Online communities can grow quickly, but trust often takes longer, and many teams have slowly realized that contributors step back when decisions feel distant or unclear. When a DAO platform lacks clear governance flows, people do not lose belief in the vision, they simply lose a sense of participation and visibility.
That’s why businesses are choosing to build DAO platforms on the Base blockchain. Base can support affordable voting, secure shared treasuries, automated governance rules, delegation, role-based permissions, and on-chain execution, while onboarding members smoothly without heavy gas costs or complex user flows.
Over the years, we’ve built multiple DAO platforms and governance-driven products on Base blockchain, powered by account abstraction frameworks and modular governance smart contracts. As IdeaUsher has this expertise, we’re sharing this blog to discuss the steps to build a DAO platform on Base.
Key Market Takeaways for DAO Platforms
This growth aligns with rising Web3 adoption: active DAOs crossed 13,000 in 2025, and governance tooling platforms recorded around 40% growth in usage, indicating sustained, practical demand rather than hype-driven activity.
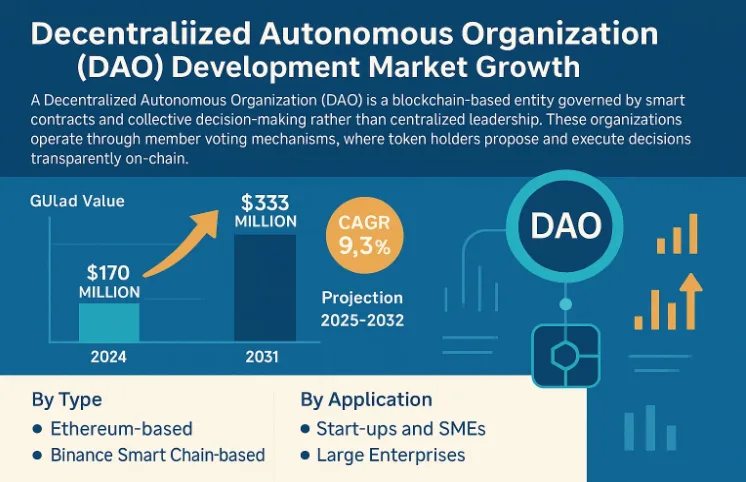
Source: IntelMarketResearch
Product capability is now a major driver of adoption. More than 200 DAOs are already using decentralized identity systems, while AI-supported treasury and governance tools are becoming standard for capital efficiency and risk visibility.
Beyond finance, non-financial DAOs in gaming and media grew over 25% year over year, and the Asia-Pacific region, led by China, South Korea, and India, is emerging as the fastest-growing hub for DAO experimentation and deployment.
Platform leaders demonstrate how scale is achieved through ecosystem alignment. Aragon supports major protocols such as Lido DAO and Aave, leveraging Ethereum interoperability to manage large treasuries and voting activity.
DAOhaus, inspired by Moloch-style governance, works with Bankless DAO and enables rapid funding through tools like Yeeter, showing how focused governance models can support research, grants, and community-led capital allocation at scale.

What Is a DAO Platform?
A DAO platform is a software system that enables communities to create and manage decentralized organizations using blockchain-based rules instead of centralized control. It allows members to propose decisions, vote using tokens, and execute outcomes automatically through smart contracts. This structure can reduce reliance on intermediaries while ensuring transparency, shared ownership, and rule-based governance.
How Is Base Better Than Other L2s for Building DAO Platforms?
While many Layer 2 solutions, like Arbitrum or Polygon, offer the essential benefits of low fees and Ethereum-level security, Base is engineered from the ground up to address the human and business challenges that have historically held DAOs back. It is not just another scalable blockchain. It is a consumer-first ecosystem, purpose-built for mainstream adoption.
Here is what truly sets Base apart for your DAO platform.
1. A Coinbase-backed, Consumer-First foundation
Base is not just another tech project. It is a public good incubated by Coinbase, a company with over 100 million verified users and a decade of experience in safe and compliant crypto onboarding. This heritage means Base is designed with a simple but radical goal. It aims to bring the next billion users on-chain.
For a DAO, this translates to an unprecedented ability to reach beyond the crypto native niche and engage real-world communities, employees, or customers.
2. Engineered for High Participation & Low Friction
Other L2s reduce cost, but Base actively removes participation friction, which is the silent killer of most DAOs.
From Gas Fees to Gasless
With native Account Abstraction through ERC 4337, you can build DAOs where the platform sponsors transaction fees via Paymasters. Members can vote without ever needing to buy or hold crypto.
From Seed Phrases to FaceID
Base’s native integration with Smart Wallets and Passkeys means members can sign a critical proposal using a fingerprint or FaceID scan. There are no browser extensions and no 12 word recovery phrases. The experience feels intuitive and familiar.
From Slow to Instant
With consistent two-second block times, governance becomes responsive. Micro governance and time-sensitive decisions become practical, especially for fast-moving analytics or betting-focused DAOs.
3. Native Alignment with Identity, Wallets, and Fiat
This is Base’s unique trifecta. These capabilities are often fragmented or unavailable on other chains.
On Chain Identity
Through integrations such as Coinbase Verifications and Basenames, you can build Sybil-resistant, compliance-aware DAOs. Participation can be gated to verified humans using KYC-based attestations, without the platform handling sensitive personal data. This supports true one person one vote integrity.
Smart Wallet Infrastructure
Base provides the rails for the wallet experience itself. This enables advanced flows such as bundled transactions, where a user can join, stake, and vote in a single action directly within the dApp.
Built-in Fiat On and Off Ramps
The seamless bridge between Base and the Coinbase ecosystem allows DAO treasuries to operate like real businesses. Converting between crypto and fiat for payroll, vendor payments, or distributions becomes significantly simpler, solving a major operational barrier to real-world adoption.
4. Regulatory Aware by Design
For enterprise and institutional use cases, this is the critical differentiator. Base’s close ties to a regulated and publicly traded entity, combined with its native identity tooling, allow DAO platforms to be built within a framework of accountability.
This enables use cases that were previously considered too risky, including investment DAOs, legal entity wrappers such as DAO LLCs, and professional guilds where verified participation is non-negotiable.
Types of DAO Platforms Businesses Are Building on Base
Businesses are building DAO platforms on Base that focus on governance, shared treasuries, and coordinated execution while keeping participation simple. Teams can design these systems to manage protocols, fund initiatives, or organize work in a way that feels efficient and predictable.
1. Governance and Community DAOs
These DAOs are built to let communities collectively make decisions about products, ecosystems, or shared initiatives. Members usually hold governance tokens and guide long-term direction through proposals and voting. Base makes this practical by keeping participation fast and low-cost.
Example: Nouns DAO – A DAO where members collectively govern a shared treasury funded by daily NFT auctions and vote on how funds are used.
2. Investment and Treasury DAOs
Investment-focused DAOs allow members to pool capital and collectively decide how funds are deployed across startups, protocols, or digital assets. This structure replaces traditional fund managers with transparent onchain governance. Base supports this by enabling frequent treasury actions without heavy fees.
Example: MetaCartel Ventures: A venture style DAO that invests in early stage Web3 startups using community driven capital allocation.
3. Grant and Ecosystem DAOs
Grant DAOs are designed to fund builders and public goods through community reviewed proposals and onchain disbursements. Decisions are transparent and execution is automated through smart contracts. Base is well suited because smaller grants remain economically viable.
Example: Gitcoin DAO – A DAO focused on funding open source software and public goods through grants and quadratic funding.
4. Protocol Governance DAOs
These DAOs govern live protocols and platforms by allowing token holders to vote on upgrades, parameters, and treasury usage. Governance directly affects how the product behaves in production. Base enables smoother governance cycles by lowering the cost of voting and execution.
Example: Uniswap DAO – A protocol DAO where token holders control upgrades, fee structures, and treasury decisions for a major decentralized exchange.
5. NFT and Collector DAOs
NFT-focused DAOs coordinate collective ownership, curation, and management of digital assets. Members decide what to acquire, how assets are displayed, and when they are sold. Base supports this model with low-cost minting and transfers.
Example: Flamingo DAO – A collector DAO that pools capital to acquire, manage, and curate high-value NFTs as shared assets.
6. Service and Work DAOs
Service DAOs organize contributors around delivering real work, such as development, design, or research, using on-chain coordination and payments. Tasks are approved and compensated through DAO processes instead of traditional management. Base allows frequent payouts without friction.
Example: Developer DAO – A global developer collective that coordinates learning, collaboration, and opportunities through DAO governance.
7. Hybrid and Experimental DAOs
Hybrid DAOs combine governance, funding, rewards, and operations into a single structure tailored to niche use cases. These models often evolve quickly as communities experiment with new coordination mechanics. Base provides the flexibility to iterate without high operational costs.
Example: Friends With Benefits DAO – A social and creator DAO that blends membership access, cultural curation, and community-driven governance.

How do DAO Platforms Built on Base Blockchain Work?
DAO platforms built on Base usually run governance logic through smart contracts while users interact through simple app-like flows. Members can join with passkeys, vote without paying gas, and still rely on Ethereum-level security in the background. Base should quietly handle execution fast and cheaply so governance feels responsive rather than technical.
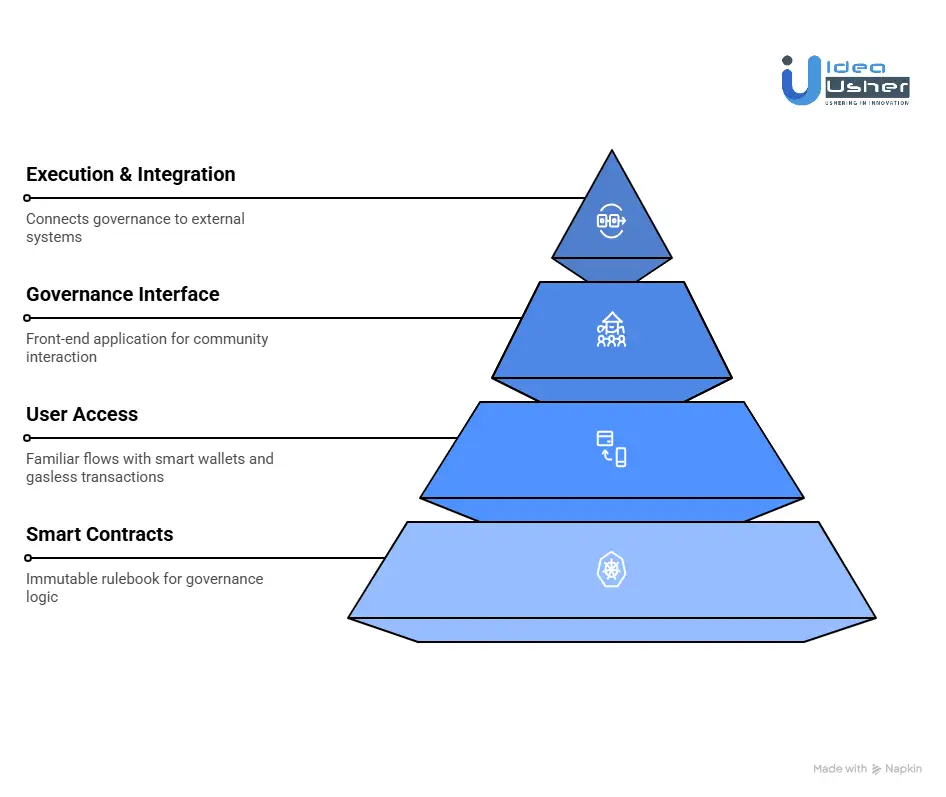
1. The Smart Contract Layer
This is the immutable rulebook deployed on Base’s blockchain. Built with Solidity and frameworks such as OpenZeppelin Governor, these contracts lay the foundation for governance.
- Governance Logic: Who can propose? How voting power is calculated by token holdings or verified identity. What quorum rules apply?
- Treasury Management: How funds are stored. This is typically handled through a Safe wallet. Funds are released only after successful votes.
- Execution: How approved proposals automatically trigger actions such as transferring funds or adjusting protocol parameters.
Base Advantage: Thanks to Base’s ultra-low fees, complex governance models like quadratic voting or conviction voting become practical. These models would be prohibitively expensive on the Ethereum mainnet.
2. The User Access Layer
This layer is where Base fundamentally improves the DAO experience. Instead of constant wallet popups, members interact through familiar flows.
- Smart Wallets: Users create wallets using email or passkeys (e.g., FaceID or TouchID) via SDKs such as Coinbase Smart Wallet or Privy.
- Gasless Transactions: When a user submits a vote, a Paymaster Contract based on ERC 4337 pays the gas fee. The cost is sponsored by the DAO treasury, and the user never sees a gas prompt.
- Identity Verification: Before voting, smart contracts can verify an on-chain Coinbase Verifications attestation to ensure only verified humans participate.
Base Advantage: Crypto complexity fades into the background. Onboarding feels instant, and participation becomes frictionless.
3. The Governance Interface Layer
This is the front-end application where the community actually interacts. It is typically built with React or Next.js and connected deeply to on-chain data.
- Proposal Dashboards: Active and historical proposals are displayed using indexing tools like The Graph.
- Voting Interfaces: Members cast votes with a single click or a FaceID scan.
- Social Integration: Forums and chats are linked to on chain identity to keep governance discussions contextual.
- Analytics Panels: Data-driven DAOs integrate advanced analytics to guide proposal creation and decision-making.
Base Advantage: With two-second block times, vote tallies and UI updates feel near instant. This keeps engagement high and governance responsive.
4. The Execution and Integration Layer
Once a proposal passes, the DAO must act. This layer connects the chain governance to external systems.
- Cross-Chain Actions: Using Base’s secure bridge through the Optimism Portal, DAOs can execute decisions across chains. This includes managing treasuries on the Ethereum mainnet for additional security.
- Real World Data: Oracles like Chainlink feed external data, such as market prices or event outcomes, into the governance process.
- Fiat Operations: Through Base’s native Coinbase integration, DAO treasuries can convert funds to fiat for payroll, grants, or vendor payments using compliant institutional on and off ramps.
Base Advantage: Base uniquely connects on-chain governance with real-world financial operations in a compliant and production-ready way.
How to Build a DAO Platform on Base?
Building a DAO platform on Base starts with designing governance that feels simple while running on secure contracts. Account abstraction and gas sponsorship may then be added to keep participation frictionless. Identity-aware voting and treasury controls help the platform scale safely over time.
Our team has built a range of DAO platforms on Base, and this is the framework we use.
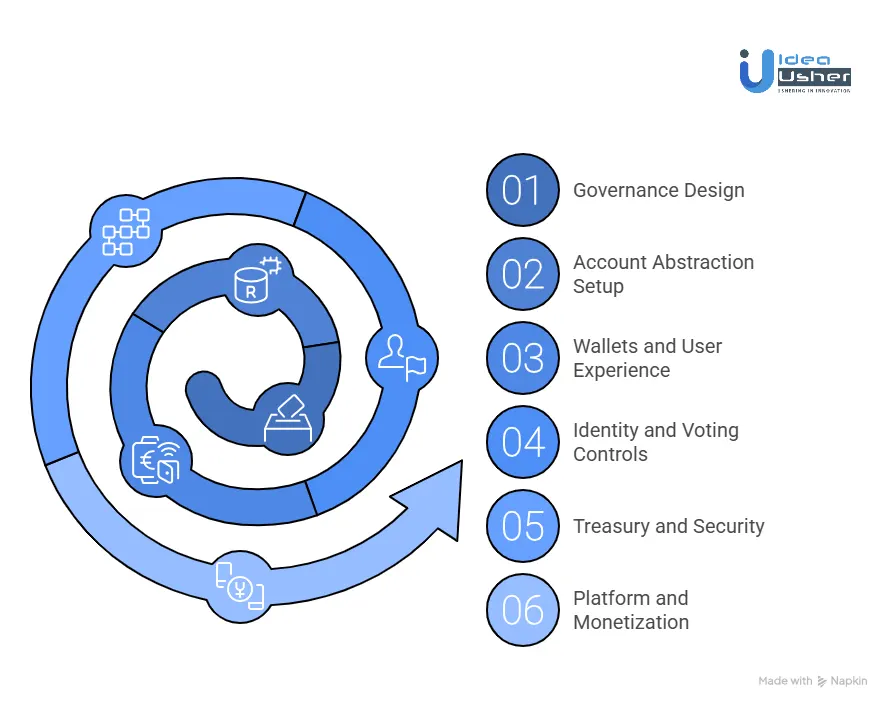
1. Governance Design
We start by defining how governance will work on Base. This includes choosing between identity-based or token-based voting, planning gas sponsorship, and deciding how quickly proposals should move. These choices set the foundation for participation and decision speed.
2. Account Abstraction Setup
We implement ERC-4337 so users can interact with the DAO without managing ETH or private keys. Paymaster logic is added to sponsor gas and enforce platform rules. This enables seamless zero-balance participation on Base.
3. Wallets and User Experience
We integrate smart wallets with passkeys to simplify onboarding. WebAuthn handles secure biometric access while wallets manage ownership in the background. The interface is designed mobile-first so governance feels simple and familiar.
4. Identity and Voting Controls
We embed identity signals directly into voting and access control. Coinbase Verifications and Basenames are used to link governance rights to real users or reputation. Governor contracts are customized to reduce Sybil attacks at the protocol level.
5. Treasury and Security
We design treasuries with operations on Base and long-term custody on Ethereum. This keeps execution costs low while maintaining strong security guarantees. Proposal execution pipelines are built to move value safely across chains.
6. Platform and Monetization
We complete the platform with DAO creation flows, monetization models, and admin dashboards. Subscription plans and fees support long-term sustainability. Management tools give platform owners visibility and control over DAO activity.
How Do We Design Governance for Base’s Fast Block Times?
Base’s 2-second block time is not just a technical detail. It fundamentally changes how DAO governance should work. When governance runs on the Ethereum mainnet, decision-making can take days or weeks. On Base, governance can move at the pace of modern teams within hours or even minutes.
We design governance systems that leverage this speed without sacrificing safety or legitimacy.
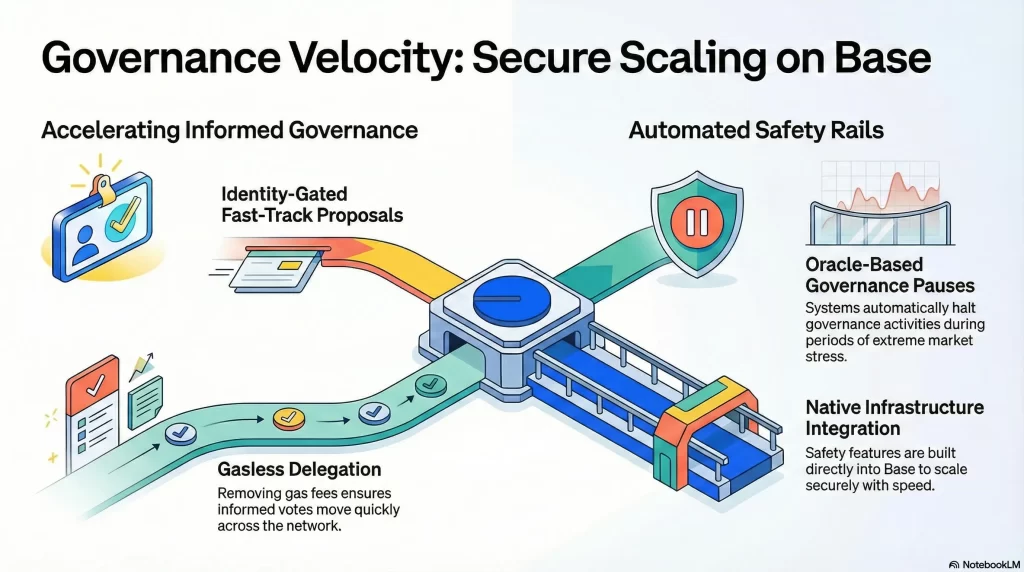
The Core Challenge We Solve
On the Ethereum mainnet, long voting periods act as a safety mechanism. They slow decisions down so participants have time to react. If we blindly reuse these parameters on Base, two problems emerge.
- Dead Time: Participants disengage when proposals sit idle longer than necessary.
- Missed Opportunities: The DAO responds too slowly to time-sensitive events.
Our design goal is simple. We replace time-based safety brakes with logic-driven safeguards that scale with risk.
Our Four Pillar Framework for Fast Governance Design
1. Multi-Tiered Proposal Systems
We start by acknowledging that not every decision carries the same risk. Governance must reflect that reality.
| Proposal Type | Duration | Purpose | Quorum |
| Signal Proposals | 24 to 48 hours | Standard fund allocations under five percent of the treasury | Low quorum |
| Treasury Proposals | 48 to 72 hours | Standard fund allocations under five percent of treasury | Moderate quorum |
| Constitutional Proposals | 5 to 7 days | Core rule, tokenomics, or major treasury changes | High quorum with sixty six percent supermajority |
Why This Works on Base: Base’s fast blocks allow us to define governance windows in hours rather than days. Lower-risk proposals can be approved and executed quickly without slowing the organization.
2. Dynamic Speed Bump Parameters
Instead of fixed delays, we design governance systems that respond dynamically to context.
Quorum Scaling
We implement time-decaying quorum models. A proposal may start with a 40% quorum and gradually decrease after the first 24 hours. This balances urgency with thoughtful participation.
Treasury Threshold Triggers
Any proposal that touches more than a predefined percentage of the treasury automatically escalates quorum and voting duration.
Emergency Circuit Breaker
We include a small trusted multisig, such as three of five technical stewards. This group can pause governance for twenty-four hours if an exploit or coordinated attack is detected.
3. Tuning Technical Parameters for Base
When we implement governance contracts using frameworks such as OpenZeppelin Governor, we tune parameters specifically for Base.
| Governance Parameter | Configuration | Purpose |
| Voting Delay | 1,000 to 2,000 blocks, around thirty to sixty minutes | Allows preparation without slowing governance |
| Voting Period | Two to twelve hours for routine votes and three to five days for constitutional changes | Matches time to decision impact |
| Proposal Threshold | Dynamic percentage of circulating supply | Prevents threshold manipulation as the DAO grows |
| Execution Timelock | Instant for small actions and twelve to twenty four hours for major treasury moves | Adds a final safety buffer |
Why Base Enables This: These logic-driven adjustments are practical on Base because transaction costs are low. We can encode more intelligence into governance without making participation expensive.
4. Using Base Native Features as Safeguards
We do not slow governance down to make it safer. We use Base’s infrastructure to enhance system-level security.
Identity Gated Urgent Proposals
We restrict fast-track proposal creation to wallets with verified Coinbase attestations or soulbound reputation NFTs. This prevents spam and anonymous governance attacks.
Paymaster Enabled Delegation
Gasless delegation makes it easy for token holders to delegate voting power. This helps informed delegate groups emerge and act quickly when decisions matter.
Oracle Triggered Governance Pauses
We integrate price feed oracles such as Chainlink. If the DAO token price drops by more than 25% within 1 hour, the system automatically pauses new proposals for 4 hours. This protects governance during periods of market stress

.
Preventing Governance Spam on DAO Platforms Built on Base
Base provides a fast, low-cost environment for DAO governance. This speed is powerful, but it also reduces the friction that normally discourages governance spam and proposal abuse. Bad actors can flood DAOs with low-quality proposals, overwhelm voters, or attempt to exploit voting mechanics for personal gain.
Designing a DAO platform on Base requires intentional and intelligent friction. The goal is to block spam without slowing down legitimate governance participation.
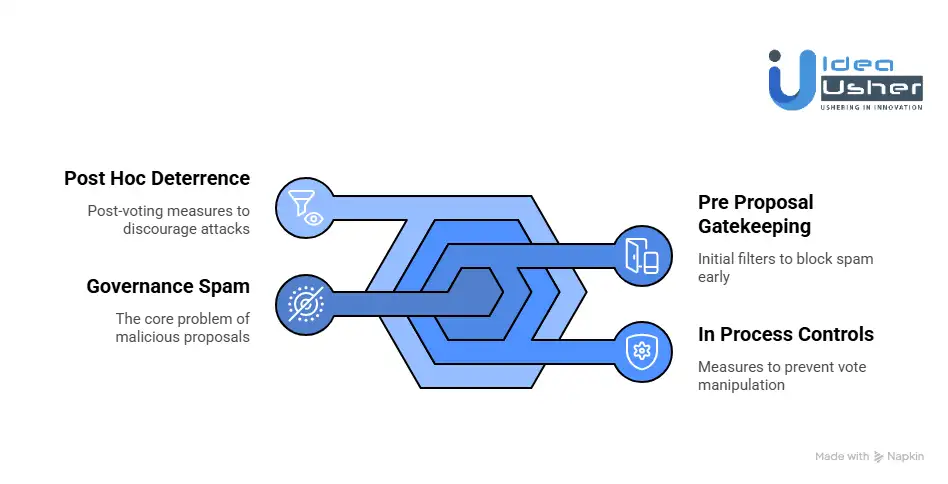
Layer 1: Pre Proposal Gatekeeping
This is the most critical defense layer because stopping spam early is far cheaper than reacting later.
Identity Bonded Proposal Submissions
Mechanism
Require proposers to stake or bond a fixed amount of the DAO governance token to submit a proposal. This bond is slashed if the proposal fails to meet a minimum participation threshold, such as a voter turnout of less than 5%.
Base Enhancement
Use Coinbase-verified attestations to reduce bond requirements for verified human participants. Anonymous wallets are required to post higher bonds. This makes automated spam expensive while still allowing real contributors to remain accessible.
Reputation and Soulbound Tokens
Mechanism: Introduce an on-chain reputation system using non-transferable Soulbound Tokens. Members earn reputation SBTs for actions such as successful proposals, consistent voting, or community moderation. Only wallets holding a Proposer SBT above a defined tier can submit proposals.
Base Advantage: Minting and validating SBTs is gas-efficient on Base. This makes dynamic reputation enforcement economically viable even for active DAOs.
Off-Chain Proposal Filters and Curation
Mechanism: Require proposals to pass an off-chain temperature check before being eligible for on-chain submission. This can be done through Snapshot signaling or token-gated governance forums.
Tooling: Integrate tools like Collab.Land to ensure only verified token or NFT holders can participate in early discussion and curation.
Consider a grant-focused DAO like the Base Ecosystem Fund. Before any on-chain funding vote, proposals must receive fifty positive votes from unique fund token holders in a token-gated forum. Proposals that fail never reach the blockchain, keeping governance queues clean.
Layer 2: In Process Controls
Once a proposal is live, the system must prevent vote manipulation and economic attacks.
Quadratic Voting or Conviction Voting
Mechanism: Quadratic voting increases voting power at a nonlinear cost, reducing the dominance of large token holders. Conviction voting requires voters to lock tokens over time, making spam voting illiquid and expensive.
Base Reality: These models are traditionally gas-intensive. Low transaction costs make advanced cryptoeconomic voting models practical for everyday governance.
Proposal Collation and Batching
Mechanism: Adopt EIP 4824-inspired DAO directory standards to batch routine proposals. Operational decisions such as recurring payments or maintenance grants are grouped into a single periodic proposal.
Impact: This can reduce the chain proposal volume by over eighty percent and preserve governance focus for strategic decisions.
For example, a large NFT DAO on Base may bundle moderator payments, infrastructure subscriptions, and marketing expenses into a single Weekly Operations Proposal. This keeps attention on high-impact votes such as protocol upgrades or product launches.
Sybil Resistant Voting with Delegation
Mechanism: Encourage delegated governance where token holders assign voting power to trusted representatives. This reduces the attack surface from thousands of wallets to a manageable number of accountable delegates.
Base Enhancement: Use gasless paymaster transactions to make delegation and voting frictionless for delegates, increasing participation quality.
Layer 3: Post Hoc Deterrence and Analysis
Governance protection does not end after voting concludes.
Transparent Treasury Honeypots and Delay Timers
Implementing time-locked execution for treasury payouts, usually forty-eight to seventy-two hours, creates a clear contestation window where any member can flag suspicious behavior before funds move.
By openly communicating this delay, the DAO makes governance attacks unattractive, as even a successful manipulation cannot yield instant profit.
Governance Analytics and Monitoring Dashboards
Deploying real-time governance monitoring dashboards using tools like Dune Analytics and The Graph allows DAOs to continuously track proposal velocity, wallet clustering, and voting correlation patterns.
By configuring automated alerts for abnormal activity, the system can quickly trigger governance pauses or escalate issues to a security council before coordinated abuse causes damage.
Popular Business Models for DAO Platforms Built on Base
Most DAO platforms on Base usually make money through subscriptions for governance tooling, small fees on treasury actions, and services around token design and management.
Because Base keeps transactions fast and cheap, platforms can often cover gas costs and still run predictable pricing models. If built well, this approach can steadily scale as DAOs grow their activity and assets.
1. Subscription & Licensing Model
Instead of a one-time development fee, you create a white-label DAO platform infrastructure that organizations license monthly or annually. This includes the smart contract suite, admin dashboard, member portal, and ongoing maintenance.
How It Works on Base:
Your platform leverages Base’s native infrastructure to offer turnkey solutions.
- Gas abstraction packages with pre-configured Paymaster contracts
- Verified identity integration using Coinbase’s attestation services
- Custom governance templates optimized for Base’s 2-second block times
- Fiat on and off-ramp integration through Base’s Coinbase pipeline
For example, Syndicate Protocol, operating across chains including Base, charges 2.5 percent of managed treasury assets annually for its DAO infrastructure suite, with minimum fees starting at $2,500 per month for enterprise clients
2. Transaction Fee & Treasury Revenue Sharing Model
Your platform takes a percentage of every transaction processed through the DAO ecosystem. This includes governance votes, treasury distributions, token swaps, and protocol interactions.
How It Works on Base:
You embed fee mechanisms into the following components.
- Governance execution contracts charging 0.1 to 0.5 percent on treasury transactions
- Cross-chain operations using Base’s native bridge infrastructure
- Payment streaming systems for contributor payroll and grants
For example, Aerodrome Finance, Base’s leading ve(3,3) DEX and liquidity hub, generates $150,000 to $400,000 daily in trading fees, with a portion flowing to governance token stakers and the protocol treasury
3. Token Engineering & Economies Design Model
The model focuses on helping DAOs design and run sustainable token economies from day one. You may handle token creation, distribution logic, liquidity setup, and long-term optimization while also managing vesting schedules for teams and contributors. Revenue usually comes from upfront design fees and ongoing management as the DAO ecosystem evolves.
How It Works on Base:
Base’s ecosystem provides several structural advantages.
- Low-cost token deployment and distribution, typically $5 to $20 versus $500 or more on Ethereum
- Built-in liquidity through Base’s DEX ecosystem, including Aerodrome and Uniswap V3
- Direct fiat integration for token sales and distributions
For instance, Friend.tech-style tokens on Base generated more than $2.5M in developer fees in their first month, with token designers capturing 5 to 15 percent of total token supply as service fees.
Top 5 DAO Platforms Built on Base
We did some digging and found a few DAO platforms built on Base that could genuinely stand out. These projects may quietly use governance to shape treasuries products and communities while staying efficient.
1. Toshi (MEOW DAO)

Toshi is a Base-native project that blends meme culture with real on-chain governance. Holders of the TOSHI token participate in the MEOW DAO, where they vote on treasury usage, partnerships, tooling decisions, and overall ecosystem direction. This structure makes Toshi one of the clearest examples of a community-driven DAO operating on Base.
2. Friends With Benefits (FWB DAO)

FWB DAO operates as a social and cultural DAO focused on creatives, builders, and digital communities. Members hold the FWB token, which grants access to governance, events, and proposals that shape collaborations and ecosystem partnerships. Decision-making is driven by token-gated participation and community consensus.
3. PartyDAO

PartyDAO functions as a shared on-chain coordination layer where members can pool assets and collectively launch NFTs or experimental projects. Governance is centered around how pooled funds are used, with participants voting on spending, ownership, and execution. It offers a flexible model for small, purpose-driven DAOs on Base.
4. Based Nouns
Based Nouns is a community-owned NFT DAO inspired by the original Nouns ecosystem. NFT holders collectively govern the treasury and decide how funds are allocated toward community initiatives, experiments, and ecosystem growth. The project uses NFTs as both identity and governance primitives on Base.
5. XDAO (via Base)
XDAO offers a modular framework for building and operating DAOs directly on Base. Communities can issue governance tokens, submit proposals, and run on-chain voting without heavy technical setup. The platform is designed to let groups focus on governance and coordination rather than smart contract complexity.
Conclusion
Base is redefining DAO platforms by turning them into practical business systems rather than experimental governance tools. When you treat a DAO as long-term infrastructure, it can support ownership coordination, treasury logic, and automated decision flows at scale. This makes choosing the right technical and strategic partner important because architecture will shape how safely the system evolves. Many enterprises are moving early on Base because it may offer low-cost execution, strong Ethereum security, and a clear path to growth without friction.
Looking to Develop a DAO Platform on Base?
IdeaUsher can help you design a DAO on Base that feels familiar to users while smart contracts quietly handle governance and treasury logic. You get clean onboarding with passkey account abstraction and gas sponsorship, so participation happens smoothly and securely.
With over 500,000 hours of coding expertise and a team of ex-MAANG developers, we turn Base’s unique tech into your unfair advantage:
- Gasless & Frictionless: We implement Paymaster systems so your members never pay to participate. Onboarding is a 1-click experience.
- Trust & Compliance: Integrate verified on-chain identities to ensure “one human, one vote” without managing private data.
- Enterprise-Ready UX: Move beyond MetaMask. We build with Smart Wallets & Passkeys, making your DAO feel like a native app.
Check out our latest projects to see how we bring high-performance, user-centric platforms to life.
Work with Ex-MAANG developers to build next-gen apps schedule your consultation now
FAQs
A1: Yes, it can work very well for non-crypto businesses. Base enables DAO platforms to behave like familiar software with clean interfaces and role-based access controls. Teams may use identity-driven logins instead of wallets. This makes adoption feel natural rather than technical.
A2: Yes, voting can happen without members holding any crypto. Gasless voting uses paymaster flows so transaction costs are covered in the background. Members can simply sign and participate. This may improve governance turnout significantly.
A3: Security is designed across layers rather than relying on a single chain. Governance logic can run on Base while assets stay secured on the Ethereum mainnet. Cross-chain execution enforces final settlement rules. This approach should balance speed and safety.
A4: Revenue can come from several structured sources. Platform fees may apply to treasury actions or governance workflows. Subscriptions for DAO creation and premium tooling can add recurring income. Managed services may support long-term sustainability.

























