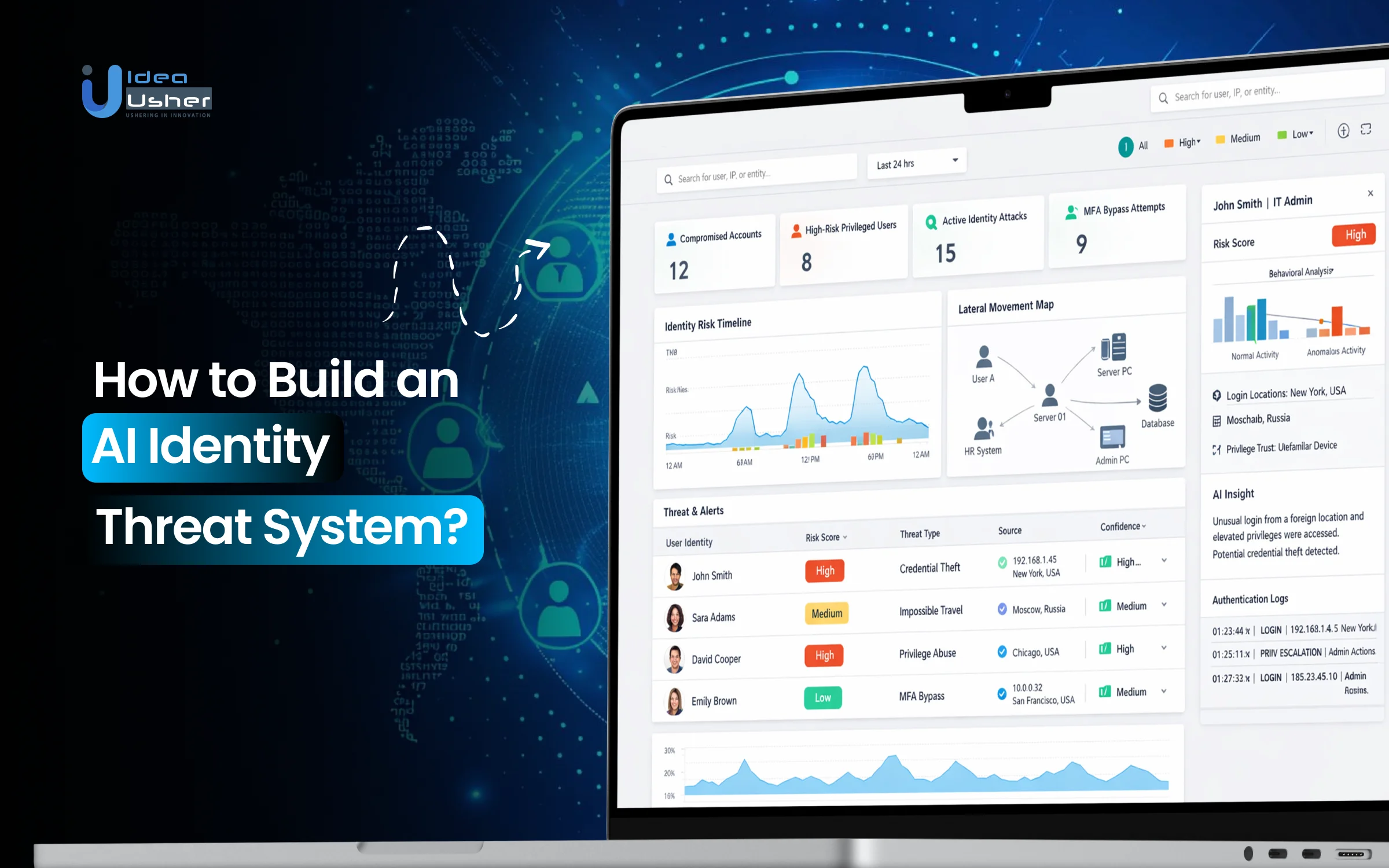
Identity has quietly become the real security perimeter in modern enterprises. Every login and session carries risk, and attackers often move faster than alerts can keep up with. Security teams should not have to guess who is behind suspicious access. As cloud access expands and users work remotely, compromised identities can easily bypass legacy controls.
An AI identity threat system can continuously monitor identity behavior and baseline normal access patterns. It may intelligently score risk in real time and automatically flag anomalies such as impossible travel or privilege misuse. This approach allows teams to act decisively and protect access with clarity rather than noise.
We’ve built numerous AI threat-detection and identity-security solutions over the years, powered by behavioral analytics and identity-graph intelligence. As IdeaUsher has this expertise, we’re writing this blog to discuss the steps to develop an AI identify threat systems. Let’s start!
Key Market Takeaways for AI Identity Threat Systems
According to Fortune Business Insights, the AI-powered cybersecurity market is rapidly expanding, with projections indicating a dramatic increase from USD 26.55 billion in 2024 to over USD 234 billion by 2032. This growth is driven by the increasing complexity of cyber threats and the growing reliance on digital technologies across industries such as finance, healthcare, and telecommunications.
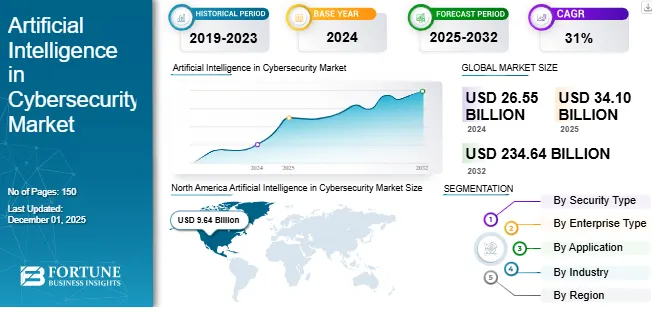
Source: Fortune Business Insights
As organizations face increasingly sophisticated attacks, the need for advanced AI solutions to predict, detect, and respond to threats in real time is more critical than ever.
Identity-based attacks have emerged as a major threat in today’s cyber landscape, pushing the adoption of Identity Threat Detection and Response solutions. Attackers often target user credentials to gain unauthorized access, making identity protection a top priority.
ITDR systems leverage machine learning and behavioral analytics to detect unusual activity across networks, enabling security teams to respond more efficiently and reduce the workload of manually sifting through data. These solutions are particularly valuable in environments where zero-trust models are becoming the norm.
As businesses prioritize identity security, industry leaders such as CrowdStrike and Stellar Cyber are delivering innovative solutions. CrowdStrike’s Falcon Identity Protection uses AI to detect and prevent identity breaches in hybrid environments, offering real-time threat correlation.
Stellar Cyber’s Open XDR platform integrates ITDR natively, providing automated responses based on identity-related telemetry.

What Is an AI Identity Threat System?
An AI identity threat System is a set of technologies and mechanisms designed to detect, analyze, and prevent threats related to the misuse or manipulation of identities, particularly those involving artificial intelligence. These systems focus on identifying when AI is used maliciously to impersonate individuals, manipulate data, or commit fraud.
Key aspects of an AI identity threat system include:
- AI-based Identity Fraud Detection: Detecting instances where AI is used to falsify identities, such as deepfakes, synthetic voices, or generated personal data.
- Behavioral Analysis: Monitoring user behavior patterns to spot inconsistencies or abnormalities that might indicate impersonation or account takeover.
- Identity Authentication: Leveraging AI to enhance the security of identity verification, using methods like biometric recognition (face, voice, fingerprint) or behavioral biometrics.
- Predictive Threat Analysis: Using AI to predict and mitigate identity-related threats before they happen by analyzing patterns of fraudulent activities.
How AI Identity Threat Systems Differ from IAM and MFA?
Traditional Identity and Access Management, IAM, and Multi Factor Authentication, MFA, remain essential, but they were never designed to detect what happens after access is granted. AI Identity Threat Systems fill that gap.
Fundamental Differences
| Feature | Traditional IAM / MFA | AI Identity Threat System |
| Primary Purpose | Access control and initial identity verification | Ongoing risk detection and identity threat monitoring |
| How It Operates | Static, policy-driven, rule-based | Dynamic, adaptive, and behavior-driven |
| Key Question It Answers | Are you allowed in | Does this activity still make sense for this identity |
| Response Model | Grant or deny access | Detect, investigate, and trigger real time response |
| Identity Coverage | Mostly human users | Humans, service accounts, APIs, bots, and AI agents |
Putting It Simply
- IAM is the rulebook and badge system. It defines who should have access.
- MFA is the door’s checkpoint. It adds extra proof before entry.
- An AI Identity Threat System is the security team inside the building. It quietly observes behavior, spots suspicious actions, and steps in when something does not add up.
For example, if an engineer’s account suddenly starts downloading executive financial data in the middle of the night from an unfamiliar location, IAM and MFA may see nothing wrong. An AI Identity Threat System recognizes abnormal behavior, assesses the risk, and can immediately trigger an investigation or additional verification.
Types of AI Identity Threat Detection Systems
AI identity threat detection systems typically focus on behavioral analysis, biometric anomaly detection, and adaptive authentication. They can continuously monitor user actions and quickly identify abnormal identity usage patterns. In practice, they often work quietly in the background and can proactively reduce identity misuse with minimal user disruption.
1. Behavioral Analytics-Based Systems
These systems analyze normal user behavior, such as login time, device usage, and navigation patterns, to detect unusual activity that may signal identity threats. AI flags deviations from established behavior profiles in real time.
Example: BioCatch monitors behavioral biometrics like typing rhythm and mouse movements to detect account takeovers.
2. Biometric Authentication Systems
Biometric systems use AI to authenticate users through unique physical traits such as fingerprints, facial features, or voice patterns. Deep learning improves accuracy and prevents spoofing attempts.
Example: Apple Face ID uses AI-powered facial recognition to securely authenticate users.
3. Machine Learning-Based Anomaly Detection
These systems use machine learning models trained on historical data to identify abnormal identity-related activities. Any action that falls outside learned patterns is flagged as suspicious.
Example: PayPal Fraud Detection uses ML to identify unusual login or transaction behavior.
4. Risk-Based Authentication
Risk-based authentication dynamically adjusts security requirements based on the risk level of a login attempt. AI evaluates contextual factors such as device, location, and behavior.
Example: Google Adaptive Authentication prompts additional verification when a login attempt appears risky.
5. Fraud Detection Systems
AI-driven fraud detection systems focus on identifying identity misuse during financial or transactional activities. They analyze transactions in real time to block fraudulent behavior.
Example: Mastercard Decision Intelligence uses AI to detect identity-related payment fraud.
6. NLP-Based Threat Detection
NLP-based systems analyze emails, messages, and online content to detect phishing, impersonation, or social engineering attacks targeting identities.
Example: Microsoft Defender for Office 365 uses NLP to detect phishing emails and credential-harvesting attempts.
7. Identity Verification and Authentication Systems
These systems use AI to verify identities by analyzing documents, selfies, and biometric data during onboarding or account recovery processes.
Example: Onfido uses AI to verify government-issued IDs and facial biometrics.
How Do AI Identity Threat Detection Systems Work?
AI identity threat detection systems continuously monitor user and machine activity to detect unusual behavior. They learn what “normal” looks like over time and then flag anything out of the ordinary. When a potential threat is detected, the system can automatically respond to contain the risk and protect the environment.
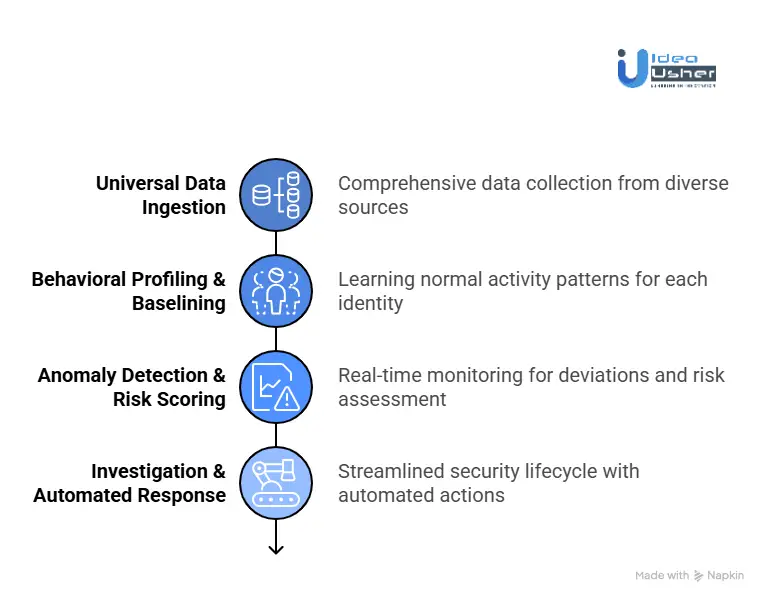
1. Universal Data Ingestion
The intelligence of an AI Identity Threat Detection System begins with data collection. It pulls information from a wide range of sources across your IT environment to provide a comprehensive view of all actions taken.
- Identity & Access Management (IAM) Logs: Who logged in, when, and from where?
- Endpoint Detection & Response (EDR): What processes are running on the user’s device?
- Cloud Infrastructure Logs (AWS, Azure, GCP): What are service accounts or workloads doing?
- Network Traffic Analysis: What data is being transferred and to which destinations?
- Application & Database Logs: What sensitive data is being accessed or queried?
By linking these diverse sources, the system can look beyond isolated alerts and piece together a complete narrative of each user’s behavior.
2. Behavioral Profiling & Baselining
AI and machine learning truly come into play during this phase. Rather than relying on manual definitions of “bad” behavior, the system learns what constitutes normal activity for each identity by observing its actions over time (typically 30–60 days).
For human users, this means the system learns their typical login times, locations, devices used, and patterns of file and application access.
For non-human identities, such as service accounts or integrations like AWS IAM roles—the system tracks typical API calls, data access patterns, and resource usage.
By observing this behavior, the system establishes a unique “pattern of life” for each identity in the network.
3. Anomaly Detection & Risk Scoring
After defining normal behavior, the system monitors activity in real time for deviations. Not every anomaly signals a threat; an employee logging in from a hotel during travel might be harmless, but when multiple risk indicators align, the system can identify serious threats.
For instance, a high-risk event might be flagged when a user’s account:
- Logs in from an unfamiliar country,
- Does so at an unusual hour,
- Immediately begins downloading large volumes of files that are outside their usual scope,
- Uploads the data to a new external cloud storage service.
Each action in this chain receives a risk score, and when combined, these events trigger a high-fidelity alert that accurately distinguishes real threats from simple policy violations.
4. Intelligent Investigation & Automated Response
Modern systems go beyond just raising alerts. They streamline the entire security lifecycle, Detection, Investigation, and Response, often referred to as ITDR.
Automated Investigation: When a high-risk session is detected, the system automatically constructs a timeline of related activities, tying together actions, privilege changes, and data movements. This produces a forensic-ready narrative within seconds, enabling security teams to respond faster.
Contextual Response: Based on the risk score and predefined playbooks, the system can initiate various automated or guided responses, such as:
- Triggering additional authentication checks (e.g., biometric verification),
- Temporarily quarantining a compromised service account,
- Revoking high-risk sessions while keeping the user’s account otherwise operational,
- Creating an incident ticket for the Security Operations Center (SOC), complete with the full event timeline.

How to Build an AI Identity Threat System?
To build an AI identity threat system, it’s important to first unify human and non-human identities into a single architecture that captures access context in real time. Intent-aware models should then be applied to evaluate behavior against the expected identity purpose, rather than just detecting anomalies. We have delivered multiple AI identity threat systems, and this is our approach.
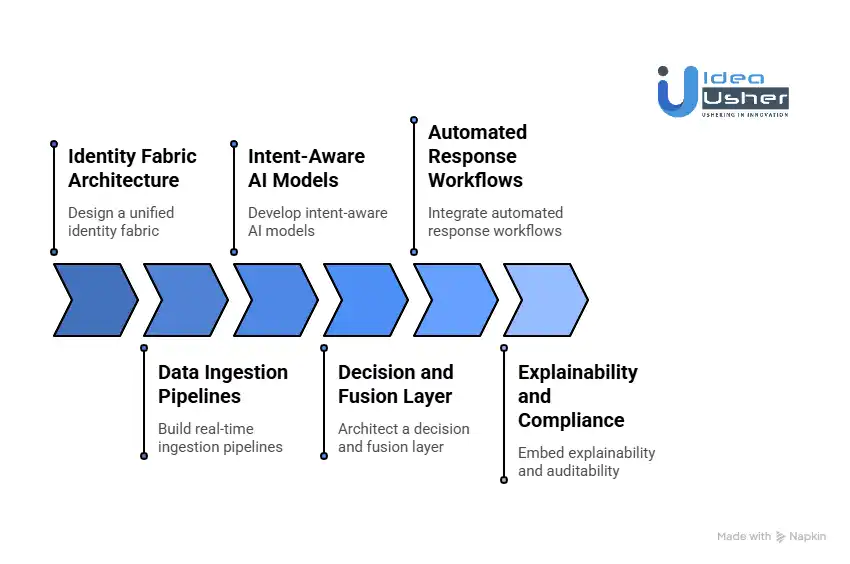
1. Identity Fabric Architecture
We start by designing a unified identity fabric that represents human users, service accounts, APIs, and AI agents within a single identity graph. This allows us to map relationships, privileges, and trust levels across the environment, ensuring every access decision is made with full identity context rather than isolated credentials.
2. Data Ingestion Pipelines
We build real-time ingestion pipelines that continuously collect behavioral telemetry, access logs, device context, visual identity signals, and API activity. By normalizing and correlating these signals, we create a high-fidelity, continuously updated view of identity behavior across cloud, on-prem, and hybrid environments.
3. Intent-Aware AI Models
We develop intent-aware AI models that analyze behavior, context, and access objectives to determine whether an identity’s actions align with legitimate use. This enables us to detect subtle identity abuse, compromised accounts, and insider threats that traditional rule-based or anomaly-only systems often miss.
4. Decision and Fusion Layer
We architect a decision and fusion layer that weighs visual, behavioral, and contextual signals through a confidence-based consensus engine. This layer resolves conflicting inputs and produces a single, risk-informed identity decision that adapts dynamically as sessions evolve.
5. Automated Response Workflows
We integrate automated response workflows that enforce security actions instantly, including step-up authentication, session revocation, privilege restriction, and identity quarantine. This automation reduces attacker dwell time while ensuring responses remain proportional and aligned with business policies.
6. Explainability and Compliance
We embed explainability and auditability into every decision, providing clear, human-readable alerts and detailed audit trails. Our systems are designed to meet regulatory and compliance requirements while safeguarding sensitive logic, ensuring trust, accountability, and operational resilience.
Most Successful Business Models for AI Identity Threat Systems
The best models focus on subscription platforms for scalable, continuous monitoring and on transaction-based verification to adjust costs in response to demand. Embedding identity threat detection into core systems is also effective, reducing friction and ensuring reliability.
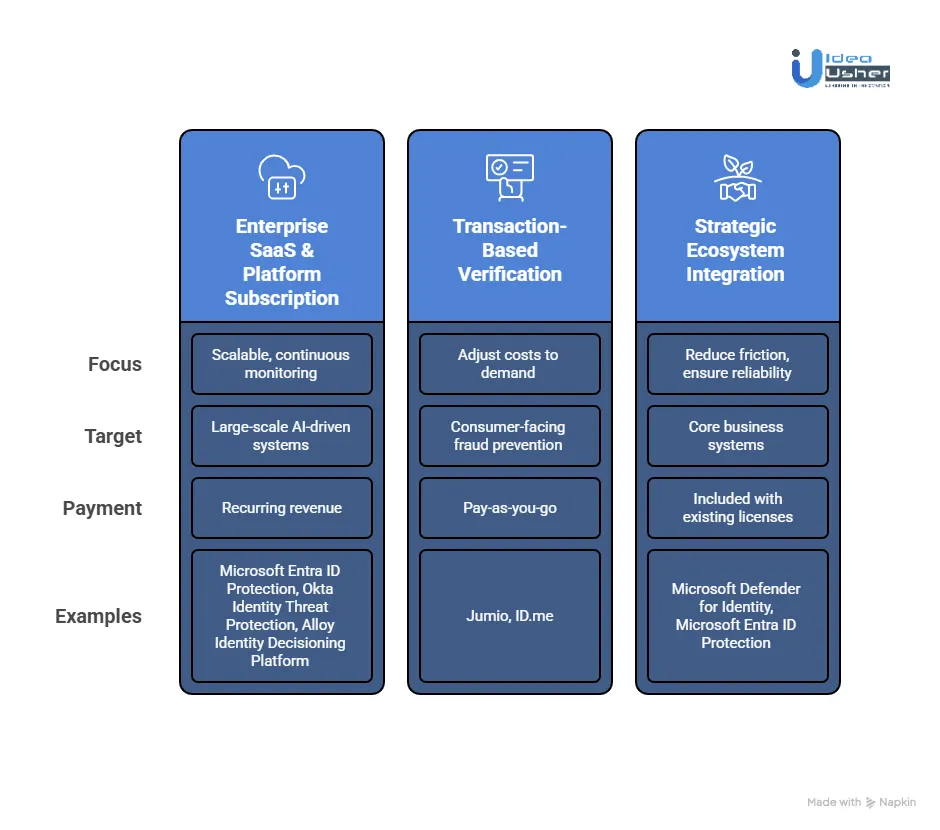
1. Enterprise SaaS & Platform Subscription Model
This business model has become the go-to for large-scale AI-driven identity threat systems, particularly for comprehensive platform-level solutions.
How It Works & Why It’s Successful:
In this model, the provider delivers an end-to-end solution via a cloud service. For vendors, recurring revenue provides predictability, enabling them to fund ongoing research and development.
Examples & Justification:
Microsoft Entra ID Protection and Okta Identity Threat Protection are critical components of their broader security ecosystems, including Microsoft 365 and Okta’s Workforce Identity Cloud. Microsoft’s Intelligent Security segment, which includes these tools, reported over $20 billion in revenue for fiscal year 2023.
Alloy Identity Decisioning Platform is another example operating on a SaaS model, where costs are tied to the volume of identity decisions (e.g., loan or account applications). By transforming compliance-driven tasks like KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (Anti-Money Laundering) checks into scalable, efficient operations, Alloy enables fintechs and banks to streamline their processes.
2. Transaction-Based Verification Model
This model thrives in the consumer-facing fraud-prevention space, where identity verification is often billed on a per-transaction basis.
How It Works & Why It’s Successful:
A “pay-as-you-go” model works well for businesses that experience fluctuating application volumes. This model allows companies to avoid high upfront costs and offers a low-risk, flexible solution.
Examples & Justification:
Jumio is a prime example of this model. The company charges per verification transaction for AI-powered document and biometric liveness checks. Jumio’s valuation has exceeded $1 billion, solidifying its position as a leader in identity verification.
ID.me operates on a unique hybrid model. While it’s free for individuals, it charges government agencies and businesses for secure access to its verified identity network. This creates a powerful incentive for institutions to pay for per-verification services, making the model scalable and successful.
3. Strategic Ecosystem Integration Model
This business model positions the AI identity threat system not as a standalone product, but as an integral feature embedded within a broader, essential business system.
How It Works & Why It’s Successful:
The AI threat detection system is embedded as an always-on, default layer within a platform that companies are already committed to using.
Examples & Justification:
Microsoft is the textbook example of this model. AI-driven anomaly detection in tools such as Microsoft Defender for Identity (which monitors on-premises Active Directory) and Microsoft Entra ID Protection (which monitors cloud identities) is included with premium versions of Microsoft 365 and Azure security licenses.
The integration into Microsoft’s existing cloud ecosystem reduces vendor management complexity and delivers cost savings atenterprise scale.
AI Can Help Manage the 53.3 Billion Stolen Identity Crisis
According to reports, more than 53.3 billion unique identity records are now exposed and circulating online, representing a 22% increase in just one year. This staggering amount of stolen data poses a significant security risk to businesses. AI can help by quickly identifying compromised information, analyzing behavioral patterns, and responding in real time, reducing the risk of further exploitation.
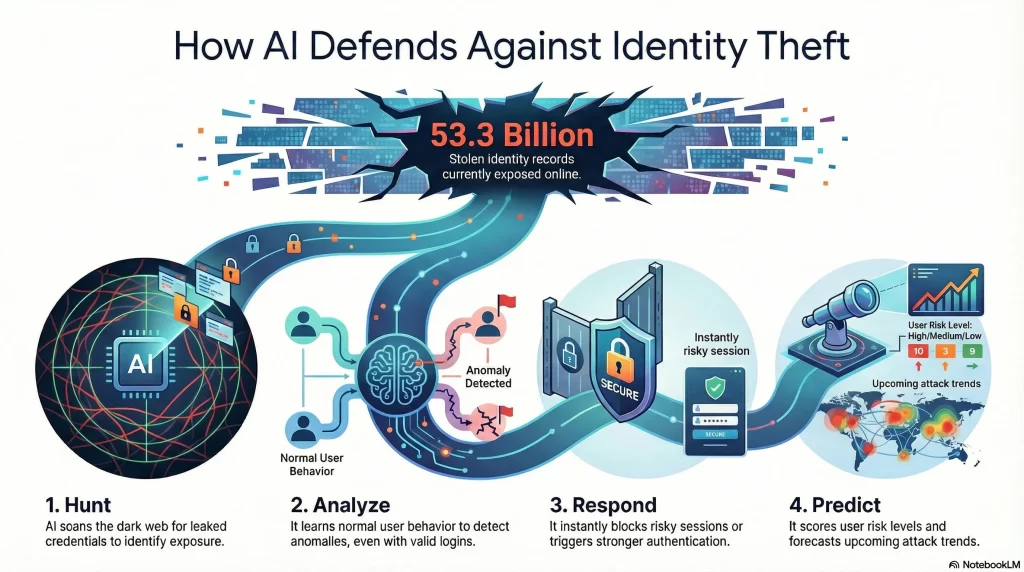
1. AI as a Proactive Hunter
The first step in combating this crisis is knowing exactly what has been stolen. AI helps in the crucial task of scanning the dark web, a task that is far too vast for humans to handle manually.
- Automated Deep & Dark Web Scraping: AI agents continuously monitor underground forums, black-market websites, and encrypted messaging platforms. These agents interpret context, understanding when a dataset contains credentials for a particular company or when there is a new malware variant being sold.
- Fuzzy Matching & Correlation: AI excels at connecting the dots between seemingly unrelated pieces of data. By correlating these data points, AI can create a “profile” of a high-value target, highlighting the full scope of exposure and attack surface.
2. AI as a Behavioral Analyst
Once attackers gain access to credentials, they waste no time exploiting them. AI-powered Identity Threat Detection and Response platforms act as a last line of defense inside your network.
- Establishing Dynamic Baselines: AI constantly learns the typical behavior patterns of each user or service account, login times, access locations, devices used, and the usual sequence of applications accessed.
- Detecting Subtle Anomalies: When a stolen credential is used, attackers’ behavior will differ from the usual. Even if a valid password and MFA token are used, AI can identify suspicious sessions based on behavior anomalies.
- Graph-Based Attack Mapping: Advanced AI leverages graph analytics to map out relationships between users, devices, and resources. It can visualize and alert security teams in real time when attackers move laterally within a network.
3. AI as an Automated Responder
The time between detection and containment is crucial. This is where AI truly shines by acting instantly.
- Risk-Based Adaptive Authentication: When AI detects a high-risk login attempt, for example, from a proxy service used by criminals, it can dynamically trigger extra layers of authentication, such as a biometric check, to ensure that even a stolen password won’t give the attacker access.
- Autonomous Response Playbooks: For confirmed high-risk sessions, AI can take immediate action without waiting for human intervention. It can quarantine a compromised endpoint, revoke session tokens, or freeze sensitive data transfers temporarily, helping to contain the threat.
4. AI as a Predictive Forecaster
AI doesn’t just react to threats. It can predict them.
- Predictive Risk Scoring: By analyzing internal behavior and cross-referencing it with external threat intelligence, such as the 53.3 billion stolen records, AI can assign a risk score to each user.
- Trend Analysis & Threat Forecasting: AI can analyze global attack patterns to predict the next wave of attacks. For example, if it sees an uptick in attacks targeting a particular SaaS platform, AI can warn organizations using that platform, allowing them to tighten their security measures.

How a New Entrant Can Break Into the AI ITDR Market?
Entering the AI Identity Threat Detection and Response or ITDR market is not a technology problem. It is a positioning and execution problem. Incumbents like Microsoft, CrowdStrike, and Okta already dominate distribution, budgets, and buyer mindshare. A new entrant cannot outbuild them broadly.
Winning market penetration requires focus, restraint, and credibility earned through execution. The companies that break through do not try to replace the giants. They become indispensable where the giants are weakest.
The Foundational Mindset
Early-stage ITDR companies fail when they try to sound enterprise-ready too soon. Broad claims dilute credibility. Buyers are not looking for another full-stack platform.
- Avoid this positioning: “We are a complete ITDR platform, but more modern than Microsoft.”
- Adopt this positioning: “We solve this specific identity threat for this specific type of customer.”
Depth beats breadth. Precision beats ambition. A narrow win creates leverage that a wide promise never will.
1. Build Unfair Advantage in a High-Pain Niche
Incumbents ship good-enough features across dozens of domains. A challenger must deliver something materially better in one area that genuinely concerns security leaders.
High-leverage specialization areas include:
- Agentic AI Identity Governance: Autonomous AI agents, including coding copilots, data bots, and workflow automations, are quietly becoming privileged actors inside enterprises.
- Deepfake-Resistant Liveness and Biometrics: Standard liveness checks already lag behind modern synthetic media. A new entrant can win by focusing on near-real-time detection of advanced presentation attacks.
- Non-Human Identity Discovery and Risk Scoring: Most breaches exploit machine identities no one remembers creating. A differentiated engine that actively discovers unknown service accounts, APIs, tokens, and workloads can help.
Credibility Accelerator: Create a visible research function. If analysts and journalists cite your company when discussing that identity threat, half the market education is already done.
2. Remove Commercial and Operational Friction
Security buyers are conservative by necessity. The easier it is to try a product, the faster trust forms.
Deployment Philosophy
The product should be API-first and cloud-native. Integration should take hours, not quarters. Pre-built connectors to Okta, Entra ID, AWS, GCP, CrowdStrike, and common SOAR tools should be table stakes. Position the product as an augmentation layer, not a replacement.
Pricing That Reduces Fear
Avoid opaque pricing tied to data ingestion or abstract license units. Buyers want predictability. Stronger alternatives include cost per protected high-risk identity, flat pricing tiers for small and mid-sized teams, or usage-based models with clear caps.
Offer a tightly scoped pilot with a single, concrete outcome. Examples include identifying the top 100 riskiest service accounts or detecting AI agents acting outside policy.
3. Execute a Surgical Go-To-Market Strategy
Early GTM success comes from precision, not scale.
Ideal Customer Profile: Start with organizations that acutely feel the problem. Fintech and financial services face heavy regulation and machine identity sprawl. SaaS companies treat identity as core infrastructure.
Sales Motion: Founder-led sales is essential early on. The first 25 to 50 customers should directly shape product direction, messaging, and pricing.
Marketing That Signals Authority
Generic thought leadership does not move security buyers. Deep technical analysis does Instead of publishing introductory ITDR content, focus on breach postmortems and identity attack path analysis. If prospects forward your content internally, the positioning is working.
A Phased Market Entry Playbook
| Phase | Goal | Key Activities |
| Phase 1: Lighthouse Customers (Months 1–12) | Prove real-world value | – Secure 5 to 10 customers in your ICP- Focus on close collaboration with customers- Optimize for outcomes, not revenue |
| Phase 2: Niche Ownership (Year 2) | Become the default solution for your problem | – Expand within initial verticals- Formalize partner programs- Engage analysts covering the niche |
| Phase 3: Strategic Expansion (Year 3 and Beyond) | Convert credibility into leverage | – Expand into adjacent identity risks- Introduce a second tightly scoped module- Explore resale, OEM, or acquisition paths |
Top 5 AI Identity Threat Systems in the USA
We conducted extensive research and identified several AI identity threat systems that perform well in real-world environments. Each platform can address identity risks differently and may respond intelligently to modern attack patterns.
1. Okta Identity Threat Protection
Okta uses AI to analyze login behavior and identity signals in real time, detecting anomalies such as suspicious sign-ins, credential abuse, and account takeover attempts. It helps organizations proactively stop identity-based attacks within their identity and access management infrastructure.
2. LexisNexis ThreatMetrix
ThreatMetrix applies machine learning to evaluate digital identity risk by analyzing devices, locations, and user behavior. It is widely used to detect identity fraud, synthetic identities, and credential misuse during online transactions.
3. Sardine AI Risk & Identity Platform
Sardine leverages AI-driven behavioral analytics and real-time monitoring to identify identity fraud across the customer lifecycle. It helps businesses detect impersonation, document fraud, and abnormal user activity before financial or account damage occurs.
4. Entrust AI Identity & Fraud Solution
Entrust uses AI to verify identities by analyzing government IDs, biometrics, and contextual signals. Its systems detect manipulated documents and impersonation attempts, strengthening trust during onboarding and authentication processes.
5. Vectra AI Identity Threat Detection
Vectra AI focuses on detecting identity-centric cyberattacks by correlating user identity behavior with network and cloud activity. Its AI models help security teams identify compromised accounts and stop lateral movement early in an attack.
Conclusion
AI-driven identity threat systems have become a critical need for enterprises operating in today’s AI-focused environments. These systems not only enhance security but also continuously and intelligently protect identities. For platform owners and enterprises, creating such systems is both a necessary defense and a potential revenue stream. By selecting the right architecture, AI models, and integration partner, organizations can build scalable platforms well-positioned to address future challenges.
Looking to Develop an AI Identity Threat System?
IdeaUsher can help you design an AI identity threat system that actively understands behavior rather than merely verifying access. We can architect models that may detect intent in real time and respond intelligently across human and machine identities.
With 500,000+ coding hours, our ex-MAANG/FAANG team builds AI identity threat systems that protect humans, service accounts, and AI agents.
Why Choose Us?
- From Pattern Detection to Protection: We implement sophisticated engines like Zcode and Florence, designed to not only detect anomalies but also understand intent.
- Securing the Machine Workforce: With the rise of Non-Human Identities (NHIs), we are creating systems to effectively manage and monitor them to prevent advanced identity-based attacks.
- Actionable Intelligence, Not Just Alerts: Our solutions span the full ITDR (Identity Threat Detection and Response) lifecycle.
Explore our latest projects to see the cutting-edge security architecture we can build for you.
Work with Ex-MAANG developers to build next-gen apps schedule your consultation now
FAQs
A1: To develop an AI identity threat system, you first need to gather relevant data and identify potential risks associated with user behavior. Then you can design and implement AI models to analyze patterns and detect anomalies in real time. The system must integrate with existing security infrastructure and be continuously updated to adapt to evolving threats.
A2: The key features of an AI identity threat system include real-time anomaly detection, risk scoring, and automated response capabilities. It should also support integration with multiple data sources, provide detailed reporting, and offer a scalable architecture to handle growing data. Additionally, it must be able to learn and adapt to new data and threats over time.
A3: The cost of developing an AI identity threat system can vary based on factors such as system complexity, data volume, and required customization. Typical costs include AI model development, infrastructure setup, ongoing maintenance, and integration with existing systems. It’s essential to account for both the initial development and long-term operational costs.
A4: AI identity threat systems can generate revenue by offering subscription-based services to enterprises, providing value through enhanced security and continuous monitoring. These systems may also monetize through premium features like advanced analytics or compliance reporting. In some cases, revenue can also be generated by licensing the technology to other organizations or offering consulting services for system implementation.