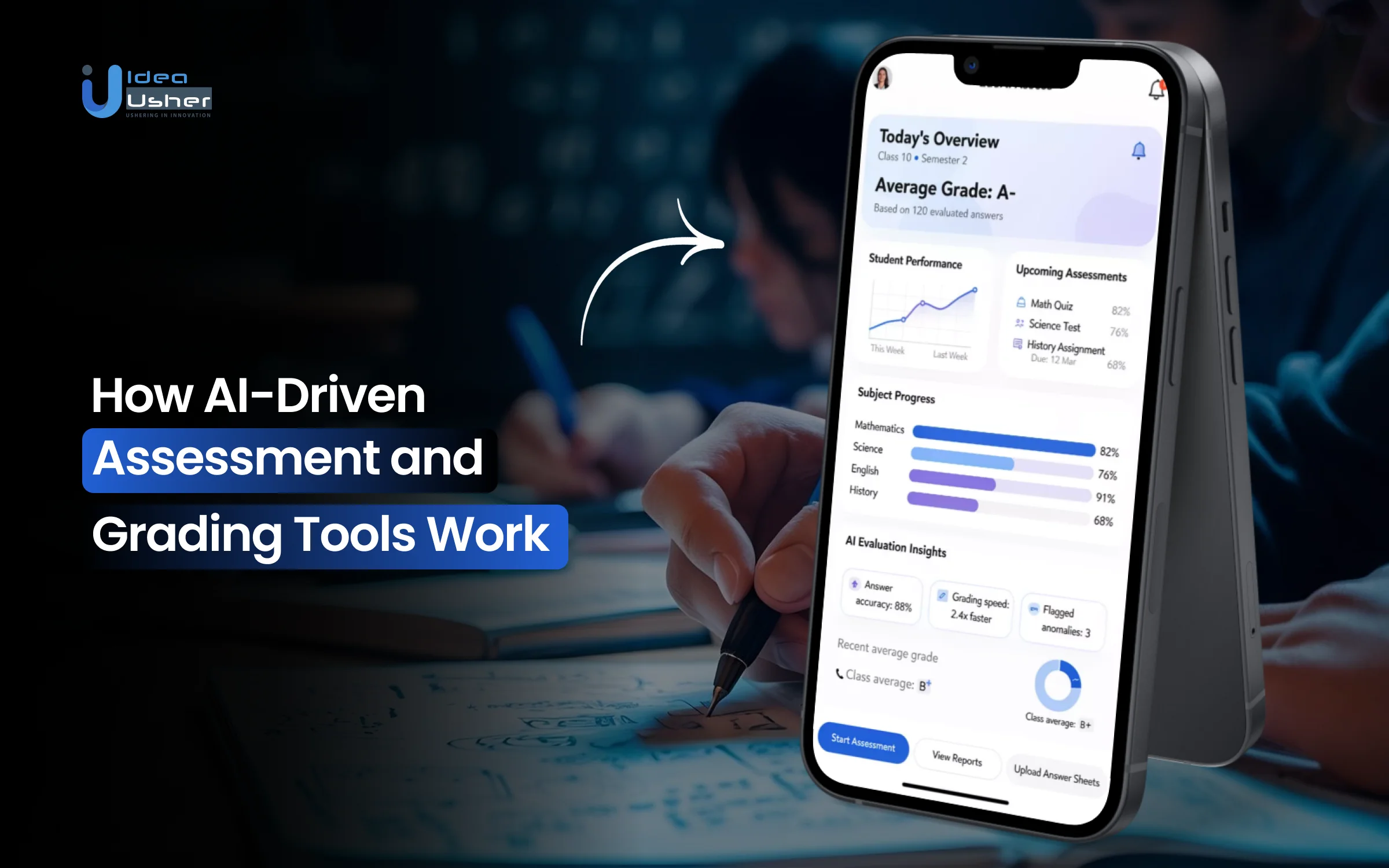
Teachers and institutions spend countless hours reviewing assignments, grading exams, and giving feedback, tasks that often take more time than the teaching itself. As class sizes grow and expectations rise, it becomes harder to maintain fairness, consistency, and quick turnaround times. These challenges are pushing educators to explore an AI-Driven Assessment Platform that can reduce manual workload while improving accuracy and student outcomes.
AI-powered assessment tools transform grading by analyzing student responses, detecting patterns, and providing real-time insights. They evaluate multiple-choice questions, essays, and knowledge gaps, while delivering personalized feedback using natural language processing. By automating routine grading and deepening evaluation, these platforms allow educators to focus on teaching instead of paperwork.
In this guide, we’ll break down how AI-driven assessment and grading tools work, the technology behind them, and why they’re becoming essential in modern education. This blog will help you understand the mechanics and value of building or adopting an AI-based assessment solution.
What Are AI-Driven Assessment and Grading Tools?
AI-driven assessment and grading tools are software platforms that use artificial intelligence to evaluate student work, ranging from quizzes and assignments to essays and projects. They automate scoring, deliver consistent and unbiased feedback, and accelerate turnaround times. These tools interpret responses, analyze patterns, and apply learned criteria to assess performance with high reliability.
They also generate actionable learning analytics, highlighting strengths, gaps, and trends across individuals or groups. By reducing manual workload and enabling data-driven decision-making, AI-driven assessment tools support scalable, efficient, and more personalized education and training environments.
- Enable real-time formative assessment, adjusting questions or feedback dynamically.
- Support multimodal evaluation, including text, audio, code, and problem-solving steps.
- Improve assessment integrity through AI-powered anomaly detection and plagiarism checks.
- Provide institution-level insights, helping organizations optimize curriculum and resource allocation.
Rule-Based, ML, and Generative AI Scoring Methods: Key Differences
Understanding how rule-based, machine learning, and generative AI scoring differ helps educators and enterprises choose the right assessment technology for accuracy, scalability, and efficiency.
| Scoring Type | How It Works | Strengths | Limitations |
| Rule-Based | Uses predefined rules or keywords to match responses. | Transparent, predictable; great for structured tasks. | Not adaptable; weak with open-ended or creative answers. |
| ML Scoring | Learns patterns from labeled training data to predict scores. | Handles varied responses; improves with data; consistent. | Can reflect data biases; limited explainability. |
| Generative AI Scoring | Uses large language models to interpret and evaluate complex responses. | Highly flexible; strong with reasoning; rich feedback. | Harder to ensure consistency; needs guardrails. |
Key Use Cases of AI-Driven Assessment and Grading Tools
AI-driven assessment and grading tools are transforming education by automating routine tasks, providing deeper insights into student learning, and enabling more personalized educational experiences. Here are the primary use cases across different educational contexts:
1. Automated Grading & Feedback
AI automates grading for objective and subjective assessments using NLP, answer-pattern recognition, and instant feedback systems, reducing manual scoring time and helping students learn from mistakes while concepts remain fresh.
Real-world platform: Gradescope uses AI to automate grading for digital and paper-based assignments. It recognizes answer patterns, applies consistent rubrics, and delivers instant feedback, significantly reducing manual scoring time for educators.
2. Formative Assessment & Learning Analytics
AI tracks performance in real-time using learning analytics, behavior patterns, and misconception detection, giving educators actionable insights to target interventions and enable data-driven instructional decisions.
Real-world platform: Canvas Analytics provides real-time insights into student engagement, learning patterns, and performance trends. Its dashboards help educators identify misconceptions early and make informed, data-driven instructional decisions.
4. Personalized Learning Pathways
Adaptive assessment engines adjust question difficulty, deliver tailored practice, and map mastery levels using skill models and adaptive algorithms, ensuring every learner progresses within their optimal challenge zone.
Real-world platform: ALEKS creates individualized learning paths using AI-driven knowledge space theory. Its adaptive engine adjusts difficulty in real time to keep students progressing within their optimal learning zone.
5. Plagiarism Detection & Academic Integrity
AI compares submissions against vast databases to detect plagiarism, paraphrasing, translation patterns, and AI-generated text, helping institutions uphold academic integrity and teach proper citation habits.
Real-world platform: Turnitin compares submissions against extensive databases to detect plagiarism, paraphrasing, and AI-generated content, supporting institutions in maintaining academic integrity and high-quality writing standards.
6. Skill-Based Competency Assessment
AI evaluates practical skills through simulations, video analysis, coding environments, and portfolio scoring, assessing technical abilities, problem-solving processes, and communication skills across various vocational domains.
Real-world platform: CodeSignal uses AI-driven coding assessments to measure technical proficiency and problem-solving skills through realistic simulations. Its scoring engine evaluates logic, efficiency, and code execution accuracy.
7. Predictive Analytics for Student Success
Machine learning predicts at-risk students by analyzing engagement patterns and historical performance, triggering early alerts that help educators deliver timely tutoring, advising, or instructional interventions.
Real-world platform: Civitas Learning applies machine learning to identify at-risk students by analyzing engagement behavior and historical performance, allowing institutions to deliver timely academic interventions.
8. Language Learning & Writing Development
AI supports language learning with speech recognition, fluency analysis, grammar evaluation, and writing feedback, giving students detailed, real-time support for pronunciation, structure, clarity, and style.
Real-world platform: Duolingo’s AI evaluates pronunciation, fluency, grammar, and writing structure, adjusting lesson difficulty dynamically to support personalized language acquisition and continuous improvement.
9. Accessibility & Inclusive Assessment
AI enables inclusive assessments with voice input, simplified text, adaptive interfaces, and real-time descriptions, ensuring fair evaluation for students with diverse disabilities and learning needs.
Real-world platform: BeMyEyes AI uses advanced vision models to support blind and low-vision students during assessments, interpreting visual content in real time and enabling independent navigation of tasks and interfaces.
How 88% Student Adoption Is Creating a High-Growth Market for AI Assessment Tools?
The AI in education market was valued at USD 5.88 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 32.27 billion by 2030, with a CAGR of 31.2% from 2025 to 2030. This growth is driven mainly by high student demand for AI-powered tools that offer personalized, instant feedback, transforming education and assessment.
Generative AI has become a central part of student assessments, with usage jumping dramatically from 53% in 2024 to 88% in 2025, reflecting how quickly students are adopting AI tools to get faster feedback, better guidance, and improved learning outcomes.
A. Student-Led Demand Driving Mainstream Institutional Adoption
AI assessment platforms are increasingly adopted by students independently discovering their benefits for learning, testing, and feedback. This demand is pushing institutions to quickly embed AI tools into curricula to meet student needs.
- AI usage among university students jumped from 66% in 2024 to 92% in 2025, showing near-universal adoption and positioning AI assessment tools as core learning infrastructure in higher education.
- 60% of U.S. K-12 teachers used AI tools during the 2024–2025 school year, reflecting strong educator adoption and growing integration of AI-powered assessment features in daily instruction.
- Introducing Microsoft 365 Copilot led to a 275% increase in student self-directed learning, proving that AI assessment tools support not just evaluation but also independent learning and self-regulation.
- Personalized learning can improve outcomes by up to 30%, and AI assessment platforms enable this at scale by continuously adjusting content, difficulty, and feedback based on individual student performance.
B. Proven Operational Efficiency Creating Institutional Investment
While student demand drove adoption, institutions now accelerate AI assessment platform investments for cost savings, better accuracy, and efficiency—addressing budget issues and improving education. This mix of satisfaction and ROI creates a strong, sustainable market.
- Automating educational content creation can save $60 billion globally, with AI assessment platforms driving major reductions in faculty workload by handling test creation, grading, feedback, and analytics.
- AI-enabled grading cuts errors by 40%, delivering more consistent evaluations and reducing grade disputes and administrative corrections.
- Institutions using AI report a 22% drop in operational costs, supported by assessment platforms that reduce admin hours, eliminate physical tests, streamline proctoring, and automate compliance reporting.
- Automated feedback improves student writing quality by 26%, showing how AI assessment tools enhance learning through real-time, personalized guidance.
The surge in student adoption, combined with measurable improvements in learning outcomes and institutional efficiency, is fueling a booming market for AI assessment tools. Personalized feedback, cost savings, and scalable solutions are making these platforms indispensable in education today.
Key AI Technologies Used in Assessment Tools
AI assessment tools rely on advanced technologies that automate grading, analyze student performance, and deliver personalized feedback at scale. These core AI models and systems power accuracy, efficiency, and adaptability across modern educational platforms.
| AI Technology | What It Does | Why It Matters |
| Natural Language Processing (NLP) | Analyzes and understands written text. | Enables scalable evaluation of essays and open responses; reduces human grading load. |
| Machine Learning (ML) Scoring Models | Predicts scores by learning patterns from graded data. | Delivers consistent, data-driven scoring at scale; strengthens product defensibility. |
| Optical Character Recognition (OCR) | Converts handwritten or scanned responses into digital text. | Unlocks digitization of paper-based assessments; expands TAM. |
| Computer Vision (CV) | Interprets images, diagrams, and visual steps. | Supports assessment of STEM work and practical tasks; valuable for institutions and vocational training. |
| Speech-to-Text AI | Transcribes spoken responses into text. | Enables language learning, accessibility, and oral exams; opens new assessment modalities. |
| Generative AI Evaluation Models (LLMs) | Evaluates complex reasoning, provides feedback, and mimics expert judgment. | Powers advanced, human-like assessment; enables differentiated, adaptive learning experiences. |
How AI-Driven Assessment & Grading Tools Work?
AI-driven assessment and grading tools streamline evaluation by automatically scoring assignments, essays, and exams. They leverage machine learning and NLP to provide accurate, consistent, and personalized feedback for students.
1. Data Input & Content Parsing
Systems accept text, MCQs using optical mark recognition, coding with execution data, essays via UTF-8 parsing, and video streams through frame extraction, with multi-modal parsers converting diverse inputs into JSON.
Platform Example:
Professor Martinez uploads 120 final exam papers to EduScore AI. The platform’s intake interface accepts:
- Scanned PDFs of handwritten exams (bulk upload via mobile app)
- Digital submissions from the student portal for essay questions
- Coding assignments directly from GitHub repositories
- Video presentations recorded through the integrated webcam tool
EduScore AI processes submissions: OCR digitizes responses, code parser extracts logs, videos split into audio and visual channels. Data tags include student and question IDs, timestamps, appearing as structured entries in Professor Martinez’s grading queue.
2. AI/ML-Based Understanding of Answers
Pre-trained transformer models like BERT and GPT extract semantic meaning from text, CNN-based OCR converts handwriting with confidence scoring, ASR engines transcribe oral assessments with fluency features, and code runs in sandboxed environments with runtime and quality analysis.
Platform Example:
For student Sarah Chen’s biology exam:
- Question 5 (Essay): EduScore AI’s NLP engine processes her explanation of cellular respiration. The transformer model identifies key concepts like “mitochondria,” “ATP synthesis,” and “electron transport chain,” while analyzing argument structure and scientific accuracy.
- Question 8 (Handwritten diagram): The computer vision module recognizes her labeled cell diagram, converting handwritten annotations into text while preserving spatial relationships between components.
- Question 12 (Video explanation): The speech-to-text engine transcribes her 3-minute presentation on genetics, capturing the pronunciation of terms like “phenotype” and detecting hesitation markers that indicate confidence levels.
Professor Martinez sees a unified dashboard showing all interpreted content, with confidence scores indicating parsing accuracy (Sarah’s handwriting: 94% confidence, video transcription: 97% confidence).
3. Knowledge Mapping
AI maps responses to curriculum knowledge graphs using graph neural networks, infers mastery with Bayesian models, detects partial understanding through fuzzy logic, identifies misconceptions via pattern recognition, and analyzes prerequisite gaps to deliver diagnostic insights and personalized adaptive learning pathways.
Platform:
EduScore AI’s knowledge graph for Biology 201 contains 247 interconnected concepts across 8 learning modules. As the platform analyzes Sarah’s cellular respiration answer, it maps her response to specific nodes:
- Strong mastery: Energy transformation (LO 2.3), Metabolic pathways (LO 2.5)
- Partial understanding: Oxidative phosphorylation (LO 2.7) – mentioned but lacked detail on chemiosmosis
- Misconception detected: Incorrectly stated oxygen is needed for glycolysis (common error flagged in system)
The platform cross-references Sarah’s knowledge from Chemistry 101, finding her weak understanding of electrochemical gradients causes comprehension issues. This appears in Professor Martinez’s review and Sarah’s feedback report with targeted advice.
4. Scoring Engine
Rule-based expert systems score objective questions through deterministic matching, while supervised ML models trained on human-graded data evaluate subjective responses. AI also generates weighted rubrics using clustering to define scoring dimensions and assigns partial credit through probabilistic scoring with confidence intervals.
Platform Example:
EduScore AI applies three scoring methods for Sarah’s exam:
- It uses automated grading for Sarah’s multiple-choice questions, awarding 8 out of 10 points through rule-based answer key matching.
- The platform’s machine-learning model, trained on 50,000 professor-graded biology essays, scores her cellular respiration response at 18 out of 25, noting strong conceptual understanding but limited mechanistic detail.
- For a new COVID-19 analysis question, EduScore AI creates a dynamic rubric with weighted criteria (scientific reasoning, evidence integration, conclusion validity, creativity) and assigns Sarah 22 out of 30, giving partial credit for solid reasoning.
- Professor Martinez can review and adjust all AI-generated scores, and the system improves its future scoring based on his revisions.
5. Bias Detection & Result Validation
An ensemble approach uses multiple AI models with different architectures to evaluate responses. Statistical tests detect demographic biases, triggering human review. This feedback loop enhances fairness and accuracy.
Platform Example:
Behind the scenes, EduScore AI scores Sarah’s essay using three models: GPT-based, BERT-based, and a custom transformer trained on scientific writing. Scores are 18, 19, and 17 points within acceptable variance (±2 points).
- The system identifies a 7-point scoring discrepancy between models when evaluating Miguel Rodriguez’s essay.
- EduScore AI’s bias detection module flags the issue and notes that Miguel’s writing includes colloquial phrasing often seen in English-as-second-language learners.
- The platform notifies Professor Martinez with a recommendation for review: “Potential scoring inconsistency detected. Human review recommended.”
EduScore AI analyzes demographic fairness across 120 exams, checking for score disparities among linguistic groups. The dashboard shows no significant bias, included in Professor Martinez’s departmental report.
6. Feedback Generation
System provides personalized resources for concept gaps, with explanations of scoring highlighting strengths and weaknesses. Uses growth-mindset framing to emphasize learning and adapts to learning styles.
Platform Example:
Sarah logs into her EduScore AI student portal and receives comprehensive, personalized feedback:
Auto-generated explanation:
- “Your cellular respiration explanation demonstrated a strong understanding of the overall energy transformation process (+5 points).
- You correctly identified the three main stages and their locations (+4 points).
- However, your description of the electron transport chain lacked detail about the proton gradient mechanism (-3 points).
- Your diagram showed creativity but mislabeled the cristae structure (-2 points).”
Personalized recommendations: Based on her misconception about glycolysis, EduScore AI suggests:
- Khan Academy video: “Glycolysis: Anaerobic vs Aerobic Conditions” (8 min)
- Interactive simulation: “Build Your Own Metabolic Pathway” (matches her visual learning preference)
- Practice problems: 5 targeted questions on oxygen dependency in cellular processes
Growth-mindset framing: “You’re 85% of the way to mastering this learning objective! Focus on understanding chemiosmosis, and you’ll have the complete picture of cellular energy production.”
The platform tracks which resources Sarah engages with and adjusts future recommendations based on what proves most effective for her learning style.
7. Reporting & Analytics
Teacher dashboards show class performance and mastery rates. Student interfaces display personal progress and readiness. Early warning systems identify at-risk students for intervention.
Platform Example:
Professor Martinez’s Dashboard displays actionable insights:
- Class performance heatmap: 73% of students struggled with oxidative phosphorylation (LO 2.7) prompting him to schedule an additional review session
- Question analytics: Question 12 had unusually low scores despite being rated “medium difficulty,” suggesting poor question design or unclear wording
- Time-to-complete data: Students averaging 8+ minutes on MCQs showed 30% lower scores, indicating reading comprehension issues rather than content gaps
- Longitudinal tracking: Students who attended office hours after Exam 1 showed 12% average improvement on similar Exam 2 topics
Sarah’s Personal Analytics shows her progress across the semester:
- Mastery trajectory: Her cell biology scores improved from 68% to 87% over three assessments
- Comparative context: She’s in the 78th percentile for this exam (anonymized)
- Readiness prediction: EduScore AI forecasts 82% probability of success on next unit (genetics) based on demonstrated prerequisite mastery
- Study recommendations: Suggests focusing 60% of study time on molecular biology gaps before the cumulative final
The Institutional Dashboard (Dean’s view) aggregates data from 45 biology sections. Section 7’s low scores relate to a new adjunct instructor needing mentoring. The early warning system flags 23 students with declining engagement, prompting advisors to reach out before failure.
How IdeaUsher Will Help You Build an AI Assessment Platform?
IdeaUsher provides end-to-end product development expertise to design, build, and scale a high-performance AI-driven assessment platform. By combining technical depth with domain awareness, we ensure your solution is accurate, secure, scalable, and market-ready.
1. AI Architecture & Model Strategy
We help you identify and integrate the right mix of ML models, NLP engines, OCR, CV, and LLM-based evaluators tailored to your assessment needs.
2. Custom Scoring Engine Development
IdeaUsher builds automated rule-based, ML-driven, and generative AI scoring pipelines designed for reliability, transparency, and scalability.
3. Data Infrastructure & Training Pipelines
We set up secure systems for data collection, labeling, model training, validation, and continuous improvement.
4. LMS & EdTech Integrations
Our team enables seamless integration with major LMS platforms like Moodle, Canvas, Blackboard, and enterprise training systems for fast adoption.
5. Real-Time Analytics & Dashboards
We develop intuitive dashboards that deliver learning analytics, performance trends, cohort insights, and prediction models.
6. Continuous Support & Product Evolution
We provide ongoing monitoring, model refinement, A/B testing, and feature enhancements to keep your platform competitive and future-ready.
Real-World Examples of AI-Driven Assessment & Grading Tool Platforms
AI-driven assessment and grading tools streamline evaluation, provide personalized feedback, and enhance learning outcomes. These platforms are transforming education by automating grading, analytics, and performance insights across K-12 and higher education.
1. Gradescope
Gradescope uses machine learning to recognize handwriting, cluster similar responses, and apply consistent rubrics at scale, significantly reducing grading time. It also learns from instructor adjustments to improve grouping accuracy over time.
- AI-assisted grading that groups similar answers for faster, more consistent evaluation
- Supports paper-based and digital assignments, including STEM subjects with mathematical notation
- Rubric-based grading with auto-grading for code assignments
- Analytics dashboard showing performance trends and question-level insights
- Integrates with major LMS platforms including Canvas, Blackboard, and Moodle
Global Reach: Used by over 200,000 instructors across 2,000+ institutions worldwide including Stanford, MIT, UC Berkeley, Oxford, and Cambridge.
2. Turnitin
Turnitin uses advanced natural language processing to detect plagiarism, paraphrasing, and AI-generated text, analyzing writing patterns for originality. Its models provide instant, data-backed feedback that strengthens writing quality and academic integrity.
- Industry-leading plagiarism detection comparing against 70+ billion web pages and 200+ million student papers
- AI writing detection to identify content generated by ChatGPT and other AI tools
- Feedback Studio with automated grammar and writing feedback
- Originality checks with detailed similarity reports
- Revision Assistant for formative writing assessment
Global Reach: Serves 16,000+ institutions across 140 countries with over 2.1 million educators and 40 million students using the platform.
3. Century
Century Tech blends AI, cognitive science, and neuroscience to assess understanding in real time, adapt content difficulty, and identify knowledge gaps. Its predictive algorithms personalize learning pathways based on mastery signals and performance patterns.
- AI-powered personalized learning pathways that adapt to each student’s needs
- Real-time learning analytics and intervention recommendations
- Automated assessment with instant feedback
- Neuroscience and cognitive science-based platform design
- Teacher dashboard with workload reduction tools and student progress tracking
Global Reach: Used in over 3,000 schools across the UK, USA, Middle East, and Asia. Partners include schools in England, Wales, Scotland, UAE, and several US states.
4. Inspera
Inspera uses NLP for automated essay scoring, machine learning for answer-pattern detection, and AI proctoring to ensure exam security. Its intelligent item analysis supports fair assessments and delivers actionable insights for educators.
- Secure digital exam platform with AI-powered proctoring
- Automated grading for multiple question types including essays
- Accessibility features with screen readers and assistive technologies
- Offline exam capability with automatic synchronization
- Advanced analytics and psychometric analysis tools
Global Reach: Serves over 500 institutions across 40+ countries including major universities in Europe, UK (Imperial College London, University of Edinburgh), Australia, and North America. Conducts over 10 million assessments annually.
5. ExamSoft
ExamSoft leverages machine learning to evaluate question quality, predict student outcomes, and detect exam irregularities. Its AI automates scoring for written responses and generates psychometric insights that strengthen assessment reliability.
- Secure exam delivery with lockdown browser
- AI-assisted item analysis and psychometric reporting
- Automated grading with customizable rubrics
- Comparative data analytics across cohorts and institutions
- Assessment lifecycle management from creation to accreditation reporting
Global Reach: Used by 1,200+ programs across healthcare, law, and business education. Serves institutions in the USA, Canada, UK, Australia, and Caribbean medical schools. Administers over 30 million exams annually.
Conclusion
Building an AI-Driven Assessment Platform opens the door to faster evaluation cycles, stronger learning insights, and a more consistent grading experience for educators and institutions. As AI models mature, these systems continue to improve accuracy and adapt to diverse academic needs. The goal is to simplify assessment workflows while giving educators reliable support for managing large volumes of student responses. By understanding the core technology and implementation steps, you can plan a solution that delivers precision, scale, and long-term value in modern education environments.
Work with Ex-MAANG developers to build next-gen apps schedule your consultation now
FAQs
Building an AI-driven assessment platform requires a strong data pipeline, automated grading models, question generation modules, and secure cloud infrastructure. Teams also need expertise in NLP, machine learning, and education workflows to ensure accurate scoring and a reliable learning experience.
Training grading models involves collecting labeled datasets, cleaning responses, applying NLP techniques, and fine-tuning algorithms to identify patterns in student answers. Continuous validation and feedback loops help improve accuracy and ensure fair and consistent scoring across subjects.
A reliable tech stack includes Python, TensorFlow, PyTorch, and cloud platforms like AWS or GCP. For the backend, Node or Python works well, and React or Vue can support scalable dashboards for teachers and administrators.
Accuracy is achieved by training on diverse datasets, conducting continuous validation, and refining scoring models through feedback loops. Developers implement calibration tools, teacher review workflows, and periodic model updates to maintain fairness and reliability across different assessment formats.