Enterprises today manage vast amounts of sensitive data, from customer information and financial records to healthcare details and internal documents. With rising cyber threats and stricter privacy regulations, even a small vulnerability can have serious consequences. That’s why database tokenization is a key safeguard, protecting sensitive data without disrupting operations or slowing innovation.
Tokenization replaces real data with safe, non-exploitable tokens while storing the original information securely. This keeps sensitive details protected even if a system is breached. Along with encryption, access controls, and compliance frameworks, tokenization enables enterprises to process, analyze, and share data safely across applications and workflows.
In this blog, we’ll cover how database tokenization secures enterprise data and the key steps for effective implementation. With IdeaUsher’s expertise in enterprise solutions, we help you strengthen data protection, optimize operations, and build trust in your digital infrastructure.

What is Database Tokenization?
Database tokenization replaces sensitive data such as credit card numbers, national IDs, or patient data in a database with harmless substitute values called tokens. These tokens keep the original data’s format and usability so business systems continue to work normally, while the real sensitive information is stored in a secure, tightly controlled vault. This greatly reduces breach impact because unauthorized users see only tokens instead of actual data.
In practical terms, database tokenization helps organizations operate more safely and with lower compliance risk by minimizing where sensitive information exists across systems. Its business value is best understood through the key advantages it provides:
- Limits exposure: If attackers access an analytics database, they see only tokens instead of the real data.
- Reduces regulatory scope: PCI DSS, HIPAA, GDPR costs drop because less sensitive data is “in scope.”
- Enables safe data sharing: Teams or vendors can use data sets without seeing real personal information.
- Improves customer trust: “Even if someone breaks in, they can’t see real data.”
Tokenization vs. Encryption vs. Masking – Key Differences
Tokenization replaces data, encryption secures it with access controls, and masking conceals it for non-production use. The table below highlights their differences and effectiveness.
| Method | What It Does | Reversible? | Ideal For | Business Impact |
| Tokenization | Replaces sensitive data with a non-sensitive token stored separately from the real value | Yes, only through the tokenization system | Payments, PII, healthcare data, customer databases | Strong breach protection and reduced compliance scope |
| Encryption | Scrambles data so only someone with the correct key can read it | Yes, with the key | Data in transit, files, backups, whole-database protection | Good security but full risk if keys are stolen or mismanaged |
| Masking | Hides or partially obscures data for non-production use (e.g., 555-22-####) | No | Testing, training, analytics with no need for real values | Prevents accidental exposure but not suitable for security protection |
Simple Analogy
A simple analogy to understand the difference between Tokenization, Encryption & Masking:
- Tokenization = replacing money with chips. The chips work inside the system but are worthless anywhere else.
- Encryption = locking money in a safe. If someone steals and opens the safe, they get the real money.
- Masking = photocopying money with parts blacked out. Useful for training or testing, but not real protection.
Key Benefits of Database Tokenization for Enterprises
Database tokenization gives enterprises a powerful way to reduce data exposure while keeping systems fully operational. It strengthens security, simplifies compliance, and lowers breach-related risks across critical business environments.

1. Stronger Security Posture
Tokenization strengthens security by keeping real sensitive data in one protected vault while the rest of the enterprise operates on non-sensitive tokens. This greatly reduces the number of systems at risk and limits the damage from insider threats or external breaches. Even if attackers access multiple environments, the information exposed holds no value.
2. Reduced Compliance Scope
When sensitive data is removed from most systems, those systems often fall outside the strictest regulatory requirements. This lowers audit workloads, reduces compliance-related costs, and accelerates certifications. Enterprises benefit from simpler governance and faster approvals when expanding products, regions, or partnerships.
3. Lower Breach Impact
Because attackers gain access only to tokens, a breach results in minimal financial and legal exposure. The risk of identity theft, payment fraud, and regulatory penalties is significantly reduced. This containment effect makes security events far less damaging and preserves customer trust and market confidence.
4. Supports Scalable, Cloud-Forward Architecture
Tokenization enables safe adoption of cloud, multi-cloud, and microservices by ensuring that only non-sensitive tokens flow through distributed environments. This allows teams to scale infrastructure, modernize applications, and integrate new services without increasing risk or changing existing workflows.
5. Enables Data Utility Without Exposure
Tokenization keeps data functional while removing sensitive value, giving analysts and data teams safe access to meaningful datasets. They can run models, experiments, and reports without handling raw personal or financial information. This maintains strong privacy protection while supporting data-driven innovation.
6. De-risking Cross-Border Data Flows
Global operations often require sharing data across regions with different privacy laws. Tokenization reduces risk by allowing organizations to move tokens instead of regulated personal data, lowering legal complexity and enabling smoother international collaboration. This is especially useful for distributed teams, vendors, and cloud services.

Why 98% of Enterprises Are Turning to Tokenization to Secure Sensitive Data?
The data tokenization market hit USD 2.42 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 15.20 billion by 2033 at a 20.5% CAGR. This growth shows organizations are quickly adopting tokenization security, moving away from older methods for better data protection.
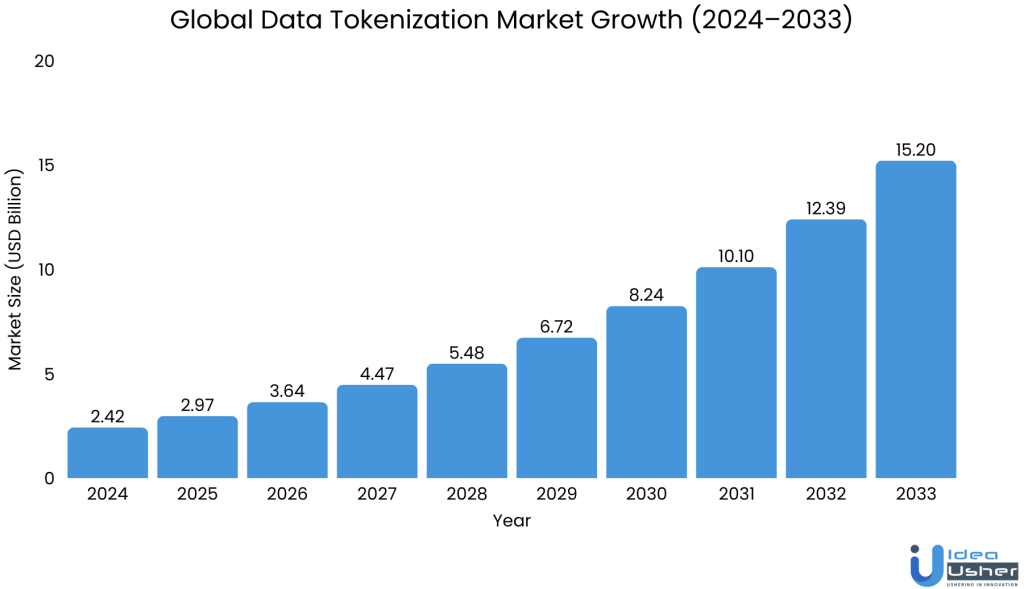
According to the State of Enterprise Tokenization Report, 98% of enterprises say they are ready to adopt modern tokenization because traditional data-security systems no longer provide the protection needed for today’s sensitive information.
A. Tokenization Adoption Driven by Enterprise Security Priorities
Enterprises prioritize tokenization for security, compliance, and operational complexity. A CACEIS × Funds Europe survey shows 52% of asset managers see cyber-security resilience as key when choosing a provider, emphasizing security’s importance for data protection.
Tokenization is increasingly central to digital transformation, with 32% of financial institutions viewing tokenized systems and distributed ledgers as key to their strategies, emphasizing its role as a vital technological shift, not just a security upgrade.
B. Enterprises Accelerate Tokenization to Strengthen Data Security
Tokenization is now a major investment for businesses. Reports 40% of companies spend over USD 1 million annually on tokenization, underscoring the importance of data protection and compliance in enterprise plans.
Industry research indicates operational efficiency and data usability as main incentives. State Street’s Digital Asset Survey shows 52% of institutions see tokenization increasing transparency, and 39% expect improved data efficiency, highlighting tokenization’s benefits: security and streamlined workflows.
These trends show enterprises increasingly adopt tokenization for securing data, enabling safer analytics, better compliance, and resilient infrastructure. As it becomes the standard driven by adoption and performance benefits, tokenization shifts from innovation to necessity. Early movers will be better prepared for a safer, future-ready data environment.
Types of Sensitive Enterprise Data Commonly Tokenized
Sensitive enterprise data spans multiple business functions, and tokenization helps protect the information that poses the highest risk if exposed. Below is an overview of the key data types organizations commonly secure using tokens.
1. Financial Data
Financial information is sensitive and attractive to attackers. Tokenization prevents fraud, secures transactions, and simplifies compliance in finance by allowing operations without exposing real account data.
- Bank account numbers: Prevents fraudulent withdrawals or account takeovers by ensuring operational and analytics systems never store actual account details.
- Credit card details: A core requirement for PCI DSS compliance and reduces the blast radius of a breach in payment systems.
- Wire information: Protects large corporate transfers from manipulation or interception by attackers.
- Financial routing numbers: Reduces fraud risk in automated clearing house (ACH) and international payment flows.
- Loan or credit application data: Shields high-value personal financial information to prevent reputational and legal damage in case of exposure.
2. Personally Identifiable Information (PII)
PII is highly sensitive as it can identify individuals. Tokenizing PII reduces exposure in operations, HR workflows, and analytics, while also lessening regulatory pressure under GDPR, CCPA, and other privacy laws by limiting actual data visibility to essential systems.
- Names: Protects the identity of customers and employees in internal systems, especially when sharing data with external partners.
- Addresses: Reduces leakage of personal residence information across logistics, marketing, or CRM platforms.
- Phone numbers: Prevents misuse for spam, fraud, or unauthorized contact attempts.
- Social security numbers / national IDs: Eliminates one of the highest-value targets for identity theft and fraud.
- Dates of birth: Harder to exploit in identity fraud scenarios when tokenized instead of stored in raw form.
- Email addresses: Protects against phishing risk when databases or marketing systems are compromised.
3. Healthcare Data
Healthcare data is highly sensitive and strictly regulated due to its financial, legal, and personal risks. Tokenization allows hospitals, insurers, and health-tech companies to run analytics, research, and patient services without exposing real patient identities or violating HIPAA and related laws.
- Patient records: Allows care coordination and analytics without exposing medical history or identity.
- Insurance details: Prevents fraudulent claims and unauthorized access to coverage information.
- Medical identifiers (MRNs, claim IDs): Secures patient tracking workflows while enabling operational efficiency.
- Lab results or diagnoses (when outsourced): Ensures third-party analytics providers cannot re-identify individuals.
- Appointment histories: Mitigate privacy risks when scheduling systems interface with external vendors.
4. Enterprise Operational Data
Operational data often contains hidden sensitive elements that can expose employees, partners, and proprietary business operations. Tokenization limits internal access, reducing insider threats and preventing sensitive operational details from leaking into analytics environments or third-party systems.
- Employee information (ID, salary, contacts): Protects workforce privacy and reduces internal access risk.
- Vendor or partner details: Safeguards pricing, contract terms, and business relationship data.
- Internal transaction logs: Contains system identifiers and operational metadata that can be exploited if exposed.
- Access credentials or system keys: When tokenized, limit the risk of privilege escalation or unauthorized system entry.
- HR data (performance reviews, onboarding details): Reduces legal exposure and ensures confidentiality in HR operations.
5. Customer Behavioral Data
Behavioral data is often underestimated, but it can reveal patterns, preferences, and identity-linked activity. Tokenizing this data allows businesses to run analytics, personalization engines, and fraud models without storing directly identifiable attributes.
- User IDs: Supports session tracking and analytics without exposing the underlying real identity.
- Device identifiers (IMEI, MAC address, device fingerprint): Helps fraud teams operate safely without collecting raw device data.
- Sensitive analytics attributes: Allows behavioral segmentation without revealing individual preferences or habits.
- Geolocation data: Protects customers from tracking-related risks while still enabling regional analytics.
- Login or usage patterns: Supports product intelligence while preventing attackers from mapping individual user behavior.
How Database Tokenization Secures Sensitive Enterprise Data?
Database tokenization protects high-risk information by replacing it with safe, non-sensitive tokens that preserve usability without exposing the real data. This approach ensures sensitive values remain locked in a secure vault while applications continue to operate normally.
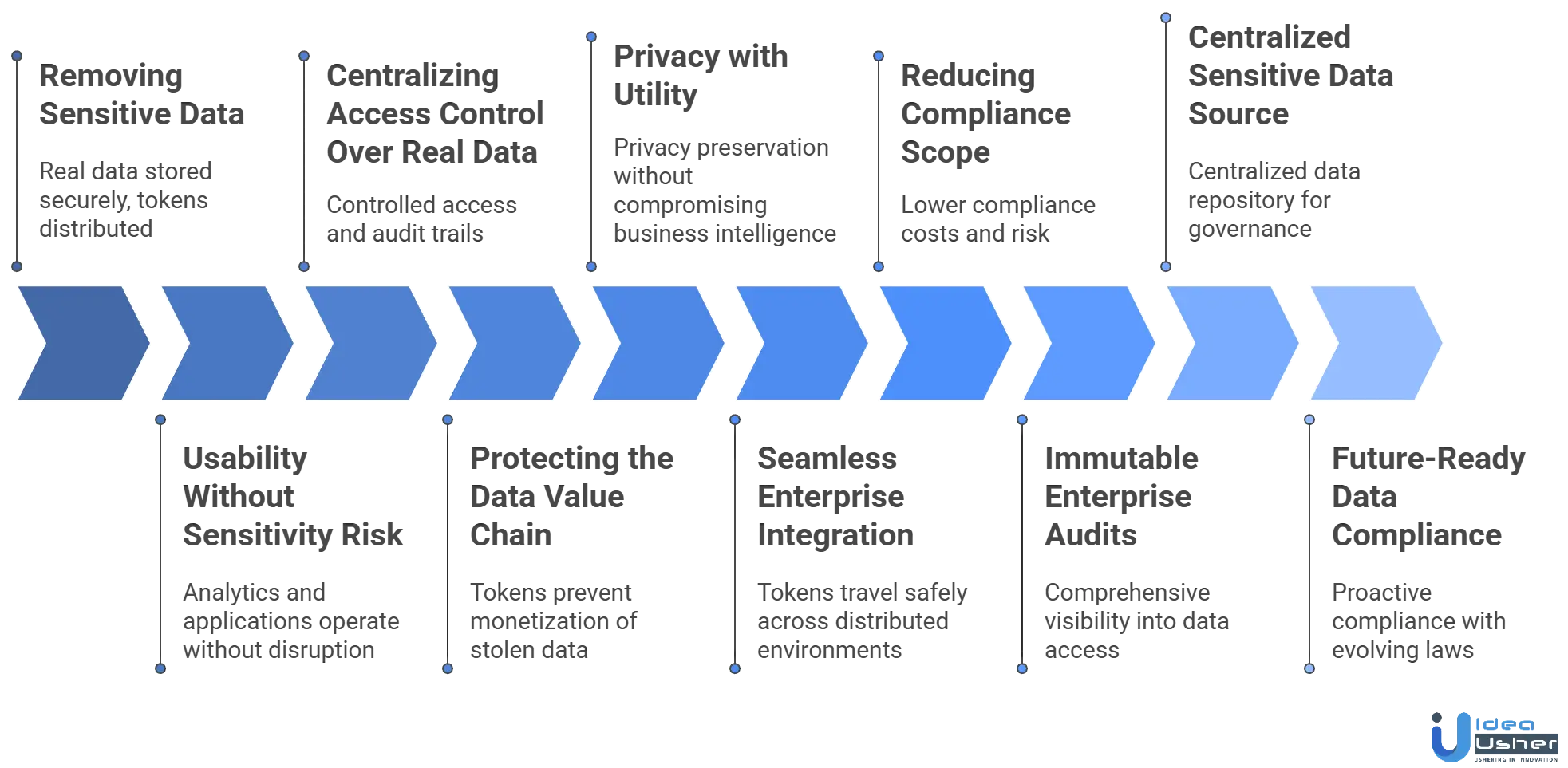
1. Removing Sensitive Data From Everyday Systems
Tokenization minimizes sensitive data exposure by storing originals securely and distributing tokens, reducing breach points across systems like databases, logs, and APIs.
What this achieves:
- Real data is stored only in the tokenization vault, reducing exposure across the enterprise.
- All other systems operate with tokens, which cannot be reverse-engineered or exploited.
- Even if multiple systems are breached, no sensitive information is revealed.
This approach sharply reduces the attack surface instead of trying to protect dozens of systems individually.
2. Separating Data Usability From Data Sensitivity
Most security controls weaken usability, but tokenization preserves data structure, length, and format, allowing systems to operate without disruption. This separation keeps applications functional while protecting the sensitive value behind the token.
What this enables:
- Analytics teams can run queries normally, without accessing raw sensitive data.
- Applications retain validation and business logic, since formats do not change.
- Integrations continue working without major redesign or custom handling.
- Microservices exchange tokens instead of personal data, reducing internal risk.
The business keeps all functional benefits while the security team eliminates sensitive exposure.
3. Centralizing Access Control Over Real Data
Without tokenization, access to sensitive data is scattered across databases and applications. Tokenization centralizes control: only the tokenization platform can reveal real values, turning every detokenization request into a tightly governed event.
Key security benefits:
- Only authorized users or systems can detokenize data, based on strict access policies.
- Every request is logged, providing full transparency and accountability.
- Role-based and attribute-based controls ensure least-privilege access.
- Contextual checks (location, device, system type, time of day) enhance security further.
This transforms data access from a broad privilege into a controlled, monitored, and auditable process.
4. Breaking the Value Chain of a Data Breach
Breaches are harmful as attackers steal data for use or monetization. Tokenization eliminates this risk by replacing data with meaningless tokens that have no link to the original, so even with unauthorized access, attackers only get useless tokens.
How it reduces breach impact:
- Data warehouses only contain tokens, not real PII or financial data.
- CRMs, billing systems, and reporting tools store tokens, eliminating valuable exposure.
- Partner integrations receive tokens, preventing external leakage risks.
Since attackers cannot turn tokens into money, identity theft, or fraud, tokenization reduces breach severity from catastrophic to containable.
5. Enabling Privacy Without Sacrificing Data Utility
Enterprises often face a tension between protecting privacy and enabling analytics. Tokenization removes that conflict by allowing business units to work with tokens while keeping the original values accessible only when absolutely necessary.
Why this matters:
- Analytics and ML pipelines function normally, without holding raw sensitive data.
- Teams can collaborate and share datasets without privacy risks.
- Only authorized workflows access raw values, reducing unnecessary exposure.
- Sensitive identifiers stay hidden, while insights and patterns remain intact.
Tokenization delivers privacy preservation without compromising business intelligence.
6. Integrating Seamlessly With Modern Enterprise Architecture
Tokenization aligns naturally with cloud-first, API-driven, and microservices-based environments. In modern architectures, data moves rapidly across distributed systems, making traditional perimeter-based security insufficient.
How tokenization fits modern systems:
- Tokens travel safely across distributed environments, even untrusted ones.
- API-based detokenization supports flexible, controlled access across services.
- Less sensitive data touches cloud providers, reducing external risk.
- Zero-trust environments benefit, as microservices exchange only low-risk tokens.
Tokenization strengthens security while supporting architectural modernization and scalability.
7. Reducing Compliance Scope and Legal Exposure
Sensitive data drives regulatory scope. When tokenization removes that data from most systems, compliance workloads drop dramatically. This directly impacts budgets, audit effort, and legal exposure.
Compliance advantages:
- Fewer systems fall under PCI DSS, HIPAA, GDPR, CCPA, SOX, or GLBA requirements.
- Audits are easier and faster, since tokens are not regulated data.
- Operational costs decrease, especially in large enterprises with many applications.
- Legal and regulatory risk drops, since raw data is no longer widely stored.
Tokenization becomes a strategic lever for lowering compliance cost and organizational risk.
8. Delivering Immutable Audit Trails for Enterprise Accountability
All attempts to access sensitive data, whether successful or denied, are recorded. This process ensures comprehensive visibility into the use of sensitive information across the enterprise.
What organizations gain:
- Clear, tamper-resistant logs showing who accessed which data and when.
- Strong evidence for regulatory audits and certifications.
- Transparency during internal investigations or incident responses.
- Higher trust from investors, partners, and clients due to demonstrable accountability.
Such visibility is essential in industries where data handling must be provably secure.
9. Creating a Single Source of Sensitive Truth
Enterprises often suffer from sensitive data sprawl to copies of PII or financial values appearing in logs, backups, caches, exports, and sandbox environments. Tokenization stops this by consolidating real data in one protected repository.
Why this matters:
- Data lifecycle management becomes easier, including updates and deletion requests.
- Ownership and responsibility are clearly defined, improving governance.
- Incidents become easier to contain, with only one system requiring investigation.
- Data quality improves since the authoritative value lives in a single location.
Centralization greatly strengthens governance, risk management, and operational clarity.
10. Preparing the Enterprise for Future Data Regulations
Global data laws are changing quickly. Tokenization naturally helps meet many new compliance requirements, which makes it a smart investment for the future.
Key long-term advantages:
- Natural support for pseudonymization and privacy-by-design principles.
- Simpler data minimization, as fewer systems hold real sensitive data.
- Safer cross-border data flows, since many tokens qualify as non-personal data.
- Stronger retention and deletion controls, aligned with global privacy mandates.
Tokenization positions organizations ahead of regulatory changes rather than reacting to them later.

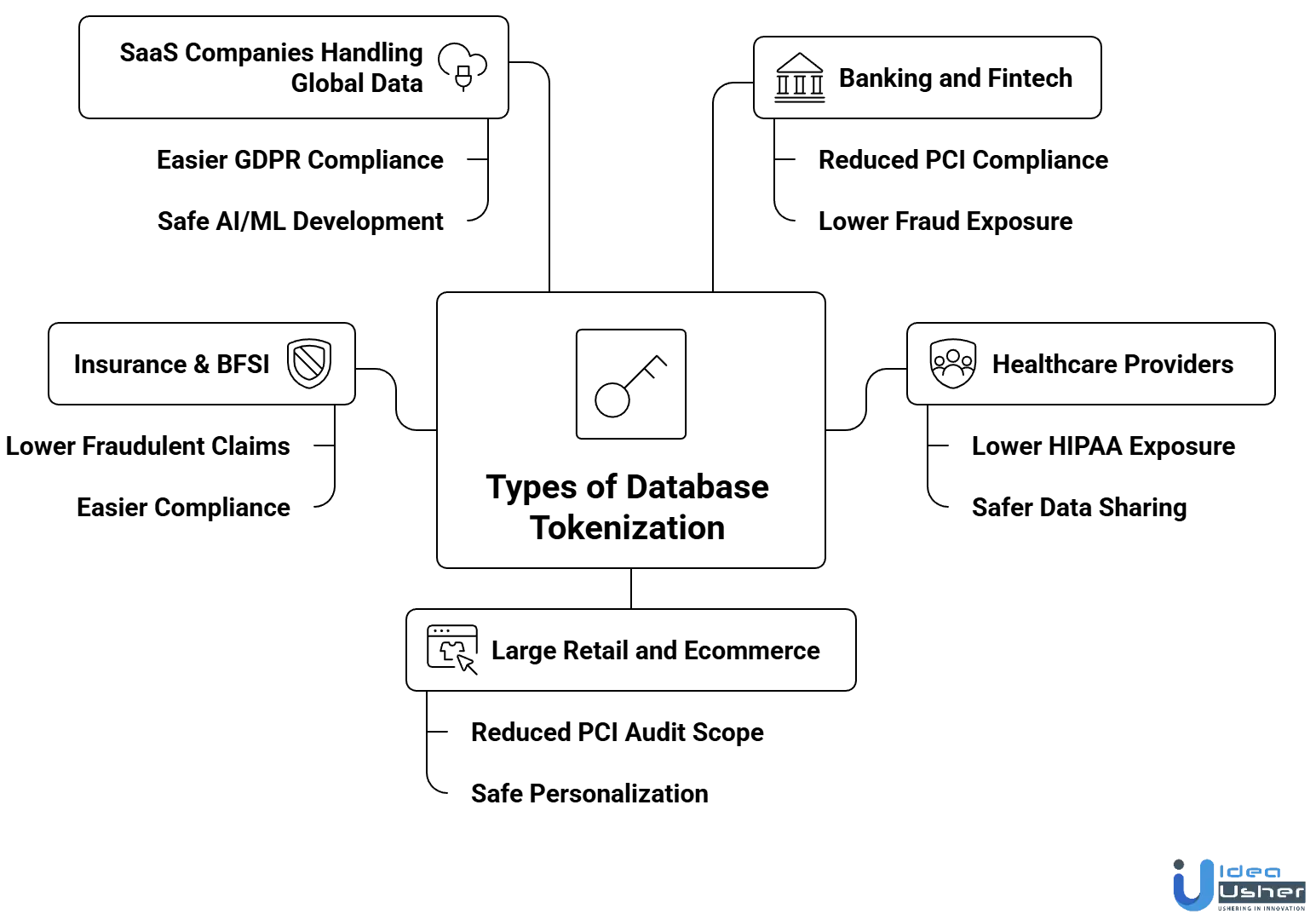
Real-World Use Cases of Database Tokenization
Tokenization delivers measurable ROI by reducing breach risk, lowering compliance costs, and enabling secure data-driven operations. Below are key industry use cases showing the business impact.
1. Banking and Fintech
Banks and fintechs handle extremely sensitive financial data that attracts attackers. They face high regulatory pressure, fraud risk, and compliance costs.
Tokenization value: Tokenization replaces account numbers, card data, and transaction identifiers with secure tokens that can be safely stored and shared across systems.
Business outcome:
- Reduced PCI compliance scope
- Lower fraud exposure
- Safer data sharing with partners and payment processors
- Stronger customer trust and regulatory alignment
Real-world example:
Adyen, collaborating with Visa network tokens, reported authorization uplifts of 2-7% over PAN-based transactions, translating into tens of millions of additional revenue for merchants.
2. Healthcare Providers
Hospitals and clinics must protect patient information while enabling fast access for doctors, billing teams, and insurance partners. Breaches can lead to lawsuits, fines, and patient harm.
Tokenization value: Tokenization replaces PHI, such as patient IDs, medical record numbers, lab results, and insurance identifiers, with tokens that can be used across clinical and billing systems.
Business outcome:
- Lower HIPAA exposure
- Safer data sharing with labs, insurers, and research platforms
- Higher operational efficiency without privacy risk
- Reduced the likelihood of litigation after breaches
Real-world example:
GoodRx, a leading US health-tech company, uses Skyflow’s Healthcare Data Privacy Vault to tokenize PHI and medical data for over 800 million customer records. This enables analytics and integrations while keeping patient data isolated and out of application databases.
3. Large Retail and Ecommerce
Retailers process millions of transactions containing payment data and customer PII. High-volume environments increase the risk of data leakage across internal systems and third-party integrations.
Tokenization value: Tokenization secures customer profiles, payment details, and loyalty program data, ensuring analysts and marketing teams work with safe versions of customer attributes.
Business outcome:
- Reduced PCI audit scope
- Safe personalization and analytics
- Lower risk of large-scale PII exposure
- More trust during online checkout
Real-world example:
A Discover® Global Network case study with a large ecommerce merchant showed that stored payment tokens delivered up to a 50% decrease in fraud compared with PAN transactions and a 2–3% authorization lift, resulting in $175M+ in additional annual volume from improved approvals.
4. Insurance & BFSI
Insurers manage high-value personal and financial data across underwriting, claims, and policy administration systems. Fraud and regulatory scrutiny are constant challenges.
Tokenization value: Tokenization protects sensitive policyholder information such as SSNs, claim histories, health-related data, and bank details used for payouts.
Business outcome:
- Lower risk of fraudulent claims and identity misuse
- Reduced data exposure across claims processing
- Easier compliance with GDPR, NAIC, and state insurance regulations
- Faster onboarding of partners and third-party assessors
Real-world example:
A Fortune 500 US health insurer used Comforte’s tokenization platform to meet NACHA data protection requirements and secure PII (including bank data and SSNs) across hybrid-cloud claims systems. This allowed large-scale analytics and fraud detection in AWS and Google BigQuery without exposing raw personal data.
5. SaaS Companies Handling Global Data
SaaS companies often serve customers in multiple regions with different privacy laws. They must protect user data while enabling analytics, product features, and cross-border operations.
Tokenization value: Tokenization secures user IDs, emails, device identifiers, and usage logs while allowing global teams to collaborate and build features without handling raw data.
Business outcome:
- Easier compliance with GDPR, CCPA, and other international laws
- Safe AI/ML development using tokenized datasets
- Lower breach liability for multi-tenant systems
- Faster enterprise sales due to stronger security posture
Real-world example:
An AWS case study highlights how SaaS platforms use Skyflow’s Data Privacy Vault on AWS to tokenize and localize sensitive customer data, helping them meet GDPR data residency requirements and support global SaaS growth without replicating raw PII across regions or cloud environments.
Why Tokenization is Vital for Future Enterprise Security?
As data volumes grow and cyber threats become more advanced, tokenization offers a proactive way to secure sensitive information at its core. It equips enterprises with a future-ready defense model that minimizes exposure and strengthens long-term resilience.
1. Rising Data Volumes Increase Exposure Risk
Enterprises generate more sensitive data via apps, cloud, IoT, and global operations. As data disperses, exposure risk increases. Tokenization limits where real data exists, reducing the sensitive information at risk even as systems grow complex.
2. Traditional Perimeter Security Is Obsolete
Legacy security relied on firewalls and networks, but modern distributed architectures, remote teams, and cloud workloads make these boundaries obsolete. Tokenization secures data at the data layer, ensuring protection follows the information, which is vital for zero-trust adoption.
3. Global Regulations Are Becoming Stricter
Governments are broadening personal data definitions and increasing penalties. Tokenization supports data minimization, pseudonymization, and access control, helping enterprises stay compliant as laws evolve. Early adoption prepares organizations for future regulations without costly re-engineering.
4. Cloud and AI Require Safe Data Sharing
Cloud modernization, AI workflows, and analytics need large datasets, but sharing raw data risks privacy, compliance, and security. Tokenization enables safe use of data for AI, reporting, and collaboration, fostering innovation without compromising security.
5. Attackers Are Increasingly Targeting Data Value
Modern cyberattacks now target data theft for profit rather than infrastructure disruption. Tokenization neutralizes this by preventing access to valuable information, reducing the financial gain from breaches.
Conclusion
Strengthening enterprise data protection depends on the right mix of security practices, and this is where Database Tokenization proves its value. It removes exposure to sensitive information while preserving data usability across business workflows. By replacing vulnerable data with controlled tokens, organizations reduce risk without slowing daily operations. As enterprises move toward stronger compliance and privacy standards, adopting a tokenization approach helps create a more resilient security framework. It gives teams confidence that sensitive information remains protected at every stage of storage, processing, and access.
Why Choose IdeaUsher for Your Enterprise Database Tokenization Solution?
IdeaUsher helps organizations strengthen their data protection strategies by building robust tokenization systems that secure sensitive customer, financial, and operational information. Our solutions integrate seamlessly into enterprise workflows, ensuring compliance, performance, and long-term data security.
Why Work with Us?
- Security First Approach: We follow industry best practices to design tokenization frameworks that eliminate exposure of raw data.
- Enterprise Integration: From legacy databases to modern cloud environments, our solutions blend smoothly into your existing infrastructure.
- Regulatory Compliance: We help you align with GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and other mandatory data protection requirements.
- Future Ready Architecture: Our platforms are scalable, low-latency, and optimized for high-volume enterprise operations.
Explore our portfolio to learn how we have helped companies modernize their data security systems.
Reach out today for a free consultation and build an enterprise tokenization solution that keeps your data protected at all times.
Work with Ex-MAANG developers to build next-gen apps schedule your consultation now
FAQs
Database tokenization replaces sensitive data with random non-exploitable tokens stored securely in a separate vault. This prevents direct exposure of customer or business information during storage, processing, and transmission across enterprise systems.
Tokenization isolates real data from the operational database. Even if attackers access the system, the tokens have no meaningful value without the secure vault. This reduces risk during breaches and strengthens data protection across applications.
Enterprises use tokenization to secure payment details, personal identifiers, financial records, and healthcare data. Any information that can identify a customer or employee benefits from tokenization to meet compliance and improve internal security measures.
Tokenization and encryption serve different purposes. Tokenization prevents exposure by replacing data entirely, while encryption protects data through mathematically reversible methods. For regulated data like payment or personal information, tokenization often provides stronger breach resistance.

























