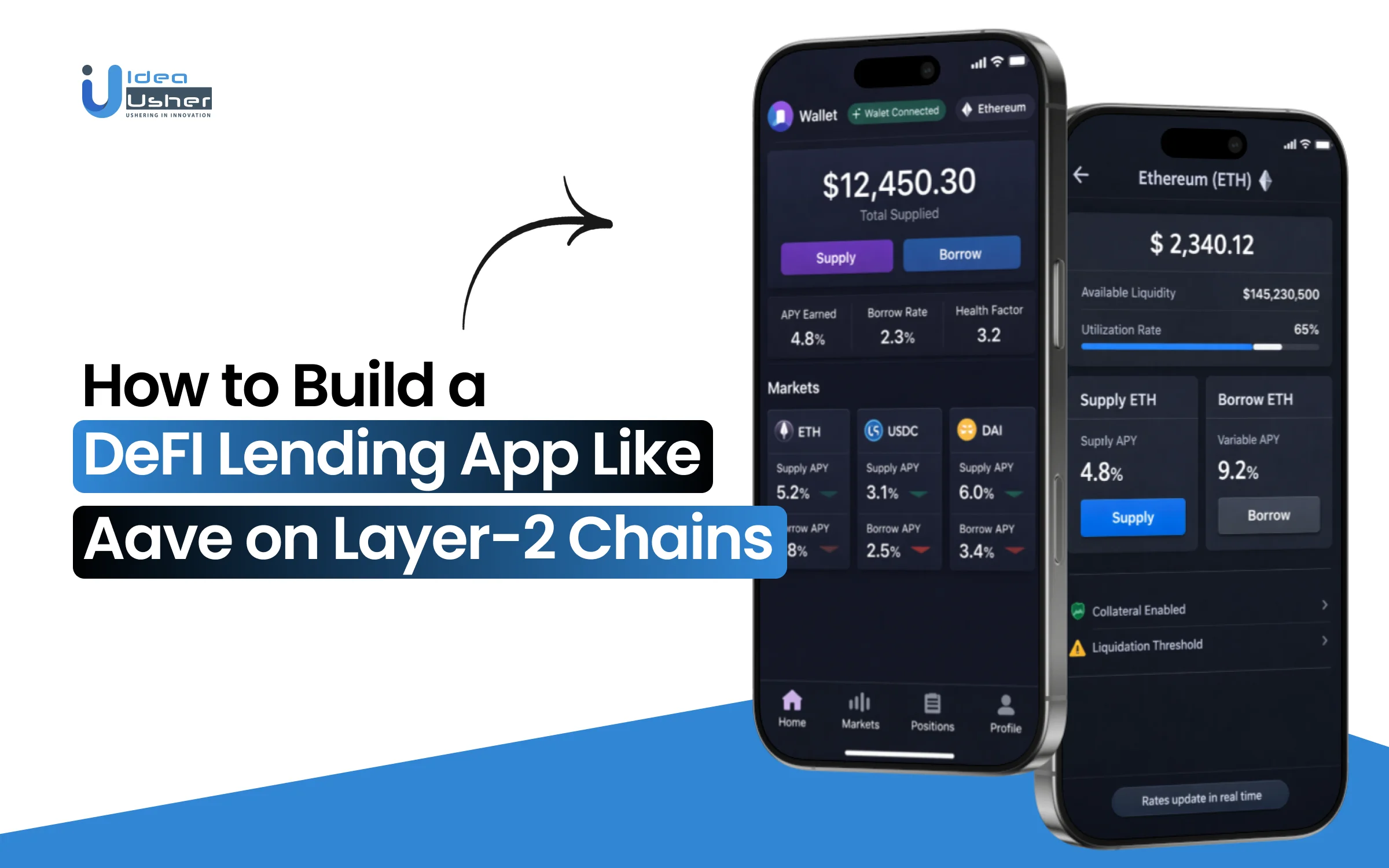
DeFi lending protocols succeed or fail based on how well they manage liquidity, risk, and user trust under real market conditions. Interest rate models, collateral ratios, liquidation logic, and oracle accuracy all need to operate reliably as volumes scale. These fundamentals shape Aave DeFi lending app development, where protocol design matters as much as the blockchain it runs on.
Moving a lending protocol to Layer-2 chains introduces new considerations beyond lower fees. Transaction speed, cross-chain liquidity flows, oracle updates, and user experience all influence how borrowing and lending behave in practice. Protocols inspired by Aave must adapt their architecture to maintain security, capital efficiency, and predictable liquidations while taking advantage of Layer-2 performance improvements.
In this blog, we explain how to build a DeFi lending app like Aave on Layer-2 chains by breaking down core protocol components, architectural decisions, and execution considerations involved in launching a scalable and secure on-chain lending platform.

What is a DeFi Lending App on Layer-2 Chains, Aave?
Aave is an open-source, non-custodial decentralized lending protocol that allows users to supply and borrow crypto assets through permissionless smart contracts. Deposits pool into liquidity markets where lenders earn interest and borrowers access over-collateralized loans. Core functions including interest accrual, collateral checks, health factors, and liquidations, execute autonomously, ensuring transparent, trust-minimized operations.
On Layer-2 chains, Aave leverages rollup infrastructure to reduce costs and improve speed, enhancing scalability while preserving Ethereum-level security. Protocol governance operates through a DAO, enabling token holders to control risk parameters, asset listings, upgrades, and multi-chain expansion.
- Lending (Supplying): Users deposit crypto assets into “liquidity pools”. In exchange, they receive aTokens (e.g., aUSDC), which represent their share in the pool and accrue interest in real-time.
- Borrowing: Users can take out loans by providing collateral that exceeds the value of the loan (over-collateralization).
- Flash Loans: Aave pioneered these instant, collateral-free loans that must be borrowed and repaid within the same blockchain transaction.
A. Business Model — How Aave Operates
Aave operates as a decentralized, non-custodial liquidity marketplace powered entirely by smart contracts.
- Decentralized Liquidity Pools: Users supply crypto assets into shared liquidity pools that other users can borrow from, without intermediaries like banks.
- Smart Contract Automation: All lending, borrowing, interest calculation, and liquidations are executed automatically by on-chain smart contracts.
- Dynamic Interest Rate Mechanism: Interest rates adjust algorithmically based on real-time supply and demand within each asset pool.
- Over-Collateralized Lending: Borrowers must deposit collateral worth more than the loan value to mitigate default risk.
- Flash Loans Innovation: Aave enables uncollateralized flash loans that must be borrowed and repaid within a single blockchain transaction.
- DAO-Based Governance: Protocol parameters (fees, supported assets, risk limits) are governed by the community through AAVE token voting.
B. Revenue Model — How Aave Makes Money
Aave generates revenue through protocol fees tied directly to on-chain lending, borrowing, and liquidation activity.
- Interest Rate Spread: Borrowers pay interest on loans, while depositors earn interest; a portion of this interest is retained by the protocol.
- Flash Loan Fees: A small fee is charged on every flash loan transaction, contributing directly to protocol revenue.
- Liquidation Fees: When under-collateralized positions are liquidated, Aave collects a fee from the liquidation process.
- Stablecoin (GHO) Revenue: Revenue is generated from interest and fees associated with minting and using Aave’s over-collateralized stablecoin.
- Protocol Treasury Accrual: Fees collected are directed to the Aave DAO treasury to fund development, risk management, and ecosystem growth.
- Token-Driven Value Capture: AAVE token mechanisms (staking, safety modules, potential buybacks) capture long-term value from protocol usage.
Why Does Aave Use Layer-2 for DeFi Lending?
Aave uses Layer-2 networks to reduce transaction costs, improve execution speed, and scale lending activity while maintaining Ethereum-level security and decentralization.
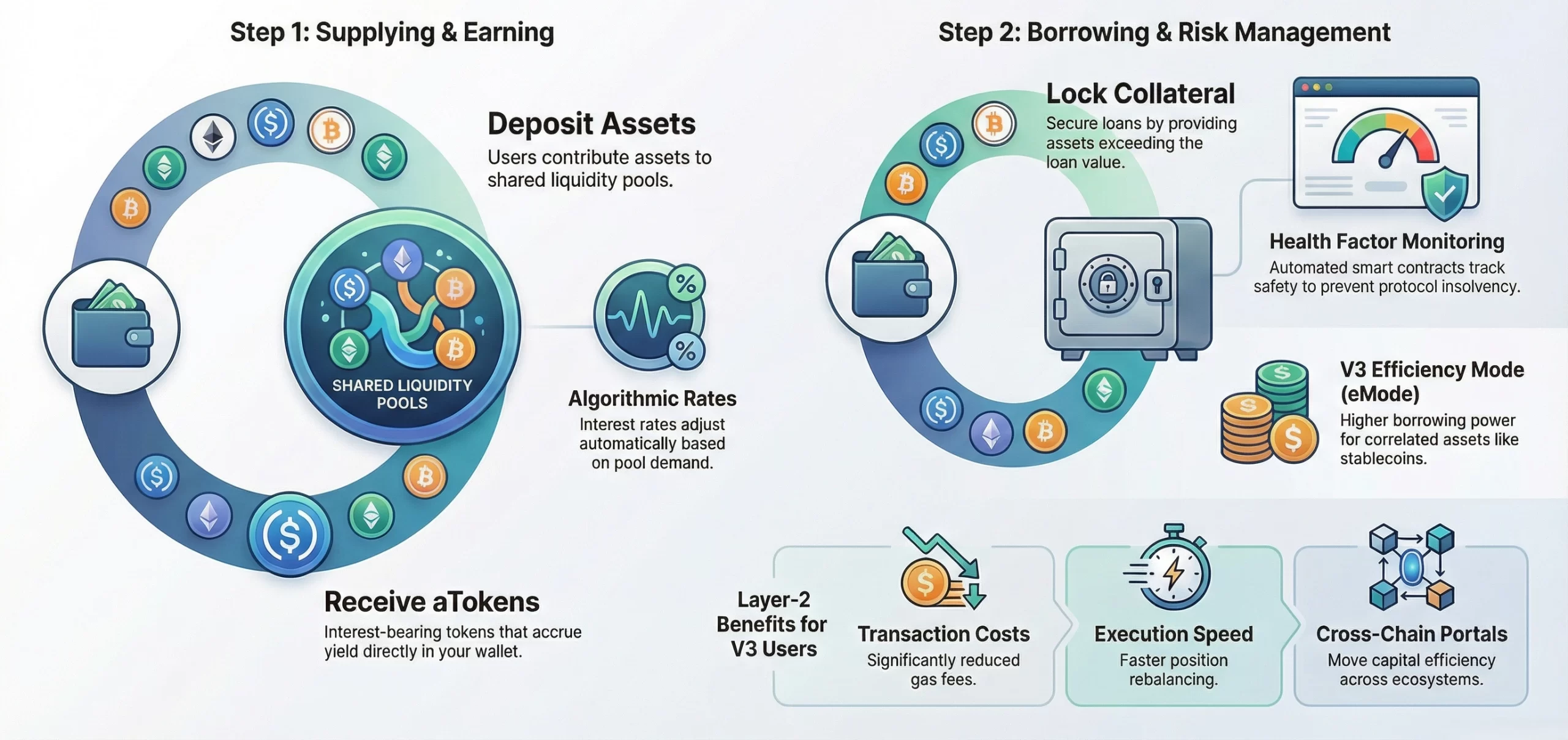
1. Liquidity Pools & aTokens
Aave creates shared liquidity pools where users deposit assets. In return, they receive interest-bearing aTokens. These tokens represent their deposit share and accrue yield in real-time directly within their wallet.
2. Over-Collateralized Borrowing
To borrow, users must lock collateral exceeding the loan’s value. This loan-to-value ratio protects the protocol. Automated smart contracts monitor positions, liquidating collateral if its value falls below a safe threshold.
3. Algorithmic Interest Rates
Interest rates are dynamic, automatically adjusting via smart contracts based on pool utilization. High borrowing demand increases rates to attract more lenders, while low demand lowers them to incentivize borrowing, balancing the pool efficiently.
4. Risk Management & Liquidations
Aave uses a Health Factor metric to gauge each position’s safety. If this factor drops below 1 due to price shifts, liquidators can repay part of the debt for discounted collateral, ensuring protocol solvency.
5. Capital Efficiency with V3 Features
Aave V3 on L2 introduces Efficiency Mode (eMode). It allows higher borrowing power for correlated assets like stablecoins, maximizing capital use. This creates a cheaper, more powerful lending experience exclusive to scalable networks.
6. Cross-Chain Portals
This V3 feature lets users leverage collateral supplied on one chain to borrow on another via secure bridges. It unlocks unified capital efficiency across ecosystems without manually moving assets, a key L2 advantage.
7. Gas Optimization & UX
Minimal L2 transaction fees enable complex operations like rate switching or collateral rebalancing. This allows for sophisticated, frequent position management previously cost-prohibitive on the Ethereum mainnet, democratizing advanced DeFi strategies.
How Layer-2 Scaling Enhances Aave Liquidity and Smart Contracts?
Aave’s shift to Layer-2 chains addresses Ethereum’s high transaction fees and limited throughput. This migration lowers user costs and enables richer, more frequent smart contract interactions, directly increasing capital efficiency and protocol utility.
1. Multi-Chain Liquidity Pools
Deploying on chains like Arbitrum, Base, and Polygon zkEVM attracts significant capital that was previously deterred by high fees. By unifying this fragmented liquidity into a cohesive network, Aave creates deeper, more resilient markets accessible to a global audience.
2. Enables Advanced Protocol Features
Lower fees make feature-heavy smart contracts economically viable. Users can actively manage complex positions involving E-Mode for correlated assets or Isolation Mode for newer tokens without prohibitive costs, unlocking greater capital efficiency.
3. Optimizes Smart Contract Gas Consumption
With users performing more frequent actions, contract-level gas optimization becomes critical. Techniques like caching storage reads and struct memory management reduce per-transaction costs, making the protocol more sustainable on any EVM chain.
4. Fosters Composable Automation Layers
Efficient L2 execution enables third-party automation. Projects like Maxshot AI deploy agents that auto-rebalance yields across Aave’s multi-chain deployments, improving capital allocation and liquidity stickiness without protocol changes.
5. Prepares for Modular Architecture
L2s are the testing ground for Aave’s future “Hub and Spoke” architecture (V4), where a central liquidity hub serves specialized spokes. This design mitigates liquidity fragmentation, a common multi-chain issue, setting the stage for scalable, institutional-grade infrastructure.
How a DeFi Lending App Like Aave Works on Layer-2 Chains?
A DeFi lending app like Aave on Layer-2 chains operates through smart contracts that manage pooled liquidity, interest rates, and collateral while leveraging Layer-2 scaling to deliver faster transactions and lower gas fees.
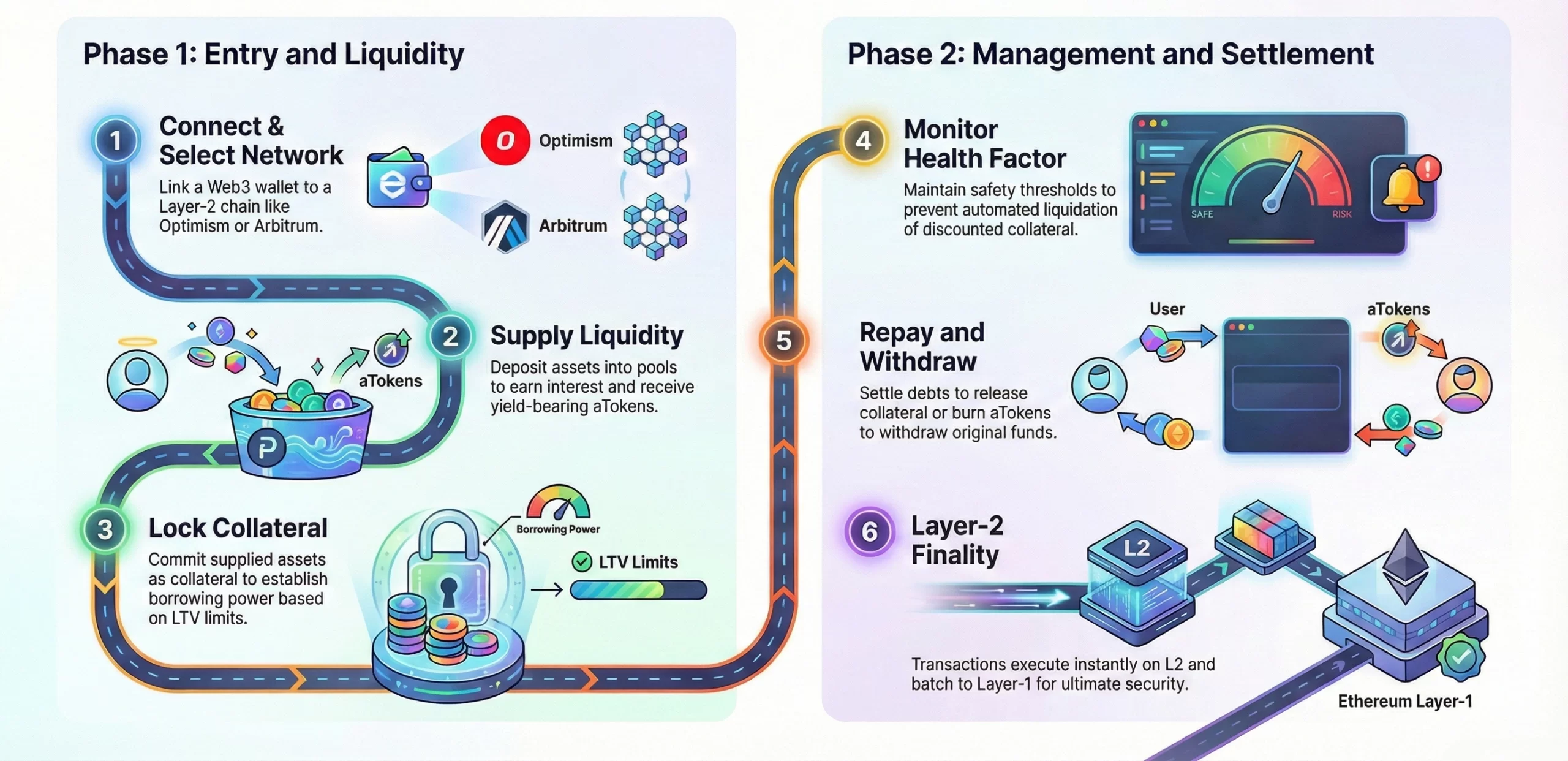
1. Wallet Connection and Layer-2 Selection
Users access Aave and connect their Web3 wallet configured for the chosen Layer-2 network (Optimism, Arbitrum, Polygon, Base). Transactions occur on Layer-2, benefiting from lower fees and faster confirmations. Users need a small amount of native token for gas.
2. Supplying Liquidity to DeFi Pools
Users select an asset to supply (e.g., USDC, ETH) and send tokens to the protocol’s Layer-2 smart contracts. Assets enter a shared liquidity pool available for borrowing. Users receive aTokens representing their pool share that automatically accrue interest.
3. Pool Interest & Utilization Rate Mechanism
Interest rates in each pool are algorithmic and dynamic, adjusting based on utilization (how much liquidity is borrowed). High utilization raises borrowing costs and supplier interest, while low utilization decreases rates to balance supply and demand.
4. Borrowing Against Collateral
Users lock collateral by supplying or adding assets to the protocol to borrow. The protocol calculates a health factor based on the collateral and borrowed value and enforces loan-to-value limits to cap borrowing power. Once users lock their collateral, they can borrow other supported assets up to their allowed limit.
5. Monitoring Health Factor & Liquidations
The system continuously monitors each position’s health factor. If market prices shift or health factor falls below thresholds, the protocol enables liquidation: a liquidator repays part of the debt and seizes discounted collateral. This enforces protocol solvency and prevents bad debt.
6. Repayment & Withdrawal
Borrowers can repay loans anytime, plus accrued interest. Once the debt is repaid and the health factor restored, collateral is released. Suppliers withdraw by burning aTokens, receiving underlying assets plus interest, provided there is unborrowed liquidity.
7. Layer-2 Efficiency & State Finality
All transactions execute on Layer-2 smart contracts. Rollup structure batches transactions, reducing gas costs and speeding confirmations versus Layer-1. Periodically, summarized state data commits to Layer-1 for security and finality.
8. Governance & Protocol Parameter Updates
Aave’s protocol parameters (interest rate curves, risk thresholds, supported assets) are governed by token holders through decentralized governance. Approved proposals are executed by governance smart contracts across all networks, including Layer-2 chains.

Global DeFi Lending Market Overview and Growth
The global Decentralized Finance (DeFi) market is projected to hit USD 616.1 billion by 2033, increasing from USD 21.3 billion in 2023 with a CAGR of 40% from 2024 to 2033. This swift growth is driven by rising demand for permissionless financial services, yield-generating products, and on-chain credit markets.
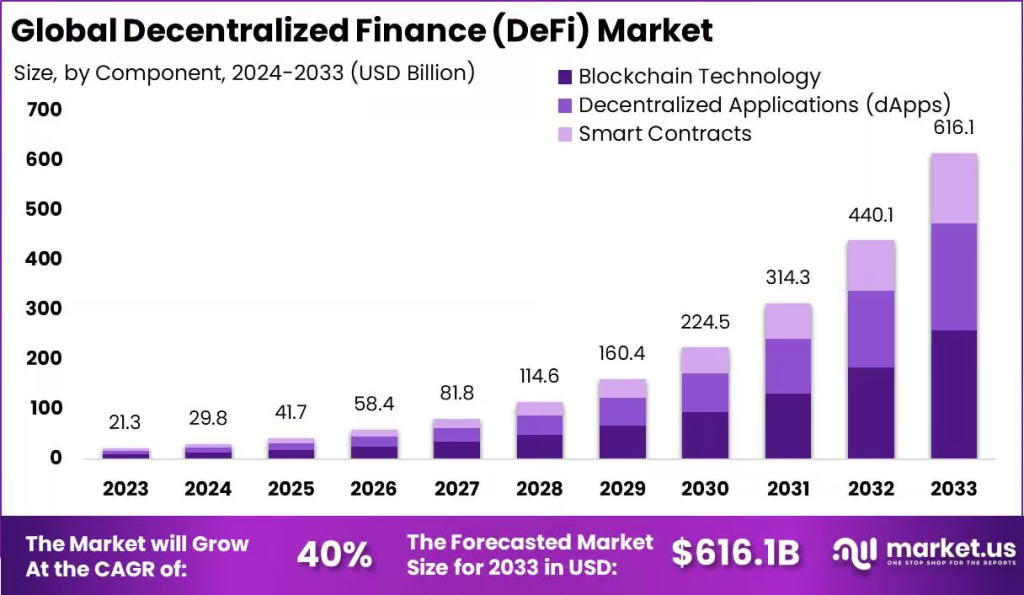
DeFi lending adoption reached 7.8 million users in 2025, a 26% increase year-on-year. Millions actively use DeFi platforms to borrow, lend, and manage capital, attracted by features like over-collateralized loans, real-time interest, and composability with other protocols.
The migration to Layer-2 chains like Arbitrum and Base has reduced average transaction costs by over 90%, directly correlating with a 50% quarter-over-quarter increase in the number of small-ticket loans (under $1,000) in 2024, democratizing access.
Aave dominates DeFi lending with $29.94 billion in total value locked, about 60 percent of the market, and a peak above $50 billion in mid 2025.
The protocol supports around 350,000 daily active users, over 1.2 million unique wallets, and significant institutional activity, including a $769 million USDT deposit in January 2026. Its ecosystem is backed by a $1.94 billion AAVE market cap and $125.8 million in DAO-managed treasury assets.
Aave’s strategic position is strengthened by growing regulatory clarity, highlighted by the U.S. SEC’s late 2025 decision not to pursue enforcement action. Looking ahead, Aave V4 and the expansion of its GHO stablecoin signal a focused roadmap aimed at improving capital efficiency and protocol resilience.
Core Features of a DeFi Lending App like Aave on Layer-2 Chains
Aave defi lending app development on Layer-2 chains focuses on scalable smart contracts, efficient liquidity pools, dynamic interest rates, and secure collateral management to deliver faster transactions, lower costs, and reliable decentralized lending functionality.

1. Algorithmic Interest Rate Models
Sophisticated utilization-based interest rate models dynamically adjust borrowing and lending rates based on real-time pool liquidity. Kink-based rate curves introduce strategic inflection points where rates accelerate sharply, incentivizing liquidity rebalancing and maintaining protocol stability during market volatility.
2. Over-Collateralized Lending
Borrowing requires excess collateralization governed by dynamic loan-to-value ratios calibrated to each asset’s volatility profile. This creates protocol-native safety buffers that protect liquidity providers during extreme market movements while enabling capital-efficient access to liquidity without forced asset liquidation.
3. Real-Time Health Factor Monitoring
Each lending position maintains a continuously updated health factor calculated using Layer-2-native oracle feeds. This real-time solvency metric updates with every block, enabling proactive risk management before liquidation thresholds are breached, a major advantage over slower Layer-1 environments.
4. Liquidation Mechanisms
The protocol employs partial and full liquidation triggers based on collateral risk levels. Layer-2 execution enables smaller, more frequent liquidations at low cost, preserving borrower equity while preventing systemic bad debt accumulation through optimized incentive structures for liquidators.
5. aTokens & Interest Accrual
Liquidity suppliers receive interest-bearing tokens that represent their pool share and compound yield directly in-wallet via rebasing or index-based accrual mechanisms. These tokens maintain a 1:1 peg with underlying assets while remaining fully composable across DeFi applications.
6. Multi-Asset Support & Cross-Chain Assets
Beyond native Layer-2 assets, the protocol supports bridged canonical tokens and wrapped synthetic assets with customized risk parameters. Cross-chain collateralization expands borrowing capacity while preserving asset provenance through secure bridge and verification architectures.
7. Capital Efficiency Features (eMode)
Capital efficiency modes group highly correlated assets such as stablecoins under optimized risk profiles. This unlocks higher borrowing power through enhanced loan-to-value ratios while maintaining strict risk containment within predefined asset categories.
8. Cross-Chain Portals & Composability
Secure cross-chain messaging frameworks enable asset and position mobility across networks. Collateral on one chain can be used to secure debt on another, creating unified liquidity networks and enhancing composability across the multi-chain DeFi ecosystem.
9. Gas Optimization & Transaction Bundling
Layer-2’s low transaction costs enable complex multi-action operations such as supply-borrow-swap loops within single transactions. This granularity unlocks advanced financial strategies that were previously cost-prohibitive on the 1Ethereum mainnet.
10. Oracle Integration & Price Feeds
Layer-2-native oracle networks deliver low-latency, high-frequency price updates essential for accurate collateral valuation. Faster price discovery enables precise liquidation thresholds and real-time risk assessment compared to slower Layer-1 oracle systems.
11. Advanced Risk Management Tools
Beyond standard parameters, advanced controls include reserve factor allocation, interest slope tuning, supply and borrow caps, and emergency pause mechanisms. These layered safeguards enable protocol resilience during extreme market events while ensuring operational continuity.
How to Build a DeFi Lending App Like Aave?
Our approach to Aave defi lending app development on Layer-2 chains combines secure smart contract engineering, protocol-level risk controls, and scalable infrastructure to deliver efficient lending solutions with optimized performance and reduced transaction costs.
1. Consultation & Financial Model Planning
We begin by designing the protocol’s financial foundation. Our developers define supported assets, over-collateralization ratios, interest rate curves, liquidation thresholds, reserve factors, and capital efficiency rules. These assumptions guide every smart contract decision that follows.
2. Select the Optimal Layer-2 Infrastructure
We evaluate Layer-2 chains based on EVM compatibility, liquidity depth, oracle reliability, bridge security, and transaction finality. Our goal is to ensure low-cost execution, efficient liquidations, and long-term scalability without compromising security.
3. Smart Contract Design
Our developers structure the protocol into isolated, upgrade-safe smart contract modules for liquidity pools, interest calculation, collateral management, liquidations, and governance execution. This modular approach improves auditability, security, and future extensibility.
4. Liquidity Pools & Interest Rate Logic
We build pooled lending markets where deposits and borrows are managed algorithmically. Utilization-based and kinked interest rate models dynamically balance supply and demand, protecting liquidity during periods of high volatility.
5. Oracles & Risk Metrics Integration
We integrate decentralized oracle feeds to power price discovery, health factor calculations, and liquidation triggers. On Layer-2, our implementation prioritizes low-latency updates to enable near real-time solvency monitoring and faster risk response.
6. Build the Liquidation & Incentive Engine
Our developers implement partial and full liquidation mechanisms that activate when risk thresholds are breached. We carefully design liquidator incentives to protect protocol solvency while minimizing borrower losses and preventing bad debt accumulation.
7. Develop Interest-Bearing Tokens
We issue interest-bearing tokens that represent supplied assets and accrue yield automatically. Our accounting logic ensures a stable 1:1 backing with underlying assets while maintaining full composability across DeFi protocols.
8. Add Capital Efficiency & Risk Controls
We implement efficiency modes, isolated markets, asset caps, and borrow limits to maximize capital utilization while containing downside risk. These controls allow the protocol to scale safely across volatile and correlated asset classes.
9. Frontend Development & Wallet Integration
We develop a responsive user interface for deposits, borrows, health monitoring, and repayments. Our frontend integrates Layer-2 compatible wallets and indexing services to deliver fast, accurate, and gas-efficient user experiences.
10. Test & Deploy
Before launch, we conduct internal testing, economic simulations, and third-party security audits. We deploy progressively with conservative parameters, then activate decentralized governance to manage upgrades, asset listings, and ongoing risk optimization.

Cost to Build a DeFi Lending App like Aave
The cost of Aave defi lending app development depends on protocol complexity, security requirements, and Layer-2 infrastructure choices, with budgets shaped by smart contract depth, audits, and long-term scalability considerations.
| Development Phase | What Our Developers Deliver | Estimated Cost |
| Consultation | Protocol risk framework, collateral rules, interest rate curves, liquidation thresholds, reserve factors, capital efficiency assumptions | $8,000 – $12,000 |
| Layer-2 Infrastructure Selection | Layer-2 evaluation, network setup, bridge and oracle compatibility assessment, deployment strategy | $5,000 – $10,000 |
| Smart Contract Architecture Design | Modular contract blueprint, upgrade patterns, access control design, security-first architecture | $10,000 – $18,000 |
| Liquidity Pools & Logic Development | Pooled lending contracts, utilization-based and kinked interest models, reserve accounting | $20,000 – $35,000 |
| Oracle Integration & Risk Metrics | Decentralized price feeds, health factor calculation, fallback logic, oracle failure handling | $8,000 – $15,000 |
| Liquidation Engine Development | Partial and full liquidation logic, liquidator incentives, bad debt prevention mechanisms | $12,000 – $22,000 |
| Interest-Bearing Token Logic | Yield-accruing token contracts, accounting mechanisms, composability support across DeFi | $10,000 – $18,000 |
| Capital Efficiency & Risk Controls | Efficiency modes, isolated markets, borrow caps, supply limits, asset-level risk tuning | $8,000 – $15,000 |
| Frontend Development | User dashboard, Layer-2 wallet integration, indexing services, real-time protocol data | $15,000 – $30,000 |
| Testing & Deployment | Protocol simulations, internal QA, audit coordination, phased and secure mainnet launch | $25,000 – $50,000 |
Total Estimated Cost: $64,000 – $124,000+
Note: The Aave lending app development costs reflect a production-ready DeFi lending protocol. Final estimates depend on assets, Layer-2 selection, cross-chain scope, and audit depth.
Consult with IdeaUsher for your Aave Defi lending app development, choose the right Layer-2 strategy, and define a roadmap aligned with your business goals.
Challenges & How Our Developers Solve Them?
Teams face challenges across security, scalability, and risk management during Aave Defi lending app development. Our developers address these through audited smart contracts, optimized Layer-2 architecture, and carefully tuned protocol-level controls.
1. Risk Parameter Design Without L2 History
Challenge: Many Layer-2 networks lack long-term historical data for liquidation behavior, volatility spikes, and oracle latency. Copy-pasting Layer-1 risk parameters often leads to overexposure or overly conservative markets.
How Our Developers Solve It: We simulate stress scenarios using forked environments, synthetic volatility models, and conservative initial caps. Parameters are deployed with adaptive limits and adjusted post-launch using real usage and liquidation data.
2. Oracle Latency on Layer-2 Networks
Challenge: Price feeds on Layer-2 can lag or temporarily desync from Layer-1 during high volatility, leading to delayed liquidations or false triggers.
How Our Developers Solve It: We implement multi-feed validation, heartbeat checks, and fallback pricing logic. Health factor calculations are designed to tolerate short-term oracle delays without triggering unnecessary liquidations.
3. Bad Debt Prevention During Market Crashes
Challenge: Sudden price drops can overwhelm liquidators, especially if liquidation incentives or gas economics are misaligned.
How Our Developers Solve It: We design gas-efficient liquidation paths, partial liquidation logic, and dynamic incentive curves. Layer-2 execution allows faster, smaller liquidations that reduce slippage and protect protocol solvency.
4. Cross-Chain Liquidity Fragmentation
Challenge: Deploying on multiple Layer-2s splits liquidity, reducing capital efficiency and increasing utilization risk in individual pools.
How Our Developers Solve It: We implement conservative borrow caps per chain, cross-chain risk isolation, and optional liquidity routing strategies. Markets are scaled progressively based on real demand, not assumptions.
5. Liquidation Logic Edge Cases
Challenge: Edge cases such as simultaneous oracle updates, partial repayments during liquidation, or extreme utilization can break naive liquidation logic.
How Our Developers Solve It: We explicitly model and test edge cases during development. Liquidation paths are simplified, state transitions are tightly controlled, and invariant checks are enforced at every critical execution point.
How to Choose the Right Layer-2 Chain for a Lending Protocol?
Selecting the optimal Layer-2 chain requires a multidimensional evaluation beyond technical specifications. A lending protocol’s success hinges on liquidity depth, security guarantees, developer ecosystem, and long-term strategic alignment. The decision impacts capital efficiency, operational costs, and scalability potential for years.
1. Security Model & Finality Guarantees
The underlying security architecture, Optimistic Rollups with 7-day fraud-proof windows versus ZK-Rollups with instant cryptographic validity, defines risk exposure. For lending, faster finality reduces oracle manipulation windows and enables quicker liquidations, directly impacting protocol safety and user confidence.
2. Ecosystem Liquidity & Network Effects
A chain’s existing Total Value Locked and composable DeFi primitives (DEXs, yield aggregators, money markets) create immediate synergy. Mature ecosystems like Arbitrum offer deeper integration opportunities and shared liquidity, reducing cold-start challenges and accelerating user adoption through existing financial pipelines.
3. EVM Equivalence & Developer Experience
Full EVM equivalence (Optimism) versus EVM compatibility (zkSync) determines migration complexity and tooling availability. Chains preserving Ethereum’s execution environment enable seamless deployment of existing smart contracts and libraries, significantly reducing development time and audit requirements for complex financial logic.
4. Cross-Chain Interoperability
Evaluate native cross-chain messaging protocols and the security of canonical bridges. A lending protocol’s ability to securely import assets from other chains expands its collateral base, but it depends entirely on the underlying bridge’s battle-tested security and decentralization.
5. Decentralization & Sequencer Resilience
The degree of sequencer centralization impacts censorship resistance and uptime guarantees. Protocols must assess sequencer failure scenarios, forced inclusion mechanisms, and the chain’s roadmap toward decentralized validation to ensure operational continuity during network stress.
6. Native Oracle Support & Data Availability
Examine Layer-2 native Oracle solutions and their update frequency/cost. Price feed latency directly affects liquidation efficiency and position safety. Chains with integrated, low-latency oracles like Chainlink or Pyth provide critical infrastructure advantages for real-time financial applications.
Conclusion
Building a DeFi lending app like Aave on Layer-2 chains is a strategic exercise in scalability, security, and user trust. The process brings together protocol design, smart contract rigor, risk controls, and seamless integrations that respect cost efficiency and performance. Layer-2 infrastructure supports faster transactions while preserving decentralization. When approached thoughtfully, Aave defi lending app development becomes less about copying features and more about adapting proven mechanics to a sustainable architecture that aligns with long-term ecosystem growth. It rewards teams who prioritize clarity, governance discipline, and resilient user experiences globally.
Why Choose IdeaUsher to Build Your Layer-2 DeFi Lending App?
We leverage hands-on experience building blockchain and DeFi solutions for Aave Defi lending app Development on Layer-2 chains. By reducing gas fees, improving throughput, and enabling faster, scalable operations, we help businesses build high-performance lending protocols that deliver seamless user experiences without compromising security or decentralization.
What Sets Us Apart?
- Layer-2 & DeFi Expertise: We design and deploy lending protocols on Layer-2 networks to ensure faster transactions, lower costs, and seamless user experiences.
- End-to-End DeFi Development: From smart contract architecture and liquidity pool design to UI/UX and wallet integrations, we handle everything.
- Security-First Approach: Our DeFi platforms are built with rigorous smart contract audits, risk management mechanisms, and protocol-level safeguards.
- Customizable & Scalable: Whether you want variable interest rates, flash loans, or multi-asset lending, we tailor the platform to your vision.
Explore our portfolio to see how we’ve helped blockchain startups and enterprises launch robust DeFi & DApp solutions.
Connect with us today for a free consultation and start your Layer-2 Aave Defi lending app development that scales efficiently and competitively.
Work with Ex-MAANG developers to build next-gen apps schedule your consultation now
FAQs
A.1. A DeFi lending app needs pooled liquidity, interest rate models, collateralized borrowing, liquidation mechanisms, and governance controls. On Layer-2 chains, additional focus is required on transaction batching, gas optimization, and secure bridge integrations.
A.2. Layer-2 chains reduce transaction fees and improve throughput while maintaining Ethereum security. This makes lending protocols more accessible for users, supports higher transaction volumes, and enables complex interactions without cost friction affecting adoption or retention.
A.3. Interest rates are algorithmically adjusted based on asset utilization within liquidity pools. Higher borrowing demand increases rates, while lower utilization reduces them. This dynamic model balances liquidity availability and incentivizes participation from both lenders and borrowers.
A.4. Oracles provide real-time asset pricing used for collateral valuation and liquidation triggers. Reliable oracle integrations are essential to prevent incorrect liquidations, manipulation attacks, and systemic protocol risks that can impact user funds and platform credibility.