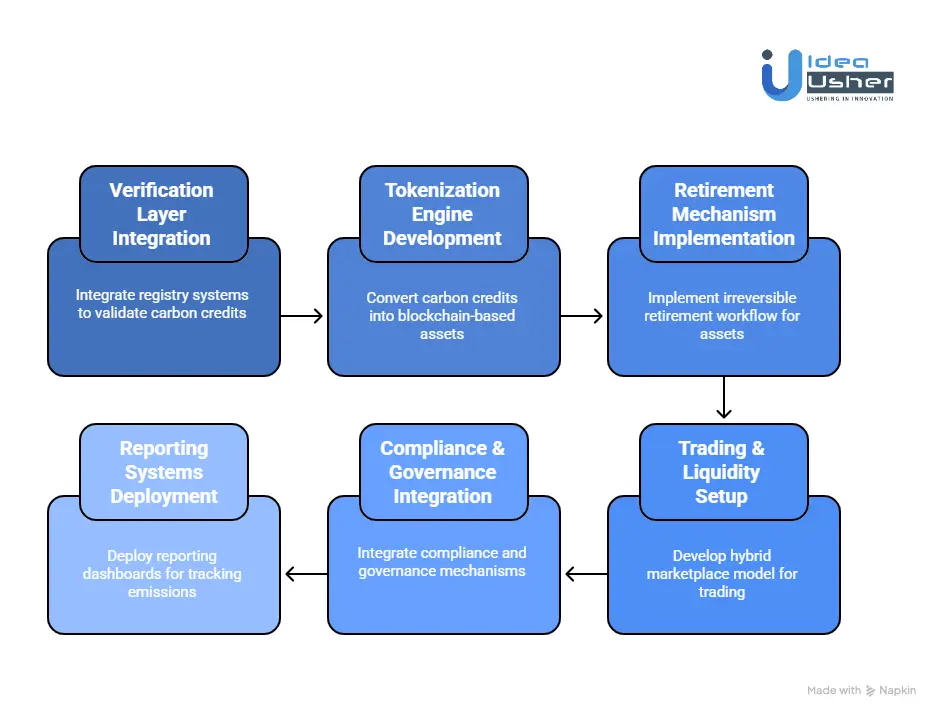
Step 1: Verification Layer
We begin by integrating registry systems such as Verra, Gold Standard, and ICR to validate every carbon credit entering the platform. Automated ESG data pipelines ingest climate performance metrics and verification reports in real time to ensure each asset has documented legitimacy.
Step 2: Tokenization Engine
After verification, we convert approved carbon credits into blockchain-based assets. ERC-721 tokens represent unique certificates, and ERC-20 tokens enable fractional ownership, with ESG and MRV metadata embedded directly into the token structure.
Step 3: Retirement Mechanism
Next, we implement the irreversible retirement workflow that permanently burns the asset once redeemed. The system also generates an immutable on-chain retirement certificate that corporations and auditors can verify at any time.
Step 4: Trading & Liquidity
We develop a hybrid marketplace model that combines order-book trading with AMM liquidity pools across different carbon categories and vintages. Pricing and routing algorithms help maintain fair execution and sustainable liquidity.
Step 5: Compliance & Governance
Compliance is integrated directly into the platform, including identity verification, sanctions screening, and geographic trading rules. Governance mechanisms such as multi-signature treasury controls strengthen institutional trust.
Step 6: Reporting Systems
Finally, we deploy reporting dashboards for corporations and investors to track emissions, offsets, and climate impact. Automated reporting modules generate certificates and compliance documentation required for regulatory alignment.

ESG Token Market is Getting a Boost with 3.8M Tokenized Carbon Credits
It is becoming clear that ESG tokenization is no longer just a theory, and the data proves it. From 2021 to 2022, around 3.8 million tokenized carbon credits entered blockchain markets, and nearly 2.8 million of them were already burned, leaving about 1 million still available.
When that much verified volume moves with transparent retirement records, the market starts looking scalable, and investors may finally treat ESG tokens as credible financial infrastructure rather than an experiment.
Why Carbon Credits Sparked the Breakthrough
Carbon credits made the ideal starting point for ESG tokenization. Each credit represents one tonne of CO₂ avoided or removed, which makes it both measurable and globally standardized.
The real breakthrough is not simply that these credits were digitized. It is what happened afterward:
- Approximately 2.8 million of the tokenized credits were retired (burned).
- Roughly 1 million remain available for trading.
Burning a tokenized carbon credit shows it was used for the intended environmental purpose and not acquired only for speculation. This confirms the mechanism functions as designed.
Blockchain Solved ESG’s Biggest Problem: Proof
For decades, ESG investing faced one core challenge:
How do we verify environmental or social performance rather than just accept stated claims?
Tokenized carbon credits finally introduce a way to verify outcomes.
Every token carries its own timestamped activity record, including issuance, ownership, and retirement. Nothing can be hidden or duplicated in the process. This approach moves the conversation from trust-based reporting to cryptographic verification and accountability.
The Ripple Effect Across the ESG Token Ecosystem
Once tokenized carbon credits demonstrated scale and real usage, three significant effects followed.
1. The Infrastructure Is Proven
Platforms such as Toucan, Moss, and Carbonmark built functioning systems that handle registry integration, verification logic, digital MRV (monitoring, reporting, and verification), and marketplace settlement. Future assets such as biodiversity credits or renewable-energy certificates can now plug into this framework rather than starting from zero.
2. Institutional Confidence Increased
Millions of verified tokenized credits give large financial institutions a clear success case. This makes ESG tokenization harder to dismiss as a speculative trend. The involvement of groups like J.P. Morgan through Kinexys reflects this shift.
3. Real-Time ESG Data Becomes Possible
Tokenization transitions ESG from annual reporting cycles to continuous measurement.
Examples include:
- Satellite and IoT data are updating the quality or status of environmental assets.
- Renewable energy credits are adjusted dynamically based on generation data.
- Governance rights and voting are recorded transparently rather than buried in PDF disclosures.
This turns ESG metrics from static metrics into living financial instruments.
Where the Market Goes Next
Those 3.8 million tokenized carbon credits mark a turning point.
They show that environmental assets can be digitized, tracked, verified, and retired transparently. Once this is demonstrated for carbon, the logic applies to many ESG-aligned categories.
Future ESG tokenization models may include:
| ESG Category | Example Token Asset |
| Environmental | Carbon credits, water rights, ocean restoration, biodiversity credits |
| Social | Tokenized microfinance outcomes, education access credits, impact bonds |
| Governance | Shareholder voting tokens, compliance tokens, transparency-linked assets |
A New Model for Accountability and Capital
- Traditional ESG scored intentions.
- Tokenized ESG scores verified action.
Digitization introduces liquidity and real pricing signals, enabling capital to flow efficiently to projects that deliver measurable environmental and social outcomes.
Most Successful Business Models for Carbon Credit & ESG Token Exchange
Tokenizing carbon credits and ESG-linked assets is not just another blockchain use case. It represents the creation of a new asset class and an entirely new financial infrastructure. The most successful platforms in this category do not rely on a single revenue stream.
Instead, they combine multiple business models that reinforce one another, creating scalability, predictable revenue, and strong competitive barriers.
1. Marketplace and Transaction Fee Model
This model mirrors traditional commodity exchanges and digital asset platforms. The exchange earns fees whenever carbon or ESG assets are bought, sold, transferred, or retired.
How It Generates Revenue
- A percentage fee applied to every executed trade (typically 0.1% to 2%)
- A separate retirement fee, which is often higher due to compliance requirements and audit assurance
Why It Works
Revenue scales with activity. As trading volume, institutional adoption, and liquidity increase, platform earnings grow without high added operational costs.
Xpansiv’s CBL exchange processed more than 100 million tonnes of carbon credits in 2021. At an estimated average fee of $0.10 per tonne, this translates to roughly $10 million in transaction-based revenue before tokenization even becomes mainstream.
2. SaaS and Infrastructure Licensing Model
Many enterprises need carbon trading, tokenization, or reporting functionality, but few are willing to build the technology themselves. Licensing ready-made infrastructure is faster, cheaper, and more secure.
What Can Be Licensed
- Tokenization engines and retirement ledgers
- Registry and compliance integrations
- White-label trading modules
- Automated retirement and reporting systems
Pricing Structure
- Recurring annual licenses or monthly subscriptions
- Integration and implementation fees
- Optional API usage fees based on call volume
Typical enterprise pricing ranges from $10,000 to over $100,000 per month.
Market Validation
Systems like J.P. Morgan’s Kinexys demonstrate that institutional infrastructure requires millions in development. Licensing a ready platform removes that burden and accelerates adoption. Comparable financial data platforms such as Plaid or Bloomberg already price access between $5,000 and $50,000 per month, depending on usage.
3. Tokenization and Issuance Fees
Every asset entering the blockchain ecosystem goes through a minting and verification step. The exchange can monetize that process by charging project developers, registries, or intermediaries.
Pricing Options
- Flat minting fee per tonne or per asset
- Percentage-based fee aligned with asset value
- Tiered pricing based on verification level or volume
Why This Matters
Tokenization fees capture value from the supply side. Revenue is generated before assets even begin trading.
Benchmarks
- Registries like Verra or Gold Standard already charge $0.05 to $0.20 per credit during issuance.
- Early blockchain models such as Toucan showed fast adoption and large tokenization volumes, demonstrating real market appetite.
Common Challenges of a Carbon Credit & ESG Token Exchange
After building platforms for climate asset marketplaces across North America, Europe, Asia, and the Middle East, our team at Idea Usher has seen the same core obstacles arise again and again.
Some are technical, others are regulatory, and a few are deeply tied to how legacy carbon markets historically operate. What matters is that every challenge can be solved with the right architecture and execution strategy.
1. Double Counting
Double-counting is one of the most damaging issues in carbon markets. If multiple buyers can claim a credit, the environmental value collapses and trust disappears. Manual registry workflows, delayed updates, and insufficient validation create room for error and fraud. One mistake can permanently affect investor confidence.
Our Solution: Atomic Retirement and Registry Synchronization
We prevent double-counting using a two-part control framework.
- Smart Contract Retirement Logic: Each token has built-in rules that allow only a single official use. When the retirement function is triggered, the token is burned permanently, and anyone can verify the retirement event on-chain.
- Registry Synchronization Workflow: Our system integrates directly with existing standards like Verra and Gold Standard. Tokens are only minted after a confirmed registry lock and only burned when retirement is validated back in the registry.
This framework creates a tamper-proof ledger where every retired credit has a single owner and a permanent public record.
2. Questionable ESG Data and Greenwashing
Many markets suffer from weak reporting, outdated documentation, or unverifiable sustainability claims. Corporate disclosures and project documents alone are no longer enough. Buyers want measurable proof that a project has generated real environmental benefit.
Our Solution
We integrate verification into the token lifecycle from the beginning.
Core components include:
- Real-time satellite data feeds
- On-site IoT sensor tracking for emissions and renewable energy output
- Machine learning anomaly detection
- A decentralized oracle scoring layer that assigns and updates a live “quality score” to each credit or project
This approach transforms carbon credits from static certificates into continuously monitored and performance-based assets.
3. Regulatory Fragmentation Across Regions
There is no single global policy framework for digital carbon assets. A token may be treated as a commodity in one country, a regulated instrument in another, or undefined in emerging markets. Building a rigid platform often leads to costly redesigns as policies evolve.
Our Solution
We design an exchange infrastructure that can adjust to regulation instead of fighting it.
Key elements include:
- Modular smart contract rules that activate based on jurisdiction or user profile
- Permissioned sidechains for sensitive regulatory operations like identity-linked transfers
- Automated reporting modules that align with regional tax, disclosure, and trading requirements
- A sandbox testing layer where new markets can be simulated before launch
This adaptability allows exchanges to expand with regulations rather than falling behind them.
4. Low Liquidity During Early Launch Stages
Even a highly engineered platform will struggle without market participants. Supply-and-demand imbalances are common in climate markets, especially during the first six to twelve months.
Our Solution
We accelerate platform liquidity through structured strategies that align incentives.
This includes:
- Partnerships with established market makers in environmental finance
- Tiered liquidity rewards based on asset integrity and climate impact
- Co-investment models with ESG funds and institutional buyers
- Fractional trading to open the market to a larger buyer base
- Staking models where platform fees support verified climate initiatives
The result is a self-reinforcing loop where value, participation, and trust grow together.
Tools & APIs to Build a Carbon Credit & ESG Token Exchange
Building a Carbon Credit and ESG token marketplace is not just another blockchain initiative. It sits at the intersection of climate science, financial regulation, and advanced digital asset infrastructure. The right stack determines whether the platform can meet institutional requirements, operate legally, and scale globally.
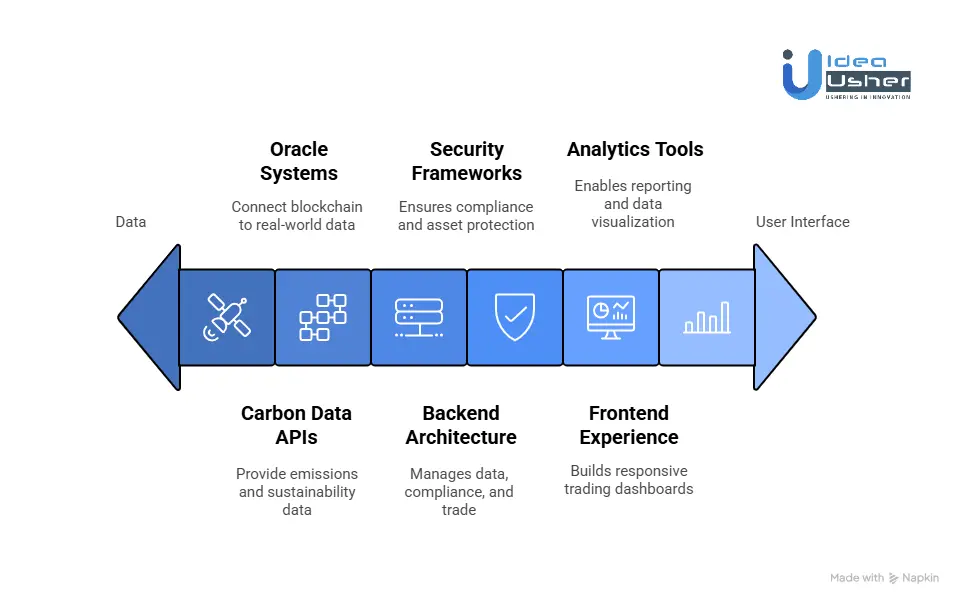
1. Blockchain and Smart Contracts
Core Chains
- Ethereum, Polygon, and Avalanche are preferred for security and liquidity access. Polygon is suitable for frequent fractional trading due to lower fees, while Avalanche offers rapid transaction finality expected by institutional desks.
- Solana and Algorand serve high-throughput scenarios where millions of asset-linked events may occur daily, such as automated carbon consumption tracking or IoT-driven emissions verification.
Development Toolkit
- Solidity and Vyper allow for auditable, security-focused smart contracts that govern token issuance, burning, and compliance logic.
- Hardhat or Foundry supports local development, forking, debugging, and automated testing.
- OpenZeppelin Contracts provide audited ERC-20 and ERC-721 libraries along with role-based access controls required for regulated carbon markets.
Smart contracts in this sector function as enforceable digital financial agreements. Every interaction must be written with the same care as regulated financial software.
2. Carbon and ESG Data APIs
Registry Integrations
- Verra Registry API and Gold Standard API support verification and retirement of carbon credit serial numbers.
- American Carbon Registry and Climate Action Reserve enable compliance coverage for the North American market.
ESG and Environmental Data Sources
- Sustainalytics and MSCI ESG APIs provide corporate emissions scoring and sustainability data.
- Planet Labs and Sentinel Hub deliver satellite-based monitoring for dMRV, helping validate forest protection claims, deforestation events, and renewable energy output.
- NASA Earthdata and Copernicus offer climate models and historical datasets for environmental baselining.
- IoT sensor platforms track methane leakage, soil carbon, and renewable energy production for real-time verification.
The strength of the exchange is linked to the credibility of its data sources. Digital verification transforms climate claims from marketing language into measurable evidence.
3. Oracle and Validation Systems
- Chainlink provides decentralized access to market pricing, dMRV data feeds, and secure external API data.
- Custom oracle layers may be needed for proprietary ESG scoring or multi-party verification workflows.
Verification Methods
- Proof of Reserve frameworks confirm that on-chain credits correspond to real retired certificates.
- Zero-knowledge validation oracles allow companies to prove compliance metrics without exposing sensitive internal data.
Reliable oracles are essential because they connect blockchain transactions with real-world environmental conditions.
4. Backend Architecture and Infrastructure
| Category | Tools / Technologies | Purpose |
| Core Application Stack | Node.js, Python (FastAPI, Django) | Run authentication, user workflows, compliance logic, and trade execution engines |
| Go, Rust | Power ultra-low-latency components such as matching engines and high-frequency data pipelines | |
| Storage and Data Management | PostgreSQL with TimescaleDB | Store and query time-series data including emissions reductions, pricing history, and market performance metrics |
| MongoDB | Store flexible ESG metadata, project documentation, and dynamic datasets | |
| IPFS, Filecoin, Arweave | Provide permanent, tamper-resistant storage for certificates, satellite verification records, and MRV documentation | |
| Infrastructure | Kubernetes, Docker | Enable scalable deployment, automated orchestration, and modular system upgrades |
| Kafka, RabbitMQ | Operate event-driven architecture for market events, verification inputs, and IoT data ingestion | |
| Redis, Memcached | Provide accelerated data access and caching for faster user experience and reduced load on core services |
Infrastructure in climate asset markets must handle both predictable trading volume and unpredictable regulatory or climate-driven demand spikes.
5. Security and Compliance Frameworks
Compliance and Identity
Onfido, Sumsub, and Jumio automate KYC, KYB, identity document checks, and sanctions screening. Chainalysis and Elliptic extend compliance by monitoring wallet activity and detecting suspicious blockchain transactions.
Custody and Asset Protection
Fireblocks, BitGo, and Copper provide insured custody and MPC-based protection for digital assets. Gnosis Safe and Argent support programmable access rules for treasury control and shared governance.
Advanced Privacy and Cryptography
ZoKrates and Circom enable zero-knowledge verification for private ESG and emissions reporting. ConsenSys Diligence, Trail of Bits, and CertiK conduct smart contract audits, and OpenZeppelin Defender assists with secure upgrades and real-time monitoring.
In a regulated environmental finance market, a security failure impacts financial trust and damages market credibility.
6. Frontend and User Experience
Web Platforms
React, Next.js, and Vue are used to build responsive interfaces for trading dashboards and reporting tools. Web3.js, Ethers.js, and Wagmi handle wallet connectivity and blockchain interactions. For analytics and ESG visualization, libraries like D3.js and Chart.js help display carbon provenance, asset status, and emissions trends.
Mobile
React Native and Flutter enable cross-platform mobile trading, asset management, and portfolio tracking. WalletConnect supports secure wallet integration across devices without exposing private keys.
7. Analytics and Monitoring
- Tableau, Looker, or Metabase enable regulatory reporting and ESG data visualization.
- The Graph and Covalent provide indexed blockchain analytics that simplify querying.
- Datadog, New Relic, and Sentry support performance observability and error resolution.

Top 5 Carbon Credit and ESG Token Exchanges
We dug deep into the carbon markets and explored platforms that are actually doing something meaningful in the space. Each exchange works differently because it focuses on technical precision and verifiable environmental impact.
1. CTX Global
CTX Global is one of the earliest digital voluntary carbon credit marketplaces, offering verified, registry-backed credits to companies and individuals seeking to offset emissions. It operates similarly to a financial exchange, enabling efficient trading and automatic retirement of carbon credits.
2. Xpansiv CBL

Xpansiv’s CBL is one of the largest environmental-asset marketplaces, supporting carbon offsets and renewable energy certificates. It introduced standardized carbon credit contracts and collaborated with CME Group to launch carbon futures, making ESG assets more accessible to traditional markets.
3. Climate Impact X
Climate Impact X offers a curated marketplace for high-quality nature-based carbon credits and focuses on transparency and biodiversity reporting. It also supports enterprise-level procurement, enabling corporations to participate in large-scale climate compensation strategies.
4. Toucan Protocol
Toucan Protocol tokenizes certified carbon credits and brings them onto decentralized finance markets. By converting credits into digital tokens, it enables transparency and fractional ownership, making carbon markets more globally accessible.
5. Carbon Credit Capital
Carbon Credit Capital is a U.S.-focused carbon offset and sustainability organization that works with businesses and consumers to integrate offsets into ESG strategies. Its hybrid approach connects traditional carbon markets with emerging digital carbon solutions.
Conclusion
Carbon credit and ESG token exchanges are becoming essential infrastructure, and if you are watching the space closely, you can already see how fast standards and expectations are forming. These platforms unlock verified sustainability markets at a global scale and give companies a way to track, retire, and trade environmental assets with far more accuracy and automation. The groups building now will likely control ESG liquidity, compliance automation, and the broader green finance ecosystem as it matures. If you plan to enter this market, Idea Usher can help you build a full platform that meets technical, regulatory, and scalability requirements so you can compete with confidence.
Looking to Develop a Carbon Credit and ESG Token Exchange?
Idea Usher can help you design and build a fully compliant carbon credit and ESG token exchange that aligns with current standards and emerging regulations. You get end-to-end support from smart contract engineering to permissioned blockchain architecture and integration with verification registries.
Why Partner with Idea Usher?
500,000+ hours of coding experience focused on blockchain, fintech, and DeFi solutions.
- Led by ex-MAANG/FAANG developers who architect for scale, security, and compliance from day one.
- Full-cycle development: From smart contract auditing and dMRV oracle integration to regulatory-compliant UI/UX and deployment.
- We don’t just build software. We help you engineer trust, liquidity, and transparency into the climate economy.
Ready to transform climate assets into high-integrity, liquid digital assets? Let’s build.
Work with Ex-MAANG developers to build next-gen apps schedule your consultation now
FAQs
A1: A carbon credit token avoids double-counting by using on-chain retirement and synchronized registry status, so once the credit is tokenized and retired, the system locks it and prevents reuse, while smart contracts enforce a single ownership record that cannot be duplicated or reassigned later.
A2: In many jurisdictions, ESG tokens are treated as securities because they represent investment value or yield potential, and this means platforms may need to follow licensing rules, investor protections, and disclosure requirements similar to traditional regulated financial products.
A3: Yes, enterprises can build private ESG token exchanges by using permissioned blockchain frameworks that allow controlled access, identity-based participation, and integration with internal compliance systems, and this approach may suit organizations that handle sensitive data or operate under strict regulatory oversight.
A4: Building a carbon and ESG exchange may take six to ten months, depending on scope, regulatory needs, and platform features and the timeline usually includes architecture design, compliance alignment, smart contract development, testing phases, and final deployment into a production environment.