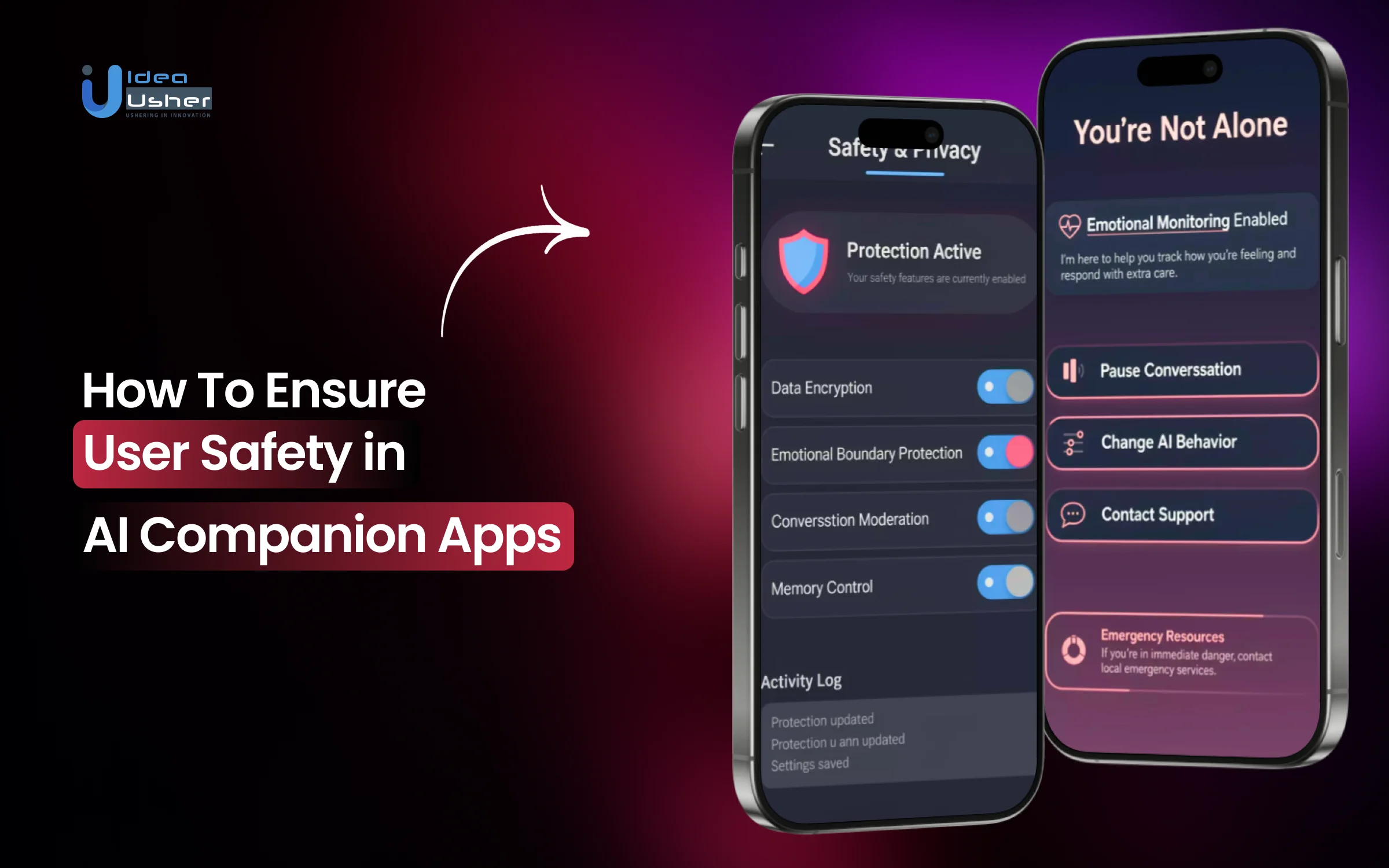
AI companion apps are designed to be always present, emotionally responsive, and easy to rely on, which makes safety a critical concern. Users may share vulnerable thoughts, seek guidance during difficult moments, or form emotional attachments over time. When boundaries are unclear or responses are mishandled, consequences can be serious. This is why AI companion app user safety is a foundational responsibility, not a feature choice.
Protecting users requires intentional system design rather than reactive fixes. Safety mechanisms influence how the AI communicates, what it avoids, when concerns escalate, and how sensitive topics are handled. These controls help manage distress, dependency risks, and misuse while preserving a natural conversational experience.
In this blog, we explore how user safety can be built into AI companion apps from the ground up, covering practical safeguards, design decisions, and ongoing monitoring. Understanding these systems helps teams create supportive experiences without crossing ethical or emotional boundaries.
Understanding User Safety in AI Companion Apps
User safety in AI companion apps extends beyond account security to emotional interactions that influence user behavior and decisions. Because AI companions respond and simulate empathy, effective safety depends on technical reliability and understanding AI user psychological and behavioral dynamics.
A. What User Safety Means in AI Companion Apps?
User safety refers to protecting users from harm that may arise through interaction with the system itself. This includes emotional, psychological, and behavioral risks, as well as exposure to inappropriate or misleading content.
- Emotional well-being: AI companions can provide comfort but may also create emotional dependency or distress if poorly designed. User safety requires avoiding isolation, unhealthy reliance, or harmful coping behaviors.
- Appropriate interaction boundaries: AI companions must maintain clear conversational boundaries, avoiding manipulative language, inappropriate intimacy, or responses that resemble authoritative advice in sensitive contexts.
- Exposure to harmful or misleading content: AI-generated responses may be inaccurate or unsafe. User safety focuses on reducing the risk of harmful guidance that could cause real-world consequences.
- User vulnerability and edge cases: Users may interact during stress or loneliness. Safety design must address responses to distress, vulnerability, or crisis situations.
B. Why User Safety Requires a Different Approach?
Traditional safety measures like content filtering or reporting tools may not suffice for AI companion apps. Their conversational and adaptive nature can create risks gradually through tone, reinforcement, or long-term interaction patterns, not just from single harmful outputs.
Ensuring user safety needs a holistic approach with technical safeguards, thoughtful conversation design, and ongoing monitoring. This foundation allows evaluation of safety mechanisms and shows why safety should be a core design principle, not an afterthought.
What an 88% YoY Growth Says About AI Companion App Adoption?
The global AI companion market, valued at USD 28.19 billion in 2024, is projected to reach USD 140.75 billion by 2030, with a CAGR of 30.8% from 2025 to 2030. Growth driven by increasing demand for conversational, emotionally responsive AI across regions and demographics, signifying AI companion apps shifting from niche to mainstream adoption.
An 88% year-over-year increase in AI companion app downloads in 2025 further reinforces this trend. The surge signals rapid user uptake and sustained interest rather than short-term curiosity, highlighting a shift in how people engage with AI-driven interaction and support.
A. What Rapid Adoption Means in Simple Terms?
The sharp rise in AI companion app usage suggests a fundamental change in how users interact with technology. AI companions are no longer treated as novelty tools but as recurring points of engagement in users’ daily lives.
- AI companions as habitual products: Users increasingly return to these apps regularly, deepening interactions over time and extending impact beyond one-time experimentation.
- Evolving user expectations: Growing adoption leads users to expect responsiveness, emotional awareness, and consistency, shaping reliance on AI responses.
- Expanding user diversity: Broader adoption introduces users with diverse emotional needs, cultural contexts, and digital literacy, increasing safety and design complexity.
B. Why the Adoption Scale Matters for User Safety?
As AI companion apps scale quickly, the implications extend beyond market success. Increased adoption changes the responsibility surface for developers and product teams.
- More users mean more edge cases: At scale, AI systems face diverse emotional states, vulnerabilities, and unexpected inputs, requiring safety designs beyond ideal usage assumptions.
- Repeated interaction amplifies impact: Frequent engagement means subtle response patterns can shape behavior and emotional well-being over time, making long-term design critical.
- Growth accelerates responsibility: Rapid adoption reduces tolerance for error, making proactive safety planning essential as small issues can quickly scale.
The rapid growth of the AI companion app market highlights how quickly these products are becoming part of everyday digital interaction. As adoption accelerates and usage deepens, understanding this shift provides essential context for why user safety considerations must scale alongside growth, not trail behind it.
Common User Safety Risks in AI Companion Apps
AI companion apps carry safety risks tied to conversational design. Repeated interactions, tone reinforcement, or emotional responses can gradually create harm, making early identification essential for implementing effective safeguards.
1. Emotional Dependency & Over-Reliance
A key risk of AI companion apps is emotional dependency. Constant availability may cause users to rely on AI as their primary emotional support, potentially harming real-world relationships and reinforcing unhealthy attachment through frequent use or validation reliance.
2. Blurred Boundaries Between AI & Human Relationships
AI companion apps simulate empathy, enhancing user experience but blurring lines between artificial and human relationships. Users may assign authority or emotion to AI, which lacks real-world accountability, and exaggerated claims can distort expectations and influence decisions.
3. Inappropriate or Harmful Responses
Despite safety filters, AI companion apps can generate misleading or inappropriate responses that users may trust. These replies can reinforce negative thoughts, provide incorrect guidance, or respond poorly to distress, with conversational context amplifying potential harm.
4. Vulnerable User Scenarios
Users often engage with AI companion apps during loneliness or stress, increasing the risk of harmful reinforcement. If distress signals are missed or mishandled, AI may fail to de-escalate harm, making vulnerable situations require dedicated safety measures.
5. Long-Term Behavioral Impact
AI companion apps influence beyond chats; long-term use may alter behavior, self-view, or coping strategies. Recognizing these risks justifies safety measures. Addressing them helps developers create safer, engaging systems.
For example, an AI that consistently agrees with a user or avoids challenging harmful assumptions may unintentionally reinforce negative behaviors. These long-term impacts make user safety a continuous concern rather than a one-time design task.
Safety-by-Design Principles for AI Companion Apps
Ensuring safety in AI companion apps begins at design. Safety by design anticipates user interactions and embeds safeguards into structure and behavior, reducing harm proactively rather than relying on reactive measures.
1. Establishing Clear Interaction Boundaries
AI companion apps should clearly define what the AI can and cannot do, avoiding language that suggests exclusivity, authority, or emotional dependence. The AI should not replace human relationships or professional support. Clear boundaries help prevent misunderstanding and over-reliance.
2. Avoiding Emotional Manipulation
AI companions adapt to user emotions, risking to unintentionally shape behavior via reinforcement. Safety-by-design must avoid patterns that promote over-engagement, dependency, or emotional validation without balance. Neutral tone, varied responses, and promoting real-world connections help prevent manipulative dynamics.
3. Transparency About AI Capabilities & Limitations
Users should recognize they interact with an AI, not a human or authority. Transparency about the AI’s functions, capabilities, and limits is crucial, including avoiding claims suggesting emotional understanding, moral judgment, or decision-making beyond its actual abilities.
4. Designing for Failure & Edge Cases
Safety-by-design accepts errors and prepares for them as no AI system is perfect, including inappropriate responses, misinterpretations, or unexpected uses. Anticipating failures allows developers to create fallback behaviors, escalation paths, or safety prompts to reduce harm.
5. Treating Safety as an Ongoing Process
User safety isn’t a one-time design choice. As AI apps evolve, risks can emerge with new features, growth, or changing use. Safety-by-design requires ongoing review, testing, and updates to protect users’ well-being. These principles support safety measures, with sections on tools, controls, and practices to enforce these goals.
Content Moderation and Response Safety Mechanisms
Content moderation is vital for user safety in AI companion apps, as their dynamic responses can’t rely solely on static rules or one-time reviews. Effective moderation needs multiple control layers to manage the AI’s replies across diverse topics and user conditions.
1. Preventing Unsafe or Inappropriate Outputs
AI companion apps should minimize harmful, offensive, or misleading responses through moderation before and after generating replies. Pre-response safeguards restrict what the AI can say, while post-response checks catch and correct unsafe outputs, reducing the risk during interactions.
2. Handling Sensitive Topics Carefully
Users may discuss sensitive topics like mental health, trauma, or distress. AI apps should respond carefully and consistently, offering neutral support and prompting external help when needed. Consistent handling prevents unsafe interactions.
3. Managing Escalation & High-Risk Scenarios
High-risk user inputs such as severe distress or harmful intent, should trigger AI to provide safer responses. This includes limiting deep talks, avoiding emotional or speculative replies, and guiding users to support. Escalation prevents AI from worsening high-risk situations.
4. Balancing Safety & Natural Interaction
Overly restrictive moderation can make conversations seem artificial or dismissive, frustrating users or reducing trust. Conversely, too little safeguards increase the risk. Effective safety measures balance meaningful interaction with safeguards to protect users from unsafe or misleading content.
5. Monitoring & Refining AI Responses Over Time
Monitoring AI companion interactions over time helps identify unsafe patterns, missed edge cases, and response inconsistencies. Regular review and refinement ensure moderation systems remain effective as user behavior, language, and real-world usage evolve.
Human Oversight and Intervention in AI Companion Apps
Human oversight in AI companion apps ensures safe, responsible interactions by monitoring behavior and guiding responses. Effective intervention balances user support with system reliability, highlighting the importance of oversight in AI design.
1. Why Human Oversight Is Necessary
Human oversight is critical because AI companion apps operate in emotionally complex contexts. Automated systems may miss nuance, intent, or risk escalation, making human judgment essential for interpreting edge cases and preventing harm.
2. Identifying When Intervention Is Required
Effective oversight depends on clear escalation signals such as repeated safety flags, distress indicators, or ambiguous content. Defined thresholds ensure human review is applied strategically, reducing risk without disrupting normal conversational experiences.
3. Forms of Human Intervention
Human intervention may include reviewing flagged interactions, refining response guidelines, adjusting moderation logic, or temporarily restricting system behaviors. These actions help correct unsafe patterns that automated safeguards alone cannot adequately resolve.
4. Accountability and User Trust
Human involvement introduces accountability into AI companion systems. Knowing that real people can review safety concerns reinforces user trust and demonstrates responsibility for how the AI behaves in sensitive or high-impact situations.
5. Integrating Oversight Into Operations
Oversight must be embedded into operational workflows through documentation, review processes, and feedback loops. Integrating human insights into system updates ensures safety improvements scale alongside product growth and user adoption.
User Controls, Transparency and Reporting Tools
User safety in AI companion apps improves when users can easily control and see how the system works. Safety relies not only on internal measures but also on features that help users understand and address unsafe interactions.
1. Giving Users Control Over Their Experience
AI companion apps should provide users with meaningful controls that allow them to shape how the AI interacts with them. This can include adjusting conversation tone, limiting certain topics, or resetting interaction history.
Providing these controls helps users maintain boundaries and reduces the risk of prolonged exposure to interactions that may negatively affect their well-being.
2. Transparency About AI Behavior and Limitations
Transparency is a key component of user safety. Users should understand that they are interacting with an AI system, not a human, and be aware of the system’s limitations.
Clear explanations about what the AI can and cannot do help prevent unrealistic expectations and reduce the likelihood that users place inappropriate trust in the system’s responses.
3. Reporting Unsafe or Uncomfortable Interactions
Accessible reporting tools allow users to flag interactions that feel unsafe, misleading, or distressing. These reports provide valuable insight into real-world risks that may not be captured through automated monitoring alone.
Effective reporting mechanisms should be easy to use, clearly explained, and integrated into the app experience without discouraging user feedback.
4. Closing the Feedback Loop
Reporting tools are most effective when users know their feedback is taken seriously. Communicating how reports are reviewed and used helps reinforce trust and accountability.
By combining user controls, transparency, and reporting tools, AI companion apps can create a safety framework that actively involves users in maintaining a healthier and more secure interaction environment.
Ongoing Safety Governance and Continuous Improvement
Ongoing safety governance in AI companion apps ensures risks are regularly assessed, addressed, and improved over time. Continuous review, monitoring, and policy refinement support responsible system behavior and long-term user protection.
1. Establishing Safety Governance Processes
Effective safety governance begins with clearly defined processes and ownership. Teams should establish internal responsibility for reviewing safety performance, managing incidents, and approving changes that affect user interaction.
Having structured governance ensures that safety decisions are consistent, documented, and aligned with product goals rather than being handled reactively.
2. Regular Safety Reviews and Audits
Periodic reviews help evaluate how well safety mechanisms are functioning in practice. This includes reviewing flagged interactions, moderation outcomes, and user reports to identify trends or recurring issues.
Audits allow teams to assess whether existing safeguards still align with current usage patterns and whether adjustments are needed as the product evolves.
3. Adapting to Product and User Changes
As AI companion apps introduce new features or attract new types of users, safety risks may shift. What was safe at an earlier stage may no longer be sufficient as engagement deepens or use cases expand.
Continuous improvement requires revisiting safety assumptions, updating response guidelines, and refining controls to reflect these changes.
4. Learning From Incidents and Feedback
Safety incidents and user feedback provide valuable insight into system behavior. Rather than treating these events as isolated problems, teams should use them to inform broader improvements.
Analyzing why an issue occurred and how it can be prevented in the future strengthens the overall safety framework and reduces the likelihood of repeated harm.
5. Embedding Safety Into Long-Term Strategy
Ongoing safety governance works best when it is integrated into long-term product planning. Treating safety as a strategic priority helps ensure that new features, partnerships, or deployments do not introduce unmanaged risks.
By committing to continuous improvement, AI companion app developers can create safer experiences that evolve responsibly alongside technological and user expectations.
Building Safer AI Companion Apps Over Time
Building safer AI companion apps requires ongoing evaluation, updates, and safeguards as user behavior evolves. Long-term safety depends on responsible design, monitoring, and adaptation throughout the product lifecycle.
1. Treating Safety as a Continuous Responsibility
User safety in AI companion apps evolves as products grow and user behavior changes. Safeguards must be revisited regularly to ensure they remain effective in real-world conditions rather than only in controlled or early-stage environments.
2. Aligning Safety With Product Growth
As new features, interaction patterns, or user groups emerge, safety risks may shift. Integrating safety reviews into product updates helps prevent new functionality from introducing unintended harm or weakening existing protections.
3. Building Trust Through Responsible Design
Long-term user trust depends on clear boundaries, transparency, and responsiveness to feedback. AI companion apps that prioritize these principles are better positioned to maintain healthy and responsible user relationships over time.
4. Designing for Long-Term Resilience
Approaching safety as an ongoing practice rather than a one-time implementation allows AI companion apps to adapt responsibly. This mindset supports resilience as technology advances and user expectations continue to evolve.
Conclusion
User safety is not a feature that can be added later. It is built through thoughtful design, clear boundaries, and respect for human vulnerability. When discussing AI companion app user safety, the focus should remain on prevention, transparency, and accountability. Users deserve systems that protect emotional well-being, discourage harmful dependency, and respond responsibly to risk. Developers, regulators, and users all share a role in setting expectations. Safety becomes sustainable when trust is earned through consistent, understandable, and ethically grounded practices. This shared responsibility defines long-term protection for people engaging.
Why Choose IdeaUsher for Your AI Companion App Development?
At IdeaUsher, we help AI companion app founders navigate complex US privacy laws while building platforms that are compliant by design. From data collection flows to consent management and secure AI pipelines, we ensure your product aligns with regulatory expectations from day one.
Why Work with Us?
- Privacy-First System Design: We architect AI companion apps with GDPR, CCPA, COPPA, and HIPAA considerations mapped directly into backend workflows and data storage.
- Regulatory Risk Mitigation: Our team translates legal requirements into technical controls, reducing exposure to fines, app store rejections, and trust issues.
- Secure AI Data Handling: We implement encryption, access controls, and audit trails to protect sensitive user interactions and personal data.
- Launch-Ready Compliance: Your platform is built to scale across states without reworking privacy logic later.
Explore our portfolio to see how we have delivered secure, regulation-aware AI and SaaS platforms across industries.
Reach out to our team to discuss how to build a compliant AI companion app that earns user trust and regulatory confidence.
Work with Ex-MAANG developers to build next-gen apps schedule your consultation now
FAQs
A.1. User safety includes protecting emotional well-being, preventing harmful dependency, and responding appropriately to distress or sensitive topics. AI companion app user safety requires both technical safeguards and clear behavioral boundaries within conversations.
A.2. Apps can limit anthropomorphic language, avoid exclusivity cues, and encourage real-world support when needed. Clear disclosures and design choices help ensure users understand the system is a tool, not a replacement for human relationships.
A.3. AI companion apps should detect high-risk signals, provide supportive but neutral responses, and redirect users to external help when appropriate. Safety systems must prioritize de-escalation without attempting diagnosis or emotional manipulation.
A.4. Safety expectations should be clearly explained through onboarding, in-app disclosures, and accessible policies. Transparent communication builds trust and ensures users understand limitations, risks, and how the app handles sensitive interactions.