- Precision Farming Market Size
- What Is Precision Agriculture?
- How Precision Agriculture Works?
- How Precision Agriculture Are Transforming Farming Practices?
- Challenges Of AI Implementation In Agriculture
- How ChatGPT Empowers Precision Agriculture?
- Benefits Of AI In Agriculture
- How Is Data Analytics Transforming Agriculture?
- Examples Of Businesses Using AI For Precision Agriculture
- How To Implement AI In Precision Agriculture?
- Cost Affecting Factors to Implement AI in Precision Agriculture
- Conclusion
- How We Can Help?
- FAQ

Precision agriculture has recently acquired significance in the agricultural industry. This strategy combines artificial intelligence (AI) and data-driven insights to transform traditional farming practices.
Precision agriculture is gradually being recognized for its role in upgrading farming operations, providing multiple benefits, and enhancing sustainability and efficiency.
The major goal is to offer farmers real-time information on soil conditions, climatic patterns, crop health, and other elements to aid decision-making. Essentially, precision farming enables farmers to make precise decisions by using data on land, weather, crops, and other aspects.
Read on to understand how precision agriculture works with the environment to help farmers make better decisions and farm with greater efficiency.
- Precision Farming Market Size
- What Is Precision Agriculture?
- How Precision Agriculture Works?
- How Precision Agriculture Are Transforming Farming Practices?
- Challenges Of AI Implementation In Agriculture
- How ChatGPT Empowers Precision Agriculture?
- Benefits Of AI In Agriculture
- How Is Data Analytics Transforming Agriculture?
- Examples Of Businesses Using AI For Precision Agriculture
- How To Implement AI In Precision Agriculture?
- Cost Affecting Factors to Implement AI in Precision Agriculture
- Conclusion
- How We Can Help?
- FAQ
Precision Farming Market Size
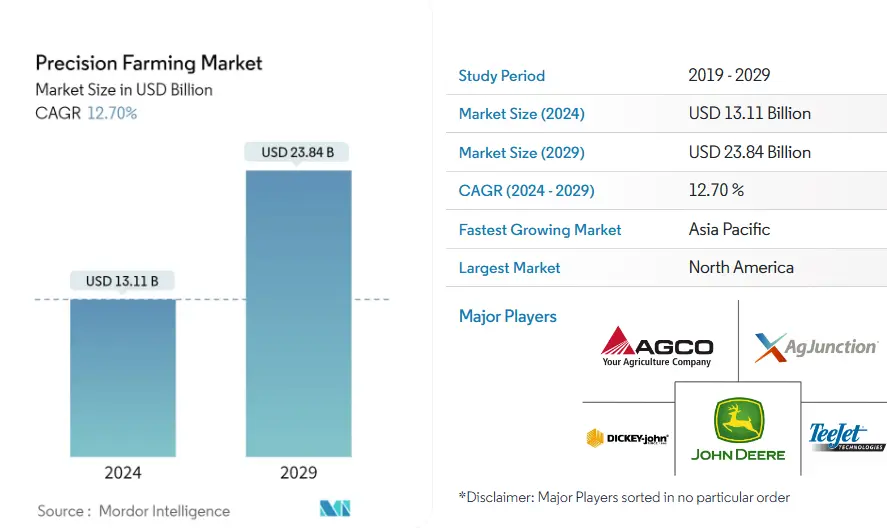
Source: MordorIntelligence
A thriving precision farming business represents an abundance of opportunities for entrepreneurial minds. This expansion reflects the increasing demand for data-driven farming techniques. Entrepreneurs can benefit on this trend by developing unique solutions that address the market’s specific needs.
By delivering technologies that improve efficiency, reduce waste, and increase yields, entrepreneurs may position themselves at the forefront of a transformative agricultural movement.
What Is Precision Agriculture?
Precision agriculture, also referred to as site-specific crop management, is revolutionizing the way we farm. It’s a management approach that utilizes modern technology to optimize crop production and resource use. Instead of relying on broad-brush techniques, precision agriculture focuses on understanding and responding to variations within a field, and even between individual plants.
Imagine a field that has areas with richer soil or better drainage. Traditionally, farmers might treat the entire field the same way. Precision agriculture allows them to pinpoint these variations. Through tools like GPS, sensors, and satellite imagery, they can collect data on factors like soil moisture, nutrient levels, and crop health. By analyzing this data, they can create detailed field maps that reveal areas needing more or less water, fertilizer, or pesticides.
This targeted approach has numerous benefits. Farmers can reduce waste by applying inputs only where they’re truly needed. This saves money on resources and minimizes potential environmental impacts from excess fertilizers or pesticides. Precision agriculture also allows for better decision-making. With real-time data on crop health, farmers can identify pest outbreaks or nutrient deficiencies early and take corrective measures to improve yields.
Overall, precision agriculture is a powerful tool for increasing farm efficiency, sustainability, and profitability. It empowers farmers to become data-driven stewards of their land, producing more food while using fewer resources.
How Precision Agriculture Works?
Precision agriculture is using technology to farm smarter, not harder. It’s a method that relies on collecting data about a field and then using that data to make decisions about what to plant, how much water to use, and how much fertilizer to apply.
Here’s a breakdown of how it works:
1. Data Collection
The first step is to gather information about the land. This can involve things like soil sampling, using drones or satellites to take pictures of the field, and even tracking weather patterns.
2. Data Analysis
Once all this data is collected, it needs to be analyzed. Farmers can use special software to create maps that show things like soil quality, crop health, and moisture levels.
3. Variable Rate Application (VRA)
This is where the real magic happens. With a detailed map of their field, farmers can now apply things like fertilizer and pesticides at exactly the right rates in exactly the right places. This means they’re not wasting resources on areas that don’t need them.
4. Technology Implementation
There are a number of technologies that make precision agriculture possible. These include:
- GPS: This satellite navigation system helps farmers track the location of their equipment and apply inputs with greater precision.
- GIS (Geographic Information System): This software allows farmers to store, analyze, and visualize all of their data on a map.
- Sensors: Sensors can be placed in fields to collect data on things like soil moisture, temperature, and nutrient levels.
How Precision Agriculture Are Transforming Farming Practices?
Precision agriculture is a revolutionary approach to farming that leverages technology and data to optimize crop production. It marks a significant shift from traditional, intuition-based practices to a data-driven, intelligent system. Let’s explore seven key ways precision agriculture is transforming farming:
1. Targeted Inputs
Farmers can use sensors and digital maps to identify areas within a field that require specific amounts of fertilizer, water, or pesticides. This eliminates unnecessary waste and ensures resources are directed where they provide the most benefit.
2. Boosted Yields
By precisely meeting the crop’s needs, precision agriculture helps farmers maximize yields. This translates to increased production on existing farmland, contributing to global food security.
3. Environmental Benefits
Reduced reliance on fertilizers and pesticides minimizes environmental pollution. Precision agriculture promotes sustainable practices, conserving water and fostering healthier soil.
4. Data-Driven Decisions
Farmers gain valuable insights from real-time data on crop health, soil conditions, and weather patterns. This empowers them to make informed decisions about planting, irrigation, and pest control.
5. Empowering Smallholders
Precision agriculture technologies are becoming increasingly accessible, enabling even small-scale farmers to benefit from data-driven practices. This promotes agricultural development and improves livelihoods.
6. Automation and Efficiency
Advanced systems like GPS-guided tractors and automated irrigation techniques streamline farm operations, reducing labor costs and improving efficiency.
Challenges Of AI Implementation In Agriculture
AI promises to revolutionise agriculture, but hurdles like cost and data remain. Let’s explore the challenges of implementing AI on the farm.
1. High Upfront Costs
Implementing AI in agriculture requires investment in hardware, software, data infrastructure, and expert training. This can be a significant challenge, especially for small-scale farmers or those in developing countries
2. Data Availability and Quality
AI models rely on vast amounts of high-quality data for training and operation. However, collecting and managing agricultural data can be complex due to factors like weather variability, sensor limitations, and fragmented land ownership.
3. Limited Infrastructure
AI-powered solutions often depend on reliable internet connectivity and robust computing power. These resources may not be readily available in rural areas, hindering implementation and effectiveness.
4. Farmer Skepticism and Adoption
Some farmers might hesitate to embrace new, complex technologies. Understanding and trusting AI’s decision-making capabilities can be a hurdle, slowing down widespread adoption.
5. Lack of Expertise
Using and maintaining AI systems effectively requires technical know-how. A shortage of skilled professionals who can bridge the gap between AI technology and agricultural practices can hinder implementation.
6. Ethical Considerations
Bias in data can result in biased AI decisions. Ethical considerations surrounding automation and potential job displacement in the agricultural sector also need to be addressed.
How ChatGPT Empowers Precision Agriculture?
ChatGPT offers a range of applications to enhance agricultural practices. From real-time crop management advice to market analysis, this tool empowers farmers with data-driven decision making.
1. Data-Driven Crop Management
ChatGPT analyzes weather, soil conditions, and growth patterns to provide real-time recommendations for irrigation, fertilization, and pest control, all tailored to each farm’s unique needs.
2. Combating Crop Threats
By analyzing images or descriptions, ChatGPT can identify diseases and weeds, suggesting suitable treatment or management strategies to safeguard crops.
3. Marketing Benefits
Uncover market trends, crop recommendations, and pricing strategies through ChatGPT’s data analysis. Like a data-powered farming partner, it considers past prices, consumer demand, and market fluctuations to guide informed decisions.
Benefits Of AI In Agriculture
Agriculture faces numerous obstacles, but artificial intelligence (AI) is emerging as a game changer. AI has the potential to change agriculture by boosting crop yields and optimizing resource utilization.
1. High Upfront Costs
Implementing AI in agriculture necessitates investments in hardware, software, data infrastructure, and specialized training. This can be a substantial challenge, particularly for small-scale farmers and those in poor countries.
2. Data Quality
AI models rely on vast amounts of high-quality data for training and operation. However, collecting and managing agricultural data can be complex due to factors like weather variability, sensor limitations, and fragmented land ownership.
3. Limited Infrastructure
AI-powered solutions often depend on reliable internet connectivity and robust computing power. These resources may not be readily available in rural areas, hindering implementation and effectiveness.
4. Farmer Skepticism and Adoption
Some farmers might hesitate to embrace new, complex technologies. Understanding and trusting AI’s decision-making capabilities can be a hurdle, slowing down widespread adoption.
5. Lack of Expertise
Using and maintaining AI systems effectively requires technical know-how. A shortage of skilled professionals who can bridge the gap between AI technology and agricultural practices can hinder implementation.
6. Data Privacy & Ethical Concerns
As AI in agriculture gathers and analyzes vast amounts of farm data, questions arise regarding data ownership, security, and potential misuse. Also, bias in training data can lead to biased AI decisions. Ethical considerations surrounding automation and potential job displacement in the agricultural sector also need to be addressed.
How Is Data Analytics Transforming Agriculture?
The agricultural industry is undergoing a huge shift, fueled by data analytics, allowing farmers to make data-driven decisions and enhance their operations. Here’s a closer look at how data analytics is transforming agriculture:
1. Data-Driven Insights
Data encompasses vital details like soil conditions, weather patterns, and crop health. By analyzing this information, farmers gain valuable insights that enable them to make informed choices, ultimately leading to improved outcomes.
2. Predictive Power
Data analytics isn’t just about understanding the present; it’s about anticipating the future. By analyzing historical and current data trends, farmers can leverage predictive models to forecast crop yields, potential disease outbreaks, and even market trends. This foresight allows them to plan efficiently, minimize risks, and make strategic decisions for long-term success.
3. Precision and Optimization
Data analytics goes beyond mere prediction; it allows for precise resource management. By analyzing soil health data, farmers can optimize irrigation and fertilization practices, ensuring that crops receive exactly what they need. This data-driven approach not only maximizes yield but also minimizes resource wastage, promoting both economic and environmental sustainability.
4. Proactive Pest and Disease Control
Data analytics plays a vital role here by enabling early identification of potential problems. AI tools can analyze data and identify signs of crop damage, allowing farmers to intervene promptly and implement appropriate pest management strategies.
5. Prescriptive Recommendations
Data analytics doesn’t stop at providing information; it offers actionable guidance. Through analysis, farmers receive prescriptive recommendations on various aspects of their operations, such as crop selection, resource application, and timing. This data-driven approach allows for informed choices that enhance overall operational efficiency and maximize output.
Examples Of Businesses Using AI For Precision Agriculture
AI is having a big impact on agriculture, and several businesses are offering innovative solutions for farmers. Here are a few examples:
1. John Deere
An agricultural equipment giant uses AI-powered sensors and GPS on their machines. This gathers data on factors like soil conditions and allows for optimized planting, watering, and fertilization practices tailored to specific areas of a field.
2. Carbon Robotics
Carbon Robotics uses computer vision and AI to create weed-killing robots. These robots can distinguish between crops and weeds, allowing for more precise weed control, which means less herbicide is used and crop yields can be boosted.
3. Plenty
This company focuses on indoor vertical farming, and leverages AI to automate and optimize plant growth conditions like lighting, temperature, and irrigation. This allows them to achieve higher yields while using less water and land.
4. The Climate Corporation
Offering a robust digital farming platform that utilizes AI for weather forecasting, yield prediction, and field-specific recommendations on planting, irrigation, and nutrient management.
5. Granular
This company leverages AI to analyze farm data and suggest targeted applications of crop protection products. This minimizes waste and optimizes pest and disease control.
6. Prospera Technologies
This company focuses on AI-powered irrigation solutions. Their systems use sensors and weather data to create precise irrigation plans that can reduce water usage significantly while maintaining crop health.
7. Indigo Agriculture
This company uses AI to analyze soil microbiome data. This allows them to develop customized microbial inoculants that improve soil health and nutrient uptake for crops, leading to increased yields and reduced reliance on fertilizers.
How To Implement AI In Precision Agriculture?
AI is revolutionizing agriculture by enabling a data-driven approach known as precision agriculture. This method optimizes resource use and crop health by tailoring decisions to specific field conditions. Here’s a breakdown of the steps involved in implementing AI for precision agriculture:
1. Data Collection
The first step is gathering comprehensive data about your farm. This involves deploying a network of sensors across your fields. These sensors can be ground-based, providing real-time data on factors like soil moisture, temperature, and nutrient levels. Additionally, drones equipped with multispectral cameras can capture detailed imagery revealing crop health variations.
2. Data Analysis
Once you have a robust dataset, it’s time to unlock its potential. Here’s where AI comes into play. Machine learning algorithms, a powerful type of AI, are used to analyze the collected data. These algorithms excel at identifying patterns and relationships between various factors that influence crop growth. However, to ensure accurate and valuable analysis, the data needs cleaning and organization. This might involve removing inconsistencies and ensuring consistency in format and units.
3. Developing AI Models
With the data prepared, it’s time to develop AI models specifically tailored to your farm’s needs. This involves a process called training, where the prepared data is fed into the chosen machine learning algorithms. Through this training, the algorithms learn to identify patterns and relationships within the data. Based on your specific goals, you can choose different AI models. For instance, you might opt for yield prediction models to forecast future harvests, disease detection models to identify potential outbreaks early, or irrigation optimization models to ensure water efficiency.
4. Action and Implementation
Translate the insights generated by the AI models into actionable recommendations for your farm. This could involve adjusting fertilizer application rates, optimizing irrigation schedules, or identifying areas prone to pest outbreaks.
Integrate AI with farm management software or mobile applications to provide real-time decision support to farmers.
5. Monitoring and Refinement
Continuously monitor the performance of your AI models and the impact on your crops.
Refine and retrain the models as needed based on new data and observations to ensure their ongoing effectiveness.
Cost Affecting Factors to Implement AI in Precision Agriculture
While AI holds immense potential for revolutionizing agriculture, its implementation in precision farming comes with a significant cost hurdle. Here are five key factors that can affect the overall cost:
1. Hardware Infrastructure
Precision agriculture with AI relies heavily on data collection from various sources like sensors, drones, and yield monitors. Acquiring and installing these sensors across a farm can be expensive, especially for smaller farms. Additionally, the ongoing maintenance and data storage needs of this infrastructure add to the financial burden.
2. Software and Data Analytics
Utilizing AI effectively requires specialized software platforms that can handle the complex data analysis and generate actionable insights. These software licenses can be costly, and depending on the chosen platform, ongoing subscription fees might apply. Furthermore, the expertise needed to manage and interpret the data generated by AI systems may necessitate hiring additional personnel or outsourcing services, further increasing costs.
3. Farm Size and Complexity
The cost of implementing AI in precision agriculture is often directly proportional to the farm’s size and operational complexity. Larger farms with diverse crops and activities may require more extensive sensor networks, data analysis capabilities, and potentially even custom AI models, leading to higher overall expenses.
4. Connectivity and Internet Access
AI-powered solutions often rely on real-time data transmission and access to cloud computing resources. Farms in remote locations with poor or unreliable internet connectivity may face additional costs for infrastructure upgrades or alternative data transmission methods.
5. Expertise and Training
Successfully implementing and utilizing AI in agriculture requires a certain level of technical expertise from the farm management. Farmers may need training on using the software, interpreting AI-generated insights, and integrating them into decision-making processes. In some cases, hiring additional staff with specific skillsets in data analysis or AI technology might be necessary, adding to the overall cost.
Here’s a table outlining estimated cost ranges for each of the factors affecting the implementation of AI in precision agriculture:
| Factors | Estimated Cost Range |
| Hardware Infrastructure | $10,000 – $100,000+ (depending on farm size and sensors) |
| Software and Data Analytics | $5,000 – $50,000+ (including software licenses and subscriptions) |
| Farm Size and Complexity | $20,000 – $200,000+ (for larger and more complex operations) |
| Connectivity and Internet Access | $2,000 – $20,000+ (for upgrades or alternative methods) |
| Expertise and Training | $5,000 – $50,000+ (for training and potentially hiring specialized staff) |
Conclusion
Farming is undergoing a revolution with the help of artificial intelligence (AI) and data analysis in precision agriculture. This tech allows farmers to streamline their operations, boost yields, and reduce environmental impact. AI-powered solutions provide real-time monitoring of crops, soil, and weather, enabling informed decisions.
By integrating data insights, farmers can optimize water, fertilizer, and pesticide use, leading to sustainable and efficient practices. Ultimately, precision agriculture fosters a shift towards resilient food production methods that benefit everyone – farmers, consumers, and the environment.
However, concerns about data privacy, connection, and initial investment expenditures must be addressed. Working with an AI development company can help overcome these challenges and help you focus entirely on your business operations.
How We Can Help?
Our cutting-edge AI empowers you to revolutionize your precision agriculture. We build robust machine learning algorithms that analyze real-time data, historical trends, and specific crop needs. These algorithms identify even minor anomalies and predict potential problems before they arise.
Working hand-in-hand with your agricultural specialists, we’ll understand your unique needs and seamlessly integrate AI solutions to optimize crop management, minimize resource waste, and elevate yield quality. By embracing our AI, you’ll unlock cost savings, increased production, and significant gains in overall farm productivity.
FAQ
Q. How can AI improve our farm’s efficiency?
A. From sensors, drones, and satellites to identify areas needing more or less water, fertilizer, or pesticides. This allows for targeted application, reducing waste and optimizing resource use. Additionally, AI can automate tasks like scouting for diseases and monitoring crop health, freeing up labor for other priorities.
Q. What are the benefits of AI-powered irrigation systems?
These systems use real-time data on weather, soil moisture, and crop needs to deliver water precisely where and when it’s required. This minimizes water waste, lowers pumping costs, and ensures optimal crop growth.
Q. Can AI help predicting crop yields?
By analyzing historical data, weather patterns, and current crop health information, AI models can generate accurate yield forecasts. This allows for better planning of harvest logistics, resource allocation, and potential sales.
Q. How can AI be used for pest and disease control?
A. AI image recognition can analyze drone footage or field photos to detect pests and diseases at early stages. This enables prompt intervention with targeted treatments, minimizing crop damage and reducing reliance on broad-spectrum pesticides.
Q. Is AI a replacement for farmworkers?
AI is more of an augmenting tool. While it can automate repetitive tasks, experienced farmers are still essential for decision-making, overseeing operations, and ensuring overall farm management.
Q. What data security concerns are there with AI in agriculture?
Data security is paramount. Farms should choose AI solutions with robust security measures to protect sensitive information like crop yields, soil conditions, and financial data.
Q. How can our business get started with AI in agriculture?
Several options exist. Many agricultural equipment manufacturers now offer AI-powered features on tractors and other machinery. Cloud-based AI services can analyze data and provide actionable insights. It’s wise to start with a specific challenge you want to address and research solutions that target that need.











Gaurav Patil